Efficacy of short-course colchicine treatment in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia and hyperinflammation: a randomized clinical trial
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13424-6, Jun 2022
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
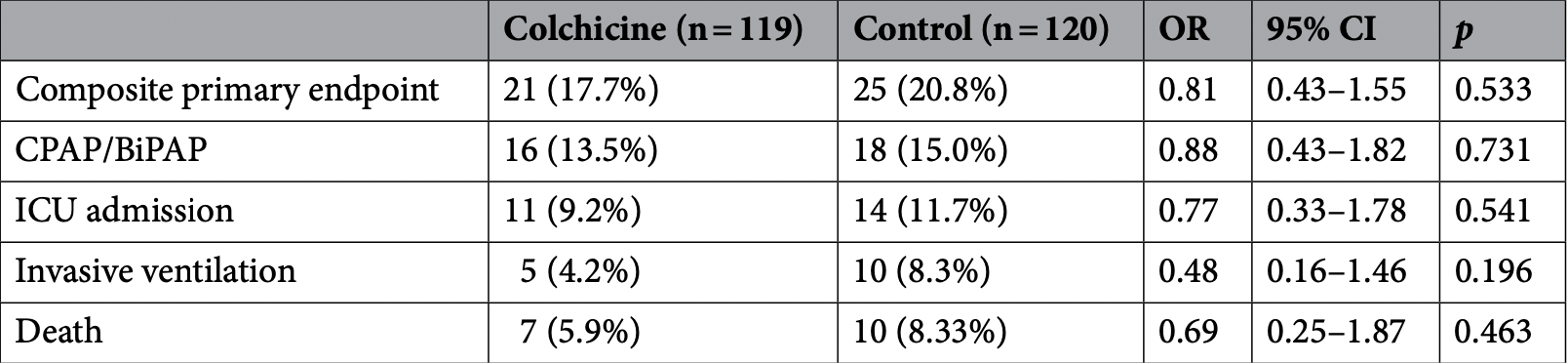
RCT 240 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, mean 9 days from the onset of symptoms, showing no significant differences with colchicine treatment. EudraCT 2020-001841-38.
Although the 29% lower mortality is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 22% lower mortality [12‑31%] from meta-analysis of the 41 mortality results to date.
|
risk of death, 29.4% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.62, treatment 7 of 119 (5.9%), control 10 of 120 (8.3%), NNT 41.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 49.6% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.29, treatment 5 of 119 (4.2%), control 10 of 120 (8.3%), NNT 24.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 20.8% lower, RR 0.79, p = 0.67, treatment 11 of 119 (9.2%), control 14 of 120 (11.7%), NNT 41.
|
|
combined NIV/ICU/ventilation/death, 15.3% lower, RR 0.85, p = 0.62, treatment 21 of 119 (17.6%), control 25 of 120 (20.8%), NNT 31, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Cecconi et al., 2 Jun 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Spain, peer-reviewed, mean age 65.0, 31 authors, study period August 2020 - March 2021, average treatment delay 9.0 days, dosage 1mg day 1, 0.5mg days 2-5.
Contact: albertocecconi@hotmail.com.
Efficacy of short-course colchicine treatment in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia and hyperinflammation: a randomized clinical trial
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13424-6
Some patients with COVID-19 pneumonia develop an associated cytokine storm syndrome that aggravates the pulmonary disease. These patients may benefit of anti-inflammatory treatment. The role of colchicine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and established hyperinflammation remains unexplored. In a prospective, randomized controlled, observer-blinded endpoint, investigator-initiated trial, 240 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and established hyperinflammation were randomly allocated to receive oral colchicine or not. The primary efficacy outcome measure was a composite of non-invasive mechanical ventilation (CPAP or BiPAP), admission to the intensive care unit, invasive mechanical ventilation requirement or death. The composite primary outcome occurred in 19.3% of the total study population. The composite primary outcome was similar in the two arms (17% in colchicine group vs. 20.8% in the control group; p = 0.533) and the same applied to each of its individual components. Most patients received steroids (98%) and heparin (99%), with similar doses in both groups. In this trial, including adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and associated hyperinflammation, no clinical benefit was observed with short-course colchicine treatment beyond standard care regarding the combined outcome measurement of CPAP/ BiPAP use, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation or death (Funded by the Community of Madrid, EudraCT Number: 2020-001841-38; 26/04/2020).
Author contributions
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
References
Cai, Obesity and COVID-19 severity in a designated hospital in Shenzhen, China, Diabetes Care
Cecconi, Effects of colchicine on atherosclerotic plaque stabilization: A multimodality imaging study in an animal model, J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res
Chen, Quach, COVID-19 cytokine storm syndrome: A threshold concept, Lancet Microbe
Cozzi, Chest X-ray in new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: Findings and correlation with clinical outcome, Radiol. Med
Deftereos, Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: The GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw. Open
Demidowich, Effects of colchicine in adults with metabolic syndrome: A pilot randomized controlled trial, Diabetes Obes. Metab
Diaz, Effect of colchicine vs usual care alone on intubation and 28-day mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw. Open
Gao, Associations between body-mass index and COVID-19 severity in 6•9 million people in England: A prospective, community-based, cohort study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Guo, Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), JAMA Cardiol
Hamer, Gale, Kivimäki, Batty, Overweight, obesity, and risk of hospitalization for COVID-19: A communitybased cohort study of adults in the United Kingdom, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A
Hyun, Effects of early corticosteroid use in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019, BMC Infect. Dis
Katz, Regardless of age, obesity and hypertension increase risks with COVID-19, JAMA Intern. Med
Leung, Yao Hui, Kraus, Colchicine-update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses, Semin. Arthritis Rheum
Lopes, Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blinded, placebocontrolled clinical trial, RMD Open
Peckham, Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission, Nat. Commun
Reyes, Anti-inflammatory therapy for COVID-19 infection: The case for colchicine, Ann. Rheum. Dis
Roubille, Tardif, Colchicine for secondary cardiovascular prevention in coronary disease, Circulation
Salamanca, COVID-19 "fulminant myocarditis" successfully treated with temporary mechanical circulatory support, JACC Cardiovas. Imaging
Tardif, Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, doubleblinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00222-8
Tardif, Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction, N. Engl. J. Med
Zein, Raffaello, Effect of colchicine on mortality in patients with COVID-19-A systematic review and metaanalysis, Diabetes Metab. Syndr
Zhu, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-13424-6",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13424-6",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Some patients with COVID-19 pneumonia develop an associated cytokine storm syndrome that aggravates the pulmonary disease. These patients may benefit of anti-inflammatory treatment. The role of colchicine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and established hyperinflammation remains unexplored. In a prospective, randomized controlled, observer-blinded endpoint, investigator-initiated trial, 240 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and established hyperinflammation were randomly allocated to receive oral colchicine or not. The primary efficacy outcome measure was a composite of non-invasive mechanical ventilation (CPAP or BiPAP), admission to the intensive care unit, invasive mechanical ventilation requirement or death. The composite primary outcome occurred in 19.3% of the total study population. The composite primary outcome was similar in the two arms (17% in colchicine group vs. 20.8% in the control group; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.533) and the same applied to each of its individual components. Most patients received steroids (98%) and heparin (99%), with similar doses in both groups. In this trial, including adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and associated hyperinflammation, no clinical benefit was observed with short-course colchicine treatment beyond standard care regarding the combined outcome measurement of CPAP/BiPAP use, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation or death (Funded by the Community of Madrid, EudraCT Number: 2020-001841-38; 26/04/2020).</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"13424"
],
"article-number": "9208",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "3 December 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "27 April 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "2 June 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cecconi",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martinez-Vives",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vera",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lavilla Olleros",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrios",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fonseca Aizpuru",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roquero",
"given": "Pilar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hernandez Muñiz",
"given": "Susana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olivera",
"given": "Maria Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ciudad",
"given": "Marianela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pampin Sanchez",
"given": "Ruben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez-Madera Martínez",
"given": "Rosa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bautista-Hernández",
"given": "Azucena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García Castillo",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iturricastillo",
"given": "Gorane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ávalos",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prada Cotado",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alejandre de Oña",
"given": "Alvaro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez Carracedo",
"given": "Eduardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marcos-Jimenez",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanz-Garcia",
"given": "Ancor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alfranca",
"given": "Aranzazu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cecconi",
"given": "Maurizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de La Fuente",
"given": "Hortensia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanz de Benito",
"given": "Maria Angeles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caballero",
"given": "Paloma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanchez-Madrid",
"given": "Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ancochea",
"given": "Julio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suarez",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jimenez-Borreguero",
"given": "Luis Jesus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alfonso",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-02T12:03:42Z",
"timestamp": 1654171422000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-02T12:14:17Z",
"timestamp": 1654172057000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Directorate-General for Research, Teaching and Documentation of the Department of Health of the Community of Madrid"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-02T12:44:26Z",
"timestamp": 1654173866159
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654128000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654128000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13424-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13424-6",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13424-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13424_CR1",
"unstructured": "Zhu, N. et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382(8), 727–733 (2020).",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30223-8",
"author": "LYC Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e49",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "13424_CR2",
"unstructured": "Chen, L. Y. C. & Quach, T. T. T. COVID-19 cytokine storm syndrome: A threshold concept. Lancet Microbe 2(2), e49-50 (2021).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13424_CR3",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 384(8), 693–704 (2021).",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.06.013",
"author": "YY Leung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "341",
"journal-title": "Semin. Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "13424_CR4",
"unstructured": "Leung, Y. Y., Yao Hui, L. L. & Kraus, V. B. Colchicine-update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 45, 341–350 (2015).",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12265-020-09974-7",
"author": "A Cecconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "150",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res.",
"key": "13424_CR5",
"unstructured": "Cecconi, A. et al. Effects of colchicine on atherosclerotic plaque stabilization: A multimodality imaging study in an animal model. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 14(1), 150–160 (2021).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1912388",
"author": "J-C Tardif",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2497",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13424_CR6",
"unstructured": "Tardif, J.-C. et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 381(26), 2497–2505 (2019).",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017",
"author": "T Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "811",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol.",
"key": "13424_CR7",
"unstructured": "Guo, T. et al. Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 5(7), 811 (2020).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.05.003",
"author": "J Salamanca",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2457",
"journal-title": "JACC Cardiovas. Imaging",
"key": "13424_CR8",
"unstructured": "Salamanca, J. et al. COVID-19 “fulminant myocarditis” successfully treated with temporary mechanical circulatory support. JACC Cardiovas. Imaging 13, 2457–2459 (2020).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051240",
"author": "F Roubille",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1901",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "13424_CR9",
"unstructured": "Roubille, F. & Tardif, J. C. Colchicine for secondary cardiovascular prevention in coronary disease. Circulation 142, 1901 (2020).",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00222-8",
"author": "J-C Tardif",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "13424_CR10",
"unstructured": "Tardif, J.-C. et al. Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, double-blinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Respir. Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00222-8 (2021).",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"author": "SG Deftereos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2013136",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "13424_CR11",
"unstructured": "Deftereos, S. G. et al. Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: The GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 3(6), e2013136 (2020).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00435-5",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1419",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "13424_CR12",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Colchicine in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 9(12), 1419–1426 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11547-020-01232-9",
"author": "D Cozzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "730",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Radiol. Med.",
"key": "13424_CR13",
"unstructured": "Cozzi, D. et al. Chest X-ray in new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: Findings and correlation with clinical outcome. Radiol. Med. 125(8), 730–737 (2020).",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00089-9",
"author": "M Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "350",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "13424_CR14",
"unstructured": "Gao, M. et al. Associations between body-mass index and COVID-19 severity in 6·9 million people in England: A prospective, community-based, cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 9(6), 350–359 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.5313",
"author": "MH Katz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "379",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "13424_CR15",
"unstructured": "Katz, M. H. Regardless of age, obesity and hypertension increase risks with COVID-19. JAMA Intern. Med. 181, 379–381 (2021).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6",
"author": "H Peckham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "13424_CR16",
"unstructured": "Peckham, H. et al. Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 1–10 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06221-5",
"author": "JH Hyun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "506",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "13424_CR17",
"unstructured": "Hyun, J. H. et al. Effects of early corticosteroid use in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019. BMC Infect. Dis. 21(1), 506 (2021).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219174",
"author": "AZ Reyes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "550",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "13424_CR18",
"unstructured": "Reyes, A. Z. et al. Anti-inflammatory therapy for COVID-19 infection: The case for colchicine. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 80(5), 550–557 (2021).",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102395",
"author": "AFMZ Zein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102395",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "13424_CR19",
"unstructured": "Zein, A. F. M. Z. & Raffaello, W. M. Effect of colchicine on mortality in patients with COVID-19—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 16(2), 102395 (2022).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001455",
"author": "MI Lopes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e001455",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "RMD Open",
"key": "13424_CR20",
"unstructured": "Lopes, M. I. et al. Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. RMD Open 7(1), e001455 (2021).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.41328",
"author": "R Diaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2141328",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "13424_CR21",
"unstructured": "Diaz, R. et al. Effect of colchicine vs usual care alone on intubation and 28-day mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 4(12), e2141328–e2141328 (2021).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2011086117",
"author": "M Hamer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21011",
"issue": "35",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "13424_CR22",
"unstructured": "Hamer, M., Gale, C. R., Kivimäki, M. & Batty, G. D. Overweight, obesity, and risk of hospitalization for COVID-19: A community-based cohort study of adults in the United Kingdom. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117(35), 21011–21013 (2020).",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0576",
"author": "Q Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1392",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "13424_CR23",
"unstructured": "Cai, Q. et al. Obesity and COVID-19 severity in a designated hospital in Shenzhen, China. Diabetes Care 43(7), 1392–1398 (2020).",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.13702",
"author": "AP Demidowich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1642",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes. Metab.",
"key": "13424_CR24",
"unstructured": "Demidowich, A. P. et al. Effects of colchicine in adults with metabolic syndrome: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 21(7), 1642–1651 (2019).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13424-6"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of short-course colchicine treatment in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia and hyperinflammation: a randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}
