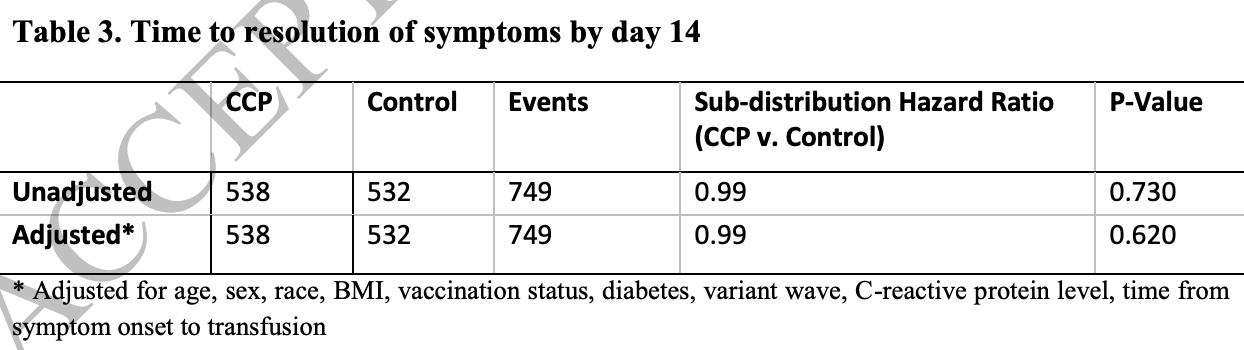
Symptom duration and resolution with early outpatient treatment of convalescent plasma for COVID-19: a randomized trial
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad023, NCT04373460, Jan 2023
RCT 1,070 outpatients in the USA, showing no significant difference in recovery with convalescent plasma treatment. Long COVID results are from Gebo et al.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments2.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of no recovery, 1.0% higher, RR 1.01, p = 0.62, treatment 381 of 538 (70.8%), control 381 of 532 (71.6%), NNT 125, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, day 14.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 4.4% higher, RR 1.04, p = 0.78, treatment 533, control 528, all patients.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 9.0% lower, OR 0.91, p = 0.67, treatment 232, control 234, ≤5 days, full population, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 18.0% higher, OR 1.18, p = 0.41, treatment 301, control 294, >5 days, full population, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Baksh et al., 31 Jan 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 26 authors, study period 3 June, 2020 - 1 October, 2021, average treatment delay 6.0 days, trial NCT04373460 (history).
Symptom Duration and Resolution With Early Outpatient Treatment of Convalescent Plasma for Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Trial
The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad023
Background: COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP) reduces hospitalizations among outpatients treated early after symptom onset. It is unknown if CCP reduces time to symptom resolution among outpatients.
Methods: We evaluated symptom resolution at day 14 by trial arm using an adjusted subdistribution hazard model, with hospitalization as a competing risk. Additionally, we assessed prevalence of symptom clusters at day 14 between treatments. Clusters were defined based on biologic clustering, impact on ability to work, and an algorithm. Results: Among 1,070 outpatients followed after transfusion, 381 of 538 (70.8%) receiving CCP and 381 of 532 (71.6%) receiving control plasma were still symptomatic (p=0.78) at day 14. Associations between CCP and symptom resolution by day 14 were not statistically different from those in controls after adjusting for baseline characteristics (adjusted sub-distribution hazard ratio: 0.99; p=0.62). The most common cluster consisted of cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, and headache, found in 308 (57.2%) and 325 (61.1%) of CCP and control plasma recipients, respectively (p=0.16).
Conclusions: In this trial of outpatients with early COVID-19, CCP was not associated with faster resolution of symptoms compared to control. Overall, there were no differences in the prevalence of each symptom or symptom clusters at day 14 by treatment.
DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad023 Disclosures: Dr. Bloch is a member of the FDA's Blood Products Advisory Committee. All opinions in this manuscript are of the authors and do not reflect the Blood Products Advisory Committee or the position of the FDA. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. Dr. Casadevall serves on the Scientific Advisory Board of Sabtherapeutics, which is developing cow-derived human immunoglobulins for the treatment of COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. Dr. Gebo is a paid consultant for UptoDate, Teach for America, and the Aspen Institute. No other authors declare a potential conflict of interest.
References
Al-Aly, Bowe, Xie, Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Med
Arnold, Hamilton, Milne, Patient outcomes after hospitalisation with COVID-19 and implications for follow-up: results from a prospective UK cohort, Thorax
Bellan, Soddu, Balbo, Respiratory and Psychophysical Sequelae Among Patients With COVID-19 Four Months After Hospital Discharge, JAMA Netw Open
Blomberg, Mohn, Brokstad, Long COVID in a prospective cohort of home-isolated patients, Nat Med
Burke, Killerby, Newton, Symptom Profiles of a Convenience Sample of Patients with COVID-19 -United States, January-April 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Carfì, Bernabei, Landi, Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19, Jama
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study, Bmj
Dougan, Azizad, Chen, Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab in Mild or Moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Halpin, Mcivor, Whyatt, Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional evaluation, J Med Virol
Hartigan, Wong, Algorithm AS 136: A K-Means Clustering Algorithm, J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat
Klein, Asseo, Karni, Onset, duration and unresolved symptoms, including smell and taste changes, in mild COVID-19 infection: a cohort study in Israeli patients, Clin Microbiol Infect
Korley, Durkalski-Mauldin, Yeatts, Early Convalescent Plasma for High-Risk Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Early High-Titer Plasma Therapy to Prevent Severe Covid-19 in Older Adults, N Engl J Med
Liu, Jayasundara, Pye, Whole of population-based cohort study of recovery time from COVID-19 in New South Wales Australia, Lancet Reg Health West Pac
Logue, Franko, Mcculloch, Sequelae in Adults at 6 Months After COVID-19 Infection, JAMA Netw Open
Pollock, Lancaster, Asymptomatic transmission of covid-19, BMJ
Sullivan, Gebo, Shoham, Early Outpatient Treatment for Covid-19 with Convalescent Plasma, N Engl J Med
Tenforde, Kim, Lindsell, Symptom Duration and Risk Factors for Delayed Return to Usual Health Among Outpatients with COVID-19 in a Multistate Health Care Systems Network -United States, March, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Tsang, Wu, Lin, Lau, Leung et al., Effect of changing case definitions for COVID-19 on the epidemic curve and transmission parameters in mainland China: a modelling study, Lancet Public Health
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Woodhead, Blasi, Ewig, Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections, Eur Respir J
Wynberg, Van Willigen, Dijkstra, Evolution of COVID-19 symptoms during the first 12 months after illness onset, Clin Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiad023",
"ISSN": [
"0022-1899",
"1537-6613"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiad023",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) convalescent plasma (CCP) reduces hospitalizations among outpatients treated early after symptom onset. It is unknown whether CCP reduces time to symptom resolution among outpatients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We evaluated symptom resolution at day 14 by trial arm using an adjusted subdistribution hazard model, with hospitalization as a competing risk. We also assessed the prevalence of symptom clusters at day 14 between treatments. Clusters were defined based on biologic clustering, impact on ability to work, and an algorithm.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Among 1070 outpatients followed up after transfusion, 381 of 538 (70.8%) receiving CCP and 381 of 532 (71.6%) receiving control plasma were still symptomatic (P = .78) at day 14. Associations between CCP and symptom resolution by day 14 did not differ significantly from those in controls after adjustment for baseline characteristics (adjusted subdistribution hazard ratio, 0.99; P = .62). The most common cluster consisted of cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, and headache and was found in 308 (57.2%) and 325 (61.1%) of CCP and control plasma recipients, respectively (P = .16).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this trial of outpatients with early COVID-19, CCP was not associated with faster resolution of symptoms compared with control. Overall, there were no differences by treatment in the prevalence of each symptom or symptom clusters at day 14.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trials Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>NCT04373460.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8341-860X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology Bloomberg Johns Hopkins School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Baksh",
"given": "Sheriza N",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Alabama at Birmingham , Birmingham, Alabama , USA"
}
],
"family": "Heath",
"given": "Sonya L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Baylor College of Medicine , Houston, Texas , USA"
}
],
"family": "Fukuta",
"given": "Yuriko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology Bloomberg Johns Hopkins School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Shade",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Research Institute of Luminis Health , Annapolis, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Meisenberg",
"given": "Barry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bloch",
"given": "Evan M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Tobian",
"given": "Aaron A R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Utah , Salt Lake City, Utah , USA"
}
],
"family": "Spivak",
"given": "Emily S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center , Houston, Texas , USA"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Bela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology and Oncology, University of Massachusetts , Worchester, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Gerber",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, University of New Mexico , Albuquerque, New Mexico , USA"
}
],
"family": "Raval",
"given": "Jay S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California, Irvine , Irvine, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Forthal",
"given": "Donald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Wayne State University , Detroit, Michigan , USA"
}
],
"family": "Paxton",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Northshore University Health System, Division of Allergy and Immunology , Evanston, Illinois , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mosnaim",
"given": "Giselle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7761-1163",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Miami , Miami, Florida , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Anjan",
"given": "Shweta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Mayo Clinic , Phoenix, Phoenix, Arizona , USA"
}
],
"family": "Blair",
"given": "Janis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California, San Diego , La Jolla, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Cachay",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4279-4737",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California, Los Angeles , Los Angeles, California , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Currier",
"given": "Judith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Das",
"given": "Piyali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Cincinnati Medical Center , Cincinnati, Ohio , USA"
}
],
"family": "Huaman",
"given": "Moises",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology Bloomberg Johns Hopkins School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sutcliffe",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Yarava",
"given": "Anusha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9402-9167",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departments of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Casadevall",
"given": "Arturo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departments of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sullivan",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Brain Injury Outcomes Division, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hanley",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Gebo",
"given": "Kelly A",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-01T19:30:57Z",
"timestamp": 1675279857000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-29T16:41:59Z",
"timestamp": 1685378519000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100010677",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Health"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100006108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100006492",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Division of Intramural Research, NIAID,"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100009318",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Shear"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-01T15:42:19Z",
"timestamp": 1706802139960
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
31
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
29
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675123200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiad023/49149128/jiad023.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/227/11/1266/50482123/jiad023.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/227/11/1266/50482123/jiad023.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1266-1273",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
31
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6928a2",
"article-title": "Symptom profiles of a convenience sample of patients with COVID-19—United States, January-April 2020",
"author": "Burke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "904",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B1",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1985",
"article-title": "Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study",
"author": "Docherty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1985",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B2",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.05.00055705",
"article-title": "Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections",
"author": "Woodhead",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1138",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B3",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30089-X",
"article-title": "Effect of changing case definitions for COVID-19 on the epidemic curve and transmission parameters in mainland China: a modelling study",
"author": "Tsang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e289",
"journal-title": "Lancet Public Health",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B4",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m4851",
"article-title": "Asymptomatic transmission of covid-19",
"author": "Pollock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m4851",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B5",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26368",
"article-title": "Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: a cross-sectional evaluation",
"author": "Halpin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1013",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B6",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36142",
"article-title": "Respiratory and psychophysical sequelae among patients with COVID-19 four months after hospital discharge",
"author": "Bellan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2036142",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B7",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216086",
"article-title": "Patient outcomes after hospitalisation with COVID-19 and implications for follow-up: results from a prospective UK cohort",
"author": "Arnold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B8",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6930e1",
"article-title": "Symptom duration and risk factors for delayed return to usual health among outpatients with COVID-19 in a multistate health care systems network—United States, March-June 2020",
"author": "Tenforde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "993",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B9",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.008",
"article-title": "Onset, duration and unresolved symptoms, including smell and taste changes, in mild COVID-19 infection: a cohort study in Israeli patients",
"author": "Klein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "769",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B10",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100193",
"article-title": "Whole of population-based cohort study of recovery time from COVID-19 in New South Wales Australia",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100193",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health West Pac",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B11",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab759",
"article-title": "Evolution of COVID-19 symptoms during the first 12 months after illness onset",
"author": "Wynberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e482",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B12",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01840-0",
"article-title": "Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Al-Aly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1461",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B13",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119657",
"article-title": "Early outpatient treatment for COVID-19 with convalescent plasma",
"author": "Sullivan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1700",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B14",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Algorithm AS 136: a K-means clustering algorithm",
"author": "Hartigan",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B15",
"volume": "28",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12603",
"article-title": "Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19",
"author": "Carfì",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B16",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0830",
"article-title": "Sequelae in adults at 6 months after COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Logue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e210830",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B17",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01433-3",
"article-title": "Long COVID in a prospective cohort of home-isolated patients",
"author": "Blomberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1607",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B18",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2108163",
"article-title": "REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e81",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B19",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103784",
"article-title": "Early convalescent plasma for high-risk outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Korley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1951",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B20",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"article-title": "Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults",
"author": "Libster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "610",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B21",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B22",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100",
"article-title": "Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID-19",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B23",
"volume-title": "medRxiv"
},
{
"author": "U.S. Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "2023052916412439000_jiad023-B24",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/227/11/1266/7017764"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Symptom Duration and Resolution With Early Outpatient Treatment of Convalescent Plasma for Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "227"
}