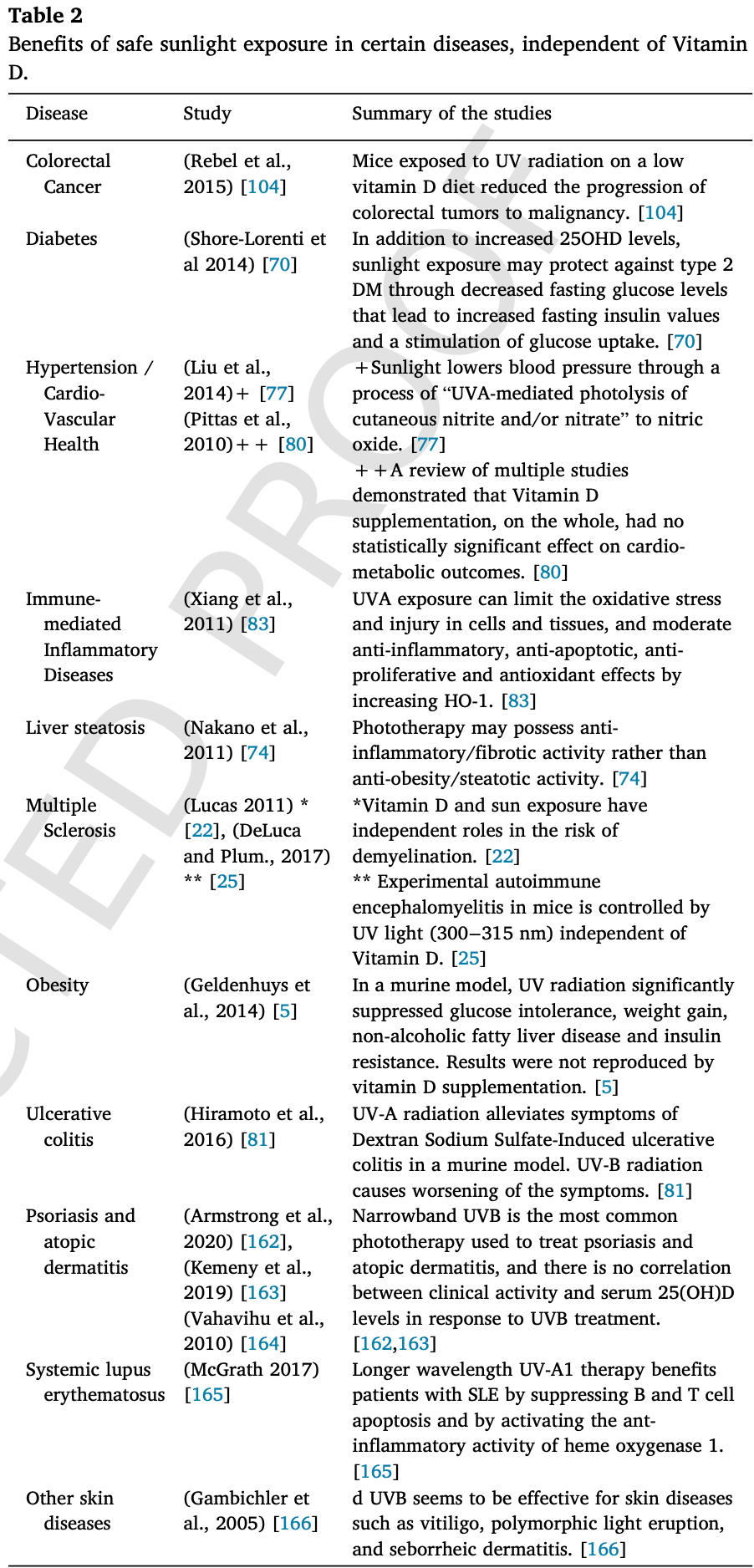
Vitamin D-independent benefits of safe sunlight exposure
et al., The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957, Oct 2021
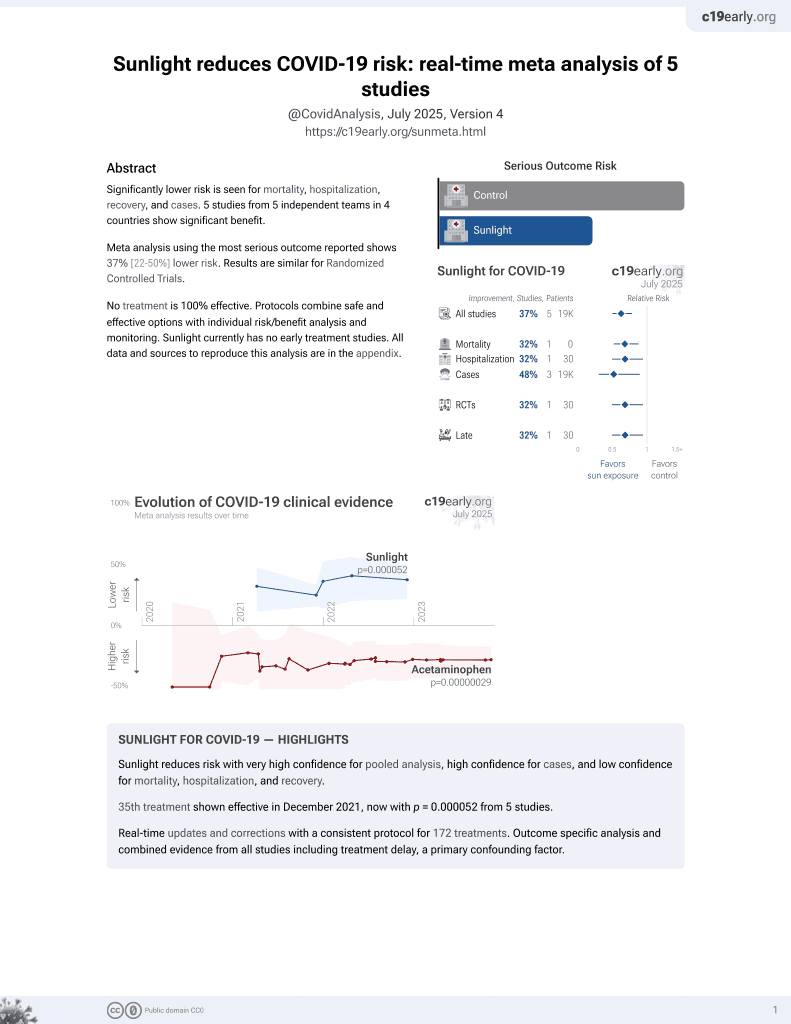
Sunlight for COVID-19
35th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the benefits of sunlight exposure independent of vitamin D.
1.
Gong et al., Natural and socio-environmental factors in the transmission of COVID-19: a comprehensive analysis of epidemiology and mechanisms, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-024-19749-3.
2.
Limaheluw et al., Associations between meteorological factors and COVID-19: a global scoping review, Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2024.1183706.
3.
Seheult, R., The Case for Sunlight in COVID 19 Patients: Oxidative Stress, MedCram, www.youtube.com/watch?v=2Zzo4SJopcY&t=268s.
Erem et al., 31 Oct 2021, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Vitamin D-independent benefits of safe sunlight exposure
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957
This review examines the beneficial effects of ultraviolet radiation on systemic autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes, where the epidemiological evidence for the vitamin D-independent effects of sunlight is most apparent. Ultraviolet radiation, in addition to its role in the synthesis of vitamin D, stimulates anti-inflammatory pathways, alters the composition of dendritic cells, T cells, and T regulatory cells, and induces nitric oxide synthase and heme oxygenase metabolic pathways, which may directly or indirectly mitigate disease progression and susceptibility. Recent work has also explored how the immune-modulating functions of ultraviolet radiation affect type II diabetes, cancer, and the current global pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2. These diseases are particularly important amidst global changes in lifestyle that result in unhealthy eating, increased sedentary habits, and alcohol and tobacco consumption. Compelling epidemiological data shows increased ultraviolet radiation associated with reduced rates of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer, non-Hodgkins lymphoma, and ultraviolet radiation exposure correlated with susceptibility and mortality rates of COVID-19. Thus, understanding the effects of ultraviolet radiation on both vitamin D-dependent andindependent pathway is necessary to understand how they influence the course of many human diseases.
References
Abraham, Dowling, Florentine, Can Optimum Solar Radiation Exposure or Supplemented Vitamin D Intake Reduce the Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms?, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health
Adorini, Penna, Giarratana, Dendritic cells as key targets for immunomodulation by Vitamin D receptor ligands, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Akbar, Wibowo, Pranata, Setiabudiawan, Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (vitamin D) level is associated with susceptibility to COVID-19, severity, and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front. Nutr
Anderson, Parrish, The optics of human skin, J. Invest. Dermatol
Annweiler, Beaudenon, Gautier, COvid-19 and high-dose VITamin D supplementation TRIAL in high-risk older patients (COVIT-TRIAL): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Annweiler, Cao, Sabatier, Point of view: Should COVID-19 patients be supplemented with vitamin D?, Maturitas
Annweiler, Hanotte, Grandin De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: a quasi-experimental study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Armstrong, Pathophysiology, Clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review, JAMA
Autier, Dore, Ultraviolet radiation and cutaneous melanoma: a historical perspective, Melanoma Res
Baarnhielm, Hedstrom, Kockum, Sunlight is associated with decreased multiple sclerosis risk: no interaction with human leukocyte antigen-DRB1*15, Eur. J. Neurol
Baker, Yang, Vecchi, Metcalf, Grenfell, Susceptible supply limits the role of climate in the early SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, Science
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad. Med. J
Becklund, Severson, Vang, Deluca, UV radiation suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis independent of vitamin D production, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Beveridge, Struthers, Khan, Effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating individual patient data, JAMA Intern. Med
Bogh, Schmedes, Philipsen, Thieden, Wulf, Vitamin D production after UVB exposure depends on baseline vitamin D and total cholesterol but not on skin pigmentation, J. Invest. Dermatol
Bolland, Grey, Avenell, Gamble, Reid, Calcium supplements with or without vitamin D and risk of cardiovascular events: reanalysis of the Women's Health Initiative limited access dataset and meta-analysis, BMJ
Bourdrel, Annesi-Maesano, Alahmad, Maesano, Bind, The impact of outdoor air pollution on COVID-19: a review of evidence from in vitro, animal, and human studies, Eur. Respir. Rev
Breuer, Schwab, Schneider-Hohendorf, Ultraviolet B light attenuates the systemic immune response in central nervous system autoimmunity, Ann. Neurol
Brown, Haq, Stanford, Razzaque, Vitamin et al., None, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol
Bruhs, Haarmann-Stemmann, Frauenstein, Krutmann, Schwarz et al., Activation of the arylhydrocarbon receptor causes immunosuppression primarily by modulating dendritic cells, J. Invest. Dermatol
Bustamante, Hernandez-Ferrer, Tewari, Dose and time effects of solar-simulated ultraviolet radiation on the in vivo human skin transcriptome, Br. J. Dermatol
Cadario, Savastio, Pagliardini, Vitamin D levels at birth and risk of type 1 diabetes in childhood: a case-control study, Acta Diabetol
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiol. Infect
Carakushansky, Patel, Ben Khallouq, Gurnurkar, Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus, Cureus
Carleton, Cornetet, Huybers, Meng, Proctor, Global evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Casteels, Gysemans, Waer, Sex difference in resistance to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in NOD mice: treatment with 1,25(OH)2D3 restores defect, Diabetes
Casteels, Waer, Bouillon, 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 restores sensitivity to cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice and protects against diabetes, Clin. Exp. Immunol
Castillo, Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Chen, Chimeh, Lu, Factors that influence the cutaneous synthesis and dietary sources of vitamin D, Arch. Biochem. Biophys
Chen, Prettner, Kuhn, Climate and the spread of COVID-19, Sci. Rep
Correale, Farez, Modulation of multiple sclerosis by sunlight exposure: role of cis-urocanic acid, J. Neuroimmunol
Craveiro, Cabral, Araujo, Falcao, Guimaraes et al., Association of serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentration with pulmonary function in young adults, Nutrients
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Dawson-Hughes, Staten, Knowler, Intratrial exposure to vitamin D and new-onset diabetes among adults with prediabetes: a secondary analysis from the vitamin D and type 2 diabetes (D2d) study, Diabetes Care
Deluca, Plum, UVB radiation, vitamin D and multiple sclerosis, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci
Denos, Mai, Asvold, Sorgjerd, Chen et al., Vitamin D status and risk of type 2 diabetes in the Norwegian HUNT cohort study: does family history or genetic predisposition modify the association?, BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care
Diaz-Valencia, Bougneres, Valleron, Covariation of the incidence of type 1 diabetes with country characteristics available in public databases, PLoS One
Diaz-Valencia, Bougneres, Valleron, Global epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in young adults and adults: a systematic review, BMC Public Health
Dimeglio, Evans-Molina, Oram, Type 1 diabetes, Lancet
Dopico, Evangelou, Ferreira, Widespread seasonal gene expression reveals annual differences in human immunity and physiology, Nat. Commun
Erem, Razzaque, None, Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology xxx
Ferrari, Locatelli, Briguglio, Lombardi, Is there a link between vitamin D status, SARS-CoV-2 infection risk and COVID-19 severity?, Cell Biochem. Funct
Gallagher, Lee, Adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation: a brief review, Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol
Gambichler, Breuckmann, Boms, Altmeyer, Kreuter, Narrowband UVB phototherapy in skin conditions beyond psoriasis, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol
Gandini, Boniol, Haukka, Meta-analysis of observational studies of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and colorectal, breast and prostate cancer and colorectal adenoma, Int. J. Cancer
Garland, Comstock, Garland, Helsing, Shaw et al., Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and colon cancer: eight-year prospective study, Lancet
Garland, Garland, Do sunlight and vitamin D reduce the likelihood of colon cancer?, Int. J. Epidemiol
Garland, Shekelle, Barrett-Connor, Criqui, Rossof et al., Dietary vitamin D and calcium and risk of colorectal cancer: a 19-year prospective study in men, Lancet
Geldenhuys, Hart, Endersby, Ultraviolet radiation suppresses obesity and symptoms of metabolic syndrome independently of vitamin D in mice fed a high-fat diet, Diabetes
Ginde, Mansbach, Camargo, Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Arch. Intern. Med
Gorman, Black, Feelisch, Hart, Weller, Can skin exposure to sunlight prevent liver inflammation?, Nutrients
Granfors, Augustin, Ludvigsson, Brekke, No association between use of multivitamin supplement containing vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of Type 1 Diabetes in the child, Pediatr. Diabetes
Grant, Giovannucci, The possible roles of solar ultraviolet-B radiation and vitamin D in reducing case-fatality rates from the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic in the United States, Dermatoendocrinology
Grant, Roles of solar UVB and vitamin D in reducing Cancer risk and increasing survival, Anticancer Res
Grant, The role of geographical ecological studies in identifying diseases linked to UVB exposure and/or vitamin D, Dermatoendocrinology
Green, Wallingford, Mcbride, Childhood exposure to ultraviolet radiation and harmful skin effects: epidemiological evidence, Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients
Halliday, Norval, Byrne, Huang, Wolf, The effects of sunlight on the skin, Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech
Hart, Norval, Byrne, Rhodes, Exposure to ultraviolet radiation in the modulation of human diseases, Annu. Rev. Pathol
Hernandez, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Herrick, Storandt, Afful, vitamin D status in the United States, 2011-2014, Am. J. Clin. Nutr
Hiramoto, Yamate, Sato, The effects of ultraviolet eye irradiation on dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice, Photochem. Photobiol
Hoel, Berwick, De Gruijl, Holick, The risks and benefits of sun exposure, Dermatoendocrinology
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Holick, Cancer, sunlight and vitamin D, J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol
Hollis, Wagner, Clinical review: the role of the parent compound vitamin D with respect to metabolism and function: why clinical dose intervals can affect clinical outcomes, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Hope-Simpson, The role of season in the epidemiology of influenza, J. Hyg. (Lond.)
Hoseinzadeh, Taha, Wei, The impact of air pollutants, UV exposure and geographic location on vitamin D deficiency, Food Chem. Toxicol
Hossein-Nezhad, Spira, Holick, Influence of vitamin D status and vitamin D3 supplementation on genome wide expression of white blood cells: a randomized double-blind clinical trial, PLoS One
Hou, Song, Jin, Xia, Song et al., A dose-response meta-analysis between serum concentration of 25-hydroxy vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes mellitus, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr
Hussen, Yang, Cnattingius, Moradi, Type I diabetes among children and young adults: the role of country of birth, socioeconomic position and sex, Pediatr. Diabetes
Hypponen, Laara, Reunanen, Jarvelin, Virtanen, Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes: a birth-cohort study, Lancet
Infante, Ricordi, Sanchez, Influence of vitamin D on islet autoimmunity and beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes, Nutrients
Irving, Marling, Plum, Deluca, Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by ultraviolet light is not mediated by isomerization of urocanic acid, BMC Neurosci
Irving, Marling, Seeman, Plum, Deluca, UV light suppression of EAE (a mouse model of multiple sclerosis) is independent of vitamin D and its receptor, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Ismailova, Poudel, Parlesak, Frederiksen, Heitmann, Vitamin D in early life and later risk of multiple sclerosis-A systematic review, meta-analysis, PLoS One
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci. Rep
Jansen, Daiber, Direct antioxidant properties of bilirubin and Biliverdin. Is there a role for biliverdin reductase?, Front. Pharmacol
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Kachapati, Adams, Bednar, Ridgway, The non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse as a model of human type 1 diabetes, Methods Mol. Biol
Kakodkar, Kaka, Baig, A Comprehensive Literature Review on the Clinical Presentation, and Management of the Pandemic Coronavirus Disease, COVID-19
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS One
Kemeny, Varga, Novak, Advances in phototherapy for psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol
Khalili, Huang, Ananthakrishnan, Geographical variation and incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among US women, Gut
Kim, He, Ultraviolet radiation-induced non-melanoma skin cancer: regulation of DNA damage repair and inflammation, Genes Dis
Kok, Marsh-Wakefield, Marshall, Gillis, Halliday et al., B cells are required for sunlight protection of mice from a CNS-targeted autoimmune attack, J. Autoimmun
Krishnan, Feldman, Mechanisms of the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory actions of vitamin D, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol
Langer-Gould, Lucas, Xiang, MS sunshine study: sun exposure but not vitamin D is associated with multiple sclerosis risk in blacks and hispanics, Nutrients
Langer-Gould, Lucas, Xiang, Vitamin D-Binding protein polymorphisms, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, sunshine and multiple sclerosis, Nutrients
Lanham-New, Webb, Cashman, vitamin D and SARS-CoV-2 virus/COVID-19 disease, BMJ Nutr. Prevent. Health
Lim, Roychoudhuri, Peto, Schwartz, Baade et al., Cancer survival is dependent on season of diagnosis and sunlight exposure, Int. J. Cancer
Liu, Fernandez, Hamilton, UVA irradiation of human skin vasodilates arterial vasculature and lowers blood pressure independently of nitric oxide synthase, J. Invest. Dermatol
Lucas, Byrne, Correale, Ilschner, Hart, Ultraviolet radiation, vitamin D and multiple sclerosis, Neurodegener. Dis. Manag
Lucas, Ponsonby, Dear, Sun exposure and vitamin D are independent risk factors for CNS demyelination, Neurology
Lucas, Yazar, Young, Human health in relation to exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation under changing stratospheric ozone and climate, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci
Makinen, Mykkanen, Koskinen, Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in children progressing to autoimmunity and clinical type 1 diabetes, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Mariani, Gimenez, Bergam, Association between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 incidence, complications, and mortality in 46 countries: an ecological study
Marsh-Wakefield, Ashhurst, Trend, IgG3 (+) B cells are associated with the development of multiple sclerosis, Clin. Transl. Immunology
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mathieu, Laureys, Sobis, Vandeputte, Waer et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 prevents insulitis in NOD mice, Diabetes
Mathieu, Waer, Casteels, Laureys, Bouillon, Prevention of type I diabetes in NOD mice by nonhypercalcemic doses of a new structural analog of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, KH1060, Endocrinology
Mathieu, Waer, Laureys, Rutgeerts, Bouillon, Prevention of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice by 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3, Diabetologia
Matsuoka, Wortsman, Dannenberg, Hollis, Lu et al., Clothing prevents ultraviolet-B radiation-dependent photosynthesis of vitamin D3, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Mcgrath, Ultraviolet-A1 irradiation therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus, Lupus
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli populationbased study, FEBS J
Miller, Hart, De Klerk, Davis, Lucas, Are low sun exposure and/or vitamin D risk factors for type 1 diabetes?, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci
Moan, Baturaite, Dahlback, Porojnicu, Ultraviolet radiation and cutaneous malignant melanoma, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol
Mohan, Cherian, Sharma, Exploring links between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19, PLoS Pathog
Mohr, Garland, Gorham, Garland, The association between ultraviolet B irradiance, vitamin D status and incidence rates of type 1 diabetes in 51 regions worldwide, Diabetologia
Moozhipurath, Kraft, Skiera, Evidence of protective role of Ultraviolet-B (UVB) radiation in reducing COVID-19 deaths, Sci. Rep
Nakano, Cheng, Lai, Impact of artificial sunlight therapy on the progress of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats, J. Hepatol
Navid, Bruhs, Schuller, The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor is involved in UVR-induced immunosuppression, J. Invest. Dermatol
Neale, Khan, Lucas, Waterhouse, Whiteman et al., The effect of sunscreen on vitamin D: a review, Br. J. Dermatol
Nerich, Jantchou, Boutron-Ruault, Low exposure to sunlight is a risk factor for Crohn's disease, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther
Oh, Ansell, Nawaz, Yang, Wood et al., Global breast cancer seasonality, Breast Cancer Res. Treat
Olaogun, Farag, Hamid, The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus in non-obese individuals: an overview of the current understanding, Cureus
Olsson, Barcellos, Alfredsson, Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis, Nat. Rev. Neurol
Oscanoa, Amado, Vidal, Laird, Ghashut et al., The relationship between the severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration -a metaanalysis, Adv. Respir. Med
Otter, Donskey, Yezli, Douthwaite, Goldenberg et al., Transmission of SARS and MERS coronaviruses and influenza virus in healthcare settings: the possible role of dry surface contamination, J. Hosp. Infect
Otterbein, Bach, Alam, Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, Nat. Med
Pantavou, Bagos, Season of birth and multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis, J. Neurol
Pereira, Dantas Damascena, Galvao Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr
Pham, Waterhouse, Baxter, The effect of vitamin D supplementation on acute respiratory tract infection in older Australian adults: an analysis of data from the D-Health Trial, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Pittas, Chung, Trikalinos, Systematic review: vitamin D and cardiometabolic outcomes, Ann. Intern. Med
Pittas, Dawson-Hughes, Sheehan, vitamin D supplementation and prevention of type 2 diabetes, N. Engl. J. Med
Plum, Deluca, Vitamin D, disease and therapeutic opportunities, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov
Powers, Murphy, Ralph, O'gorman, Murphy, Mitochondrial DNA deletion percentage in sun exposed and non sun exposed skin, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B
Rana, Rogers, Halliday, Systemic low-dose UVB inhibits CD8 T cells and skin inflammation by alternative and novel mechanisms, Am. J. Pathol
Razzaque, Can adverse effects of excessive vitamin D supplementation occur without developing hypervitaminosis D?, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Rebel, Der Spek, Salvatori, Van Leeuwen, Robanus-Maandag et al., UV exposure inhibits intestinal tumor growth and progression to malignancy in intestine-specific Apc mutant mice kept on low vitamin D diet, Int. J. Cancer
Rewers, Ludvigsson, Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes, Lancet
Rhodes, Dunstan, Laird, Subramanian, Kenny, COVID-19 mortality increases with northerly latitude after adjustment for age suggesting a link with ultraviolet and vitamin D, BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther
Rogers, Weinstock, Harris, Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States, 2006, Arch. Dermatol
Sahay, Sahay, Rickets-vitamin D deficiency and dependency, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab
Sancar, Van Gelder, Clocks, cancer, and chronochemotherapy, Science
Shore-Lorenti, Brennan, Sanders, Neale, Lucas et al., Shining the light on Sunshine: a systematic review of the influence of sun exposure on type 2 diabetes mellitus-related outcomes, Clin Endocrinol (Oxf)
Silvis, Aronsson, Liu, Maternal dietary supplement use and development of islet autoimmunity in the offspring: TEDDY study, Pediatr. Diabetes
Simpson, Blizzard, Otahal, Van Der Mei, Taylor, Latitude is significantly associated with the prevalence of multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry
Simpson, Wang, Otahal, Blizzard, Van Der Mei et al., Latitude continues to be significantly associated with the prevalence of multiple sclerosis: an updated meta-analysis, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry
Sloka, Grant, Newhook, The geospatial relation between UV solar radiation and type 1 diabetes in Newfoundland, Acta Diabetol
Soares, Bach, Heme oxygenase-1: from biology to therapeutic potential, Trends Mol. Med
Soderstrom, Aman, Hjern ; U N C O R R E C T E D P R O O F S, Erem, Razzaque, Being born in Sweden increases the risk for type 1 diabetes -a study of migration of children to Sweden as a natural experiment, Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology xxx
Srivastava, Garg, Bansal, Kumar, SARS-CoV-2 infection: physiological and environmental gift factors at high altitude, Virusdisease
Staples, Ponsonby, Lim, Mcmichael, Ecologic analysis of some immune-related disorders, including type 1 diabetes, in Australia: latitude, regional ultraviolet radiation, and disease prevalence, Environ. Health Perspect
Stene, Joner, Norwegian, Diabetes, Study G. Use of cod liver oil during the first year of life is associated with lower risk of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes: a large, population-based, case-control study, Am. J. Clin. Nutr
Takiishi, Ding, Baeke, Dietary supplementation with high doses of regular vitamin D3 safely reduces diabetes incidence in NOD mice when given early and long term, Diabetes
Tang, Liu, Ren, Sunlight ultraviolet radiation dose is negatively correlated with the percent positive of SARS-CoV-2 and four other common human coronaviruses in the U, Sci. Total Environ
Tapia, Marild, Dahl, Maternal and newborn vitamin D-Binding protein, vitamin D levels, vitamin D receptor genotype, and childhood type 1 diabetes, Diabetes Care
Taylor, Davies, A review of the growing risk of vitamin D toxicity from inappropriate practice, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol
Vahavihu, Ala-Houhala, Peric, Narrowband ultraviolet B treatment improves vitamin D balance and alters antimicrobial peptide expression in skin lesions of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, Br. J. Dermatol
Van Der Leun, The ozone layer, Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed
Van Der Rhee, Coebergh, Vries, Is prevention of cancer by sun exposure more than just the effect of vitamin D? A systematic review of epidemiological studies, Eur. J. Cancer
Veldurthy, Wei, Oz, Dhawan, Jeon et al., Vitamin D, calcium homeostasis and aging, Bone Res
Walrand, Autumn COVID-19 surge dates in Europe correlated to latitudes, not to temperature-humidity, pointing to vitamin D as contributing factor, Sci. Rep
Watad, Azrielant, Bragazzi, Seasonality and autoimmune diseases: the contribution of the four seasons to the mosaic of autoimmunity, J. Autoimmun
Webb, Kazantzidis, Kift, Farrar, Wilkinson et al., Colour counts: sunlight and skin type as drivers of vitamin D deficiency at UK latitudes, Nutrients
Weller, Schwentker, Billiar, Vodovotz, Autologous nitric oxide protects mouse and human keratinocytes from ultraviolet B radiation-induced apoptosis, Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol
Whittemore, COVID-19 fatalities, latitude, sunlight, and vitamin D, Am. J. Infect. Control
Xia, Qiu, Peng, Lo-Dauer, Clare-Salzler, Apoptotic non-beta cells suppress beta cell antigen-reactive T cells and induce beta cell antigen-specific regulatory T cells, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci
Xiang, Liu, Yang, Zhong, UVA-induced protection of skin through the induction of heme oxygenase-1, Biosci. Trends
Youl, Janda, Kimlin, Vitamin D and sun protection: the impact of mixed public health messages in Australia, Int. J. Cancer
Young, Morgan, Ho, Melanin has a small inhibitory effect on cutaneous vitamin D synthesis: a comparison of extreme phenotypes, J. Invest. Dermatol
Zimmet, Alberti, Magliano, Bennett, Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: facts and fallacies, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957",
"ISSN": [
"0960-0760"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957",
"alternative-id": [
"S0960076021001503"
],
"article-number": "105957",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Vitamin D-independent benefits of safe sunlight exposure"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1393-764X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Erem",
"given": "Anna S.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Razzaque",
"given": "Mohammed S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology",
"container-title-short": "The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-27T15:58:45Z",
"timestamp": 1627401525000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-05T14:45:18Z",
"timestamp": 1657032318000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-08T05:25:50Z",
"timestamp": 1670477150838
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0960076021001503?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0960076021001503?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "105957",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0781.2004.00091.x",
"article-title": "The ozone layer",
"author": "van der Leun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "159",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0005",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1523-1747.ep12479191",
"article-title": "The optics of human skin",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0010",
"volume": "77",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"article-title": "Ultraviolet radiation and cutaneous malignant melanoma",
"author": "Moan",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0015",
"volume": "810",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Ultraviolet radiation and cutaneous melanoma: a historical perspective",
"author": "Autier",
"journal-title": "Melanoma Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0020",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db13-1675",
"article-title": "Ultraviolet radiation suppresses obesity and symptoms of metabolic syndrome independently of vitamin D in mice fed a high-fat diet",
"author": "Geldenhuys",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3759",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0025",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jid.2019.11.019",
"article-title": "Melanin has a small inhibitory effect on cutaneous vitamin D synthesis: a comparison of extreme phenotypes",
"author": "Young",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0030",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd3318",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, disease and therapeutic opportunities",
"author": "Plum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "941",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0035",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/boneres.2016.41",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, calcium homeostasis and aging",
"author": "Veldurthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16041",
"journal-title": "Bone Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0040",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2006.12.017",
"article-title": "Factors that influence the cutaneous synthesis and dietary sources of vitamin D",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "213",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0045",
"volume": "460",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.93732",
"article-title": "Rickets-vitamin D deficiency and dependency",
"author": "Sahay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "164",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0050",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"article-title": "Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1911",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0055",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012809",
"article-title": "Exposure to ultraviolet radiation in the modulation of human diseases",
"author": "Hart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Pathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0060",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301574",
"article-title": "Geographical variation and incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among US women",
"author": "Khalili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1686",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0065",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04601.x",
"article-title": "Low exposure to sunlight is a risk factor for Crohn’s disease",
"author": "Nerich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "940",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0070",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrneurol.2016.187",
"article-title": "Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Olsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Neurol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0075",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/nmt.15.33",
"article-title": "Ultraviolet radiation, vitamin D and multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Lucas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "413",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Neurodegener. Dis. Manag.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0080",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jnnp.2011.240432",
"article-title": "Latitude is significantly associated with the prevalence of multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Simpson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1132",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0085",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jnnp-2018-320189",
"article-title": "Latitude continues to be significantly associated with the prevalence of multiple sclerosis: an updated meta-analysis",
"author": "Simpson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1193",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0090",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0221645",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in early life and later risk of multiple sclerosis-A systematic review, meta-analysis",
"author": "Ismailova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0221645",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0095",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00415-019-09346-5",
"article-title": "Season of birth and multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis",
"author": "Pantavou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2815",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0100",
"volume": "267",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03650.x",
"article-title": "Sunlight is associated with decreased multiple sclerosis risk: no interaction with human leukocyte antigen-DRB1*15",
"author": "Baarnhielm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "955",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Neurol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0105",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820af93d",
"article-title": "Sun exposure and vitamin D are independent risk factors for CNS demyelination",
"author": "Lucas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "540",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Neurology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0110",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10030268",
"article-title": "MS sunshine study: sun exposure but not vitamin D is associated with multiple sclerosis risk in blacks and hispanics",
"author": "Langer-Gould",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0115",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10020184",
"article-title": "Vitamin D-Binding protein polymorphisms, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, sunshine and multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Langer-Gould",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0120",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C6PP00308G",
"article-title": "UVB radiation, vitamin D and multiple sclerosis",
"author": "DeLuca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "411",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Photochem. Photobiol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0125",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1001119107",
"article-title": "UV radiation suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis independent of vitamin D production",
"author": "Becklund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6418",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0130",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1913294116",
"article-title": "UV light suppression of EAE (a mouse model of multiple sclerosis) is independent of vitamin D and its receptor",
"author": "Irving",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "22552",
"issue": "45",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0135",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.02.016",
"article-title": "Systemic low-dose UVB inhibits CD8 T cells and skin inflammation by alternative and novel mechanisms",
"author": "Rana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2783",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Pathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0140",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ana.24165",
"article-title": "Ultraviolet B light attenuates the systemic immune response in central nervous system autoimmunity",
"author": "Breuer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "739",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann. Neurol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0145",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.013",
"article-title": "Dendritic cells as key targets for immunomodulation by Vitamin D receptor ligands",
"author": "Adorini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "437",
"issue": "1–5",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0150",
"volume": "89-90",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jid.2013.221",
"article-title": "The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor is involved in UVR-induced immunosuppression",
"author": "Navid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2763",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0155",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jid.2014.419",
"article-title": "Activation of the arylhydrocarbon receptor causes immunosuppression primarily by modulating dendritic cells",
"author": "Bruhs",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "435",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0160",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.05.014",
"article-title": "Modulation of multiple sclerosis by sunlight exposure: role of cis-urocanic acid",
"author": "Correale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroimmunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0165",
"volume": "261",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12868-016-0323-2",
"article-title": "Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by ultraviolet light is not mediated by isomerization of urocanic acid",
"author": "Irving",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Neurosci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0170",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2016.05.016",
"article-title": "B cells are required for sunlight protection of mice from a CNS-targeted autoimmune attack",
"author": "Kok",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Autoimmun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0175",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cti2.1133",
"article-title": "IgG3 (+) B cells are associated with the development of multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Marsh-Wakefield",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Clin. Transl. Immunology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0180",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31320-5",
"article-title": "Type 1 diabetes",
"author": "DiMeglio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2449",
"issue": "10138",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0185",
"volume": "391",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092185",
"article-title": "Influence of vitamin D on islet autoimmunity and beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes",
"author": "Infante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0190",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30507-4",
"article-title": "Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes",
"author": "Rewers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2340",
"issue": "10035",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0195",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2017.06.001",
"article-title": "Seasonality and autoimmune diseases: the contribution of the four seasons to the mosaic of autoimmunity",
"author": "Watad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "J. Autoimmun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0200",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C6PP00294C",
"article-title": "Are low sun exposure and/or vitamin D risk factors for type 1 diabetes?",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Photochem. Photobiol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0205",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-015-1591-y",
"article-title": "Global epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in young adults and adults: a systematic review",
"author": "Diaz-Valencia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0210",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0118298",
"article-title": "Covariation of the incidence of type 1 diabetes with country characteristics available in public databases",
"author": "Diaz-Valencia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0215",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-008-1061-5",
"article-title": "The association between ultraviolet B irradiance, vitamin D status and incidence rates of type 1 diabetes in 51 regions worldwide",
"author": "Mohr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1391",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0220",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-009-0100-0",
"article-title": "The geospatial relation between UV solar radiation and type 1 diabetes in Newfoundland",
"author": "Sloka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0225",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1289/ehp.5941",
"article-title": "Ecologic analysis of some immune-related disorders, including type 1 diabetes, in Australia: latitude, regional ultraviolet radiation, and disease prevalence",
"author": "Staples",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "518",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Environ. Health Perspect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0230",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1399-5448.2012.00904.x",
"article-title": "Type I diabetes among children and young adults: the role of country of birth, socioeconomic position and sex",
"author": "Hussen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0235",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1651-2227.2011.02410.x",
"article-title": "Being born in Sweden increases the risk for type 1 diabetes - a study of migration of children to Sweden as a natural experiment",
"author": "Soderstrom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Paediatr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0240",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc18-2176",
"article-title": "Maternal and newborn vitamin D-Binding protein, vitamin D levels, vitamin D receptor genotype, and childhood type 1 diabetes",
"author": "Tapia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "553",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0245",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "A dose-response meta-analysis between serum concentration of 25-hydroxy vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Hou",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0250",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-015-0772-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D levels at birth and risk of type 1 diabetes in childhood: a case-control study",
"author": "Cadario",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1077",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0255",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Carakushansky",
"first-page": "e7836",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0260",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2015-3504",
"article-title": "Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in children progressing to autoimmunity and clinical type 1 diabetes",
"author": "Makinen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "723",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0265",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/pedi.12334",
"article-title": "No association between use of multivitamin supplement containing vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of Type 1 Diabetes in the child",
"author": "Granfors",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "525",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0270",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Maternal dietary supplement use and development of islet autoimmunity in the offspring: TEDDY study",
"author": "Silvis",
"first-page": "86",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0275",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06580-1",
"article-title": "Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes: a birth-cohort study",
"author": "Hypponen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1500",
"issue": "9292",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0280",
"volume": "358",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s001250051112",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplement in early childhood and risk for Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. The EURODIAB Substudy 2 Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0285",
"volume": "42",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/78.6.1128",
"article-title": "Norwegian Childhood Diabetes Study G. Use of cod liver oil during the first year of life is associated with lower risk of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes: a large, population-based, case-control study",
"author": "Stene",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1128",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0290",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"article-title": "The non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse as a model of human type 1 diabetes",
"author": "Kachapati",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0295",
"volume": "933",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00403372",
"article-title": "Prevention of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice by 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3",
"author": "Mathieu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "552",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0300",
"volume": "37",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endo.136.3.7867594",
"article-title": "Prevention of type I diabetes in NOD mice by nonhypercalcemic doses of a new structural analog of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, KH1060",
"author": "Mathieu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "866",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0305",
"volume": "136",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diab.41.11.1491",
"article-title": "1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 prevents insulitis in NOD mice",
"author": "Mathieu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1491",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0310",
"volume": "41",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00568.x",
"article-title": "1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 restores sensitivity to cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice and protects against diabetes",
"author": "Casteels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "181",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0315",
"volume": "112",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diabetes.47.7.1033",
"article-title": "Sex difference in resistance to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in NOD mice: treatment with 1,25(OH)2D3 restores defect",
"author": "Casteels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0320",
"volume": "47",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db13-1559",
"article-title": "Dietary supplementation with high doses of regular vitamin D3 safely reduces diabetes incidence in NOD mice when given early and long term",
"author": "Takiishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2026",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0325",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1196/annals.1447.038",
"article-title": "Apoptotic non-beta cells suppress beta cell antigen-reactive T cells and induce beta cell antigen-specific regulatory T cells",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0330",
"volume": "1150",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrendo.2016.105",
"article-title": "Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: facts and fallacies",
"author": "Zimmet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0335",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus in non-obese individuals: an overview of the current understanding",
"author": "Olaogun",
"first-page": "e7614",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cureus.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0340",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001948",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and risk of type 2 diabetes in the Norwegian HUNT cohort study: does family history or genetic predisposition modify the association?",
"author": "Denos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0345",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.12567",
"article-title": "Shining the light on Sunshine: a systematic review of the influence of sun exposure on type 2 diabetes mellitus-related outcomes",
"author": "Shore-Lorenti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "799",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0350",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1900906",
"article-title": "vitamin D supplementation and prevention of type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Pittas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "520",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0355",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1765",
"article-title": "Intratrial exposure to vitamin D and new-onset diabetes among adults with prediabetes: a secondary analysis from the vitamin D and type 2 diabetes (D2d) study",
"author": "Dawson-Hughes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2916",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0360",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2013-2653",
"article-title": "Clinical review: the role of the parent compound vitamin D with respect to metabolism and function: why clinical dose intervals can affect clinical outcomes",
"author": "Hollis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4619",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0365",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.028",
"article-title": "Impact of artificial sunlight therapy on the progress of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats",
"author": "Nakano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "415",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0370",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7053219",
"article-title": "Can skin exposure to sunlight prevent liver inflammation?",
"author": "Gorman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3219",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0375",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpcell.00462.2002",
"article-title": "Autologous nitric oxide protects mouse and human keratinocytes from ultraviolet B radiation-induced apoptosis",
"author": "Weller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "C1140",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0380",
"volume": "284",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jid.2014.27",
"article-title": "UVA irradiation of human skin vasodilates arterial vasculature and lowers blood pressure independently of nitric oxide synthase",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1839",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0385",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqz037",
"article-title": "vitamin D status in the United States, 2011-2014",
"author": "Herrick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0390",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0237",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating individual patient data",
"author": "Beveridge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "745",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0395",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-152-5-201003020-00009",
"article-title": "Systematic review: vitamin D and cardiometabolic outcomes",
"author": "Pittas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0400",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/php.12620",
"article-title": "The effects of ultraviolet eye irradiation on dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice",
"author": "Hiramoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "728",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Photochem. Photobiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0405",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmed.2008.12.004",
"article-title": "Heme oxygenase-1: from biology to therapeutic potential",
"author": "Soares",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "50",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Trends Mol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0410",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5582/bst.2011.v5.6.239",
"article-title": "UVA-induced protection of skin through the induction of heme oxygenase-1",
"author": "Xiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "239",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Biosci. Trends",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0415",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/74680",
"article-title": "Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway",
"author": "Otterbein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "422",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0420",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2012.00030",
"article-title": "Direct antioxidant properties of bilirubin and Biliverdin. Is there a role for biliverdin reductase?",
"author": "Jansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0425",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.10.030",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial DNA deletion percentage in sun exposed and non sun exposed skin",
"author": "Powers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "J. Photochem. Photobiol. B",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0430",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gendis.2014.08.005",
"article-title": "Ultraviolet radiation-induced non-melanoma skin cancer: regulation of DNA damage repair and inflammation",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "188",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Genes Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0435",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archdermatol.2010.19",
"article-title": "Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States, 2006",
"author": "Rogers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Arch. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0440",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.08.010",
"article-title": "Childhood exposure to ultraviolet radiation and harmful skin effects: epidemiological evidence",
"author": "Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "349",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0445",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"author": "Statistics ABo",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0450",
"series-title": "Australian Health Survey: Biomedical Results for Nutrients, 2011–2012",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.24154",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and sun protection: the impact of mixed public health messages in Australia",
"author": "Youl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1963",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0455",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C8PP90060D",
"article-title": "Human health in relation to exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation under changing stratospheric ozone and climate",
"author": "Lucas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "641",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Photochem. Photobiol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0460",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19381980.2015.1137400",
"article-title": "The role of geographical ecological studies in identifying diseases linked to UVB exposure and/or vitamin D",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1137400",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Dermatoendocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0465",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/9.3.227",
"article-title": "Do sunlight and vitamin D reduce the likelihood of colon cancer?",
"author": "Garland CF, Garland FC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0470",
"volume": "9",
"year": "1980"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(85)91082-7",
"article-title": "Dietary vitamin D and calcium and risk of colorectal cancer: a 19-year prospective study in men",
"author": "Garland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"issue": "8424",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0475",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(89)91789-3",
"article-title": "Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and colon cancer: eight-year prospective study",
"author": "Garland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1176",
"issue": "8673",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0480",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"article-title": "Roles of solar UVB and vitamin D in reducing Cancer risk and increasing survival",
"author": "Grant",
"first-page": "1357",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0485",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19381980.2016.1248325",
"article-title": "The risks and benefits of sun exposure 2016",
"author": "Hoel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1248325",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Dermatoendocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0490",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejca.2012.11.001",
"article-title": "Is prevention of cancer by sun exposure more than just the effect of vitamin D? A systematic review of epidemiological studies",
"author": "van der Rhee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1422",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0495",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.22052",
"article-title": "Cancer survival is dependent on season of diagnosis and sunlight exposure",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1530",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0500",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10549-009-0676-7",
"article-title": "Global breast cancer seasonality",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Breast Cancer Res. Treat.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0505",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.25439",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of observational studies of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and colorectal, breast and prostate cancer and colorectal adenoma",
"author": "Gandini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1414",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0510",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Cancer, sunlight and vitamin D",
"author": "Holick",
"first-page": "179",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0515",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.29002",
"article-title": "UV exposure inhibits intestinal tumor growth and progression to malignancy in intestine-specific Apc mutant mice kept on low vitamin D diet",
"author": "Rebel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0520",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010510-100611",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory actions of vitamin D",
"author": "Krishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "311",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0525",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjd.18527",
"article-title": "Dose and time effects of solar-simulated ultraviolet radiation on the in vivo human skin transcriptome",
"author": "Bustamante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1458",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0530",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms8000",
"article-title": "Widespread seasonal gene expression reveals annual differences in human immunity and physiology",
"author": "Dopico",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7000",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0535",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb0738",
"article-title": "Clocks, cancer, and chronochemotherapy",
"author": "Sancar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6524",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0540",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0058725",
"article-title": "Influence of vitamin D status and vitamin D3 supplementation on genome wide expression of white blood cells: a randomized double-blind clinical trial",
"author": "Hossein-nezhad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e58725",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0545",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "A Comprehensive Literature Review on the Clinical Presentation, and Management of the Pandemic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Kakodkar",
"first-page": "e7560",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0550",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2015.08.027",
"article-title": "Transmission of SARS and MERS coronaviruses and influenza virus in healthcare settings: the possible role of dry surface contamination",
"author": "Otter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "235",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Hosp. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0555",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0022172400068728",
"article-title": "The role of season in the epidemiology of influenza",
"author": "Hope-Simpson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Hyg. (Lond.)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0560",
"volume": "86",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"article-title": "Epidemic influenza and vitamin D",
"author": "Cannell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0565",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.07.006",
"article-title": "Can adverse effects of excessive vitamin D supplementation occur without developing hypervitaminosis D?",
"author": "Razzaque MS",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0570",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.1.4.9063",
"article-title": "The possible roles of solar ultraviolet-B radiation and vitamin D in reducing case-fatality rates from the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic in the United States",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Dermatoendocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0575",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajic.2020.06.193",
"article-title": "COVID-19 fatalities, latitude, sunlight, and vitamin D",
"author": "Whittemore PB",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1042",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Infect. Control",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0580",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15777",
"article-title": "Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1434",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0585",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000110",
"article-title": "COVID-19 mortality increases with northerly latitude after adjustment for age suggesting a link with ultraviolet and vitamin D",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "118",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0590",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-81419-w",
"article-title": "Autumn COVID-19 surge dates in Europe correlated to latitudes, not to temperature-humidity, pointing to vitamin D as contributing factor",
"author": "Walrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1981",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0595",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-87692-z",
"article-title": "Climate and the spread of COVID-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9042",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0600",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 incidence, complications, and mortality in 46 countries: an ecological study",
"author": "Mariani",
"journal-title": "Health Secur.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0605",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5603/ARM.a2021.0037",
"article-title": "The relationship between the severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration - a metaanalysis",
"author": "Oscanoa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Adv. Respir. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0610",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (vitamin D) level is associated with susceptibility to COVID-19, severity, and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Akbar",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0615",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels",
"author": "Kaufman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0620",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141816",
"article-title": "Sunlight ultraviolet radiation dose is negatively correlated with the percent positive of SARS-CoV-2 and four other common human coronaviruses in the U.S",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0625",
"volume": "751",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2012370118",
"article-title": "Global evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates",
"author": "Carleton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0630",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-74825-z",
"article-title": "Evidence of protective role of Ultraviolet-B (UVB) radiation in reducing COVID-19 deaths",
"author": "Moozhipurath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17705",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0635",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/16000617.0242-2020",
"article-title": "The impact of outdoor air pollution on COVID-19: a review of evidence from in vitro, animal, and human studies",
"author": "Bourdrel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "159",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0640",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection: physiological and environmental gift factors at high altitude",
"author": "Srivastava",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virusdisease",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0645",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc2535",
"article-title": "Susceptible supply limits the role of climate in the early SARS-CoV-2 pandemic",
"author": "Baker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"issue": "6501",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0650",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30380-6",
"article-title": "The effect of vitamin D supplementation on acute respiratory tract infection in older Australian adults: an analysis of data from the D-Health Trial",
"author": "Pham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0655",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinternmed.2008.560",
"article-title": "Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey",
"author": "Ginde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "384",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0660",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0665",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0670",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18020740",
"article-title": "Can Optimum Solar Radiation Exposure or Supplemented Vitamin D Intake Reduce the Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms?",
"author": "Abraham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0675",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04928-5",
"article-title": "COvid-19 and high-dose VITamin D supplementation TRIAL in high-risk older patients (COVIT-TRIAL): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1031",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0680",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"article-title": "Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D",
"author": "Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4240",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0685",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10111728",
"article-title": "Association of serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentration with pulmonary function in young adults",
"author": "Craveiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0690",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.06.003",
"article-title": "Point of view: Should COVID-19 patients be supplemented with vitamin D?",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Maturitas.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0695",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0700",
"series-title": "Coronavirus (COVID-19) Related Deaths by Ethnic Group, England and Wales: 2 March 2020 to 15 May 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pereira",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0705",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Baktash",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0710",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"article-title": "25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D’Avolio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0715",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hernandez",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0720",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"article-title": "Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers",
"author": "Jain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20191",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0725",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3693",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0730",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Is there a link between vitamin D status, SARS-CoV-2 infection risk and COVID-19 severity?",
"author": "Ferrari",
"journal-title": "Cell Biochem. Funct.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0735",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008874",
"article-title": "Exploring links between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19",
"author": "Mohan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1008874",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0740",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: a quasi-experimental study",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0745",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0750",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000089",
"article-title": "vitamin D and SARS-CoV-2 virus/COVID-19 disease",
"author": "Lanham-New",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ Nutr. Prevent. Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0755",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10040457",
"article-title": "Colour counts: sunlight and skin type as drivers of vitamin D deficiency at UK latitudes",
"author": "Webb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0760",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jid.2009.323",
"article-title": "Vitamin D production after UVB exposure depends on baseline vitamin D and total cholesterol but not on skin pigmentation",
"author": "Bogh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "546",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Invest. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0765",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Clothing prevents ultraviolet-B radiation-dependent photosynthesis of vitamin D3",
"author": "Matsuoka",
"first-page": "1099",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0770",
"volume": "75",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjd.17980",
"article-title": "The effect of sunscreen on vitamin D: a review",
"author": "Neale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "907",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0775",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2018.01.052",
"article-title": "The impact of air pollutants, UV exposure and geographic location on vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Hoseinzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "241",
"journal-title": "Food Chem. Toxicol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0780",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.d2040",
"article-title": "Calcium supplements with or without vitamin D and risk of cardiovascular events: reanalysis of the Women’s Health Initiative limited access dataset and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bolland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "d2040",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0785",
"volume": "342",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1139/cjpp-2015-0083",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, phosphate, and vasculotoxicity",
"author": "Brown",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1077",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0790",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.13573",
"article-title": "A review of the growing risk of vitamin D toxicity from inappropriate practice",
"author": "Taylor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1121",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0795",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.02.011",
"article-title": "Adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation: a brief review",
"author": "Gallagher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0800",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ddmec.2008.04.005",
"article-title": "The effects of sunlight on the skin",
"author": "Halliday",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e201",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0805",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4006",
"article-title": "Clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review",
"author": "Armstrong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1945",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0810",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1744666X.2020.1672537",
"article-title": "Advances in phototherapy for psoriasis and atopic dermatitis",
"author": "Kemeny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1205",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0815",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09767.x",
"article-title": "Narrowband ultraviolet B treatment improves vitamin D balance and alters antimicrobial peptide expression in skin lesions of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis",
"author": "Vahavihu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0820",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0961203317707064",
"article-title": "Ultraviolet-A1 irradiation therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "McGrath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lupus",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0825",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaad.2004.08.047",
"article-title": "Narrowband UVB phototherapy in skin conditions beyond psoriasis",
"author": "Gambichler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "660",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Acad. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105957_bib0830",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2005"
}
],
"reference-count": 166,
"references-count": 166,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0960076021001503"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cell Biology",
"Clinical Biochemistry",
"Endocrinology",
"Molecular Biology",
"Molecular Medicine",
"Biochemistry",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D-independent benefits of safe sunlight exposure",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "213"
}