Electrolytes, Zinc and Vitamin D3 in COVID-19 Patients with Cardiovascular Complications
et al., Problems of Virology, doi:10.36233/0507-4088-236, Jul 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
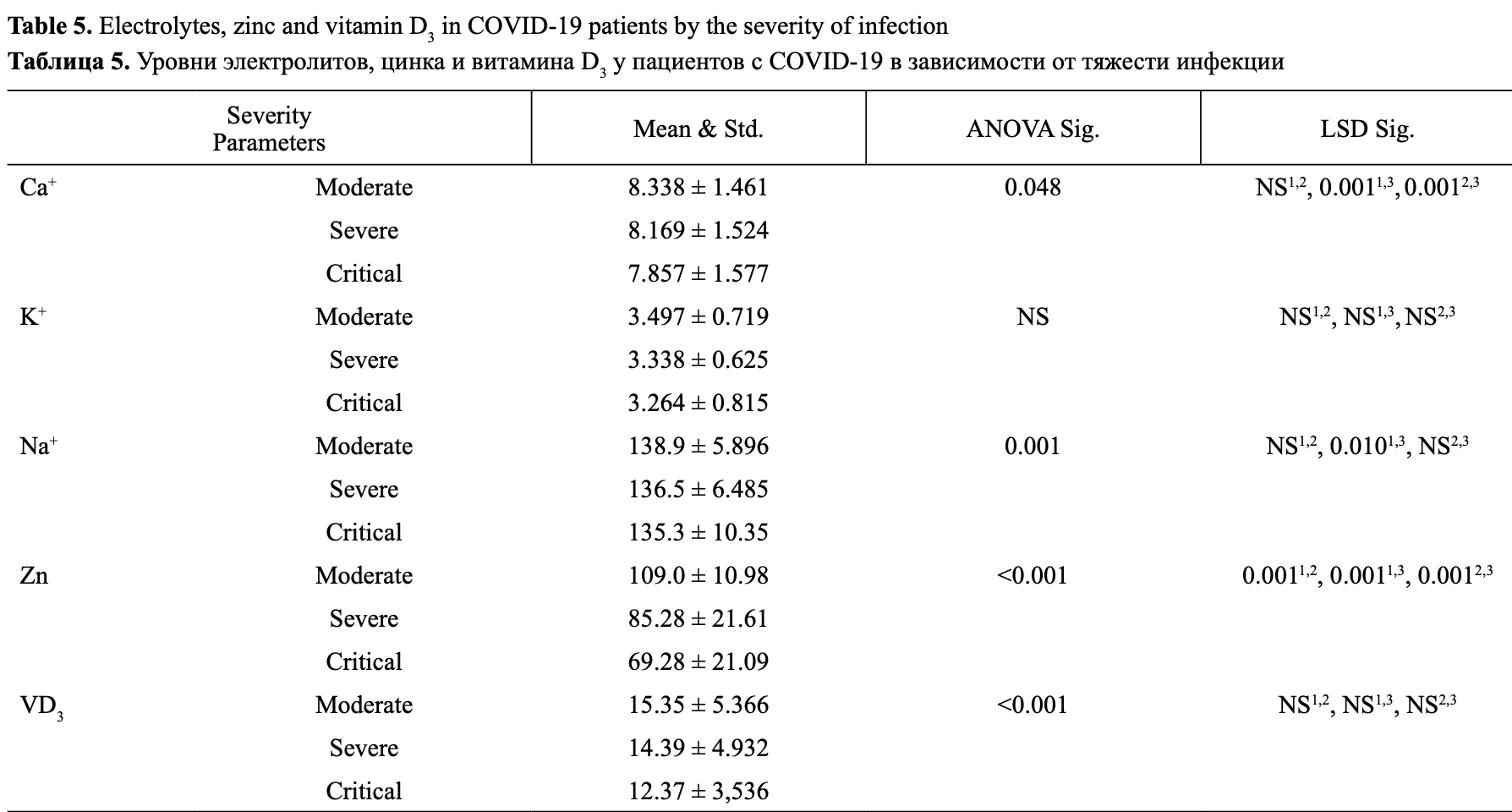
Retrospective 142 COVID-19 patients and 50 controls showing significantly lower levels of zinc, vitamin D, calcium, potassium, and sodium in COVID-19 patients compared to controls. Lower levels of zinc, vitamin D, calcium, and sodium were associated with disease severity.
Study covers vitamin D and zinc.
AlKhuzaie et al., 5 Jul 2024, retrospective, Iraq, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Electrolytes, Zinc and Vitamin D3 in COVID-19 Patients with Cardiovascular Complications
Problems of Virology, doi:10.36233/0507-4088-236
Introduction. COVID-19 is strongly linked to cardiovascular disease, with direct myocardial injury and systemic inflammation as common mechanisms. Pre-existing or infection-induced cardiovascular disease worsens the outcomes for COVID-19 patients. Materials and methods. To estimate the serum electrolytes (Na + , K + , Ca ++ , Zn) and vitamin D 3 , the study depended on ichroma ii device for Vitamin D 3 and Chemistry Analyzer for electrolytes in patient samples. Results. A study was conducted on 192 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19, including 35 critical cases, 53 severe cases, 54 moderate cases, and 50 individuals in a control group. The age group with the highest prevalence of infection was between 50-69 years, while the lowest prevalence was observed in those under 30 years. The study found significant decreases in calcium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and vitamin D 3 levels among COVID-19 patients compared to the control group. Zinc and vitamin D 3 levels showed a significant correlation with sex, with males experiencing a decline in zinc levels and females having lower vitamin D 3 levels. The concentration of calcium, sodium, and zinc showed a negative correlation with age, with older patients having the lowest levels. COVID-19 patients with chronic cardiac issues and high blood pressure exhibited the lowest levels of these markers. The severity of the disease also had a detrimental impact on electrolyte levels, zinc, and vitamin D 3 , with critical cases showing the lowest levels. The complications such as heart failure were associated with lower levels of potassium, sodium, and zinc.
Conclusion. In conclusion, the study revealed significant associations between COVID-19 and decreased electrolyte levels, zinc, and vitamin D 3 . Sex and age were found to be correlated with these markers. Patients with chronic cardiac issues and high blood pressure exhibited the lowest levels of these markers. The severity of the disease was also linked to lower electrolyte levels, zinc, and vitamin D 3 . Complications such as heart failure were associated with decreased levels of potassium, sodium, and zinc.
References
Abassi, Khoury, Karram, Aronson, Edema formation in congestive heart failure and the underlying mechanisms, Front. Cardiovasc. Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.933215
Achua, Chu, Ibrahim, Khodamoradi, Delma et al., Histopathology, and ultrastructural findings of fatal COVID-19 infections on testis, World J. Mens Health, doi:10.5534/wjmh.200170
Adrogué, Tucker, Madias, Diagnosis and management of hyponatremia: a review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.11176
Ahvanooei, Norouzian, Vahmani, Beneficial effects of vitamins, minerals, and bioactive peptides on strengthening the immune system against COVID-19 and the role of cow's milk in the supply of these nutrients, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-03045-x
Akshay, Veena, Teja, Tomar, Emerging Human Viral Diseases, Volume I: Respiratory and Haemorrhagic Fever, Springer Nature Singapore, doi:10.1007/978-981-99-2820-0_5
Al-Hijaj, Al-Rubaye, Al-Hashim, Mohammed, Habib, A study on 696 COVID-19 cases in Basrah-Southern Iraq: severity and outcome indicators, Iraqi Natl J. Med, doi:10.37319/iqnjm.2.csi.3
Alhawiti, Alhawiti, Alshalan, Alotaibi, Khobrani, Clinical outcomes of anticoagulant therapy in COVID-19 patients with pre-existing cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review, Infect. Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S410374
Ali, Overview of the vital roles of macro minerals in the human body, J. Trace Elem. Min, doi:10.1016/j.jtemin.2023.100076
Alluri, Nair, Ghosh, Differential expression of zinc transporters in functionally contrasting tissues involved in zinc homeostasis, Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, doi:10.1080/15257770.2019.1670838
Alsaidan, Al-Kuraishy, Al-Gareeb, Alexiou, Papadakis et al., The potential role of SARS-CoV-2 infection in acute coronary syndrome and type 2 myocardial infarction (T2MI): Intertwining spread, Immun. Inflamm. Dis, doi:10.1002/iid3.798
Bhattarai, Shrestha, Rokka, Shakya, Vitamin D, calcium, parathyroid hormone, and sex steroids in bone health and effects of aging, J. Osteoporos, doi:10.1155/2020/9324505
Bilehjani, Fakhari, Farzin, Tajlil, Nader, Diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular manifestations of COVID-19: A narrative review, Acta Cardiol, doi:10.1080/00015385.2023.2246200
Borborema, Lucena, Silva, Vitamin D and estrogen steroid hormones and their immunogenetic roles in Infectious respiratory (TB and COVID-19) diseases, Genet. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1590/1415-4757-GMB-2022-0158
Cao, Gaffney, Marcus, Hypokalemia-induced rhabdomyolysis in a child with autism affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr, doi:10.1097/DBP.0000000000001035
Castro, Sharma, Hypokalemia, None, StatPearls
Chatterjee, Nalla, Sharma, Sharma, Singh et al., Association of COVID-19 with comorbidities: an update, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci, doi:10.1021/acsptsci.2c00181
Davies, Klepac, Liu, Prem, Jit et al., Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9
Dominguez, Farruggia, Veronese, Barbagallo, Vitamin D sources, metabolism, and deficiency: available compounds and guidelines for its treatment, Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo11040255
Elham, Azam, Azam, Mostafa, Nasrin et al., Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19, Clin. Nutr. ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040
Gonzalez, Salinas-Parra, Cifuentes-Araneda, Reyes-Martinez, Vasopressin actions in the kidney renin angiotensin system and its role in hypertension and renal disease, Vitam. Horm, doi:10.1016/bs.vh.2019.09.003
Gruber, Beuschlein, Hypokalemia and the prevalence of primary aldosteronism, Horm. Metab. Res, doi:10.1055/a-1134-4980
Grubišić, Švitek, Ormanac, Sabo, Mihaljević et al., Molecular mechanisms responsible for diabetogenic effects of COVID-19 infection -induction of autoimmune dysregulation and metabolic disturbances, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms241411576
Hadi, Enayah, Effects of COVID-19 infection on some pancreatic functions in diabetic patients at Thi-Qar province/ Iraq, Univ. Thi-Qar J. Sci, doi:10.32792/utq/utjsci/v9i2.906
Jahangirimehr, Shahvali, Rezaeijo, Khalighi, Honarmandpour et al., Machine learning approach for automated predicting of COVID-19 severity based on clinical and paraclinical characteristics: Serum levels of zinc, calcium, and vitamin D, Clin. Nutr. ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.07.011
Joachimiak, Zinc against COVID-19? Symptom surveillance and deficiency risk groups, PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis, doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0008895
Kistamás, Veress, Horváth, Bányász, Nánási et al., Calcium handling defects and cardiac arrhythmia syndromes, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00072
Kumari, Garg, Bhawrani, Zinc homeostasis in immunity and its association with preterm births, Scand. J. Immunol, doi:10.1111/sji.13142
Latic, Erben, Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease, with emphasis on hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart failure, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21186483
Maares, Hackler, Haupt, Heller, Bachmann et al., Free zinc as a predictive marker for COVID-19 mortality risk, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14071407
Marreiro, Cruz, Oliveira, Morais, Bjesa et al., Antiviral and immunological activity of zinc and possible role in COVID-19, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114521002099
Mcguone, Farrand, Prizeman, O'brien, COVID-19 outcomes in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease and risk factors: perspectives from a hospital in Ireland, Br. J. Card. Nurs, doi:10.12968/bjca.2023.0097
Mohd, Sharma, Mishra, Ashraf, Vitamin D and its relationship with the pathways related to thrombosis and various diseases, doi:10.5772/intechopen.97299
Montezano, Camargo, Mary, Neves, Rios et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces endothelial inflammation via ACE2 independently of viral replication, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-41115-3
Mueller, Mcnamara, Sinclair, Why does COVID-19 disproportionately affect older people?, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103344
Mukherjee, Pahan, Is COVID-19 gender-sensitive?, J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s11481-020-09974-z
Musa, The Prevalence and the significance of the pulmonary bacterial super-infections among hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A scoping Review, Univ. Thi-Qar J. Sci, doi:10.32792/utq/utjsci/v10i1.930
Mushtaq, Nasir, Mahmood, Khan, Kanji et al., Older age, lack of vaccination and infection with variants other than Omicron associated with severity of COVID-19 and in-hospital mortality in Pakistan, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.30.23285170
Pallath, Ahirwar, Tripathi, Asia, Sakarde et al., COVID-19 and nutritional deficiency: a review of existing knowledge, Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1515/hmbci-2020-0074
Pannucci, Jefferson, Hampshire, Cooper, Hill et al., COVID-19-Induced myocarditis: Pathophysiological roles of ACE2 and toll-like receptors, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24065374
Pecora, Persico, Argentiero, Neglia, Esposito, The role of micronutrients in support of the immune response against viral infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12103198
Pradhan, Olsson, Sex differences in severity and mortality from COVID-19: are males more vulnerable?, Biol. Sex Differ, doi:10.1186/s13293-020-00330-7
Selvavinayagam, Yong, Joseph, Hemashree, Tan et al., Low SARS-CoV-2 viral load among vaccinated individuals infected with Delta B. 1.617. 2 and Omicron BA. 1.1. 529 but not with Omicron BA. 1.1 and BA. 2 variants, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.1018399
Severino, D'amato, Prosperi, Myftari, Francia et al., The mutual relationship among cardiovascular diseases and COVID-19: focus on micronutrients imbalance, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14163439
Su, Kuo, Wang, Chang, Gender-based differences in COVID-19, New Microbes New Infect, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100905
Tanita, Namiuchi, Onodera, Sunamura, Ogata et al., Serum zinc concentration in patients with myocardial infarction: a retrospective study, BMC Cardiovasc. Disord, doi:10.1186/s12872-024-03776-4
Teymouri, Mesbah, Navabian, Shekouh, Najafabadi et al., ECG frequency changes in potassium disorders: a narrative review, Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis
Tran, Garcia, Aniqa, Ali, Ally et al., Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and the cardiovascular system: in physiology and in disease states, Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res
Tyagi, Rai, Gautam, Kaur, Kapoor et al., Neurological manifestations of SARS-CoV-2: Complexity, mechanism and associated disorders, Eur. J. Med. Res, doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01293-2
Wang, Kang, Oxidative stress and antioxidant treatments in cardiovascular diseases, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9121292
Wessels, Rolles, Slusarenko, Rink, Zinc deficiency as a possible risk factor for increased susceptibility and severe progression of Corona Virus Disease 19, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114521000738
White, Men and COVID-19: the aftermath, Postgrad. Med, doi:10.1080/00325481.2020.1823760ВОПРОСЫВИРУСОЛОГИИ
Workeneh, Meena, Christ-Crain, Rondon-Berrios, Hyponatremia demystified: integrating physiology to shape clinical practice, Adv. Kidney Dis. Health, doi:10.1053/j.akdh.2022.11.004
Wu, Wu, The role of zinc in DNA and RNA polymerases, Metal Ions in Biological Systems
Zoccali, Mallamaci, Adamczak, De Oliveira, Massy et al., Cardiovascular complications in chronic kidney disease: a review from the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine Working Group of the European Renal Association, Cardiovasc. Res, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvad083
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.36233/0507-4088-236",
"ISSN": [
"2411-2097",
"0507-4088"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.36233/0507-4088-236",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Introduction. COVID-19 is strongly linked to cardiovascular disease, with direct myocardial injury and systemic inflammation as common mechanisms. Pre-existing or infection-induced cardiovascular disease worsens the outcomes for COVID-19 patients.\r\nMaterials and methods. To estimate the serum electrolytes (Na+, K+, Ca++, Zn) and vitamin D3, the study depended on ichroma ii device for Vitamin D3 and Chemistry Analyzer for electrolytes in patient samples.\r\nResults. A study was conducted on 192 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19, including 35 critical cases, 53 severe cases, 54 moderate cases, and 50 individuals in a control group. The age group with the highest prevalence of infection was between 50‒69 years, while the lowest prevalence was observed in those under 30 years. The study found significant decreases in calcium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and vitamin D3 levels among COVID-19 patients compared to the control group. Zinc and vitamin D3 levels showed a significant correlation with sex, with males experiencing a decline in zinc levels and females having lower vitamin D3 levels. The concentration of calcium, sodium, and zinc showed a negative correlation with age, with older patients having the lowest levels. COVID-19 patients with chronic cardiac issues and high blood pressure exhibited the lowest levels of these markers. The severity of the disease also had a detrimental impact on electrolyte levels, zinc, and vitamin D3, with critical cases showing the lowest levels. The complications such as heart failure were associated with lower levels of potassium, sodium, and zinc.\r\nConclusion. In conclusion, the study revealed significant associations between COVID-19 and decreased electrolyte levels, zinc, and vitamin D3. Sex and age were found to be correlated with these markers. Patients with chronic cardiac issues and high blood pressure exhibited the lowest levels of these markers. The severity of the disease was also linked to lower electrolyte levels, zinc, and vitamin D3. Complications such as heart failure were associated with decreased levels of potassium, sodium, and zinc.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0009-4693-2579",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "AlKhuzaie",
"given": "Ali Abdel-Moneim Mohammed-Hussain",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8327-5434",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jabbar",
"given": "Enas Abdul Kareem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5129-7700",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Albadry",
"given": "Bushra Jabbar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Problems of Virology",
"container-title-short": "Problems of Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"virusjour.crie.ru"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-05T13:11:01Z",
"timestamp": 1720185061000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-05T13:11:15Z",
"timestamp": 1720185075000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-05T13:40:11Z",
"timestamp": 1720186811143
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1720137600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://virusjour.crie.ru/jour/article/viewFile/16641/895",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://virusjour.crie.ru/jour/article/viewFile/16641/895",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "22004",
"original-title": [],
"page": "266-276",
"prefix": "10.36233",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Central Research Institute for Epidemiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-41115-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-981-99-2820-0_5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms241411576",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32792/utq/utjsci/v9i2.906",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-023-01293-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S410374",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00015385.2023.2246200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24065374",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsptsci.2c00181",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.798",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32792/utq/utjsci/v10i1.930",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12968/bjca.2023.0097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100905",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.37319/iqnjm.2.csi.3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11481-020-09974-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13293-020-00330-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5534/wjmh.200170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00325481.2020.1823760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.01.30.23285170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103344",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.1018399",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12103198",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemin.2023.100076",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Castro D., Sharma S. Hypokalemia. StatPearls. 2024; NBK482465."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/DBP.0000000000001035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1134-4980",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.11176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.akdh.2022.11.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Wessels I., Rolles B., Slusarenko A.J., Rink L. Zinc deficiency as a possible risk factor for increased susceptibility and severe progression of Corona Virus Disease 19. Br. J. Nutr. 2022; 127(2): 214–32. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521000738"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0008895",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hmbci-2020-0074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14071407",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1415-4757-GMB-2022-0158",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/metabo11040255",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-021-03045-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/9324505",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14163439",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvad083",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.07.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.00072",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"key": "ref43",
"unstructured": "Teymouri N., Mesbah S., Navabian S.M., Shekouh D., Najafabadi M.M., Norouzkhani N., et al ECG frequency changes in potassium disorders: a narrative review. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022; 12(3): 112–24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2022.933215",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.vh.2019.09.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114521002099",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"key": "ref47",
"unstructured": "Wu F.Y., Wu C.W. The role of zinc in DNA and RNA polymerases. In: Metal Ions in Biological Systems: Volume 15: Zinc and its Role in Biology and Nutrition. CRC Press; 2023: 157–92."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/sji.13142",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9121292",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15257770.2019.1670838",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12872-024-03776-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21186483",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"key": "ref53",
"unstructured": "Tran N., Garcia T., Aniqa M., Ali S., Ally A., Nauli S.M. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and the cardiovascular system: in physiology and in disease states. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2022; 15(2): 153."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5772/intechopen.97299",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref54"
}
],
"reference-count": 54,
"references-count": 54,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://virusjour.crie.ru/jour/article/view/16641"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Electrolytes, Zinc and Vitamin D<sub>3</sub> in COVID-19 Patients with Cardiovascular Complications",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.36233/0372-9311-crossmark",
"volume": "69"
}
