The Effect of Short Treatment with Nigella Sativa on Symptoms, the Cluster of Differentiation (CD) Profile, and Inflammatory Markers in Mild COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial
et al., International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph191811798, Sep 2022
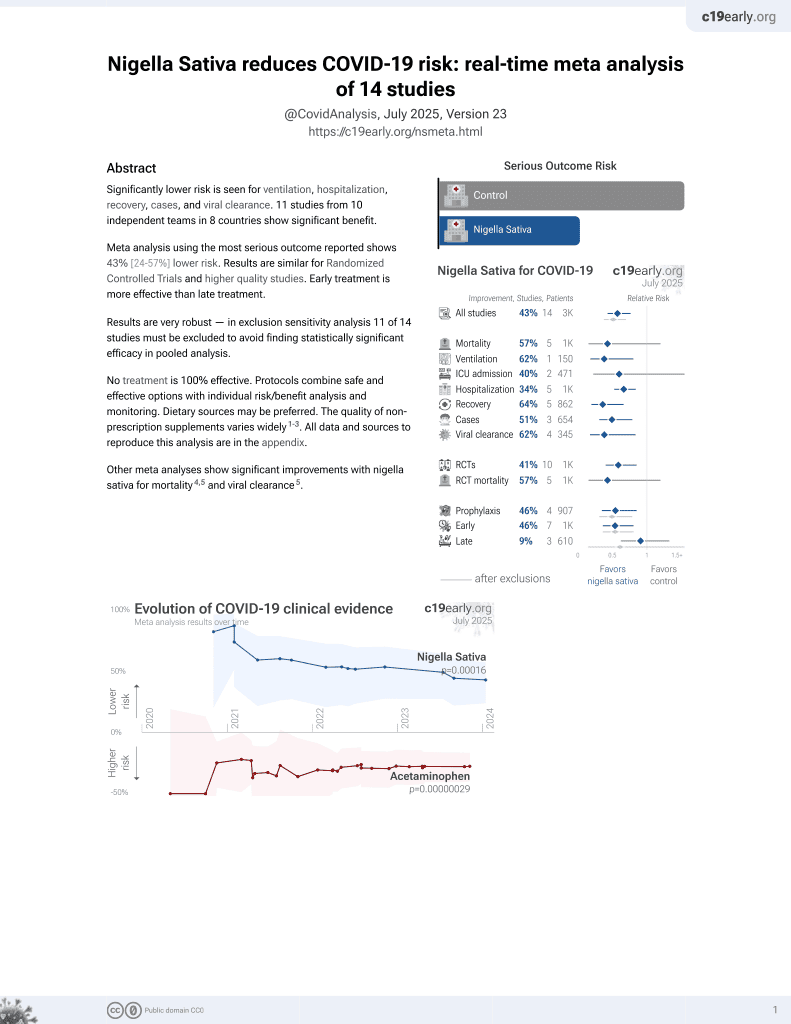
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
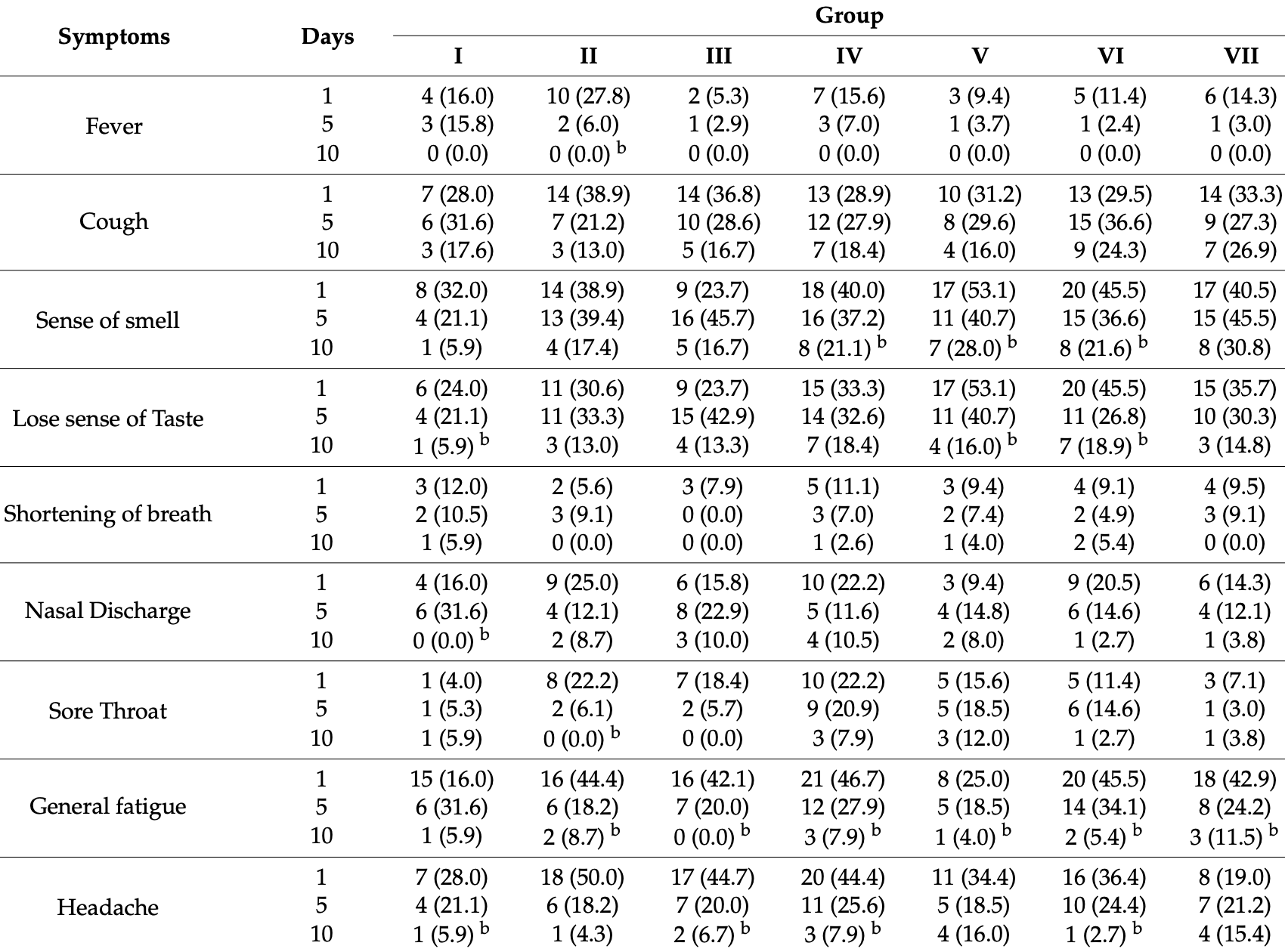
RCT 262 mild cases in Saudi Arabia, showing no significant difference in outcomes. The only symptomatic outcomes provided are for individual symptoms, with large differences in the baseline frequencies. 75 patients were lost to followup with the primary reason being early recovery. A higher percentage of patients were lost to followup in the treatment groups.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
only individual symptom data provided, differences in baseline frequencies, significant loss to followup due to recovery with greater frequency in treatment groups.
|
risk of no recovery, 62.0% lower, RR 0.38, p = 0.37, treatment 4 of 179 (2.2%), control 1 of 17 (5.9%), NNT 27, all treatment groups combined, day 10, dyspnea.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 279.9% higher, RR 3.80, p = 0.21, treatment 40 of 179 (22.3%), control 1 of 17 (5.9%), all treatment groups combined, day 10, smell.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 165.9% higher, RR 2.66, p = 0.48, treatment 28 of 179 (15.6%), control 1 of 17 (5.9%), all treatment groups combined, day 10, taste.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 4.5% higher, RR 1.04, p = 1.00, treatment 11 of 179 (6.1%), control 1 of 17 (5.9%), all treatment groups combined, day 10, fatigue.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 42.5% higher, RR 1.42, p = 1.00, treatment 15 of 179 (8.4%), control 1 of 17 (5.9%), all treatment groups combined, day 10, headache.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 41.7% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.35, treatment 13 of 212 (6.1%), control 2 of 19 (10.5%), NNT 23, all treatment groups combined, day 5, dyspnea.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 73.1% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.06, treatment 9 of 212 (4.2%), control 3 of 19 (15.8%), NNT 8.7, all treatment groups combined, day 5, fever.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 92.7% higher, RR 1.93, p = 0.14, treatment 86 of 212 (40.6%), control 4 of 19 (21.1%), all treatment groups combined, day 5, smell.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 61.3% higher, RR 1.61, p = 0.31, treatment 72 of 212 (34.0%), control 4 of 19 (21.1%), all treatment groups combined, day 5, taste.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 22.3% lower, RR 0.78, p = 0.58, treatment 52 of 212 (24.5%), control 6 of 19 (31.6%), NNT 14, all treatment groups combined, day 5, fatigue.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 3.1% higher, RR 1.03, p = 1.00, treatment 46 of 212 (21.7%), control 4 of 19 (21.1%), all treatment groups combined, day 5, headache.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bin Abdulrahman et al., 19 Sep 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Saudi Arabia, peer-reviewed, mean age 35.2, 14 authors.
Contact: kab@imamu.edu.sa (corresponding author).
The Effect of Short Treatment with Nigella Sativa on Symptoms, the Cluster of Differentiation (CD) Profile, and Inflammatory Markers in Mild COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph191811798
The current study investigated the impact of different doses of Nigella sativa seeds on the symptoms, the cluster of differentiation profile group, and inflammatory markers of mild COVID-19 cases. Methods: The study was a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Patients with mild and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection patients were randomly subdivided into seven subgroups: Group (GP) 1: received charcoal capsules as a control group, and GP 2: received three capsules of whole Nigella sativa seeds daily, two capsules in the morning and one in the evening; GP 3: received three capsules of whole Nigella sativa seeds every 12 h, GP 4: received five capsules in the morning and four capsules of whole Nigella sativa seeds in the evening, GP 5: received one capsule of Nigella sativa powder every 12 h; GP 6: received two capsules of Nigella sativa powder every 12 h; GP 7: received three capsules of Nigella sativa powder every 12 h; all treatment course was for ten days. Inflammatory parameters were assessed before and after interventions. Results: 262 subjects were included in the final analysis. No significant difference was detected regarding age, gender, and nationality. No significant differences were detected between the inflammatory marker in all groups. The WBCs showed a significant difference between before and after the intervention. While for procalcitonin, a significant difference was demonstrated in groups 1,4, and 6. Conclusions: The current randomized clinical trial did not reveal a significant effect of ten days of treatment with various doses of Nigella sativa on symptoms, differentiation profile, and inflammatory markers of patients with COVID-19. As a natural product, the effect of Nigella sativa on disease requires weeks to manifest itself.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. All coauthors have seen and agree with the manuscript's contents, and there is no financial interest to report. Furthermore, the authors certify that the submission is original work and is not under review in any other publication.
References
Ahmad, Ahmad, Ashraf, Saad, Wahab et al., An updated knowledge of Black seed (Nigella sativa Linn.): Review of phytochemical constituents and pharmacological properties, J. Herb. Med, doi:10.1016/j.hermed.2020.100404
Akhondian, Parsa, Rakhshande, The effect of Nigella sativa L. (black cumin seed) on intractable pediatric seizures, Med. Sci. Monit
Ardakani Movaghati, Yousefi, Saghebi, Sadeghi Vazin, Iraji et al., Efficacy of black seed (Nigella sativa L.) on kidney stone dissolution: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6331
Ashraf, Ashraf, Ashraf, Imran, Kalsoom et al., Honey and Nigella sativa against COVID-19 in Pakistan (HNS-COVID-PK): A multi-center placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.30.20217364
Bamosa, Kaatabi, Lebdaa, Elq, Al-Sultanb, Effect of Nigella sativa seeds on the glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol
Barakat, Wakeel, Hagag, Effects of Nigella sativa on outcome of hepatitis C in Egypt, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i16.2529
Bin Abdulrahman, Bamosa, Aseri, Bukhari, Masuadi, Clinical Presentation of Asymptomatic and Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, J. Multidiscip. Healthc, doi:10.2147/JMDH.S315718
Chan, .-W.; Yuan, Kok, To, Chu et al., A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hoang, Meddeb et al., Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Hadi, Kheirouri, Alizadeh, Khabbazi, Hosseini, Effects of Nigella sativa oil extract on inflammatory cytokine response and oxidative stress status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, Avicenna J. Phytomed
Hannan, Rahman, Sohag, Uddin, Dash et al., (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061784
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Islam, Hossain, Sarker, Ferdous, Hannan et al., Revisiting pharmacological potentials of Nigella sativa seed: A promising option for COVID-19 prevention and cure, Phytother. Res
Khazdair, Ghafari, Sadeghi, Possible therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and its thymoquinone on COVID-19, Pharm. Biol, doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1931353
Koshak, Koshak, Mobeireek, Badawi, Wali et al., Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial, Complement. Ther. Med, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102769
Kulyar, Li, Mehmood, Waqas, Li et al., Potential influence of Nigella sativa (Black cumin) in reinforcing immune system: A hope to decelerate the COVID-19 pandemic, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153277
Liu, Zhang, He, Hematological findings in coronavirus disease 2019: Indications of progression of disease, Ann. Hematol, doi:10.1007/s00277-020-04103-5
Mahboubi, Natural therapeutic approach of Nigella sativa (Black seed) fixed oil in management of Sinusitis, Integr. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.imr.2018.01.005
Mahdavi, Namazi, Alizadeh, Farajnia, Nigella sativa oil with a calorie-restricted diet can improve biomarkers of systemic inflammation in obese women: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, J. Clin. Lipidol, doi:10.1016/j.jacl.2015.11.019
Maideen, Prophetic Medicine-Nigella Sativa (Black cumin seeds)-Potential herb for COVID-19?, J. Pharmacopunct, doi:10.3831/KPI.2020.23.010
Onifade, Jewel, Okesina, Virologic and Immunologic Outcome of Treatment of HIV Infection with a Herbal Concoction, A-ZAM, Among Clients Seeking Herbal Remedy in Nigeria, Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med
Onifade, Jewell, Adedeji, Nigella Sativa Concoction Induced Sustained Seroreversion in HIV Patient, Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med, doi:10.4314/ajtcam.v10i5.18
Onifade, Jewell, Ajadi, Rahamon, Ogunrin, Effectiveness of a herbal remedy in six HIV patients in Nigeria, J. Herb. Med, doi:10.1016/j.hermed.2013.04.006
Oyero, Toyama, Mitsuhiro, Onifade, Hidaka et al., Selective inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication by alpha-zam, a Nigella sativa seed formulation, Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med
Quast, Tarlinton, B cell memory: Understanding COVID-19, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.01.014
Rosner, Fundamentals of Biostatistics; Brooks/Cole
Sajid, Saqib, Shah, Khan, Munir et al., Protective and antiviral activities of Nigella sativa against avian influenza (H9N2) in turkeys, J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jssas.2016.09.004
Salem, Hossain, Protective effect of black seed oil from Nigella sativa against murine cytomegalovirus infection, Int. J. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/S0192-0561(00)00036-9
Salem, Immunomodulatory and therapeutic properties of the Nigella sativa L. seed, Int. Immunopharmacol
Salem, Yar, Bamosa, Al-Quorain, Yasawy et al., Comparative study of Nigella Sativa and triple therapy in eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia, Saudi J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.4103/1319-3767.65201
Shad, Soubra, Cordato, The role of thymoquinone, a major constituent of Nigella sativa, in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases, Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13553
Shoaei-Hagh, Kamelan Kafi, Najafi, Zamanzadeh, Heidari Bakavoli et al., A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial to evaluate the benefits of Nigella sativa seeds oil in reducing cardiovascular risks in hypertensive patients, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7140
Tavakkoli, Mahdian, Razavi, Hosseinzadeh, Review on Clinical Trials of Black Seed (Nigella sativa) and Its Active Constituent, Thymoquinone. J. Pharmacopunct, doi:10.3831/KPI.2017.20.021
Terpos, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Elalamy, Kastritis, Sergentanis et al., Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19, Am. J. Hematol, doi:10.1002/ajh.25829
Ulasli, Gurses, Bayraktar, Yumrutas, Oztuzcu et al., The effects of Nigella sativa (Ns), Anthemis hyalina (Ah) and Citrus sinensis (Cs) extract on the replication of coronavirus and the expression of TRP genes family, Mol. Biol. Rep, doi:10.1007/s11033-014-3019-7
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wang, Yang, Zhong, Zhou, Tang et al., Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 generates T-cell memory in the absence of a detectable viral infection, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22036-z
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph191811798",
"ISSN": [
"1660-4601"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811798",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The current study investigated the impact of different doses of Nigella sativa seeds on the symptoms, the cluster of differentiation profile group, and inflammatory markers of mild COVID-19 cases. Methods: The study was a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Patients with mild and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection patients were randomly subdivided into seven subgroups: Group (GP) 1: received charcoal capsules as a control group, and GP 2: received three capsules of whole Nigella sativa seeds daily, two capsules in the morning and one in the evening; GP 3: received three capsules of whole Nigella sativa seeds every 12 h, GP 4: received five capsules in the morning and four capsules of whole Nigella sativa seeds in the evening, GP 5: received one capsule of Nigella sativa powder every 12 h; GP 6: received two capsules of Nigella sativa powder every 12 h; GP 7: received three capsules of Nigella sativa powder every 12 h; all treatment course was for ten days. Inflammatory parameters were assessed before and after interventions. Results: 262 subjects were included in the final analysis. No significant difference was detected regarding age, gender, and nationality. No significant differences were detected between the inflammatory marker in all groups. The WBCs showed a significant difference between before and after the intervention. While for procalcitonin, a significant difference was demonstrated in groups 1,4, and 6. Conclusions: The current randomized clinical trial did not reveal a significant effect of ten days of treatment with various doses of Nigella sativa on symptoms, differentiation profile, and inflammatory markers of patients with COVID-19. As a natural product, the effect of Nigella sativa on disease requires weeks to manifest itself.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijerph191811798"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4756-552X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bin Abdulrahman",
"given": "Khalid A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5941-4353",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bamosa",
"given": "Abdullah Omar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bukhari",
"given": "Abdullah I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siddiqui",
"given": "Intisar Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arafa",
"given": "Mostafa A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5669-5575",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mohsin",
"given": "Ashfaq A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Althageel",
"given": "Mamdouh Faleh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aljuaeed",
"given": "Majed Owed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldeailej",
"given": "Ibrahim Mohammed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alrajeh",
"given": "Abdulaziz Ibrahim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldosari",
"given": "Kamel Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawsawi",
"given": "Najat Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zawbaee",
"given": "Khalid Ibrahim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alsurayea",
"given": "Saad Mohammed",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health",
"container-title-short": "IJERPH",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-20T01:47:27Z",
"timestamp": 1663638447000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-20T02:43:40Z",
"timestamp": 1663641820000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"FT201758DBQB dated 23 /06/2020",
"4172 Dated 1/09/2020"
],
"name": "Al-Subaie Charitable Foundation partially funded this research project"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-20T05:36:43Z",
"timestamp": 1663652203993
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "18",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "18",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1663545600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/18/11798/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "11798",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hermed.2020.100404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3831/KPI.2020.23.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6895",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153277",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061784",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0192-0561(00)00036-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11033-014-3019-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jssas.2016.09.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21010/ajtcam.v13i6.20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v19.i16.2529",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4314/ajtcam.v10i5.18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of Nigella sativa oil extract on inflammatory cytokine response and oxidative stress status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Hadi",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "Avicenna J. Phytomed.",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacl.2015.11.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2005.06.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"author": "Rosner",
"key": "ref17",
"series-title": "Fundamentals of Biostatistics",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3831/KPI.2017.20.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1319-3767.65201",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 Coronavirus Disease Guidelines",
"author": "Ministry of Health",
"key": "ref20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13880209.2021.1931353",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1440-1681.13553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imr.2018.01.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102769",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.30.20217364",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of Nigella sativa seeds on the glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Bamosa",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6331",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of Nigella sativa L. (black cumin seed) on intractable pediatric seizures",
"author": "Akhondian",
"first-page": "CR555-9",
"journal-title": "Med. Sci. Monit.",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7140",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4314/ajtcam.v8i1.60511",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hermed.2013.04.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JMDH.S315718",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00277-020-04103-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25829",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22036-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2021.01.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/18/11798"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Health, Toxicology and Mutagenesis",
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Effect of Short Treatment with Nigella Sativa on Symptoms, the Cluster of Differentiation (CD) Profile, and Inflammatory Markers in Mild COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "19"
}