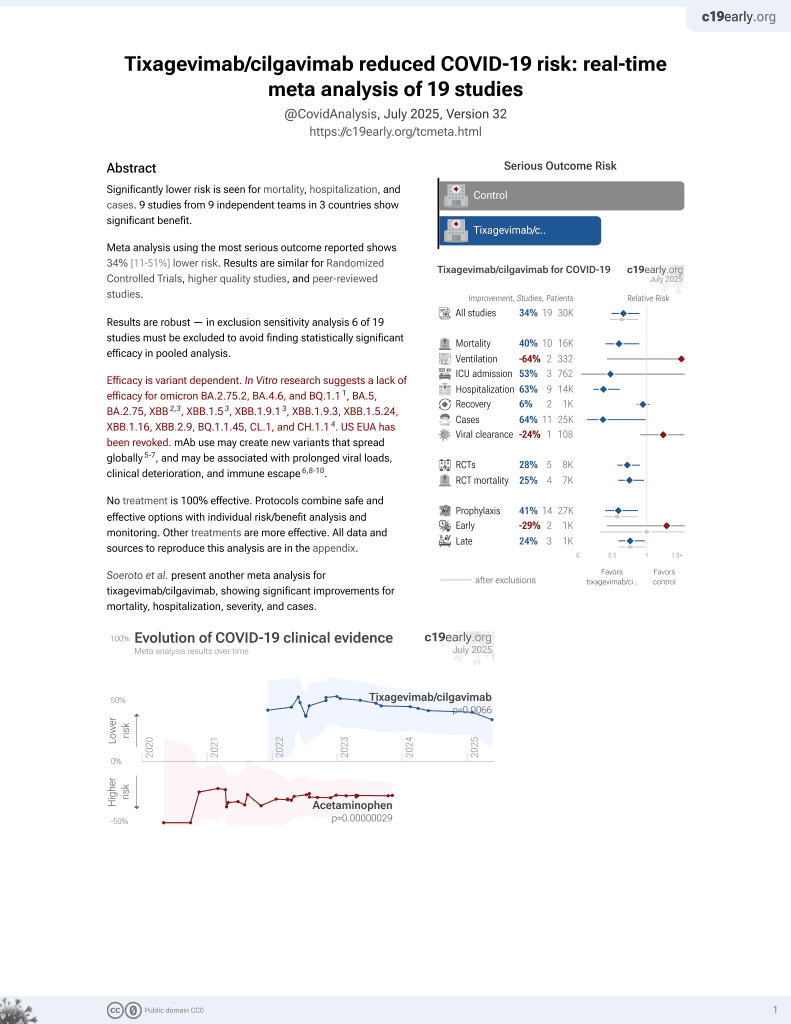
Tixagevimab and Cilgavimab (Evusheld) as Pre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Matched Cohort Study
et al., Crohn's & Colitis 360, doi:10.1093/crocol/otad047, Sep 2023
42nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2022, now with p = 0.0066 from 19 studies, recognized in 33 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
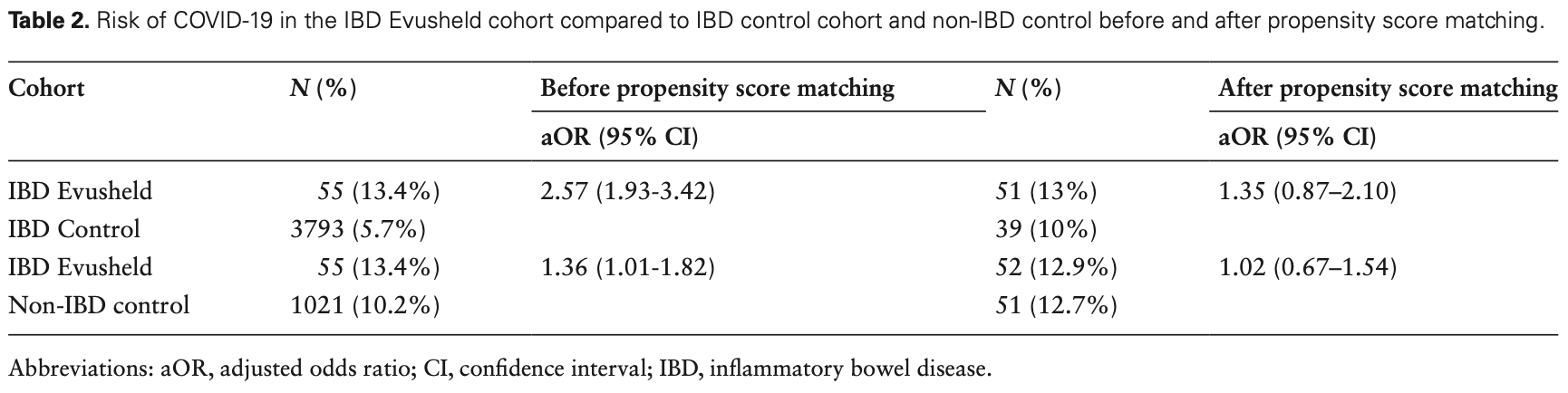
TriNetX PSM retrospective 408 IBD patients receiving tixagevimab/cilgavimab and matched controls, showing no significant difference in COVID-19 cases or hospitalization.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, BQ.1.11, BA.5, BA.2.75, XBB2,3, XBB.1.53, ХВВ.1.9.13, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.14.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments5.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of hospitalization, 12.0% lower, OR 0.88, p = 0.81, treatment 391, control 391, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 35.0% higher, OR 1.35, p = 0.18, treatment 391, control 391, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Planas et al., Resistance of Omicron subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6 and BQ.1.1 to neutralizing antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.17.516888.
2.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
3.
Uraki et al., Antiviral efficacy against and replicative fitness of an XBB.1.9.1 clinical isolate, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.108147.
Desai et al., 6 Sep 2023, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period 1 January, 2022 - 28 October, 2022.
Tixagevimab and Cilgavimab (Evusheld) as Pre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Matched Cohort Study
Crohn's & Colitis 360, doi:10.1093/crocol/otad047
Background: Tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) are 2 fully human monoclonal antibodies that received emergency-use authorization on December 21, 2021, for pre-exposure prophylaxis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients who are moderate-severely immunocompromised. The real-world efficacy of Evusheld in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is not known.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX, a multi-institutional database in patients with IBD who received Evusheld compared to patients with IBD who did not receive Evusheld (12.1.2021-10.28.2022). The primary outcome was to assess the risk of COVID-19 within 6 months. One-to-one propensity score matching (PSM) was performed for demographic parameters, comorbid conditions, IBD medications, and history of COVID-19. Risk was expressed as adjusted odds ratio (aOR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: Four hundred and eight patients (0.19%) with IBD received Evusheld (mean age 58.6 ± 15.4 years old, female 47.7%) during the study period. After PSM, there was no difference in the risk (aOR 0.88, 95% CI, 0.33-2.35) of COVID-19 in the Evusheld cohort compared to the IBD control cohort. No patients required ICU care or intubation/respiratory support or were deceased in the Evusheld cohort. Conclusions: Our study did not show that Evusheld decreases the risk of COVID-19 in patients with IBD. Prevention of moderate-severe COVID-19 in these patients should focus on vaccination strategies and early COVID-19 therapies.
Author Contributions A.D.: Data collection, data analysis and preparation of manuscript. J.G.H. and G.S.K.: Data interpretation and critical revision of the manuscript. F.A.F.: Study conceptualization, data interpretation, critical revision, and final approval of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest A.D.: None exists. J.G.H. holds the position of Associate Editor for Crohn's & Colitis 360 and has been recused from reviewing or making decisions for the manuscript. G.S.K.: Advisor Board: Corvetas Research Foundation, Lilly Pharmaceuticals, GIE medical; Stock options: Digbi Health. F.A.F. is a consultant for BMS, Braintree Labs, GSK, IBD Educational Group, Innovation Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Pfizer and Sebela. He sits on a DSMB for Adiso Therapeutics and Lilly.
References
Aqeel, Geetha, Tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) in rituximab-treated antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody vasculitis patients, Kidney Int Rep, doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2022.08.019
Coronavirus, COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes new long-acting monoclonal antibodies for pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 in certain individuals, FDA. Published
Desai, Deepak, Cross, Effect of 2 vs 3 doses of COVID-19 vaccine in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based propensity matched analysis, Inflamm Bowel Dis, doi:10.1093/ibd/izac252
Focosi, Casadevall, A critical analysis of the use of cilgavimab plus tixagevimab monoclonal antibody cocktail (Evusheld TM ) for COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14091999
Gungor, Kurtin, Mathias, Tanriover, Zangeneh, The prevention of COVID-19 in high-risk patients using tixagevimab-cilgavimab (Evusheld): Real-world experience at a large academic center, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2022.08.019
Hashah, Desai, Kochhar, Farraye, Efficacy of Paxlovid and Lagevrio for COVID-19 infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a propensity-matched study, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2022.09.011
Hutfless, Jasper, Tilak, A systematic review of Crohn's disease case definitions in administrative or claims databases, Inflamm Bowel Dis, doi:10.1093/ibd/izac131
Jurdi, Morena, Cote, Bethea, Azzi et al., Tixagevimab/cilgavimab pre-exposure prophylaxis is associated with lower breakthrough infection risk in vaccinated solid organ transplant recipients during the omicron wave, Am J Transplant, doi:10.1111/ajt.17128
Levin, Ustianowski, Wit, Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab-cilgavimab) for prevention of COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2116620
Loo, Mctamney, Arends, The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8124
Nguyen, Flahault, Chavarot, Pre-exposure prophylaxis with tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld©) for COVID-19 among 1112 severely immunocompromised patients, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.07.015
Ocon, Mustafa, Real-world experience of tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) in rheumatologic patients on rituximab, J Clin Rheumatol, doi:10.1097/rhu.0000000000001907
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/crocol/otad047",
"ISSN": [
"2631-827X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/crocol/otad047",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) are 2 fully human monoclonal antibodies that received emergency-use authorization on December 21, 2021, for pre-exposure prophylaxis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients who are moderate–severely immunocompromised. The real-world efficacy of Evusheld in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is not known.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX, a multi-institutional database in patients with IBD who received Evusheld compared to patients with IBD who did not receive Evusheld (12.1.2021–10.28.2022). The primary outcome was to assess the risk of COVID-19 within 6 months. One-to-one propensity score matching (PSM) was performed for demographic parameters, comorbid conditions, IBD medications, and history of COVID-19. Risk was expressed as adjusted odds ratio (aOR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Four hundred and eight patients (0.19%) with IBD received Evusheld (mean age 58.6 ± 15.4 years old, female 47.7%) during the study period. After PSM, there was no difference in the risk (aOR 0.88, 95% CI, 0.33–2.35) of COVID-19 in the Evusheld cohort compared to the IBD control cohort. No patients required ICU care or intubation/respiratory support or were deceased in the Evusheld cohort.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Our study did not show that Evusheld decreases the risk of COVID-19 in patients with IBD. Prevention of moderate–severe COVID-19 in these patients should focus on vaccination strategies and early COVID-19 therapies.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6604-7712",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University , Cleveland, OH , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Desai",
"given": "Aakash",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8305-9742",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic , Jacksonville, FL , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hashash",
"given": "Jana G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Allegheny Health Network , Pittsburgh, PA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kochhar",
"given": "Gursimran S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic , Jacksonville, FL , USA"
}
],
"family": "Farraye",
"given": "Francis A",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Crohn's & Colitis 360",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-06T16:30:20Z",
"timestamp": 1694017820000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-06T16:30:27Z",
"timestamp": 1694017827000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-13T17:26:03Z",
"timestamp": 1707845163613
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 67,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1693958400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/crohnscolitis360/article-pdf/5/3/otad047/51393532/otad047.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/crohnscolitis360/article-pdf/5/3/otad047/51393532/otad047.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
6
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8124",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans",
"author": "Loo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabl8124",
"issue": "635",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med.",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0001",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116620",
"article-title": "Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab–cilgavimab) for prevention of COVID-19",
"author": "Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2188",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0002",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.07.015",
"article-title": "Pre-exposure prophylaxis with tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld©) for COVID-19 among 1112 severely immunocompromised patients",
"author": "Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1654.e1",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0004",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2022.08.019",
"article-title": "The prevention of COVID-19 in high-risk patients using tixagevimab–cilgavimab (Evusheld): Real-world experience at a large academic center",
"author": "Al-Obaidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "96",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am J Med.",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0005",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ibd/izac131",
"article-title": "A systematic review of Crohn’s disease case definitions in administrative or claims databases",
"author": "Hutfless",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "705",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Bowel Dis.",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0006",
"volume": "29",
"year": "022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ibd/izac252",
"article-title": "Effect of 2 vs 3 doses of COVID-19 vaccine in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based propensity matched analysis",
"author": "Desai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "izac252",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Bowel Dis.",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0007",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14091999",
"article-title": "A critical analysis of the use of cilgavimab plus tixagevimab monoclonal antibody cocktail (EvusheldTM) for COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment",
"author": "Focosi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1999",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0008",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/RHU.0000000000001907",
"article-title": "Real-world experience of tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) in rheumatologic patients on rituximab",
"author": "Ocon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Clin Rheumatol",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0009",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ekir.2022.08.019",
"article-title": "Tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) in rituximab-treated antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody vasculitis patients",
"author": "Aqeel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2537",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int Rep",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0010",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ajt.17128",
"article-title": "Tixagevimab/cilgavimab pre-exposure prophylaxis is associated with lower breakthrough infection risk in vaccinated solid organ transplant recipients during the omicron wave",
"author": "Al Jurdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3130",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Am J Transplant.",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0011",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of Paxlovid and Lagevrio for COVID-19 infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a propensity-matched study",
"author": "Hashah",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0012",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "FDA announces Evusheld is not currently authorized for emergency use in the U.S",
"key": "2023090616205803500_CIT0013",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 13,
"references-count": 13,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/crohnscolitis360/article/doi/10.1093/crocol/otad047/7261634"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Gastroenterology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tixagevimab and Cilgavimab (Evusheld) as Pre-exposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19 in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Matched Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "5"
}