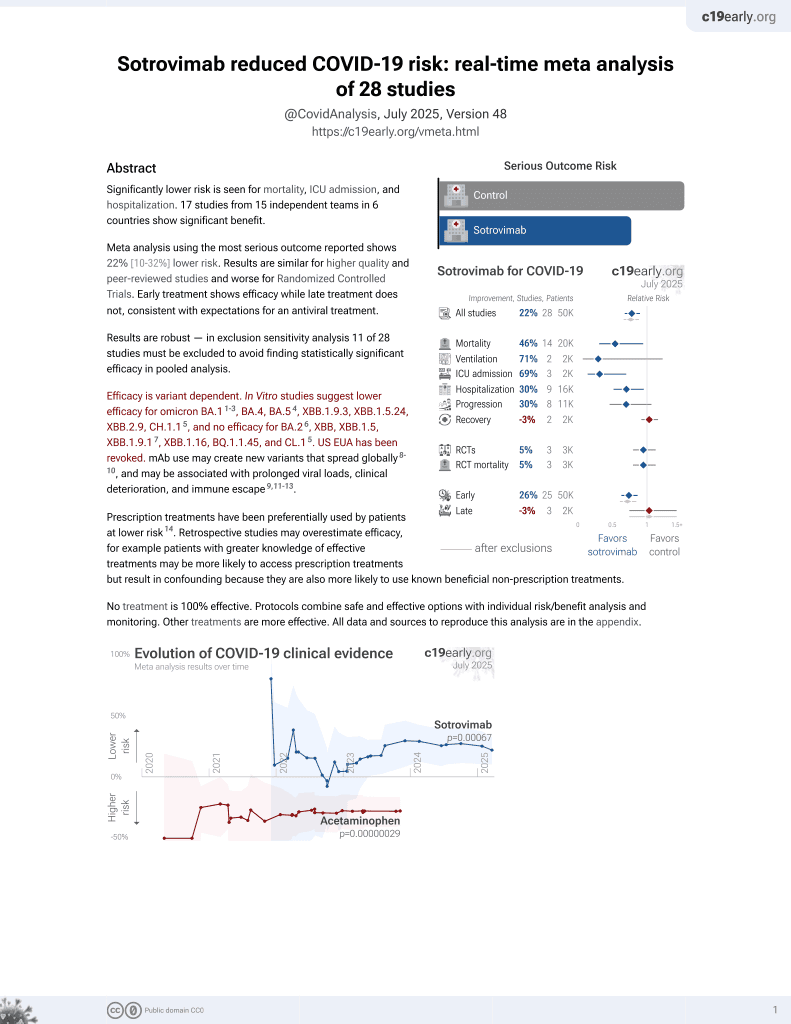
Real-world Effectiveness of Sotrovimab for the Early Treatment of COVID-19 During SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron Waves in the United States
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.09.07.22279497, Sep 2022
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
45th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00048 from 29 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 1,530,501 high-risk patients in the USA, 15,633 treated with sotrovimab, showing significantly lower mortality and hospitalization with treatment. Sotrovimab maintained efficacy throughout the period analyzed - September 2021 to April 2022.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene1,2, vitamin D3, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending sotrovimab also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out sotrovimab is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies predict lower efficacy for BA.14-6, BA.4, BA.57, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.18, and no efficacy for BA.29, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.110, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.18. US EUA has been revoked.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments11.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
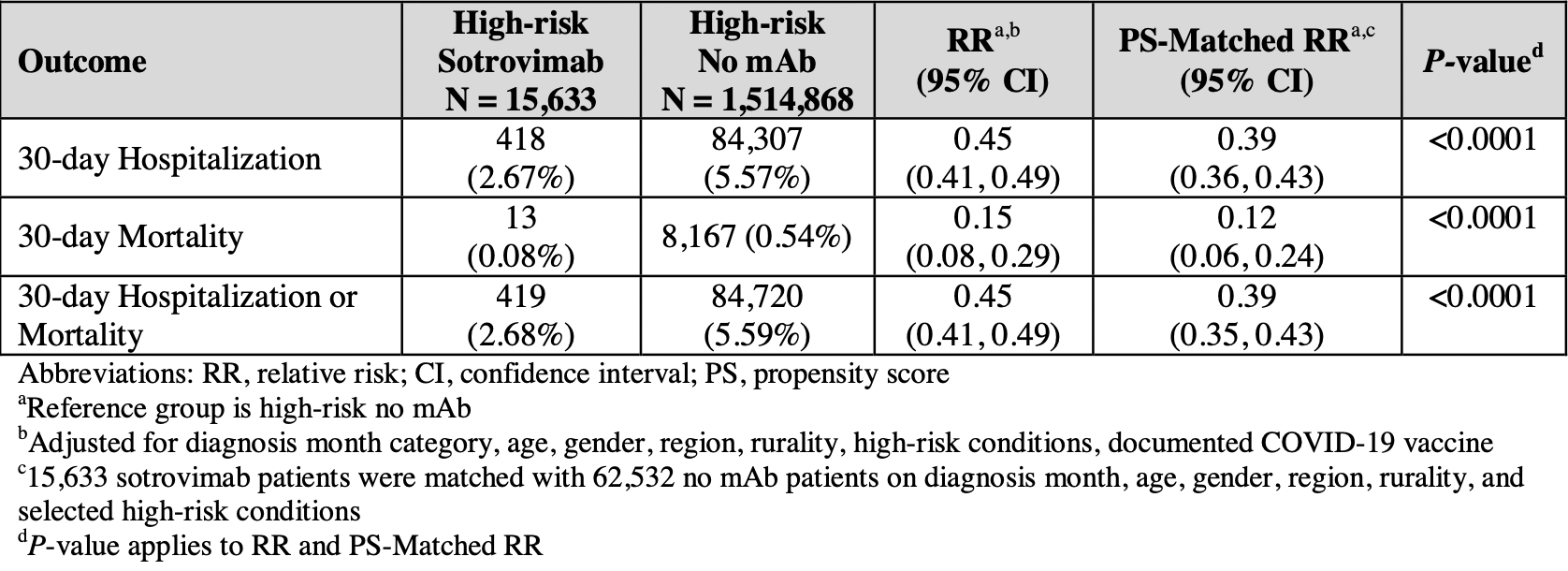
risk of death, 88.0% lower, RR 0.12, p < 0.001, NNT 219, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 61.0% lower, RR 0.39, p < 0.001, NNT 35, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
4.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
5.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
6.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
7.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
8.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
9.
Zhou et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 Variant Evades Neutralization by Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.15.480166.
Cheng et al., 11 Sep 2022, retrospective, USA, preprint, 13 authors, study period 1 September, 2021 - 30 April, 2022.
Contact: mcheng@vir.bio.
Real-world Effectiveness of Sotrovimab for the Early Treatment of COVID-19 During SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron Waves in the United States
doi:10.1101/2022.09.07.22279497
Background Sotrovimab, a recombinant human monoclonal antibody (mAb) against SARS-CoV-2 had US FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of high-risk outpatients with mildto-moderate COVID-19 from May 26, 2021 to April 5, 2022. The study objective was to evaluate the real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab in reducing the risk of 30-day all-cause hospitalization and/or mortality during the time period when the prevalence of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants was changing between Delta and Omicron sub-lineages in the US.
Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on de-identified claims data for 1,530,501 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 (ICD-10: U07.1) from September 1, 2021, to April 30, 2022, in the FAIR Health National Private Insurance Claims (FH NPIC ® ) database. Patients meeting EUA high-risk criteria were identified via pre-specified ICD-10-CM diagnoses in records ≤24 months prior to their first COVID-19 diagnosis and divided into two cohorts based on claimed procedural codes: treated with sotrovimab ("sotrovimab") and not treated with a mAb ("no mAb"). All-cause hospitalizations and facility-reported all-cause mortality within 30 days of diagnosis ("30-day hospitalization or mortality") were identified. Multivariable and propensity score-matched Poisson and logistic regressions were conducted to estimate the adjusted relative risk (RR) and odds of 30-day hospitalization or mortality among those treated with sotrovimab compared with those not treated with a mAb.
Results Of the high-risk COVID-19 patients identified, 15,633 were treated with sotrovimab and 1,514,868 were not treated with a mAb. Compared with the no mAb cohort, the sotrovimab All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity.
References
Aggarwal, Beaty, Bennett, Change in Effectiveness of Sotrovimab for Preventing Hospitalization and Mortality in COVID-19 Outpatients During the Omicron Phase, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.06.17.22276575
Aggarwal, Beaty, Bennett, Real-World Evidence of the Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Sotrovimab for Preventing Hospitalization and Mortality in COVID-19 Outpatients, JID, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac206
Case, Mackin, Errico, Resilience of S309 and AZD7442 Monoclonal Antibody Treatments Against Infection by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineage Strains, Nature Communications
Cathcart, Havenar-Daughton, Lempp, The Dual Function Monoclonal Antibodies VIR-7831 and VIR-7832 Demonstrate Potent in Vitro and in Vivo Activity Against SARS-CoV-2, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.09.434607
Covid-, Estimating Excess Mortality Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic: a Systematic Analysis of COVID-19 Related Mortality, Lancet
Elbe, Buckland-Merrett, Data, Disease and Diplomacy: GISAID's Innovative Contribution to Global Health, Global Challenges
Gavriatopoulou, Ntanasis-Stathopoulous, Korompoki, Emerging treatment strategies for COVID-19 infection, Clin Exp Med
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Early Treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab, NEJM
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Effect of Sotrovimab on Hospitalization or Death Among High-Risk Patients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19, A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Lee, Wong, Chai, Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines in Immunocompromised Patients: Systemic Review and Meta-analysis, BMJ
Parker, Desai, Marti, Response to Additional COVID-19 Vaccine Doses in People who are Immunocompromised: a Rapid Review, The Lancet Global Health
Telenti, Hodcroft, Robertson, The Evolution and Biology of SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med
Zaqout, Almaslamani, Chemaitelly, Effectiveness of the Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab Among High-risk Patients With Mild to Moderate SARS-CoV-2 in Qatar, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.04.21.22274060
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.09.07.22279497",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.07.22279497",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background \nSotrovimab, a recombinant human monoclonal antibody (mAb) against SARS-CoV-2 had US FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of high-risk outpatients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 from May 26, 2021, to April 5, 2022. The study objective was to evaluate the real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab in reducing the risk of 30-day all-cause hospitalization and/or mortality during the time period when the prevalence of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants was changing between Delta and Omicron sub-lineages in the US.\nMethods \nA retrospective analysis was conducted on de-identified claims data for 1,530,501 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 (ICD-10: U07.1) from September 1, 2021, to April 30, 2022, in the FAIR Health National Private Insurance Claims (FH NPIC®) database. Patients meeting EUA high-risk criteria were identified via pre-specified ICD-10-CM diagnoses in records ≤24 months prior to their first COVID-19 diagnosis and divided into two cohorts based on claimed procedural codes: treated with sotrovimab (″sotrovimab″) and not treated with a mAb (″no mAb″). All-cause hospitalizations and facility-reported all-cause mortality within 30 days of diagnosis (″30-day hospitalization or mortality″) were identified. Multivariable and propensity score-matched Poisson and logistic regressions were conducted to estimate the adjusted relative risk (RR) and odds of 30-day hospitalization or mortality among those treated with sotrovimab compared with those not treated with a mAb.\nResults \nOf the high-risk COVID-19 patients identified, 15,633 were treated with sotrovimab and 1,514,868 were not treated with a mAb. Compared with the no mAb cohort, the sotrovimab cohort was older and had a higher proportion of patients across the majority of high-risk conditions. In the no mAb cohort, 84,307 (5.57%) patients were hospitalized and 8,167 (0.54%) deaths were identified, while in the sotrovimab cohort, 418 (2.67%) patients were hospitalized and 13 (0.08%) deaths were identified. After adjusting for potential confounders, high-risk COVID-19 patients treated with sotrovimab had a 55% relative risk reduction of 30-day hospitalization or mortality (RR: 0.45, 95% CI: 0.41,0.49) and an 85% relative risk reduction of 30-day mortality (RR: 0.15, 95% CI: 0.08, 0.29) compared with high-risk patients not treated with a mAb. From September 2021 to April 2022, sotrovimab maintained clinical effectiveness with relative risk reductions of 30-day hospitalization or mortality ranging from 46% to 71%. Stratifying by high-risk condition, sotrovimab-treated patients exhibited statistically significant relative risk reductions of 30-day hospitalization or mortality compared with the no mAb cohort across all high-risk conditions (P<0.0001), ranging from 44% among pregnant women to 70% among patients 65 years and older. \nConclusion \nIn this large, US real-world, observational study of high-risk COVID-19 patients with reported diagnosis between September 2021 and April 2022 during the Delta and early Omicron variant waves, treatment with sotrovimab was associated with reduced risk of 30-day all-cause hospitalization and facility-reported mortality compared with no mAb treatment. Sotrovimab clinical effectiveness persisted throughout the months when Delta and early Omicron sub-lineages were the predominant circulating variants in the US, though there was an uncertain RR estimate in April 2022 with wide confidence intervals due to the small sample size. Sotrovimab clinical effectiveness also persisted among all high-risk subgroups assessed.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
11
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Mindy M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reyes",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Satram",
"given": "Sacha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Birch",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibbons",
"given": "Daniel C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drysdale",
"given": "Myriam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "Christopher F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suyundikov",
"given": "Anvar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Xiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maher",
"given": "M. Cyrus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yeh",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Telenti",
"given": "Amalio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corey",
"given": "Lawrence",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-11T15:25:10Z",
"timestamp": 1662909910000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-11T15:25:14Z",
"timestamp": 1662909914000
},
"group-title": "Health Economics",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-11T15:41:40Z",
"timestamp": 1662910900586
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
11
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2022.09.07.22279497",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
11
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2022.09.07.22279497"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Real-world Effectiveness of Sotrovimab for the Early Treatment of COVID-19 During SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron Waves in the United States",
"type": "posted-content"
}