Hydrogen peroxide as an auxiliary treatment for COVID-19 in Brazil: a randomized double-blind clinical trial
et al., Epidemiology and Health, doi:10.4178/epih.e2021051, Aug 2021
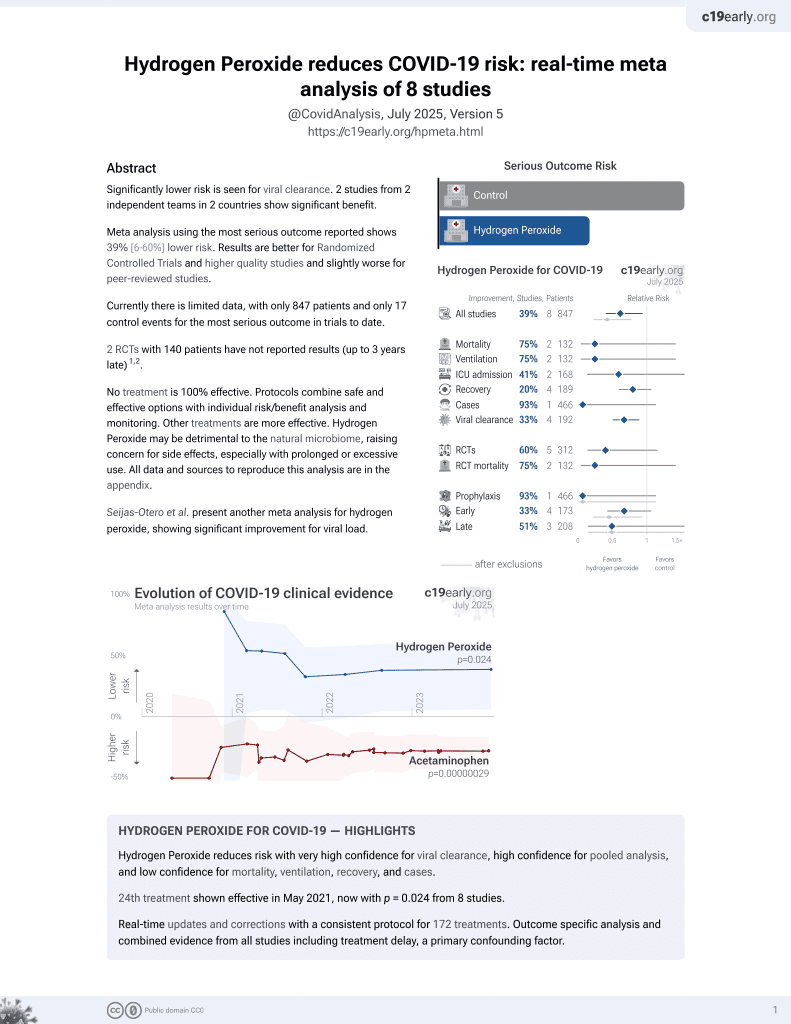
24th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.024 from 8 studies.
Lower risk for viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT very late treatment (>9 days from onset) comparing hydrogen peroxide + mint essence with water + mint essence, showing no significant differences.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
|
risk of ICU admission, 33.8% lower, RR 0.66, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 77 (2.6%), control 2 of 51 (3.9%), NNT 76.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 1.0% higher, HR 1.01, p = 0.97, treatment 63, control 43, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 31.4% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.54, treatment 6 of 51 (11.8%), control 6 of 35 (17.1%), NNT 19, antibody positive.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Di Domênico et al., 3 Aug 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Brazil, peer-reviewed, survey, 9 authors, average treatment delay 9.2 days.
Contact: pedrocorazza@upf.br.
Hydrogen peroxide as an auxiliary treatment for COVID-19 in Brazil: a randomized double-blind clinical trial
Epidemiology and Health, doi:10.4178/epih.e2021051
OBJECTIVES: This study evaluated the effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as mouthwash and nasal spray on symptom relief in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients.
METHODS: Patients positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), who were treated in a hospital or at home, and patients' family members (not positive for SARS-CoV-2), were randomized into 2 groups: experimental (1% H2O2 for gargling, 0.5% H2O2 for nasal wash), and control. Patients gargled the solution 3 times a day, and applied the nasal spray twice a day, for a 7-day period. Family members received the same treatment as the treated COVID-19 patient. The researchers contacted patients every 2 days over an 8-day period. An average post-treatment interval of 8 days passed before testing family members.
RESULTS: The most frequent symptoms on day 0 were cough, loss of taste, and hyposmia; there were no significant differences between groups, independent of the period. The symptom of dyspnea presented a significant difference between days 2 and 4 (p < 0.05). Among family members, 86.0% had no antibodies, 2.3% had antibodies, and 11.6% had active infections (4 in the experimental group and 6 in the control group). The most frequent adverse effects in the H2O2 group were a burning throat and nose. CONCLUSIONS: H2O2 was not effective for the relief of COVID-19 symptoms and was associated with reports of transient adverse effects.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this study.
FUNDING Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Conceptualization: PHC, MBDD. Data curation: KC. Formal analysis: KC. Funding acquisition: MBDD. Methodology: HC, THJP, RBS, UL, VPA, VWG. Project administration: PHC, MBDD, HC. Writing -original draft: MBDD, PHC, HC. Writing -review & editing: KC, RBS, UL, VPA, VWG, THJP.
References
Asghar, Din, The expected second wave of COVID-19, Int J Clin Virol
Candel, San-Román, Barreiro, Canora, Zapatero et al., Integral management of COVID-19 in Madrid: turning things around during the second wave, Lancet Reg Health Eur
Caruso, Prete, Lazzarino, Hydrogen peroxide and viral infections: a literature review with research hypothesis definition in relation to the current covid-19 pandemic, Med Hypotheses
Domênico, Cesca, Ponciano, Santos, Lenz et al., Effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide as auxiliary treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Brazil: preliminary results of a randomized double-blind clinical trial, Epidemiol Health
Gottsauner, Michaelides, Schmidt, Scholz, Buchalla et al., A prospective clinical pilot study on the effects of a hydrogen peroxide mouthrinse on the intraoral viral load of SARS-CoV-2, Clin Oral Investig
Grant, Geoghegan, Arbyn, Mohammed, Mcguinness, The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries, PLoS One
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Herrera, Serrano, Roldán, Sanz, Is the oral cavity relevant in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic?, Clin Oral Investig
Hu, Sun, Dai, Deng, Li et al., Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Clin Virol
Kampf, Todt, Pfaender, Steinmann, Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and their inactivation with biocidal agents, J Hosp Infect
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, Jones, Zheng et al., The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: estimation and application, Ann Intern Med
Lewis, Chu, Ye, Conners, Gharpure et al., Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States, Clin Infect Dis
Li, Pei, Chen, Song, Zhang et al., Substantial undocumented infection facilitates the rapid dissemination of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), Science
Lu, Liu, Jia, 2019-nCoV transmission through the ocular surface must not be ignored, Lancet
Maggi, Novazzi, Genoni, Baj, Spezia et al., Imported SARS-CoV-2 variant P.1 in traveler returning from Brazil to Italy, Emerg Infect Dis
Marshall, Cancro, Fischman, Hydrogen peroxide: a review of its use in dentistry, J Periodontol
O'donnell, Thomas, Stanton, Maillard, Murphy et al., Potential role of oral rinses targeting the viral lipid envelope in SARS-CoV-2, Infection. Function (Oxf)
Omidbakhsh, Sattar, Broad-spectrum microbicidal activity, toxicologic assessment, and materials compatibility of a new generation of accelerated hydrogen peroxide-based environmental surface disinfectant, Am J Infect Control
Peng, Xu, Li, Cheng, Zhou et al., Transmission routes of 2019-nCoV and controls in dental practice, Int J Oral Sci
Rosenberg, Dufort, Blog, Hall, Hoefer et al., COVID-19 testing, epidemic features, hospital outcomes, and household prevalence, Clin Infect Dis
Wang, Ma, Zheng, Wu, Zhang, Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2, J Infect
Yang, Zheng, Gou, Pu, Chen et al., Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Ban, Li et al., Serological detection of 2019-nCoV respond to the epidemic: a useful complement to nucleic acid testing, Int Immunopharmacol
Zou, Ruan, Huang, Liang, Huang et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4178/epih.e2021051",
"ISSN": [
"2092-7193"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2021051",
"abstract": "<jats:p>OBJECTIVES: This study evaluated the effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide (H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>) as mouthwash and nasal spray on symptom relief in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients.METHODS: Patients positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), who were treated in a hospital or at home, and patients’ family members (not positive for SARS-CoV-2), were randomized into 2 groups: experimental (1% H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> for gargling, 0.5% H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> for nasal wash), and control. Patients gargled the solution 3 times a day, and applied the nasal spray twice a day, for a 7-day period. Family members received the same treatment as the treated COVID-19 patient. The researchers contacted patients every 2 days over an 8-day period. An average post-treatment interval of 8 days passed before testing family members.RESULTS: The most frequent symptoms on day 0 were cough, loss of taste, and hyposmia; there were no significant differences between groups, independent of the period. The symptom of dyspnea presented a significant difference between days 2 and 4 (p<0.05). Among family members, 86.0% had no antibodies, 2.3% had antibodies, and 11.6% had active infections (4 in the experimental group and 6 in the control group). The most frequent adverse effects in the H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> group were a burning throat and nose.CONCLUSIONS: H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> was not effective for the relief of COVID-19 symptoms and was associated with reports of transient adverse effects.</jats:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-06-07"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-08-03"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-08-03"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2166-3052",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Domênico",
"given": "Marielle Bazzo Di",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7276-1074",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Collares",
"given": "Kauê",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8188-480X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Renan Brandenburg dos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7382-632X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Lenz",
"given": "Ulysses",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3059-5095",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Antunes",
"given": "Vinícius Picoli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9897-0333",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Godinho",
"given": "Vinicius Webber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2751-0329",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Cesca",
"given": "Henrique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3699-4225",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ponciano",
"given": "Thales Henrique Jincziwski",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9480-1607",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Corazza",
"given": "Pedro Henrique",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Epidemiology and Health",
"container-title-short": "Epidemiol Health",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"e-epih.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-13T05:44:51Z",
"timestamp": 1628833491000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T02:12:24Z",
"timestamp": 1661307144000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002322",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-13T09:29:16Z",
"timestamp": 1686648556462
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://e-epih.org/upload/pdf/epih-43-e2021051.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2679",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2021051",
"prefix": "10.4178",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Korean Society of Epidemiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100039",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30313-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb3221",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/m20-0504",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41368-020-0075-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmc2001737",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00784-020-03413-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109910",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2020.01.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajic.2005.06.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4178/epih.e2021032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106861",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0234765",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"key": "ref19",
"volume-title": "Coronavirus",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/function/zqaa002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00784-020-03549-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"author": "Lewis",
"first-page": "ciaa1166",
"key": "ref22",
"volume-title": "Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Rosenberg",
"first-page": "1953",
"key": "ref23",
"volume-title": "COVID-19 testing, epidemic features, hospital outcomes, and household prevalence, New York State-March 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2704.210183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1902/jop.1995.66.9.786",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://e-epih.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.4178/epih.e2021051"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Hydrogen peroxide as an auxiliary treatment for COVID-19 in Brazil: a randomized double-blind clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4178/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "43"
}