Seawater nasal wash to reduce symptom duration and viral load in COVID-19 and upper respiratory tract infections: a randomized controlled multicenter trial
et al., European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, doi:10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y, SeaCare, NCT04916639, Feb 2024
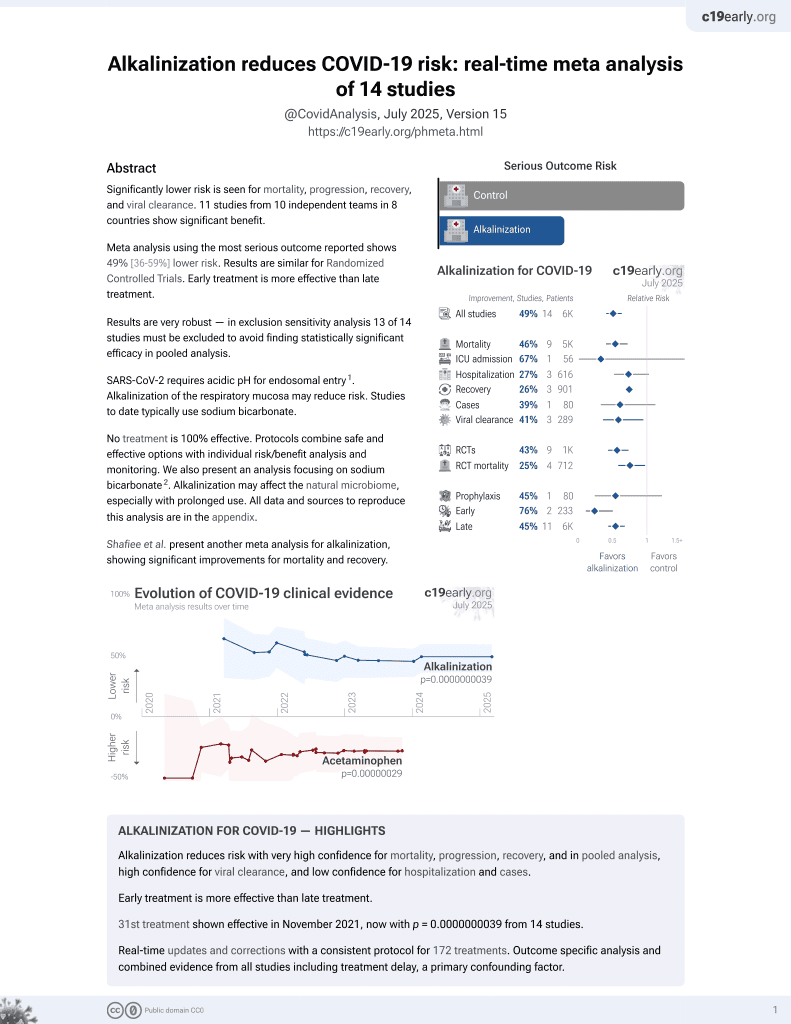
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0000000039 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
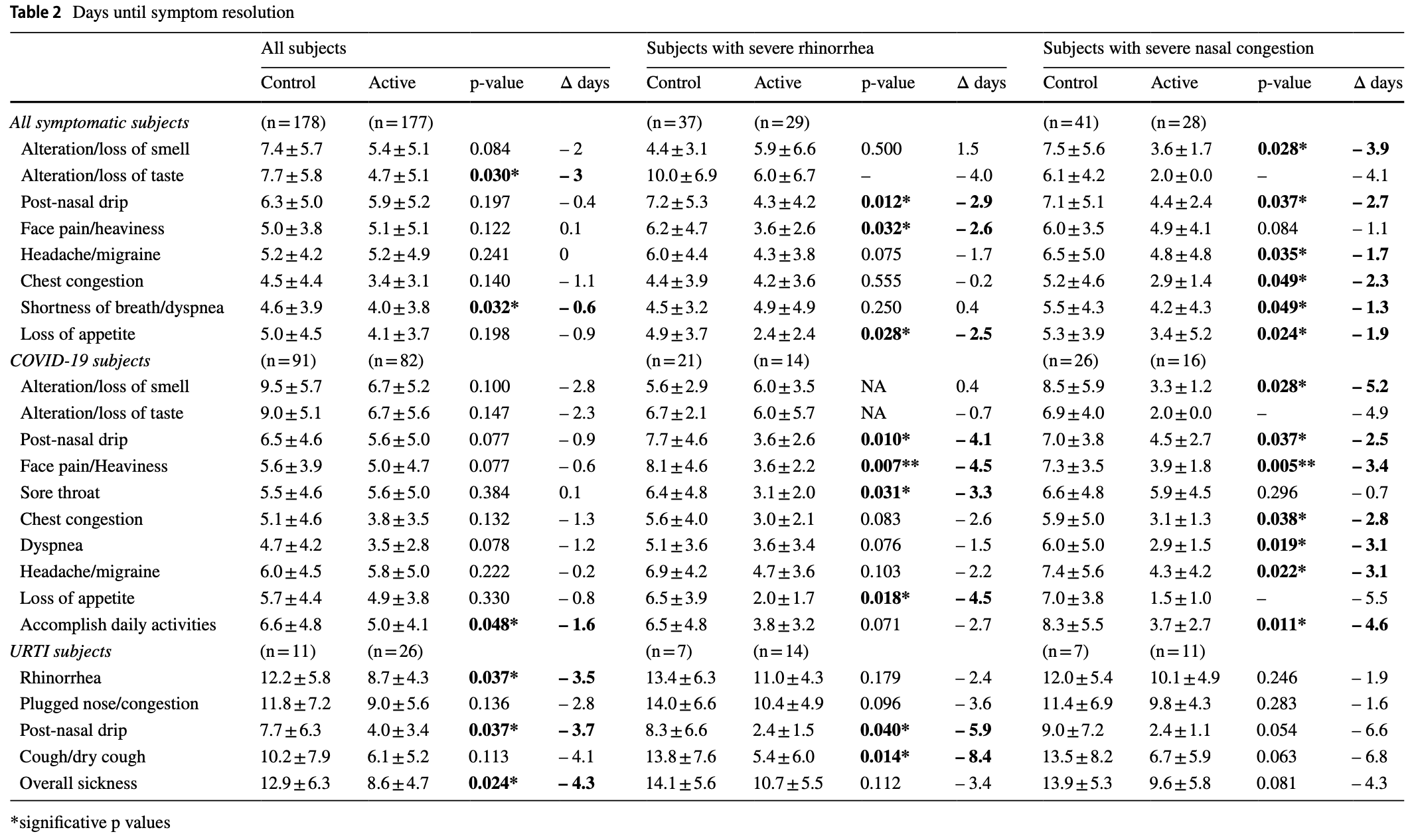
RCT 355 adults with COVID-19 or other upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs). For COVID-19 patients there was lower progression and faster symptom resolution with alkaline seawater nasal wash (pH ~8) 4 times daily for 21 days. There was significantly lower transmission for patients with the delta variant and for patients with high viral load. The seawater nasal wash was safe and well-tolerated.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action and reduced systemic side effects.
Study covers alkalinization and NaCl.
|
risk of progression, 74.9% lower, RR 0.25, p < 0.001, treatment 7 of 82 (8.5%), control 31 of 91 (34.1%), NNT 3.9, day 21.
|
|
risk of progression, 67.6% lower, RR 0.32, p = 0.003, treatment 7 of 82 (8.5%), control 24 of 91 (26.4%), NNT 5.6, day 14.
|
|
risk of progression, 35.3% lower, RR 0.65, p = 0.47, treatment 7 of 82 (8.5%), control 12 of 91 (13.2%), NNT 22, day 7.
|
|
recovery time, 24.2% lower, relative time 0.76, p = 0.02, treatment mean 5.0 (±4.1) n=82, control mean 6.6 (±4.8) n=91, time to resume daily activities.
|
|
recovery time, 17.0% lower, relative time 0.83, p < 0.001, treatment 82, control 91, all symptoms combined.
|
|
recovery time, 25.5% lower, relative time 0.74, p = 0.03, treatment mean 3.5 (±2.8) n=82, control mean 4.7 (±4.2) n=91, dyspnea.
|
|
recovery time, 29.5% lower, relative time 0.71, p < 0.001, treatment mean 6.7 (±5.2) n=82, control mean 9.5 (±5.7) n=91, loss of smell.
|
|
recovery time, 25.6% lower, relative time 0.74, p = 0.005, treatment mean 6.7 (±5.6) n=82, control mean 9.0 (±5.1) n=91, loss of taste.
|
|
recovery time, 13.8% lower, relative time 0.86, p = 0.22, treatment mean 5.6 (±5.0) n=82, control mean 6.5 (±4.6) n=91, post-nasal drip.
|
|
recovery time, 10.7% lower, relative time 0.89, p = 0.36, treatment mean 5.0 (±4.7) n=82, control mean 5.6 (±3.9) n=91, facial pain.
|
|
recovery time, 1.8% higher, relative time 1.02, p = 0.89, treatment mean 5.6 (±5.0) n=82, control mean 5.5 (±4.6) n=91, sore throat.
|
|
recovery time, 25.5% lower, relative time 0.75, p = 0.04, treatment mean 3.8 (±3.5) n=82, control mean 5.1 (±4.6) n=91, chest congestion.
|
|
recovery time, 3.3% lower, relative time 0.97, p = 0.78, treatment mean 5.8 (±5.0) n=82, control mean 6.0 (±4.5) n=91, headache.
|
|
recovery time, 14.0% lower, relative time 0.86, p = 0.20, treatment mean 4.9 (±3.8) n=82, control mean 5.7 (±4.4) n=91, loss of appetite.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 36.6% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.54, treatment 4 of 82 (4.9%), control 7 of 91 (7.7%), NNT 36, day 21.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
de Gabory et al., 20 Feb 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, France, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period July 2021 - March 2022, trial NCT04916639 (history) (SeaCare).
Contact: ludovic.de-gabory@chu-bordeaux.fr.
Seawater nasal wash to reduce symptom duration and viral load in COVID-19 and upper respiratory tract infections: a randomized controlled multicenter trial
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, doi:10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y
Purpose The objective was to assess the efficacy of seawater nasal wash on symptom duration, intranasal viral load, household transmission in COVID-19 and URTIs. Methods This prospective, randomized, controlled, multicentric, parallel study included 355 mild/moderate COVID-19 and URTI adults with rhinologic symptoms ≤ 48h. Active group performed 4-daily nasal washes with undiluted isotonic seawater versus control group (without nasal wash). Symptoms were self-assessed daily using the WURSS-21 questionnaire for 3 weeks. Viral load was measured by RT-PCR on nasopharyngeal swabs collected on Day 0, Day 5, Day 14 and Day 21. Digital droplet PCR was additionally performed for SARS-CoV-2. Results Overall COVID-19 subjects recovered earlier the ability to accomplish daily activities in the active group (-1.6 day, p = 0.0487) with earlier improvement of taste (-2 days, p = 0.0404). COVID-19 subjects with severe nasal symptoms at D0 showed the earliest resolution of anosmia (-5.2 days, p = 0.0281), post-nasal drip (-4.1 days, p = 0.0102), face pain/ heaviness (-4.5 days, p = 0.0078), headache (-3.1 days, p = 0.0195), sore throat (-3.3 days, p = 0.0319), dyspnea (-3.1 days, p = 0.0195), chest congestion (-2.8 days, p = 0.0386) and loss of appetite (-4.5 days, p = 0.0186) with nasal wash. In URTIs subjects, an earlier resolution of rhinorrhea (-3.5 days, p = 0.0370), post-nasal drip (-3.7 days, p = 0.0378), and overall sickness (-4.3 days, p = 0.0248) was reported with nasal wash. Evolution towards more severe COVID-19 was lower in active vs control, with earlier viral load reduction in youngest subjects (≥ 1.5log10 copies/10000 cells at Day 5: 88.9% vs 62.5%, p = 0.0456). In the active group, a lower percentage of SARS-CoV-2 positive household contacts (0-10.7%) was reported vs controls (3.2-16.1%) among subjects with Delta variant (p = 0.0413). Conclusion This trial showed the efficacy and safety of seawater nasal wash in COVID-19 and URTIs. Trial registration Trial registry ClinicalTrials.gov
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1007/ s00405-024-08518-y.
Author contributions Study protocol preparation and methodology: LG, SV, C R-S and GN. Data interpretation: LG, SV, C R-S and GN. Literature review: LG and GN. Manuscript preparation: LG and GN. Manuscript review: LG, SV, C R-S and GN. All the authors approved the present version for publication.
Conflict of interest LG and SV and CR-S were scientific advisors for the study and therefore received fees from Laboratoire de la Mer. Employment GN is employee of Laboratoire de la Mer. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Publisher's Note..
References
Barrett, Brown, Mundt, Thomas, Barlow et al., Validation of a short form Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptom Survey (WURSS-21), Health Qual Life Outcomes, doi:10.1186/1477-7525-7-76
Bastier, Lechot, Bordenave, Durand, De Gabory, Nasal irrigation: From empiricism to evidence-based medicine. A review, Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, doi:10.1016/J.ANORL.2015.08.001
Baxter, Schwartz, Johnson, Kuchinski, Swartout et al., Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients, Ear Nose Throat J, doi:10.1177/01455613221123737
Bonnomet, Luczka, Coraux, De Gabory, Nondiluted seawater enhances nasal ciliary beat frequency and wound repair speed compared to diluted seawater and normal saline, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, doi:10.1002/ALR.21782
Casale, Rinaldi, Sabatino, Moffa, Ciccozzi, Could nasal irrigation and oral rinse reduce the risk for COVID-19 infection?, Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, doi:10.1177/2058738420941757
De Gabory, Alharbi, Kérimian, Lafon, The influenza virus, SARS-CoV-2, and the airways: clarification for the otorhinolaryngologist, Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, doi:10.1016/j.anorl.2020.05.015
De Gabory, Escabasse, Boudard, De Bonnecaze, Rumeau et al., Prospective, randomized, controlled, open-label study to compare efficacy of a mineral-rich solution vs normal saline after complete ethmoidectomy, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1007/s00405-018-5232-9
De Gabory, Kérimian, Baux, Boisson, Bordenave, Computational fluid dynamics simulation to compare large volume irrigation and continuous spraying during nasal irrigation, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, doi:10.1002/alr.22458
Desrosiers, Evans, Keith, Wright, Kaplan et al., Canadian clinical practice guidelines for acute and chronic rhinosinusitis, Allergy Asthma Clin Immunoly, doi:10.1186/1710-1492-7-2
Domênico, Collares, Santos, Lenz, Antunes et al., Hydrogen peroxide as an auxiliary treatment for COVID-19 in Brazil: a randomized double-blind clinical trial, Epidemiol Health, doi:10.4178/epih.e2021051
Dunn, Dion, Mcmains, Efficacy of nasal irrigations and nebulizations for nasal symptom relief, Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1097/MOO.0B013E32835F80BB
Eccles, Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X
Farrell, Klatt-Cromwell, Schneider, Benefits and safety of nasal saline irrigations in a pandemic-washing COVID-19 away, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1001/JAMAOTO.2020.1622
Ferdenzi, Bousquet, Aguera, Dantec, Daudé et al., Recovery from COVID-19-related olfactory disorders and quality of life: insights from an observational online study, Chem Senses, doi:10.1093/chemse/bjab028
Fokkens, Lund, Hopkins, Hellings, Kern et al., European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps, Rhinology, doi:10.4193/Rhin20.600
Gallant, Basem, Turner, Shannon, Virgin, Nasal saline irrigation in pediatric rhinosinusitis: a systematic review, Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1016/J.IJPORL.2018.03.001
Gangadi, Georgiou, Moschotzopoulou, Antronikou, Kainis et al., Efficacy and safety of a hypertonic seawater nasal irrigation solution containing algal and herbal natural ingredients in patients with COVID-19, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202212_30495
Guenezan, Garcia, Strasters, Jousselin, Lévêque et al., Povidone iodine mouthwash, gargle, and nasal spray to reduce nasopharyngeal viral load in patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490
Gutiérrez-Cardona, Sands, Roberts, Lucas, Walker et al., The acceptability and tolerability of nasal douching in children with allergic rhinitis: a systematic review, Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1016/J.IJPORL.2017.04.040
Harrison, Lin, Wang, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 transmission and pathogenesis, Trends Immunol, doi:10.1016/J.IT.2020.10.004
Hopkins, Surda, Walker, Wolf, Speth et al., The Samter's Society, TSS, EPOS 4 Patients, doi:10.4193/Rhin20.950
Huijghebaert, Hoste, Vanham, Essentials in saline pharmacology for nasal or respiratory hygiene in times of COVID-19, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/S00228-021-03102-3
Kimura, Freeman, Wessinger, Gupta, Sheng et al., Interim analysis of an open-label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, doi:10.1002/ALR.22703
King, Mitchell, Williams, Spurling, Saline nasal irrigation for acute upper respiratory tract infections, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006821.PUB3
Leboulanger, Sagardoy, Akkari, Ayari-Khalfallah, Celerier et al., COVID-19 and ENT Pediatric otolaryngology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Guidelines of the French Association of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (AFOP) and French Society of Otorhinolaryngology (SFORL), Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, doi:10.1016/j.anorl.2020.04.010
Lechien, Vaira, Saussez, Prevalence and 24-month recovery of olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19 patients: a multicentre prospective study, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13564
Madewell, Yang, Longini, Halloran, Dean, Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.31756
Marchisio, Picca, Torretta, Baggi, Pasinato et al., Nasal saline irrigation in preschool children: a survey of attitudes and prescribing habits of primary care pediatricians working in northern Italy, Ital J Pediatr, doi:10.1186/1824-7288-40-47
Notarte, Catahay, Velasco, Pastrana, Ver et al., Impact of COVID-19 vaccination on the risk of developing long-COVID and on existing long-COVID symptoms: a systematic review, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101624
Orlandi, Kingdom, Hwang, Smith, Alt et al., International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Rhinosinusitis, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, doi:10.1002/ALR.21695
Pantazopoulos, Chalkias, Mavrovounis, Dimeas, Sinis et al., Nasopharyngeal wash with normal saline decreases SARS-CoV-2 viral load: a randomized pilot controlled trial, Can Respir J, doi:10.1155/2022/8794127
Para, Clayton, Peters, Management of rhinosinusitis: an evidence based approach, Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1097/ACI.0000000000000276
Radulesco, Lechien, Saussez, Hopkins, Michel, Safety and impact of nasal lavages during viral infections such as SARS-CoV-2, Ear Nose Throat J, doi:10.1177/0145561320950491
Ramalingam, Graham, Dove, Morrice, Sheikh, A pilot, open labelled, randomised controlled trial of hypertonic saline nasal irrigation and gargling for the common cold, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/S41598-018-37703-3
Rosenfeld, Piccirillo, Chandrasekhar, Brook, Kumar et al., Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1177/0194599815572097
Singhal, A review of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), Indian J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/S12098-020-03263-6/METRICS
Slapak, Skoupá, Strnad, Horník, Efficacy of isotonic nasal wash (seawater) in the treatment and prevention of rhinitis in children, Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1001/archoto.2007.19
Snidvongs, Thanaviratananich, Update on Intranasal Medications in Rhinosinusitis, Curr Allergy Asthma Rep, doi:10.1007/S11882-017-0720-3
Spinato, Fabbris, Costantini, Conte, Scotton et al., The effect of isotonic saline nasal lavages in improving symptoms in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a case-control study, Front Neurol, doi:10.3389/FNEUR.2021.794471
Struyf, Deeks, Dinnes, Takwoingi, Davenport et al., Cochrane COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Accuracy Group (2022) Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3
Williamson, Dennison, Greenwell, Denison-Day, Mowbray et al., Using nasal sprays to prevent respiratory tract infections: a qualitative study of online consumer reviews and primary care patient interviews, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059661
Yilmaz, Yilmaz, Ozdemir, Kocazeybek, Karaali et al., Effects of hypertonic alkaline nasal irrigation on COVID-19, Laryngosc Investig Otolaryngol, doi:10.1002/LIO2.686
Zambon, Stockton, Clewley, Fleming, Contribution of influenza and respiratory syncytial virus to community cases of influenza-like illness: an observational study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06528-X
Štanfel, Kalogjera, Ryazantsev, Hlača, Radtsig et al., The role of seawater and saline solutions in treatment of upper respiratory conditions, Mar Drugs, doi:10.3390/md20050330
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y",
"ISSN": [
"0937-4477",
"1434-4726"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Purpose</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The objective was to assess the efficacy of seawater nasal wash on symptom duration, intranasal viral load, household transmission in COVID-19 and URTIs.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This prospective, randomized, controlled, multicentric, parallel study included 355 mild/moderate COVID-19 and URTI adults with rhinologic symptoms ≤ 48h. Active group performed 4-daily nasal washes with undiluted isotonic seawater versus control group (without nasal wash). Symptoms were self-assessed daily using the WURSS-21 questionnaire for 3 weeks. Viral load was measured by RT-PCR on nasopharyngeal swabs collected on Day 0, Day 5, Day 14 and Day 21. Digital droplet PCR was additionally performed for SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Overall COVID-19 subjects recovered earlier the ability to accomplish daily activities in the active group (– 1.6 day, p = 0.0487) with earlier improvement of taste (– 2 days, p = 0.0404). COVID-19 subjects with severe nasal symptoms at D0 showed the earliest resolution of anosmia (– 5.2 days, p = 0.0281), post-nasal drip (– 4.1 days, p = 0.0102), face pain/heaviness (– 4.5 days, p = 0.0078), headache (– 3.1 days, p = 0.0195), sore throat (– 3.3 days, p = 0.0319), dyspnea (– 3.1 days, p = 0.0195), chest congestion (– 2.8 days, p = 0.0386) and loss of appetite (– 4.5 days, p = 0.0186) with nasal wash. In URTIs subjects, an earlier resolution of rhinorrhea (– 3.5 days, p = 0.0370), post-nasal drip (– 3.7 days, p = 0.0378), and overall sickness (– 4.3 days, p = 0.0248) was reported with nasal wash.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Evolution towards more severe COVID-19 was lower in active vs control, with earlier viral load reduction in youngest subjects (≥ 1.5log10 copies/10000 cells at Day 5: 88.9% vs 62.5%, p = 0.0456). In the active group, a lower percentage of SARS-CoV-2 positive household contacts (0–10.7%) was reported vs controls (3.2–16.1%) among subjects with Delta variant (p = 0.0413).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This trial showed the efficacy and safety of seawater nasal wash in COVID-19 and URTIs.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Trial registry ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04916639. Registration date: 04.06.2021.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"8518"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "30 November 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "29 January 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "20 February 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "LG and SV and CR-S were scientific advisors for the study and therefore received fees from Laboratoire de la Mer."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Employment",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "GN is employee of Laboratoire de la Mer."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0113-6121",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "de Gabory",
"given": "Ludovic",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vallet",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naelten",
"given": "Gaëlle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raherison-Semjen",
"given": "Chantal",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04916639",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology",
"container-title-short": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-20T14:02:45Z",
"timestamp": 1708437765000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-20T14:06:16Z",
"timestamp": 1708437976000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Laboratoire de la Mer"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T00:24:49Z",
"timestamp": 1708475089066
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
20
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1708387200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1708387200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X",
"author": "R Eccles",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "718",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "8518_CR1",
"unstructured": "Eccles R (2005) Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza. Lancet Infect Dis 5:718–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06528-X",
"author": "MC Zambon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1410",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "8518_CR2",
"unstructured": "Zambon MC, Stockton JD, Clewley JP, Fleming DM (2001) Contribution of influenza and respiratory syncytial virus to community cases of influenza-like illness: an observational study. Lancet 358:1410–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06528-X",
"volume": "358",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.IT.2020.10.004",
"author": "AG Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1100",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol",
"key": "8518_CR3",
"unstructured": "Harrison AG, Lin T, Wang P (2020) Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 transmission and pathogenesis. Trends Immunol 41(12):1100–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IT.2020.10.004",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.anorl.2020.05.015",
"author": "L de Gabory",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "291",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis",
"key": "8518_CR4",
"unstructured": "de Gabory L, Alharbi A, Kérimian M, Lafon ME (2020) The influenza virus, SARS-CoV-2, and the airways: clarification for the otorhinolaryngologist. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 137(4):291–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2020.05.015",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1710-1492-7-2",
"author": "M Desrosiers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Allergy Asthma Clin Immunoly",
"key": "8518_CR5",
"unstructured": "Desrosiers M, Evans GA, Keith PK, Wright ED, Kaplan A, Bouchard J, Ciavarella A, Doyle PW, Javer AR, Leith ES, Mukherji A, Schellenberg RR, Small P, Witterick IJ (2011) Canadian clinical practice guidelines for acute and chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunoly 7(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1710-1492-7-2",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MOO.0B013E32835F80BB",
"author": "JD Dunn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "248",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "8518_CR6",
"unstructured": "Dunn JD, Dion GR, McMains KC (2013) Efficacy of nasal irrigations and nebulizations for nasal symptom relief. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21(3):248–251. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0B013E32835F80BB",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD006821.PUB3",
"author": "D King",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "8518_CR7",
"unstructured": "King D, Mitchell B, Williams CP, Spurling GKP (2015) Saline nasal irrigation for acute upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006821.PUB3",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/ACI.0000000000000276",
"author": "AJ Para",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "383",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "8518_CR8",
"unstructured": "Para AJ, Clayton E, Peters AT (2016) Management of rhinosinusitis: an evidence based approach. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 16(4):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACI.0000000000000276",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0194599815572097",
"author": "RM Rosenfeld",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S1",
"issue": "2 Suppl",
"journal-title": "Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "8518_CR9",
"unstructured": "Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, Brook I, Ashok Kumar K, Kramper M, Orlandi RR, Palmer JN, Patel ZM, Peters A, Walsh SA, Corrigan MD (2015) Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 152(2 Suppl):S1–S39. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599815572097",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4193/Rhin20.600",
"author": "WJ Fokkens",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "Suppl S29",
"journal-title": "Rhinology",
"key": "8518_CR10",
"unstructured": "Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, Toppila-Salmi S, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Mullol J, Alobid I, Terezinha Anselmo-Lima W, Bachert C, Baroody F, von Buchwald C, Cervin A, Cohen N, Constantinidis J, De Gabory L, Desrosiers M, Diamant Z, Zwetsloot CP (2020) European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Rhinology 58(Suppl S29):1–464. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin20.600",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.ANORL.2015.08.001",
"author": "PL Bastier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis",
"key": "8518_CR11",
"unstructured": "Bastier PL, Lechot A, Bordenave L, Durand M, de Gabory L (2015) Nasal irrigation: From empiricism to evidence-based medicine. A review. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 132(5):281–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANORL.2015.08.001",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ALR.21695",
"author": "RR Orlandi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S22",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Int Forum Allergy Rhinol",
"key": "8518_CR12",
"unstructured": "Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Hwang PH, Smith TL, Alt JA, Baroody FM, Batra PS, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Bhattacharyya N, Chandra RK, Chiu A, Citardi MJ, Cohen NA, Delgaudio J, Desrosiers M, Dhong HJ, Douglas R, Ferguson B, Fokkens WJ, Kennedy DW (2016) International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 6(Suppl 1):S22–S209. https://doi.org/10.1002/ALR.21695",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-018-5232-9",
"author": "L de Gabory",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "447",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "8518_CR13",
"unstructured": "de Gabory L, Escabasse V, Boudard P, de Bonnecaze G, Rumeau C, Jankowski R, Debry C, Morinière S, Merino B, Mortuaire G, Malard O, Bordenave L (2019) Prospective, randomized, controlled, open-label study to compare efficacy of a mineral-rich solution vs normal saline after complete ethmoidectomy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276(2):447–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5232-9",
"volume": "276",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.IJPORL.2018.03.001",
"author": "JN Gallant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "8518_CR14",
"unstructured": "Gallant JN, Basem JI, Turner JH, Shannon CN, Virgin FW (2018) Nasal saline irrigation in pediatric rhinosinusitis: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 108:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPORL.2018.03.001",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.IJPORL.2017.04.040",
"author": "N Gutiérrez-Cardona",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "8518_CR15",
"unstructured": "Gutiérrez-Cardona N, Sands P, Roberts G, Lucas JS, Walker W, Salib R, Burgess A, Ismail-Koch H (2017) The acceptability and tolerability of nasal douching in children with allergic rhinitis: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 98:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPORL.2017.04.040",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/S11882-017-0720-3",
"author": "K Snidvongs",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Allergy Asthma Rep",
"key": "8518_CR16",
"unstructured": "Snidvongs K, Thanaviratananich S (2017) Update on Intranasal Medications in Rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11882-017-0720-3",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ALR.21782",
"author": "A Bonnomet",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1062",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Int Forum Allergy Rhinol",
"key": "8518_CR17",
"unstructured": "Bonnomet A, Luczka E, Coraux C, de Gabory L (2016) Non-diluted seawater enhances nasal ciliary beat frequency and wound repair speed compared to diluted seawater and normal saline. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 6(10):1062–1068. https://doi.org/10.1002/ALR.21782",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.22458",
"author": "L de Gabory",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int Forum Allergy Rhinol",
"key": "8518_CR18",
"unstructured": "de Gabory L, Kérimian M, Baux Y, Boisson N, Bordenave L (2020) Computational fluid dynamics simulation to compare large volume irrigation and continuous spraying during nasal irrigation. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 10(1):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22458",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ALR.22703",
"author": "KS Kimura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1325",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Int Forum Allergy Rhinol",
"key": "8518_CR19",
"unstructured": "Kimura KS, Freeman MH, Wessinger BC, Gupta V, Sheng Q, Huang LC, von Wahlde K, Das SR, Chowdhury NI, Turner JH (2020) Interim analysis of an open-label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 10(12):1325. https://doi.org/10.1002/ALR.22703",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "8518_CR20",
"unstructured": "French Society of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (SFORL); French Association of Rhinology (AFR). Consultations and medical treatments in rhinology in the context of the COVID-19 epidemic (2020). https://www.sforl.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Propositions-COVID-AFR-26-11-2020_v4.pdf. Accessed 4 Sep 2023"
},
{
"key": "8518_CR21",
"unstructured": "French Society of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (SFORL); Diagnostic and therapeutic approach of viral infections in ENT. Recommendation for clinical practice. https://www.sforl.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Reco-SFORL-Diagnostic-et-ttt-des-infections-virales-en-ORL-15092021_compressed.pdf. Accessed 4 Sep 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.anorl.2020.04.010",
"author": "N Leboulanger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "177",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis",
"key": "8518_CR22",
"unstructured": "Leboulanger N, Sagardoy T, Akkari M, Ayari-Khalfallah S, Celerier C, Fayoux P, Luscan R, Mansbach AL, Moreddu E, Pondaven S, Simon F, Teissier N, Thierry B, Fanous A, Lescanne E, Nicollas R, Couloigner V, French Association of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (AFOP), French Society of Otorhinolaryngology, & Head, Neck Surgery (SFORL) (2020) COVID-19 and ENT Pediatric otolaryngology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Guidelines of the French Association of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (AFOP) and French Society of Otorhinolaryngology (SFORL). Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 137(3):177–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2020.04.010",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FNEUR.2021.794471",
"author": "G Spinato",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Neurol",
"key": "8518_CR23",
"unstructured": "Spinato G, Fabbris C, Costantini G, Conte F, Scotton PG, Cinetto F, de Siati R, Matarazzo A, Citterio M, Contro G, de Filippis C, Agostini C, Emanuelli E, Boscolo-Rizzo P, Frezza D (2021) The effect of isotonic saline nasal lavages in improving symptoms in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a case-control study. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNEUR.2021.794471",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/01455613221123737",
"author": "AL Baxter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ear Nose Throat J",
"key": "8518_CR24",
"unstructured": "Baxter AL, Schwartz KR, Johnson RW, Kuchinski AM, Swartout KM, Srinivasa Rao ASR, Gibson RW, Cherian E, Giller T, Boomer H, Lyon M, Schwartz R (2022) Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients. Ear Nose Throat J. https://doi.org/10.1177/01455613221123737",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/8794127",
"author": "I Pantazopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Can Respir J",
"key": "8518_CR25",
"unstructured": "Pantazopoulos I, Chalkias A, Mavrovounis G, Dimeas I, Sinis S, Miziou A, Rouka E, Poulas K, Gourgoulianis K (2022) Nasopharyngeal wash with normal saline decreases SARS-CoV-2 viral load: a randomized pilot controlled trial. Can Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8794127",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41598-018-37703-3",
"author": "S Ramalingam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "8518_CR26",
"unstructured": "Ramalingam S, Graham C, Dove J, Morrice L, Sheikh A (2019) A pilot, open labelled, randomised controlled trial of hypertonic saline nasal irrigation and gargling for the common cold. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-018-37703-3",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059661",
"author": "S Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "8518_CR27",
"unstructured": "Williamson S, Dennison L, Greenwell K, Denison-Day J, Mowbray F, Richards-Hall S, Smith D, Bradbury K, Ainsworth B, Little P, Geraghty AWA, Yardley L (2022) Using nasal sprays to prevent respiratory tract infections: a qualitative study of online consumer reviews and primary care patient interviews. BMJ Open 12(6):e059661. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059661",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1824-7288-40-47",
"author": "P Marchisio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "47",
"journal-title": "Ital J Pediatr",
"key": "8518_CR28",
"unstructured": "Marchisio P, Picca M, Torretta S, Baggi E, Pasinato A, Bianchini S, Nazzari E, Esposito S, Principi N (2014) Nasal saline irrigation in preschool children: a survey of attitudes and prescribing habits of primary care pediatricians working in northern Italy. Ital J Pediatr 40:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1824-7288-40-47",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "8518_CR29",
"unstructured": "EUFOREA Allergic Rhinitis Pocket Guide. https://www.euforea.eu/sites/default/files/EUFOREA%20Paediatric%20Allergic%20Rhinitis%20Pocket%20Guide.pdf. Accessed 7 Nov 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4193/Rhin20.950",
"author": "C Hopkins",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Rhinology",
"key": "8518_CR30",
"unstructured": "Hopkins C, Surda P, Walker A, Wolf A, Speth MM, Jacques T, Hox V, Van Gerven L, Santamaria-Gadea A, Segboer C, Lourijsen E, Turri-Zanoni M, Huart C, Rennie C, Green R, Kelly CE, Knill A, Lund VJ, Fokkens WJ, The Samter’s Society, TSS (2021) EPOS 4 Patients. Rhinology. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin20.950. (Advance online publication)",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "8518_CR31",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines 2. (n.d.). https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed 4 Sep 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archoto.2007.19",
"author": "I Slapak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "67",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "8518_CR32",
"unstructured": "Slapak I, Skoupá J, Strnad P, Horník P (2008) Efficacy of isotonic nasal wash (seawater) in the treatment and prevention of rhinitis in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1001/archoto.2007.19",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1477-7525-7-76",
"author": "B Barrett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Health Qual Life Outcomes",
"key": "8518_CR33",
"unstructured": "Barrett B, Brown RL, Mundt MP, Thomas GR, Barlow SK, Highstrom AD, Bahrainian M (2009) Validation of a short form Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptom Survey (WURSS-21). Health Qual Life Outcomes 7:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-7-76",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"key": "8518_CR34",
"unstructured": "Public health recommendations for the screening of SARS-CoV-2 variants. https://sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/reply_dgs-urgent_131_actualisation_doctrine_de_criblage.pdf. Accessed 4 Sep 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3",
"author": "T Struyf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "CD013665",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "8518_CR35",
"unstructured": "Struyf T, Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Takwoingi Y, Davenport C, Leeflang MM, Spijker R, Hooft L, Emperador D, Domen J, Tans A, Janssens S, Wickramasinghe D, Lannoy V, Horn SRA, Van den Bruel A, Cochrane COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Accuracy Group (2022) Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5(5):CD013665. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "8518_CR36",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus symptoms. American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology. https://www.aaaai.org/Aaaai/media/MediaLibrary/Images/Promos/Coronavirus-Symptoms.pdf. Accessed 4 Sep 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/LIO2.686",
"author": "YZ Yilmaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1240",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Laryngosc Investig Otolaryngol",
"key": "8518_CR37",
"unstructured": "Yilmaz YZ, Yilmaz BB, Ozdemir YE, Kocazeybek BS, Karaali R, Çakan D, Ozdogan HA, Batioglu-Karaaltin A (2021) Effects of hypertonic alkaline nasal irrigation on COVID-19. Laryngosc Investig Otolaryngol 6(6):1240–1247. https://doi.org/10.1002/LIO2.686",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13564",
"author": "JR Lechien",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "82",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "8518_CR38",
"unstructured": "Lechien JR, Vaira LA, Saussez S (2023) Prevalence and 24-month recovery of olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19 patients: a multicentre prospective study. J Intern Med 293(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13564",
"volume": "293",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/chemse/bjab028",
"author": "C Ferdenzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "bjab028",
"journal-title": "Chem Senses",
"key": "8518_CR39",
"unstructured": "Ferdenzi C, Bousquet C, Aguera PE, Dantec M, Daudé C, Fornoni L, Fournel A, Kassan A, Mantel M, Moranges M, Moussy E, Richard Ortegón S, Rouby C, Bensafi M (2021) Recovery from COVID-19-related olfactory disorders and quality of life: insights from an observational online study. Chem Senses 46:bjab028. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bjab028",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/md20050330",
"author": "D Štanfel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "330",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mar Drugs",
"key": "8518_CR40",
"unstructured": "Štanfel D, Kalogjera L, Ryazantsev SV, Hlača K, Radtsig EY, Teimuraz R, Hrabač P (2022) The role of seawater and saline solutions in treatment of upper respiratory conditions. Mar Drugs 20(5):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050330",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26355/eurrev_202212_30495",
"author": "M Gangadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112",
"issue": "2 Suppl",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "8518_CR41",
"unstructured": "Gangadi M, Georgiou S, Moschotzopoulou E, Antronikou T, Kainis E, Alevizopoulos K (2022) Efficacy and safety of a hypertonic seawater nasal irrigation solution containing algal and herbal natural ingredients in patients with COVID-19. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 26(2 Suppl):112–123. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202212_30495",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/S00228-021-03102-3",
"author": "S Huijghebaert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1275",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "8518_CR42",
"unstructured": "Huijghebaert S, Hoste L, Vanham G (2021) Essentials in saline pharmacology for nasal or respiratory hygiene in times of COVID-19. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 77(9):1275–1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00228-021-03102-3",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.31756",
"author": "ZJ Madewell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2031756",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "8518_CR43",
"unstructured": "Madewell ZJ, Yang Y, Longini IM, Halloran ME, Dean NE (2020) Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 3(12):e2031756–e2031756. https://doi.org/10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.31756",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/S12098-020-03263-6/METRICS",
"author": "T Singhal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Indian J Pediatr",
"key": "8518_CR44",
"unstructured": "Singhal T (2020) A review of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). Indian J Pediatr 87(4):281–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12098-020-03263-6/METRICS",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2058738420941757",
"author": "M Casale",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol",
"key": "8518_CR45",
"unstructured": "Casale M, Rinaldi V, Sabatino L, Moffa A, Ciccozzi M (2020) Could nasal irrigation and oral rinse reduce the risk for COVID-19 infection? Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1177/2058738420941757",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/JAMAOTO.2020.1622",
"author": "NF Farrell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "787",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "8518_CR46",
"unstructured": "Farrell NF, Klatt-Cromwell C, Schneider JS (2020) Benefits and safety of nasal saline irrigations in a pandemic-washing COVID-19 away. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146(9):787–788. https://doi.org/10.1001/JAMAOTO.2020.1622",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0145561320950491",
"author": "T Radulesco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "188S",
"issue": "2_suppl",
"journal-title": "Ear Nose Throat J",
"key": "8518_CR47",
"unstructured": "Radulesco T, Lechien JR, Saussez S, Hopkins C, Michel J (2021) Safety and impact of nasal lavages during viral infections such as SARS-CoV-2. Ear Nose Throat J 100(2_suppl):188S-191S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561320950491",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4178/epih.e2021051",
"author": "MBD Domênico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Health",
"key": "8518_CR48",
"unstructured": "Domênico MBD, Collares K, Santos RBD, Lenz U, Antunes VP, Godinho VW, Cesca H, Ponciano THJ, Corazza PH (2021) Hydrogen peroxide as an auxiliary treatment for COVID-19 in Brazil: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. Epidemiol Health 43:e2021051. https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2021051",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490",
"author": "J Guenezan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "400",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "8518_CR49",
"unstructured": "Guenezan J, Garcia M, Strasters D, Jousselin C, Lévêque N, Frasca D, Mimoz O (2021) Povidone iodine mouthwash, gargle, and nasal spray to reduce nasopharyngeal viral load in patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147(4):400–401. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101624",
"author": "KI Notarte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "8518_CR50",
"unstructured": "Notarte KI, Catahay JA, Velasco JV, Pastrana A, Ver AT, Pangilinan FC, Peligro PJ, Casimiro M, Guerrero JJ, Gellaco MML, Lippi G, Henry BM, Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C (2022) Impact of COVID-19 vaccination on the risk of developing long-COVID and on existing long-COVID symptoms: a systematic review. EClinicalMedicine 53:101624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101624",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine",
"Otorhinolaryngology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Seawater nasal wash to reduce symptom duration and viral load in COVID-19 and upper respiratory tract infections: a randomized controlled multicenter trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}