Ibrutinib for Hospitalized Adults With Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection: Results of the Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled iNSPIRE Study
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac104, iNSPIRE, NCT04375397, Mar 2022
RCT 46 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 showing no significant differences with ibrutinib treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
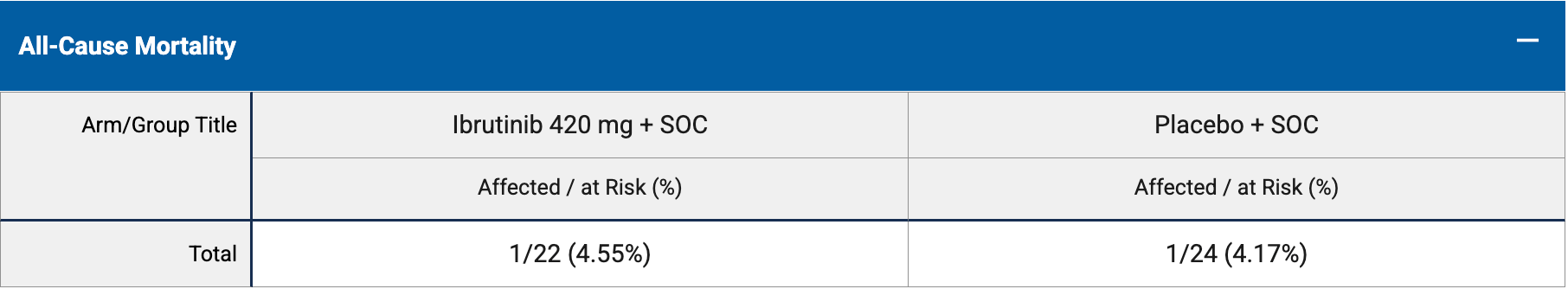
risk of death, 9.1% higher, RR 1.09, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 22 (4.5%), control 1 of 24 (4.2%), day 58.
|
|
risk of death, 209.1% higher, RR 3.09, p = 0.48, treatment 1 of 22 (4.5%), control 0 of 24 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 9.1% higher, RR 1.09, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 22 (4.5%), control 1 of 24 (4.2%), day 58.
|
|
risk of progression, 34.5% lower, RR 0.65, p = 0.70, treatment 3 of 22 (13.6%), control 5 of 24 (20.8%), NNT 14, mortality or respiratory failure, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Coutre et al., 24 Mar 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 51.5, 12 authors, study period 6 June, 2020 - 8 June, 2021, trial NCT04375397 (history) (iNSPIRE).
Contact: steven_treon@dfci.harvard.edu.
Ibrutinib for Hospitalized Adults With Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection: Results of the Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled iNSPIRE Study
Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac104
Background. Few therapies are approved for hospitalized patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 . Ibrutinib, a once-daily Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, may mitigate COVID-19-induced lung damage by reducing inflammatory cytokines. The multicenter, randomized, double-blind phase 2 iNSPIRE study evaluated ibrutinib for prevention of respiratory failure in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19. Methods. Adult patients with severe COVID-19 requiring hospitalization and supplemental oxygen but without respiratory failure were randomized 1:1 (stratified by remdesivir prescription) to ibrutinib 420 mg or placebo once daily for up to 28 days plus standard of care (SOC), including remdesivir and/or dexamethasone. Results. Forty-six patients were randomized to ibrutinib plus SOC (n = 22) or placebo plus SOC (n = 24). The primary endpoint (proportion of patients alive and without respiratory failure through day 28) was not met, with no statistically significant difference adjusting for remdesivir prescription (86% with ibrutinib plus SOC vs 79% with placebo plus SOC; adjusted difference, 5.8% [80% confidence interval, -9.2% to 20.4%]; P = .599). Secondary endpoints also showed no statistically significant improvement with ibrutinib plus SOC. Median treatment duration was 14 days for ibrutinib and placebo. Adverse events were similar with ibrutinib plus SOC vs placebo plus SOC (overall: 55% vs 50%; serious: 18% vs 13%) and were consistent with the known safety profile of ibrutinib. Conclusions. Addition of ibrutinib to SOC did not improve the proportion of patients alive and without respiratory failure through day 28 in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19. Ibrutinib had a manageable safety profile, with similar safety to placebo. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04375397.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at Open Forum Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader,
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Florence, Krupa, Booshehri, Davis, Inhibiting Bruton's tyrosine kinase rescues mice from lethal influenza-induced acute lung injury, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Greil, Tedeschi, Moreno, Anz, Pretreatment with ibrutinib reduces cytokine secretion and limits the risk of obinutuzumab-induced infusion-related reactions in patients with CLL: analysis from the iLLUMINATE study, Ann Hematol
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Marconi, Ramanan, De Bono, Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med
Mcelvaney, Mcevoy, Mcelvaney, Carroll, Characterization of the inflammatory response to severe COVID-19 illness, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Mcgonagle, Sharif, 'regan, Bridgewood, The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease, Autoimmun Rev
Treon, Castillo, Skarbnik, Soumerai, The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib may protect against pulmonary injury in COVID-19-infected patients, Blood
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac104",
"ISSN": [
"2328-8957"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofac104",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Few therapies are approved for hospitalized patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Ibrutinib, a once-daily Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, may mitigate COVID-19–induced lung damage by reducing inflammatory cytokines. The multicenter, randomized, double-blind phase 2 iNSPIRE study evaluated ibrutinib for prevention of respiratory failure in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Adult patients with severe COVID-19 requiring hospitalization and supplemental oxygen but without respiratory failure were randomized 1:1 (stratified by remdesivir prescription) to ibrutinib 420 mg or placebo once daily for up to 28 days plus standard of care (SOC), including remdesivir and/or dexamethasone.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Forty-six patients were randomized to ibrutinib plus SOC (n = 22) or placebo plus SOC (n = 24). The primary endpoint (proportion of patients alive and without respiratory failure through day 28) was not met, with no statistically significant difference adjusting for remdesivir prescription (86% with ibrutinib plus SOC vs 79% with placebo plus SOC; adjusted difference, 5.8% [80% confidence interval, –9.2% to 20.4%]; P = .599). Secondary endpoints also showed no statistically significant improvement with ibrutinib plus SOC. Median treatment duration was 14 days for ibrutinib and placebo. Adverse events were similar with ibrutinib plus SOC vs placebo plus SOC (overall: 55% vs 50%; serious: 18% vs 13%) and were consistent with the known safety profile of ibrutinib.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Addition of ibrutinib to SOC did not improve the proportion of patients alive and without respiratory failure through day 28 in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19. Ibrutinib had a manageable safety profile, with similar safety to placebo.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trials Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>NCT04375397.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford Cancer Center, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, USA"
}
],
"family": "Coutre",
"given": "Steven E",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, District of Columbia, USA"
},
{
"name": "University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA"
}
],
"family": "Barnett",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Triple O Research Institute, West Palm Beach, Florida, USA"
}
],
"family": "Osiyemi",
"given": "Olayemi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hoda",
"given": "Daanish",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Midway Immunology and Research Center, Fort Pierce, Florida, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ramgopal",
"given": "Moti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, Florida, USA"
}
],
"family": "Fort",
"given": "Alexander C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "AbbVie, North Chicago, Illinois, USA"
}
],
"family": "Qaqish",
"given": "Roula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "AbbVie, North Chicago, Illinois, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Yiran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company, South San Francisco, California, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ninomoto",
"given": "Joi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "AbbVie, North Chicago, Illinois, USA"
}
],
"family": "Alami",
"given": "Negar N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company, South San Francisco, California, USA"
}
],
"family": "Styles",
"given": "Lori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Treon",
"given": "Steven P",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Open Forum Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-25T17:01:12Z",
"timestamp": 1648227672000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-27T22:20:57Z",
"timestamp": 1651098057000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Pharmacyclics LLC"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100006483",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100006483",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "AbbVie"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T21:28:45Z",
"timestamp": 1740173325231,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 8,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1648080000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofac104/42993865/ofac104.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/9/5/ofac104/43471964/ofac104.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/9/5/ofac104/43471964/ofac104.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
24
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China.",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0001",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0002",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537",
"article-title": "The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome–like disease.",
"author": "McGonagle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102537",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0003",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-1583OC",
"article-title": "Characterization of the inflammatory response to severe COVID-19 illness.",
"author": "McElvaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "812",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0004",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00047.2018",
"article-title": "Inhibiting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase rescues mice from lethal influenza-induced acute lung injury.",
"author": "Florence",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L52",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0005",
"volume": "315",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00277-021-04536-6",
"article-title": "Pretreatment with ibrutinib reduces cytokine secretion and limits the risk of obinutuzumab-induced infusion-related reactions in patients with CLL: analysis from the iLLUMINATE study.",
"author": "Greil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1733",
"journal-title": "Ann Hematol",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0006",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020006288",
"article-title": "The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib may protect against pulmonary injury in COVID-19-infected patients.",
"author": "Treon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1912",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0007",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization.",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0008",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—final report.",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0009",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0010",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial.",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0011",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial.",
"author": "Marconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1407",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2022042722194352500_CIT0012",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofac104/6553342"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ibrutinib for Hospitalized Adults With Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection: Results of the Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled iNSPIRE Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "9"
}