Meplazumab, a CD147 antibody, for severe COVID-19: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial
et al., Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-025-02208-9, NCT05679479, Apr 2025
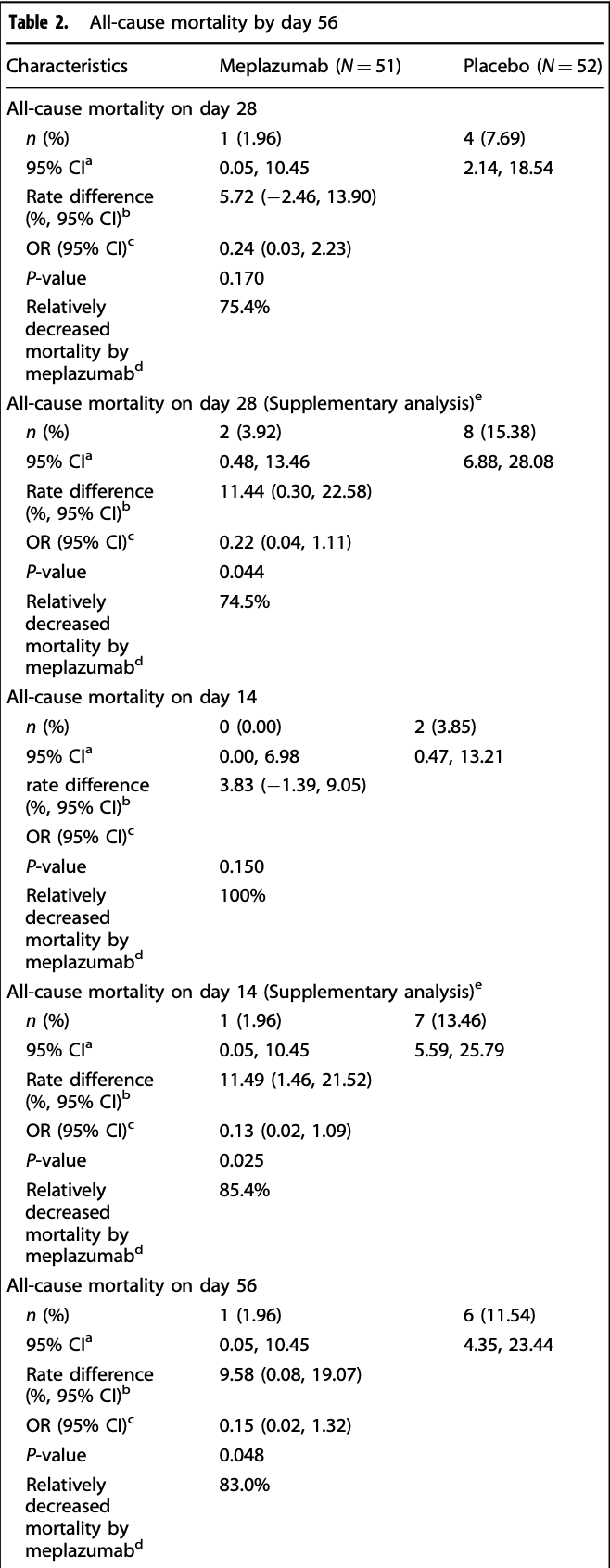
RCT 108 severe COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality (without statistical significance) with meplazumab, a CD147 antibody.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of death, 83.0% lower, RR 0.17, p = 0.11, treatment 1 of 51 (2.0%), control 6 of 52 (11.5%), NNT 10, day 56.
|
|
risk of death, 74.5% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.36, treatment 1 of 51 (2.0%), control 4 of 52 (7.7%), NNT 17, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bian et al., 14 Apr 2025, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, China, peer-reviewed, 52 authors, study period February 2023 - November 2023, trial NCT05679479 (history).
Contact: hjbian@fmmu.edu.cn, weidcq@fmmu.edu.cn, znchen@fmmu.edu.cn, zhuping@fmmu.edu.cn.
Meplazumab, a CD147 antibody, for severe COVID-19: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-025-02208-9
Meplazumab, a humanized CD147 antibody, showed favorable safety and clinical benefits in phase 1 and phase 2/3 seamless clinical studies. Further evaluation of its therapeutic efficacy in patients with severe COVID-19 is needed. In this phase 3 add-on study, we randomized patients with severe COVID-19 in a 1:1 ratio to receive 0.2 mg/kg meplazumab or placebo via intravenous injection, and evaluated efficacy and safety within 56 days. Between February 2023 and November 2023, 108 patients with severe COVID-19 were randomized to two groups, with their baseline characteristics generally balanced. The primary endpoint, 28-day allcause mortality was 1.96% in the meplazumab group vs 7.69% in the placebo group (P = 0.1703). Supplementary analysis using composite strategy indicated a significant reduction of 28-day all-cause mortality in meplazumab compared to placebo (3.92% vs 15.38%, P = 0.044). Meplazumab also significantly reduced the mortality in smoking subjects on day 28 (P = 0.047) compared to placebo in supplementary analysis. The secondary endpoint, 56-day all-cause mortality, was 1.96% in the meplazumab group and 11.54% in the placebo group (P = 0.048), which was 3.92% and 15.38%, respectively (P = 0.044) by supplementary analysis. Additional secondary endpoints showed potential benefits, including increased hospital discharge rates, improved clinical outcomes, and improved viral nucleotide conversion rate. Meplazumab demonstrated good safety and tolerability, with no grade ≥ 3 TEAEs observed. These promising results indicate that meplazumab reduces mortality and enhances clinical benefits in severe COVID-19 patients with a good safety profile, providing effective and specific therapeutics for severe COVID-19 (the trial was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05679479)).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Bian, Meplazumab in hospitalized adults with severe COVID-19 (DEFLECT): a multicenter, seamless phase 2/3, randomized, third-party doubleblind clinical trial, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Bian, Safety and efficacy of meplazumab in healthy volunteers and COVID-19 patients: a randomized phase 1 and an exploratory phase 2 trial, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Ceja-Gálvez, Severe COVID-19: drugs and clinical trials, J. Clin. Med
Chen, Correlation analysis between the viral load and the progression of COVID-19, Comput. Math. Methods Med
Cheong, Epigenetic memory of coronavirus infection in innate immune cells and their progenitors, Cell
Du, Hu, Menéndez-Arias, Zhan, Liu, Target-based drug design strategies to overcome resistance to antiviral agents: opportunities and challenges, Drug Resist. Updat. Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother
Fajnzylber, SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality, Nat. Commun
Geng, CD147 antibody specifically and effectively inhibits infection and cytokine storm of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants delta, alpha, beta, and gamma, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Geng, Immunological and metabolic characteristics of the Omicron variants infection, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Geng, Risk factors for developing severe COVID-19 in China: an analysis of disease surveillance data, Infect. Dis. Poverty
Luong, Potential broad-spectrum antiviral agents: a key arsenal against newly emerging and reemerging respiratory RNA viruses, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Macedo, Gonçalves, Febra, COVID-19 fatality rates in hospitalized patients: systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann. Epidemiol
Maltezou, Association between upper respiratory tract viral load, comorbidities, disease severity, and outcome of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, J. Infect. Dis
Marconi, Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir. Med
Mavrikaki, Lee, Solomon, Slack, Severe COVID-19 is associated with molecular signatures of aging in the human brain, Nat. Aging
Msemburi, The WHO estimates of excess mortality associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, Nature
Pantaleo, Correia, Fenwick, Joo, Perez, Antibodies to combat viral infections: development strategies and progress, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov
Pietzner, Complex patterns of multimorbidity associated with severe COVID-19 and long COVID, Commun. Med
Richardson, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA
Seyedalinaghi, Effects of smoking on COVID-19 management and mortality: an umbrella review, J. Smok. Cessat
Shenoy, Hettinger, Fernandez, Blumenthal, Baez, Early mortality benefit with COVID-19 convalescent plasma: a matched control study, Br. J. Haematol
Viermyr, High viral loads combined with inflammatory markers predict disease severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: results from the NOR-Solidarity trial, J. Intern. Med
Wang, CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Wu, CD147 contributes to SARS-CoV-2-induced pulmonary fibrosis, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Zeraatkar, Use of tocilizumab and sarilumab alone or in combination with corticosteroids for covid-19: systematic review and network meta-analysis, BMJ Med
Zheng, Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study, BMJ
Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus enters the host cells through spike protein-CD147 in an Arf6-dependent manner, Emerg. Microbes Infect
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-025-02208-9",
"ISSN": [
"2059-3635"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41392-025-02208-9",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Meplazumab, a humanized CD147 antibody, showed favorable safety and clinical benefits in phase 1 and phase 2/3 seamless clinical studies. Further evaluation of its therapeutic efficacy in patients with severe COVID-19 is needed. In this phase 3 add-on study, we randomized patients with severe COVID-19 in a 1:1 ratio to receive 0.2 mg/kg meplazumab or placebo via intravenous injection, and evaluated efficacy and safety within 56 days. Between February 2023 and November 2023, 108 patients with severe COVID-19 were randomized to two groups, with their baseline characteristics generally balanced. The primary endpoint, 28-day all-cause mortality was 1.96% in the meplazumab group vs 7.69% in the placebo group (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.1703). Supplementary analysis using composite strategy indicated a significant reduction of 28-day all-cause mortality in meplazumab compared to placebo (3.92% vs 15.38%, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.044). Meplazumab also significantly reduced the mortality in smoking subjects on day 28 (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.047) compared to placebo in supplementary analysis. The secondary endpoint, 56-day all-cause mortality, was 1.96% in the meplazumab group and 11.54% in the placebo group (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.048), which was 3.92% and 15.38%, respectively (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.044) by supplementary analysis. Additional secondary endpoints showed potential benefits, including increased hospital discharge rates, improved clinical outcomes, and improved viral nucleotide conversion rate. Meplazumab demonstrated good safety and tolerability, with no grade ≥ 3 TEAEs observed. These promising results indicate that meplazumab reduces mortality and enhances clinical benefits in severe COVID-19 patients with a good safety profile, providing effective and specific therapeutics for severe COVID-19 (the trial was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05679479)).</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"2208"
],
"article-number": "119",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "1 November 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "17 February 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "13 March 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "14 April 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "X.-C.C., H.T., H.-W.S., S.-S.L., Y.Y., and T.-Y.Y. are employees of Jiangsu Pacific Meinuoke Biopharmaceutical Co. Ltd. All other authors declare no competing interests or financial relationships relevant to the submitted work. No form of payment was given to anyone to produce the manuscript."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4690-4622",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bian",
"given": "Huijie",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Zheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wen",
"given": "Ai-Dong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Zhao-Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Li-Qiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yao",
"given": "Meng-Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6335-3346",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Ying-Xia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Xi-Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dong",
"given": "Hong-Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lian",
"given": "Jian-Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gu",
"given": "Xing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jing-Wen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Qing-Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Kui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jia",
"given": "Jun-Feng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Rong-Hua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Xing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Xiang-Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jia",
"given": "Yan-Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hou",
"given": "Jun-Na",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Qiu-Yue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Xiao-Xia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Liu-Qing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Yuan-Long",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Xiao-Xia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Qin-Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Wen-Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Rui-Xuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Xiu-Xuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Bin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Xu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Jian-Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Jiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Xiang-Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Hai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Xiao-Chun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Hong-Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Shuang-Shuang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Tian-Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Ding",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Zhi-Nan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Sig Transduct Target Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-13T23:01:52Z",
"timestamp": 1744585312000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-13T23:02:02Z",
"timestamp": 1744585322000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"92169211"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-16T12:01:56Z",
"timestamp": 1752667316387,
"version": "3.40.4"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1744588800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1744588800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-025-02208-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-025-02208-9",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-025-02208-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2208_CR1",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 epidemiological update—17 January 2025. WHO. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update-edition-175 (2025)."
},
{
"key": "2208_CR2",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 deaths|WHO COVID-19 dashboard. datadot. http://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases (2025)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annepidem.2021.02.012",
"author": "A Macedo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Ann. Epidemiol.",
"key": "2208_CR3",
"unstructured": "Macedo, A., Gonçalves, N. & Febra, C. COVID-19 fatality rates in hospitalized patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Epidemiol. 57, 14–21 (2021).",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"author": "S Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2208_CR4",
"unstructured": "Richardson, S. et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA 323, 2052–2059 (2020).",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05522-2",
"author": "W Msemburi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2208_CR5",
"unstructured": "Msemburi, W. et al. The WHO estimates of excess mortality associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. Nature 613, 130–137 (2023).",
"volume": "613",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43856-024-00506-x",
"author": "M Pietzner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Commun. Med.",
"key": "2208_CR6",
"unstructured": "Pietzner, M. et al. Complex patterns of multimorbidity associated with severe COVID-19 and long COVID. Commun. Med. 4, 1–11 (2024).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"author": "M-J Geng",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Poverty",
"key": "2208_CR7",
"unstructured": "Geng, M.-J. et al. Risk factors for developing severe COVID-19 in China: an analysis of disease surveillance data. Infect. Dis. Poverty 10, 48 (2021).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.019",
"author": "J-G Cheong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3882",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2208_CR8",
"unstructured": "Cheong, J.-G. et al. Epigenetic memory of coronavirus infection in innate immune cells and their progenitors. Cell 186, 3882–3902.e24 (2023).",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43587-022-00321-w",
"author": "M Mavrikaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1130",
"journal-title": "Nat. Aging",
"key": "2208_CR9",
"unstructured": "Mavrikaki, M., Lee, J. D., Solomon, I. H. & Slack, F. J. Severe COVID-19 is associated with molecular signatures of aging in the human brain. Nat. Aging 2, 1130–1137 (2022).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2208_CR10",
"unstructured": "Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline [Internet]. PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35917393/ (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "2208_CR11",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group. et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 693–704 (2021).",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjmed-2021-000036",
"author": "D Zeraatkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e000036",
"journal-title": "BMJ Med.",
"key": "2208_CR12",
"unstructured": "Zeraatkar, D. et al. Use of tocilizumab and sarilumab alone or in combination with corticosteroids for covid-19: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Med. 1, e000036 (2022).",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3",
"author": "VC Marconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1407",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "2208_CR13",
"unstructured": "Marconi, V. C. et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 9, 1407–1418 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1443",
"author": "S Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1443",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2208_CR14",
"unstructured": "Zheng, S. et al. Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study. BMJ 369, m1443 (2020).",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa804",
"author": "HC Maltezou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1132",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "2208_CR15",
"unstructured": "Maltezou, H. C. et al. Association between upper respiratory tract viral load, comorbidities, disease severity, and outcome of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 223, 1132–1138 (2021).",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13820",
"author": "H-K Viermyr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "249",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "2208_CR16",
"unstructured": "Viermyr, H.-K. et al. High viral loads combined with inflammatory markers predict disease severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: results from the NOR-Solidarity trial. J. Intern. Med. 296, 249–259 (2024).",
"volume": "296",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-022-00495-3",
"author": "G Pantaleo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "2208_CR17",
"unstructured": "Pantaleo, G., Correia, B., Fenwick, C., Joo, V. S. & Perez, L. Antibodies to combat viral infections: development strategies and progress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 21, 676–696 (2022).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2208_CR18",
"unstructured": "SARS-CoV-2 spike S2-specific neutralizing antibodies. PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37254830/"
},
{
"author": "S Du",
"first-page": "101053",
"journal-title": "Drug Resist. Updat. Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother.",
"key": "2208_CR19",
"unstructured": "Du, S., Hu, X., Menéndez-Arias, L., Zhan, P. & Liu, X. Target-based drug design strategies to overcome resistance to antiviral agents: opportunities and challenges. Drug Resist. Updat. Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 73, 101053 (2024).",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x",
"author": "K Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "2208_CR20",
"unstructured": "Wang, K. et al. CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 5, 283 (2020).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2059403",
"author": "Y-Q Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1135",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "2208_CR21",
"unstructured": "Zhou, Y.-Q. et al. SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus enters the host cells through spike protein-CD147 in an Arf6-dependent manner. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 11, 1135–1144 (2022).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00760-8",
"author": "J Geng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "347",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "2208_CR22",
"unstructured": "Geng, J. et al. CD147 antibody specifically and effectively inhibits infection and cytokine storm of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants delta, alpha, beta, and gamma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6, 347 (2021).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-01265-8",
"author": "J Geng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "2208_CR23",
"unstructured": "Geng, J. et al. Immunological and metabolic characteristics of the Omicron variants infection. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8, 42 (2023).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-01230-5",
"author": "J Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "2208_CR24",
"unstructured": "Wu, J. et al. CD147 contributes to SARS-CoV-2-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 382 (2022).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00603-6",
"author": "H Bian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "2208_CR25",
"unstructured": "Bian, H. et al. Safety and efficacy of meplazumab in healthy volunteers and COVID-19 patients: a randomized phase 1 and an exploratory phase 2 trial. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6, 194 (2021).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-023-01323-9",
"author": "H Bian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "2208_CR26",
"unstructured": "Bian, H. et al. Meplazumab in hospitalized adults with severe COVID-19 (DEFLECT): a multicenter, seamless phase 2/3, randomized, third-party double-blind clinical trial. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8, 46 (2023).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19057-5",
"author": "J Fajnzylber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "2208_CR27",
"unstructured": "Fajnzylber, J. et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality. Nat. Commun. 11, 5493 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "W Chen",
"first-page": "9926249",
"journal-title": "Comput. Math. Methods Med.",
"key": "2208_CR28",
"unstructured": "Chen, W. et al. Correlation analysis between the viral load and the progression of COVID-19. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 9926249 (2021).",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2023/7656135",
"author": "S SeyedAlinaghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7656135",
"journal-title": "J. Smok. Cessat.",
"key": "2208_CR29",
"unstructured": "SeyedAlinaghi, S. et al. Effects of smoking on COVID-19 management and mortality: an umbrella review. J. Smok. Cessat. 2023, 7656135 (2023).",
"volume": "2023",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "2208_CR30",
"unstructured": "ICH E9 statistical principles for clinical trials—scientific guideline. European Medicines Agency (EMA) https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-e9-statistical-principles-clinical-trials-scientific-guideline (1998)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm12082893",
"author": "HR Ceja-Gálvez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2893",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Med.",
"key": "2208_CR31",
"unstructured": "Ceja-Gálvez, H. R. et al. Severe COVID-19: drugs and clinical trials. J. Clin. Med. 12, 2893 (2023).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjh.17272",
"author": "AG Shenoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Haematol.",
"key": "2208_CR32",
"unstructured": "Shenoy, A. G., Hettinger, A. Z., Fernandez, S. J., Blumenthal, J. & Baez, V. Early mortality benefit with COVID-19 convalescent plasma: a matched control study. Br. J. Haematol. 192, 706–713 (2021).",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms26041481",
"author": "QXT Luong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1481",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "2208_CR33",
"unstructured": "Luong, Q. X. T. et al. Potential broad-spectrum antiviral agents: a key arsenal against newly emerging and reemerging respiratory RNA viruses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 1481 (2025).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hcs2.36",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2208_CR34",
"unstructured": "Released by National Health Commission of People's Republic of China & National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine on January 5, 2023 Diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 patients (tentative 10th version). Health Care Sci. 2, 10–24 (2023)."
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-025-02208-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Meplazumab, a CD147 antibody, for severe COVID-19: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "10"
}