Nigella Sativa reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 14 studies (Version 23)
, Feb 2026
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
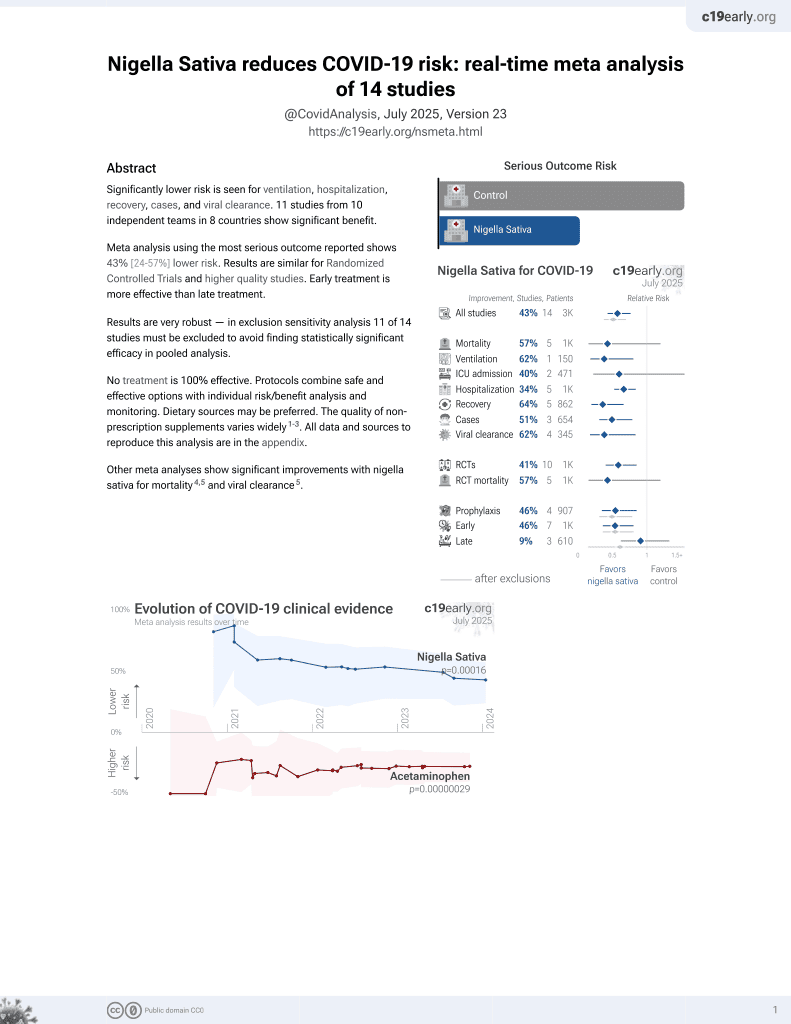
Significantly lower risk is seen for ventilation, hospitalization, recovery, cases, and viral clearance. 11 studies from 10 independent teams in 8 countries show significant benefit.
Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 43% [24‑57%] lower risk. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trials and higher quality studies. Early treatment is more effective than late treatment.
Results are very robust—in worst case exclusion sensitivity analysis 11 of 14 studies must be excluded before statistical significance is lost.
Control Nigella Sativa
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Dietary sources may be preferred. The quality of non-prescription supplements varies widely1-3. A lipid-optimized formulation may be required for therapeutic concentrations of nigella sativa, and may aid distribution to target tissues. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Other meta-analyses show significant improvements with nigella sativa for mortality4-6, progression6, and viral clearance5.
3 meta-analyses show significant improvements with nigella sativa for mortality1-3,
progression3, and
viral clearance2.
1.
Kow et al., The effect of Nigella sativa on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized trials, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7743.
Covid Analysis et al., Feb 2026, preprint, 1 author.