Early antibody treatment, inflammation, and risk of post-COVID conditions
et al., mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.00618-23, Oct 2023
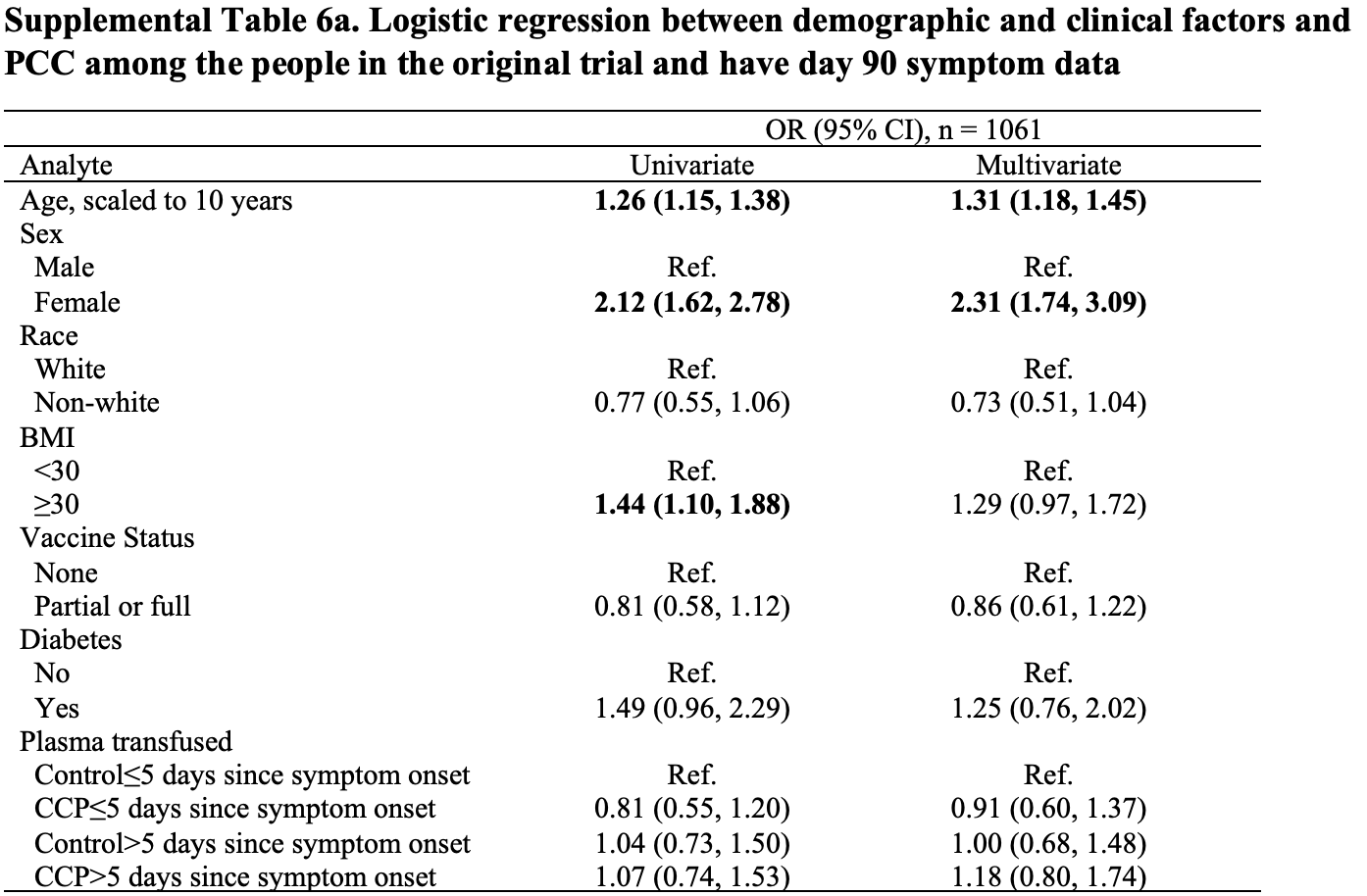
Long COVID results for Baksh et al., showing early COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP) treatment within 5 days of symptom onset was associated with lower odds of post-COVID conditions (PCC) compared to late CCP treatment within a subset of patients with blood drawn at screening, day 14 and day 90. However there was no statistically significant effect within the full trial population. The full population may be more accurate because participants missing data may be systematically different from those with complete data. Results are shown with the main trial1.
Gebo et al., 31 Oct 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 43.0, 44 authors, study period 3 June, 2020 - 1 October, 2021.
Contact: kgebo@jhmi.edu, atobian1@jhmi.edu.
Early antibody treatment, inflammation, and risk of post-COVID conditions
mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.00618-23
Post-COVID conditions (PCCs) are common and have significant morbidity. Risk factors for PCC include advancing age, female sex, obesity, and diabetes melli tus. Little is known about treatment, inflammation, and PCC. Among 882 individuals with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection participating in a randomized trial of COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP) vs control plasma with available biospecimens and symp tom data, the association between early CCP treatment, cytokine levels, and PCC was evaluated. Cytokine and chemokine levels were assessed at baseline, day 14, and day 90 using a multiplexed sandwich immunoassay (Meso Scale Discovery). Presence of any self-reported PCC symptoms was assessed at day 90. Associations between CCP treatment, cytokine levels, and PCC were examined using multivariate logistic regression models. One third of the 882 participants had day 90 PCC symptoms, with fatigue (14.5%) and anosmia (14.5%) being most common. Cytokine levels decreased from baseline to day 90. In a multivariable analysis, female sex (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 2.69 [1.93-3.81]), older age (AOR = 1.32 [1.17-1.50]), and elevated baseline levels of IL-6 (AOR = 1.59 [1.02-2.47]) were independently associated with development of PCC. Those who received early CCP treatment (≤5 days after symptom onset) compared to late CCP treatment had statistically significant lower odds of PCC. IMPORTANCE Approximately 20% of individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 experienced long-term health effects, as defined PCC. However, it is unknown if there are any early biomarkers associated with PCC or whether early intervention treatments may decrease the risk of PCC. In a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial, this study demon strates that among outpatients with SARS-CoV-2, increased IL-6 at time of infection is associated with increased odds of PCC. In addition, among individuals treated early, within 5 days of symptom onset, with COVID-19 convalescent plasma, there was a trend for decreased odds of PCC after adjusting for other demographic and clinical characteristics. Future treatment studies should be considered to evaluate the effect of early treatment and anti-IL-6 therapies on PCC development. KEYWORDS COVID-19, COVID-19 serotherapy, post-COVID condition (PCC), post-acute sequelae of COVID (PASC), interleukin-6, cytokines, chemokines S evere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has infected more than 600 million people worldwide and more than 97 million people in the United States (1). Many survivors of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) report long-term health
ETHICS APPROVAL All study activities were approved by the Johns Hopkins University single Institutional Review Board, the Navajo Nation Human Research Review Board, the Indian Health Service National Institutional Review Board, and the Human Research Protection Office of the United States Department of Defense. All study activities followed the Declaration of Helsinki, the Good Clinical Practice guidelines of the International Conference on Harmonization, and all applicable regulatory requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants.
ADDITIONAL FILES The following material is available online.
Supplemental Material Supplemental material (mBio00618-23 S0001.docx). Supplemental tables and figures.
References
Antonelli, Penfold, Merino, Sudre, Molteni et al., Risk factors and disease profile of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID symptom study app: a prospective, community-based, nested, case-control study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00460-6
Ayoubkhani, Bermingham, Pouwels, Glickman, Nafilyan et al., Trajectory of long Covid symptoms after COVID-19 vaccination: community based cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-069676
Ayoubkhani, Khunti, Nafilyan, Maddox, Humberstone et al., Post-covid syndrome in individuals admitted to hospital with COVID-19: retrospective cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n693
Azzolini, Levi, Sarti, Pozzi, Mollura et al., Association between BNT162b2 vaccination and long COVID after infections not requiring hospitalization in health care workers, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.11691
Bloch, Shoham, Casadevall, Sachais, Shaz et al., Deployment of convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI138745
Boglione, Meli, Poletti, Rostagno, Moglia et al., Risk factors and incidence of long-COVID syndrome in hospitalized patients: does remdesivir have a protective effect, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab297
Bonny, Patel, Zhu, Bloch, Grabowski et al., Cytokine and chemokine levels in Coronavirus disease 2019 convales cent plasma, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa574
Casadevall, Pirofski, The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI138003
Durstenfeld, Peluso, Kaveti, Inflammation during early post-acute COVID-19 is associated with reduced exercise capacity and long COVID symptoms after 1 year, medRxiv, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2119657
Durstenfeld, Peluso, Lin, Peyser, Isasi et al., Association of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment with Long COVID Symptoms in an Online Cohort of Non-Hospitalized Individuals Experiencing Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Omicron Era, Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS, doi:10.1101/2023.03.02.23286730
Estcourt, Cohn, Pagano, Iannizzi, Kreuzberger et al., Clinical practice guidelines from the association for the advancement of blood and biotherapies (AABB): COVID-19 convalescent plasma, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M22-1079
Fernández-Ruiz, Humar, Baluch, Keshwani, Husain et al., Baseline serum interleukin-6 to interleukin-2 ratio is associated with the response to seasonal trivalent influenza vaccine in solid organ transplant recipients, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.134
Groff, Sun, Ssentongo, Ba, Parsons et al., Short-term and longterm rates of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28568
Han, Ma, Li, Liu, Zhao et al., Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129
Jones, Jenkins, Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-018-0066-7
Joyner, Carter, Senefeld, Klassen, Mills et al., Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031893
Karaba, Zhu, Benner, Akinde, Eby et al., Higher proinflammatory cytokines are associated with increased antibody titer after a third dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in solid organ transplant recipients, Transplanta tion, doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000004057
Körper, Grüner, Zickler, Wiesmann, Wuchter et al., One-year follow-up of the CAPSID randomized trial for high-dose convalescent plasma in severe COVID-19 patients, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI163657
Laing, Lorenc, Molino, Barrio, Das et al., A dynamic COVID-19 immune signature includes associations with poor prognosis, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-01186-5
Lavillegrand, Garnier, Spaeth, Mario, Hariri et al., Elevated plasma IL-6 and CRP levels are associated with adverse clinical outcomes and death in critically ill SARS-CoV-2 patients: Inflammatory response of SARS-CoV-2 patients, Ann. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-00798-x
Littlefield, Watson, Schneider, Neff, Yamada et al., SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells associate with inflammation and reduced lung function in pulmonary post-acute Sequalae of SARS-CoV-2, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.922422
Nevalainen, Horstia, Laakkonen, Rutanen, Mustonen et al., Effect of remdesivir post hospitalization for COVID-19 infection from the randomized SOLIDARITY Finland trial, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33825-5
Peluso, Deitchman, Torres, Iyer, Munter et al., Long-term SARS-CoV-2-specific immune and inflammatory responses in individuals recovering from COVID-19 with and without post-acute symptoms, Cell Rep, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.922422
Peluso, Lu, Tang, Durstenfeld, Ho et al., Markers of immune activation and inflammation in individuals with postacute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 infection, J Infect Dis, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.922422
Queiroz, Neves, Das, Lima, Lopes et al., Cytokine profiles associated with acute COVID-19 and long COVID-19 syndrome, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.922422
Salazar, Christensen, Graviss, Nguyen, Castillo et al., Significantly decreased mortality in a large cohort of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients transfused early with convalescent plasma containing high-titer anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein IgG, Am J Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.10.008
Scully, Schumock, Fu, Massaccesi, Muschelli et al., Sex and gender differences in testing, hospital admission, clinical presentation, and drivers of severe outcomes from COVID-19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.922422
Senefeld, Johnson, Kunze, Bloch, Van Helmond et al., Access to and safety of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in the United States expanded access program: A national registry study, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003872
Sharifpour, Rangaraju, Liu, Alabyad, Nahab et al., C-reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0242400
Sneller, Liang, Marques, Chung, Shanbhag et al., A longitudinal study of COVID-19 sequelae and immunity: baseline findings, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M21-4905
Soriano, Murthy, Marshall, Relan, Diaz, WHO Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition. 2022. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00703-9
Su, Yuan, Chen, Ng, Wang et al., Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae, Cell, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.922422
Sullivan, Gebo, Shoham, Bloch, Lau et al., Early outpatient treatment for COVID-19 with Convalescent plasma, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2119657
Swank, Senussi, Alter, Walt, Persistent circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike is associated with post-acute COVID-19 sequelae, Pathology, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2119657
Tenforde, Devine, Reese, Silk, Iuliano et al., Point prevalence estimates of activity-limiting long-term symptoms among United States adults ≥1 month after reported severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, 1 November 2021, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac281
Tobian, Cohn, Shaz, COVID-19 convalescent plasma, Blood
Valle, Kim-Schulze, Huang, Beckmann, Nirenberg et al., An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9
Vimercati, Maria, Quarato, Caputi, Gesualdo et al., Association between long COVID and overweight/obesity, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10184143
Xie, Choi, Al-Aly, Nirmatrelvir and the Risk of Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19, Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS, doi:10.1101/2022.11.03.22281783
Zhang, Wang, Shen, Zhang, Cen et al., Symptoms and health outcomes among survivors of COVID-19 infection 1 year after discharge from hospitals in Wuhan, China, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27403
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.00618-23",
"ISSN": [
"2150-7511"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00618-23",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Post-COVID conditions (PCCs) are common and have significant morbidity. Risk factors for PCC include advancing age, female sex, obesity, and diabetes mellitus. Little is known about treatment, inflammation, and PCC. Among 882 individuals with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection participating in a randomized trial of COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP) vs control plasma with available biospecimens and symptom data, the association between early CCP treatment, cytokine levels, and PCC was evaluated. Cytokine and chemokine levels were assessed at baseline, day 14, and day 90 using a multiplexed sandwich immunoassay (Meso Scale Discovery). Presence of any self-reported PCC symptoms was assessed at day 90. Associations between CCP treatment, cytokine levels, and PCC were examined using multivariate logistic regression models. One third of the 882 participants had day 90 PCC symptoms, with fatigue (14.5%) and anosmia (14.5%) being most common. Cytokine levels decreased from baseline to day 90. In a multivariable analysis, female sex (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 2.69 [1.93–3.81]), older age (AOR = 1.32 [1.17–1.50]), and elevated baseline levels of IL-6 (AOR = 1.59 [1.02–2.47]) were independently associated with development of PCC. Those who received early CCP treatment (≤5 days after symptom onset) compared to late CCP treatment had statistically significant lower odds of PCC.</jats:p>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>IMPORTANCE</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Approximately 20% of individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 experienced long-term health effects, as defined PCC. However, it is unknown if there are any early biomarkers associated with PCC or whether early intervention treatments may decrease the risk of PCC. In a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial, this study demonstrates that among outpatients with SARS-CoV-2, increased IL-6 at time of infection is associated with increased odds of PCC. In addition, among individuals treated early, within 5 days of symptom onset, with COVID-19 convalescent plasma, there was a trend for decreased odds of PCC after adjusting for other demographic and clinical characteristics. Future treatment studies should be considered to evaluate the effect of early treatment and anti-IL-6 therapies on PCC development.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/mbio.00618-23"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-03-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-06-02"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2023-09-19"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gebo",
"given": "Kelly A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Alabama at Birmingham , Birmingham, Alabama, USA"
}
],
"family": "Heath",
"given": "Sonya L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Baylor College of Medicine , Houston, Texas, USA"
}
],
"family": "Fukuta",
"given": "Yuriko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3317-7449",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Xianming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Baksh",
"given": "Sheriza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, University of Colorado, Anschutz Medical Campus , Aurora, Colorado, USA"
}
],
"family": "Abraham",
"given": "Allison G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Habtehyimer",
"given": "Feben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Shade",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ruff",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departement of International Health, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ram",
"given": "Malathi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6429-4760",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, NIH , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Laeyendecker",
"given": "Oliver",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Fernandez",
"given": "Reinaldo E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2174-5004",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Eshan U.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "Owen R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Shoham",
"given": "Shmuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California , San Diego, California, USA"
}
],
"family": "Cachay",
"given": "Edward R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California , Los Angeles, California, USA"
}
],
"family": "Currier",
"given": "Judith S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology and Oncology, University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School , Worchester, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gerber",
"given": "Jonathan M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Luminis Health , Annapolis, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Meisenberg",
"given": "Barry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6687-6775",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California , Irvine, California, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Forthal",
"given": "Donald N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departement of International Health, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hammitt",
"given": "Laura L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Cincinnati , Cincinnati, Ohio, USA"
}
],
"family": "Huaman",
"given": "Moises A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Rhode Island Hospital Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University , Providence, Rhode Island, USA"
}
],
"family": "Levine",
"given": "Adam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Allergy and Immunology, Northshore University Health System , Evanston, Illinois, USA"
}
],
"family": "Mosnaim",
"given": "Giselle S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center , Houston, Texas, USA"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Bela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Wayne State University , Detroit, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Paxton",
"given": "James H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, University of New Mexico , Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA"
}
],
"family": "Raval",
"given": "Jay S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8512-8326",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
},
{
"name": "Departement of International Health, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Sutcliffe",
"given": "Catherine G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine , Miami, Florida, USA"
}
],
"family": "Anjan",
"given": "Shweta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Northshore University Health System , Evanston, Illinois, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gniadek",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Medstar Georgetown University Hospital , Washington, DC, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kassaye",
"given": "Seble",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Mayo Clinic Hospital , Phoenix, Arizona, USA"
}
],
"family": "Blair",
"given": "Janis E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Lane",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "McBee",
"given": "Nichol A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gawad",
"given": "Amy L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Das",
"given": "Piyali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0730-5224",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Klein",
"given": "Sabra L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3248-1761",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Pekosz",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8181-9517",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Bloch",
"given": "Evan M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hanley",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9402-9167",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Casadevall",
"given": "Arturo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0517-3766",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tobian",
"given": "Aaron A. R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0319-0578",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sullivan",
"given": "David J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "on behalf of the CSSC-004 Consortium",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "mBio",
"container-title-short": "mBio",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-19T13:00:32Z",
"timestamp": 1695128432000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-11T18:30:18Z",
"timestamp": 1723401018000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahalingam",
"given": "Suresh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"W911QY2090012"
],
"name": "U.S. Department of Defense"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"R01AI152078"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"award": [
"F31DA054849"
],
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse"
},
{
"award": [
"U24TR001609"
],
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000062",
"award": [
"R01DK131926"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/100000062",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases"
},
{
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Division of Intramural Research"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"R01AI120938S1"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-15T22:34:27Z",
"timestamp": 1726439667230
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 9,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.1128/AuthorWarrantyLicense.v1",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698710400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698710400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.00618-23",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.00618-23",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_2_2",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . COVID data tracker. Available from: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home. Accessed 11 March 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00703-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_3_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_4_2",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Long COVID or post-COVID conditions. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects. Accessed 11 March 2023"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_5_2",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Post-COVID conditions: Overview for Healthcare providers. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/post-covid-conditions.html. Accessed 11 March 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28568",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7121e1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_3_4_7_2",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 2020. Post–COVID conditions among adult COVID-19 survivors aged 18–64 and ≥65 years — United States. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7121e1.htm. Retrieved 11 Mar 2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac281",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27403",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M21-4905",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n693",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.11691",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2021-069676",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.11.03.22281783",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_14_2",
"unstructured": "Xie Y Choi T Al-Aly Z . 2022 Nirmatrelvir and the Risk of Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19. Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS). doi:10.1101/2022.11.03.22281783"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00798-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0242400",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-01186-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab448",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109518",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1010359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2022.922422",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.06.14.22276401",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_26_2",
"unstructured": "Swank Z Senussi Y Alter G Walt DR . 2022. Persistent circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike is associated with post-acute COVID-19 sequelae. Pathology. doi:10.1101/2022.06.14.22276401"
},
{
"article-title": "Inflammation during early post-acute COVID-19 is associated with reduced exercise capacity and long COVID symptoms after 1 year",
"author": "Durstenfeld MS",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "e_1_3_4_27_2",
"unstructured": "Durstenfeld MS , Peluso MJ , Kaveti P . 2022. Inflammation during early post-acute COVID-19 is associated with reduced exercise capacity and long COVID symptoms after 1 year. medRxiv",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119657",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.134",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa574",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TP.0000000000004057",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10184143",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.03.02.23286730",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_33_2",
"unstructured": "Durstenfeld MS Peluso MJ Lin F Peyser ND Isasi C Carton TW Henrich TJ Deeks SG Olgin JE Pletcher MJ Beatty AL Marcus GM Hsue PY . n.d. Association of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment with Long COVID Symptoms in an Online Cohort of Non-Hospitalized Individuals Experiencing Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Omicron Era. Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS). doi:10.1101/2023.03.02.23286730"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-33825-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab297",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI163657",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI138745",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031893",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-1079",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003872",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2021012248",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.10.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI138003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00460-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-018-0066-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_45_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mbio.00618-23"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early antibody treatment, inflammation, and risk of post-COVID conditions",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page",
"updated-by": [
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.02979-23",
"label": "Correction",
"type": "correction",
"updated": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1702512000000
}
}
],
"volume": "14"
}