Clinical Experience With Ivermectin and Nitazoxanide in the Management of COVID-19 Among Mexican Out- and Inpatients
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.74513, Nov 2024
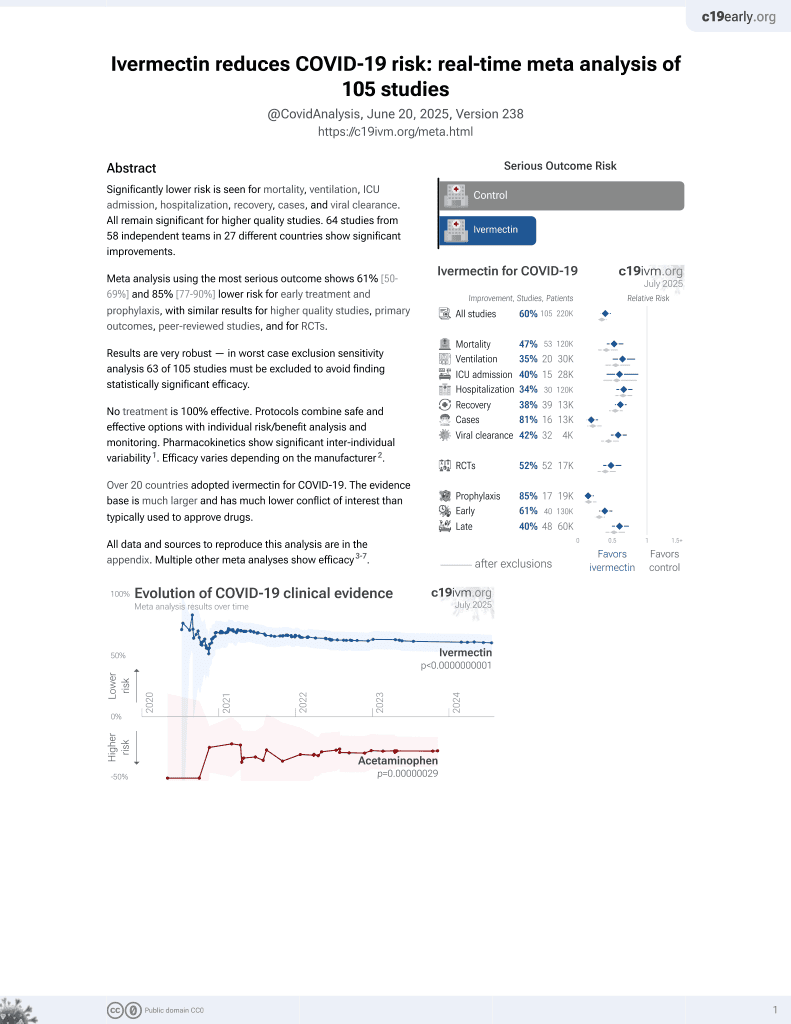
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 228 outpatients and 179 inpatients in Mexico showing potential benefits with ivermectin and nitazoxanide treatment for COVID-19. Ivermectin improved viral clearance compared to nitazoxanide, and the combination of both was more effective with early treatment. Mortality and mechanical ventilation were lower than expected rates. There was no control group.
Study covers ivermectin and nitazoxanide.
García-Méndez et al., 26 Nov 2024, retrospective, Mexico, peer-reviewed, mean age 52.2, 10 authors, study period September 2020 - November 2021.
Contact: habarrera@gmail.com.
Clinical Experience With Ivermectin and Nitazoxanide in the Management of COVID-19 Among Mexican Out- and Inpatients
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.74513
Background and objective The use of ivermectin and nitazoxanide in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been a subject of controversy. In this study, we aimed to describe our clinical experience in treating COVID-19 patients with these drugs in Mexico.
Material and methods The study involved out-and inpatient clinical assessments of COVID-19 patients conducted in Mexico City from September 2020 to November 2021. Outpatients were treated with either ivermectin, nitazoxanide, or both drugs, while all inpatients received both. Clinical and laboratory analyses were used to assess the results.
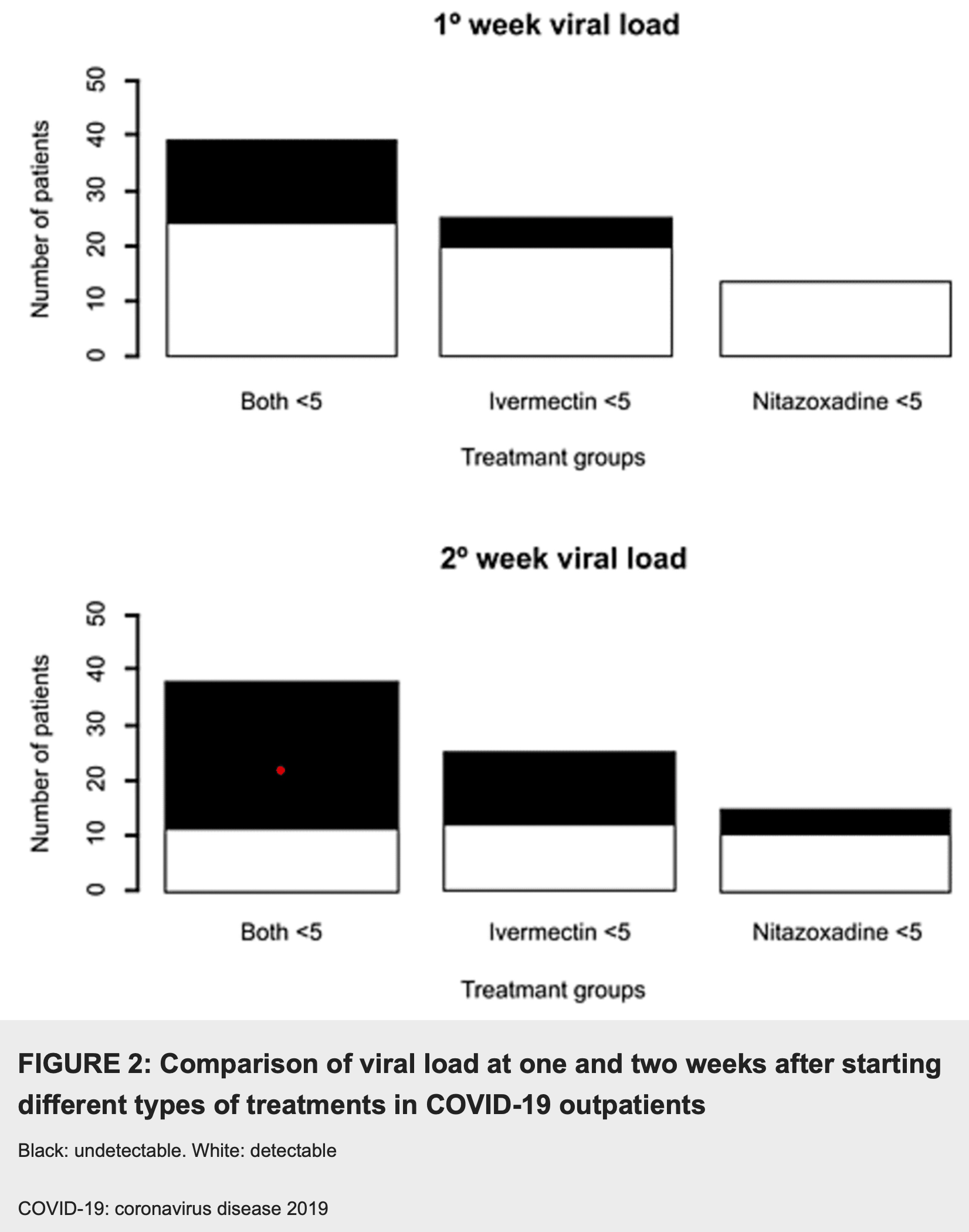
Results Of the 228 subjects in the outpatient group, 26.8% received ivermectin, 25.4% nitazoxanide, and 47.8% both. The proportion of negative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was highest in patients treated late with ivermectin (≥5 days after symptom onset; p=0.004), followed by those receiving late treatment with nitazoxanide, and those with the combination at any time. The inpatient group had 179 subjects. A significant increase was seen in neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, ferritin, and D-dimer levels, while an opposite trend was observed for C-reactive protein (CRP) and fibrinogen levels. Mechanical ventilation requirement was 15.5%, and 5% died during hospitalization.
Conclusions Despite the limitations of our study, based on its findings, ivermectin and nitazoxanide could be useful in reducing the viral load, the requirement for mechanical ventilation, proinflammatory and procoagulant parameters, and the fatality rate in COVID-19 patients. Controlled clinical trials evaluating this combination should be carried out to determine its true usefulness and safety profile.
References
Abuelazm, Ghanem, Awad, Farahat, Labieb et al., The effect of nitazoxanide on the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clin Drug Investig, doi:10.1007/s40261-022-01213-y
Ahmed, Karim, Ross, A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191
Alharbi, Jackson, Usher, The potential for COVID-19 to contribute to compassion fatigue in critical care nurses, J Clin Nurs, doi:10.1111/jocn.15314
Ambrosi, Prezioso, Checconi, SARS-CoV-2: comparative analysis of different RNA extraction methods, J Virol Methods, doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.114008
Bringas, Mortality from COVID-19 in Mexico. Preliminary notes for a sociodemographic profile, Notas de Coyuntura del CRIM
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787
Chaccour, Casellas, Matteo, The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720
Cruciani, Pati, Masiello, Malena, Pupella et al., Ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diagnostics, doi:10.3390/diagnostics11091645
Deng, Zhou, Ali, Heybati, Hou et al., Correction to: Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac072
Dinicolantonio, Barroso, Mccarty, Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350
Elalfy, Besheer, El-Mesery, Effect of a combination of nitazoxanide, ribavirin, and ivermectin plus zinc supplement (MANS.NRIZ study) on the clearance of mild COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26880
Fernández-Garza, Marfil, Neurological aspects that should not be forgotten during the COVID-19 pandemic, InterAmerican J Med Health, doi:10.31005/iajmh.v3i0.89
Fox, Saravolatz, Nitazoxanide: a new thiazolide antiparasitic agent, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1086/428839
Hadid, Kafri, Al-Katib, Coagulation and anticoagulation in COVID-19, Blood Rev, doi:10.1016/j.blre.2020.100761
Hariyanto, Halim, Gunawan, Kurniawan, Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid-19 pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trial studies, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2265
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, J Antibiot, doi:10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z
Hernandez, Liu, Roman, Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment of non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials with 7,035 participants, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107248
Hill, Garratt, Levi, Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab358
Jebril, World Health Organization declared a pandemic public health menace: a systematic review of the coronavirus disease 2019 "COVID-19, Int J Psychosoc Rehabil, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3566298
Kow, Merchant, Mustafa, Hasan, The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z
Lokhande, Devarajan, A review on possible mechanistic insights of nitazoxanide for repurposing in COVID-19, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173748
Marcolino, Meira, Guimarães, Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8
Martins-Filho, Do Nascimento-Júnior, Barreto-Alves, Fakhouri, Ferreira, Efficacy and safety of nitazoxanide in treating SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trials, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00228-022-03380-5
Ortiz-Brizuela, Villanueva-Reza, Mf, Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in a tertiary care center in Mexico City: a prospective cohort study, Rev Invest Clin, doi:10.24875/RIC.20000211
Padilla-Santamaría, Franco, Cano, COVID-19 in Mexico: epidemiological panorama (article in Spanish), Revista Cadena de Cerebros, doi:10.5281/zenodo.3926806
Ponti, Maccaferri, Ruini, Tomasi, Ozben, Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression, Crit Rev Cin Lab Sci, doi:10.24875/hgmx.20000078
Pott-Junior, Paoliello, Miguel, Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: a pilot trial, Toxicol Rep, doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.003
Quiros, Ross-Comptis, Hathaway D 3rd, Ruxolitinib and the mitigation of severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2020.0126
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: the Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009
Rao, Manissero, Steele, Pareja, A systematic review of the clinical utility of cycle threshold values in the context of COVID-19, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00324-3
Rees, Nightingale, Jafari, COVID-19 length of hospital stay: a systematic review and data synthesis, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01726-3
Rocco, Silva, Cruz, Early use of nitazoxanide in mild COVID-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.03725-2020
Roman, Burela, Pasupuleti, Piscoya, Vidal et al., Ivermectin for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab591
Silva, Espejo, Pereyra, Efficacy of nitazoxanide in reducing the viral ad in COVID-19 patients. Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blinded, parallel-group, pilot study, Med Res Arch, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i2.3364
Song, Shi, Zhang, Ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27647
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
Weng, Weng, Lai, Chao, Wang, Clinical outcomes, virological efficacy and safety of nitazoxanide in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2022.2142117
Zein, Sulistiyana, Raffaelo, Pranata, Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102186
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.74513",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.74513",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-Méndez",
"given": "Jorge O",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernández-Garza",
"given": "Luis E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vallejo-Oviedo",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gómez-Curiel",
"given": "Diana I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrera-Barrera",
"given": "Silvia A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ordaz-Cuellar",
"given": "Rosario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sosa-García",
"given": "Jesús O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-Torrentera",
"given": "Rogelio A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cervera",
"given": "Eduardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrera-Saldaña",
"given": "Hugo A",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-26T17:43:04Z",
"timestamp": 1732642984000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-26T17:43:08Z",
"timestamp": 1732642988000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-27T05:35:18Z",
"timestamp": 1732685718127,
"version": "3.28.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
26
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/237234-clinical-experience-with-ivermectin-and-nitazoxanide-in-the-management-of-covid-19-among-mexican-out--and-inpatients",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
26
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.31005/iajmh.v3i0.89",
"article-title": "Neurological aspects that should not be forgotten during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Fernández-Garza LE",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "InterAmerican J Med Health",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Fernández-Garza LE, Marfil A. Neurological aspects that should not be forgotten during the COVID-19 pandemic. InterAmerican J Med Health. 2020, 3:1-3. 10.31005/iajmh.v3i0.89",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3566298",
"article-title": "World Health Organization declared a pandemic public health menace: a systematic review of the coronavirus disease 2019 “COVID-19”",
"author": "Jebril NM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Psychosoc Rehabil",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Jebril NM. World Health Organization declared a pandemic public health menace: a systematic review of the coronavirus disease 2019 “COVID-19”. Int J Psychosoc Rehabil. 2019, 249:2784-95. 10.2139/ssrn.3566298",
"volume": "249",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jocn.15314",
"article-title": "The potential for COVID-19 to contribute to compassion fatigue in critical care nurses",
"author": "Alharbi J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Nurs",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Alharbi J, Jackson D, Usher K. The potential for COVID-19 to contribute to compassion fatigue in critical care nurses. J Clin Nurs. 2020, 29:2762-4. 10.1111/jocn.15314",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen",
"author": "Heidary F",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Antibiot (Tokyo)",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Heidary F, Gharebaghi R. Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020, 73:593-602. 10.1038/s41429-020-0336-z",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173748",
"article-title": "A review on possible mechanistic insights of nitazoxanide for repurposing in COVID-19",
"author": "Lokhande AS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Lokhande AS, Devarajan PV. A review on possible mechanistic insights of nitazoxanide for repurposing in COVID-19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021, 891:173748. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173748",
"volume": "891",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Caly L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res. 2020, 178:104787. 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, et al.. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30:269-71. 10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8",
"article-title": "Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype",
"author": "Marcolino MS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Marcolino MS, Meira KC, Guimarães NS, et al.. Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype. BMC Infect Dis. 2022, 22:639. 10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcac072",
"article-title": "Correction to: Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Deng J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "QJM",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Deng J, Zhou F, Ali S, Heybati K, Hou W, Huang E, Wong CY. Correction to: Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM. 2022, 115:706. 10.1093/qjmed/hcac072",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics11091645",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cruciani M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diagnostics (Basel)",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Cruciani M, Pati I, Masiello F, Malena M, Pupella S, De Angelis V. Ivermectin for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021, 11:14-6. 10.3390/diagnostics11091645",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab591",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Roman YM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Roman YM, Burela PA, Pasupuleti V, Piscoya A, Vidal JE, Hernandez AV. Ivermectin for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Infect Dis. 2022, 74:1022-9. 10.1093/cid/ciab591",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102186",
"article-title": "Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Zein AF",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Zein AF, Sulistiyana CS, Raffaelo WM, Pranata R. Ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021, 15:102186. 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102186",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines",
"author": "Bryant A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Bryant A, Lawrie TA, Dowswell T, Fordham EJ, Mitchell S, Hill SR, Tham TC. Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines. Am J Ther. 2021, 28:e434-60. 10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107248",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment of non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials with 7,035 participants",
"author": "Hernandez AV",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Hernandez AV, Liu A, Roman YM, et al.. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment of non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials with 7,035 participants. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2024, 64:107248. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107248",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2265",
"article-title": "Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid‐19 pneumonia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trial studies",
"author": "Hariyanto TI",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Hariyanto TI, Halim DA, Rosalind J, Gunawan C, Kurniawan A. Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid‐19 pneumonia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trial studies. Rev Med Virol. 2021, 32:e2265. 10.1002/rmv.2265",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27647",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Song Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Song Z, Shi S, Zhang Y. Ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon. 2024, 10:e27647. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27647",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-022-01213-y",
"article-title": "The effect of nitazoxanide on the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Abuelazm M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Drug Investig",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Abuelazm M, Ghanem A, Awad AK, Farahat RA, Labieb F, Katamesh BE, Abdelazeem B. The effect of nitazoxanide on the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Drug Investig. 2022, 42:1031-47. 10.1007/s40261-022-01213-y",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2022.2142117",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes, virological efficacy and safety of nitazoxanide in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Weng TC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Weng TC, Weng TS, Lai CC, Chao CM, Wang JH. Clinical outcomes, virological efficacy and safety of nitazoxanide in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022, 20:1615-22. 10.1080/14787210.2022.2142117",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-022-03380-5",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of nitazoxanide in treating SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trials",
"author": "Martins-Filho PR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Martins-Filho PR, do Nascimento-Júnior EM, Barreto-Alves JA, Fakhouri R, Ferreira LC. Efficacy and safety of nitazoxanide in treating SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trials. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022, 78:1813-21. 10.1007/s00228-022-03380-5",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.. COVID-19 case definition. (2022). Accessed: November 24, 2024: https://who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Surveillance_Case_Definition-2020.2."
},
{
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Laboratories with InDRE recognition, to carry out the diagnosis of COVID-19, for epidemiological surveillance purposes (site in Spanish). (2022). Accessed. November 24, 2024: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/688705/LISTADO_DE_LABORATORIOS_QUE_REALIZAN_EL_DIAGNOSTICO_DE_COVID-19...."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.114008",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2: comparative analysis of different RNA extraction methods",
"author": "Ambrosi C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Virol Methods",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Ambrosi C, Prezioso C, Checconi P, et al.. SARS-CoV-2: comparative analysis of different RNA extraction methods. J Virol Methods. 2021, 287:114008. 10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.114008",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00324-3",
"article-title": "A systematic review of the clinical utility of cycle threshold values in the context of COVID-19",
"author": "Rao SN",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Rao SN, Manissero D, Steele VR, Pareja J. A systematic review of the clinical utility of cycle threshold values in the context of COVID-19. Infect Dis Ther. 2020, 9:573-86. 10.1007/s40121-020-00324-3",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Medscape. ivermectin (Rx). (2021). Accessed: November 24, 2024: https://reference.medscape.com/drug/stromectol-ivermectin-342657."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/428839",
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide: a new thiazolide antiparasitic agent",
"author": "Fox LM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Fox LM, Saravolatz LD. Nitazoxanide: a new thiazolide antiparasitic agent. Clin Infect Dis. 2005, 40:1173-80. 10.1086/428839",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26880",
"article-title": "Effect of a combination of nitazoxanide, ribavirin, and ivermectin plus zinc supplement (MANS.NRIZ study) on the clearance of mild COVID-19",
"author": "Elalfy H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Elalfy H, Besheer T, El-Mesery A, et al.. Effect of a combination of nitazoxanide, ribavirin, and ivermectin plus zinc supplement (MANS.NRIZ study) on the clearance of mild COVID-19. J Med Virol. 2021, 93:3176-83. 10.1002/jmv.26880",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.003",
"article-title": "Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: a pilot trial",
"author": "Pott-Junior H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Rep",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Pott-Junior H, Paoliello MM, Miguel AQ, et al.. Use of ivermectin in the treatment of Covid-19: a pilot trial. Toxicol Rep. 2021, 8:505-10. 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.003",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"article-title": "The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Chaccour C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Chaccour C, Casellas A, Blanco-Di Matteo A, et al.. The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2021, 32:100720. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.03725-2020",
"article-title": "Early use of nitazoxanide in mild COVID-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Rocco PR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Rocco PR, Silva PL, Cruz FF, et al.. Early use of nitazoxanide in mild COVID-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Respir J. 2021, 58:4-6. 10.1183/13993003.03725-2020",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18103/mra.v11i2.3364",
"article-title": "Efficacy of nitazoxanide in reducing the viral ad in COVID-19 patients. Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blinded, parallel-group, pilot study",
"author": "Silva M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med Res Arch",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Silva M, Espejo A, Pereyra ML, et al.. Efficacy of nitazoxanide in reducing the viral ad in COVID-19 patients. Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blinded, parallel-group, pilot study. Med Res Arch. 2023, 11:2-4. 10.18103/mra.v11i2.3364",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.24875/hgmx.20000078",
"article-title": "Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression",
"author": "Ponti G",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Cin Lab Sci",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Ponti G, Maccaferri M, Ruini C, Tomasi A, Ozben T. Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression. Crit Rev Cin Lab Sci. 2021, 57:389-99. 10.24875/hgmx.20000078",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350",
"article-title": "Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19",
"author": "DiNicolantonio JJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Open Heart",
"key": "ref32",
"unstructured": "DiNicolantonio JJ, Barroso J, McCarty M. Ivermectin may be a clinically useful anti-inflammatory agent for late-stage COVID-19. Open Heart. 2020, 7:26-8. 10.1136/openhrt-2020-001350",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.blre.2020.100761",
"article-title": "Coagulation and anticoagulation in COVID-19",
"author": "Hadid T",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood Rev",
"key": "ref33",
"unstructured": "Hadid T, Kafri Z, Al-Katib A. Coagulation and anticoagulation in COVID-19. Blood Rev. 2021, 47:100761. 10.1016/j.blre.2020.100761",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.24875/RIC.20000211",
"article-title": "Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in a tertiary care center in Mexico City: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Ortiz-Brizuela E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Rev Invest Clin",
"key": "ref34",
"unstructured": "Ortiz-Brizuela E, Villanueva-Reza M, González-Lara MF, et al.. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in a tertiary care center in Mexico City: a prospective cohort study. Rev Invest Clin. 2020, 72:165-77. 10.24875/RIC.20000211",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009",
"article-title": "Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: the Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study",
"author": "Rajter JC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref35",
"unstructured": "Rajter JC, Sherman MS, Fatteh N, Vogel F, Sacks J, Rajter JJ. Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: the Ivermectin in COVID Nineteen Study. Chest. 2021, 159:85-92. 10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"article-title": "A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness",
"author": "Ahmed S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "ref36",
"unstructured": "Ahmed S, Karim MM, Ross AG, et al.. A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness. Int J Infect Dis. 2021, 103:214-6. 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01726-3",
"article-title": "COVID-19 length of hospital stay: a systematic review and data synthesis",
"author": "Rees EM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "ref37",
"unstructured": "Rees EM, Nightingale ES, Jafari Y, et al.. COVID-19 length of hospital stay: a systematic review and data synthesis. BMC Med. 2020, 18:270. 10.1186/s12916-020-01726-3",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5281/zenodo.3926806",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in Mexico: epidemiological panorama (article in Spanish)",
"author": "Padilla-Santamaría F",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Revista Cadena de Cerebros",
"key": "ref38",
"unstructured": "Padilla-Santamaría F, Maya-Franco L, Ferman-Cano F. COVID-19 in Mexico: epidemiological panorama (article in Spanish). Revista Cadena de Cerebros. 2020, 4:31-42. 10.5281/zenodo.3926806",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Mortality from COVID-19 in Mexico. Preliminary notes for a sociodemographic profile",
"author": "Bringas HH",
"journal-title": "Notas de Coyuntura del CRIM",
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Bringas HH. Mortality from COVID-19 in Mexico. Preliminary notes for a sociodemographic profile. Notas de Coyuntura del CRIM. 2020, 36:1-7.",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z",
"article-title": "The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Kow CS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "ref40",
"unstructured": "Kow CS, Merchant HA, Mustafa ZU, Hasan SS. The association between the use of ivermectin and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Pharmacol Rep. 2021, 73:1473-9. 10.1007/s43440-021-00245-z",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hill A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "ref41",
"unstructured": "Hill A, Garratt A, Levi J, et al.. Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021, 8:ofab358. 10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref42",
"unstructured": "FDA. know your treatment options for COVID-19. (2023). Accessed: November 15, 2024: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-options-covid-19#:~:text=If%20you%20are%20infected...."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2020.0126",
"article-title": "Ruxolitinib and the mitigation of severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Quiros JR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Infect Chemother",
"key": "ref43",
"unstructured": "Quiros JR, Ross-Comptis J, Hathaway D 3rd, et al.. Ruxolitinib and the mitigation of severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Chemother. 2021, 53:436-48. 10.3947/ic.2020.0126",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/237234-clinical-experience-with-ivermectin-and-nitazoxanide-in-the-management-of-covid-19-among-mexican-out--and-inpatients"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical Experience With Ivermectin and Nitazoxanide in the Management of COVID-19 Among Mexican Out- and Inpatients",
"type": "journal-article"
}