COVID-19 Outcomes and Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11061416, May 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective multicenter study of 354 hospitalized type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19 in Greece showing increased risk with DPP4 inhibitor use as part of chronic diabetes treatment. There was no significant difference with metformin use in unadjusted results. Results do not account for differences in the risk of hospitalization.
Although the 37% lower mortality is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 36% lower mortality [32‑40%] from meta-analysis of the 74 mortality results to date.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
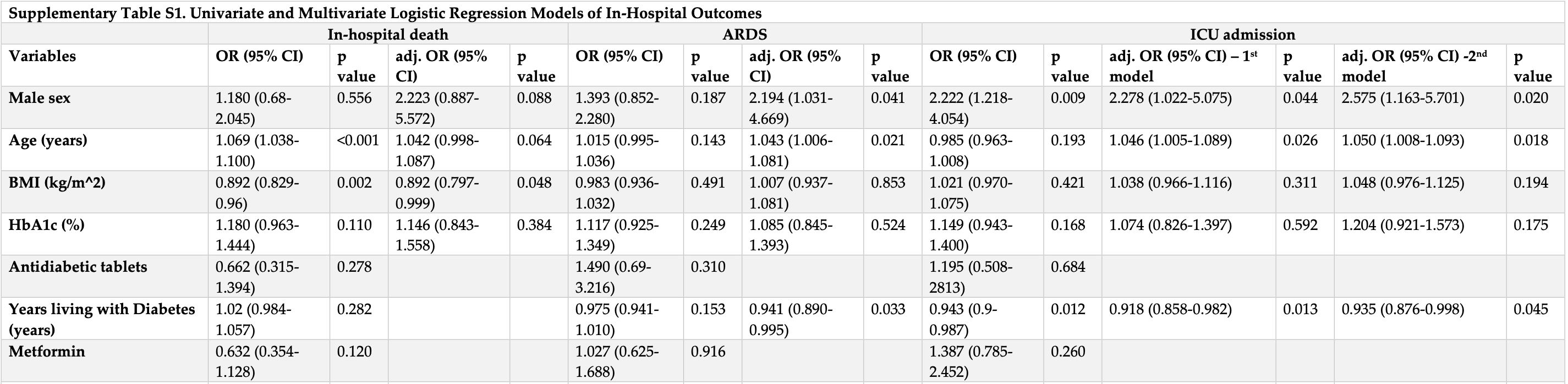
risk of death, 36.8% lower, OR 0.63, p = 0.12, treatment 147, control 207, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 38.7% higher, OR 1.39, p = 0.26, treatment 147, control 207, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ARDS, 2.7% higher, OR 1.03, p = 0.92, treatment 147, control 207, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Akinosoglou et al., 27 May 2023, prospective, Greece, peer-reviewed, median age 70.0, 23 authors, study period February 2021 - June 2021.
Contact: ntentolouris@yahoo.gr (corresponding author), akin@upatras.gr, georg.schinas@gmail.com, vasilina.dim@gmail.com, evabletsa@gmail.com, panouharis@gmail.com, leolanaras@gmail.com, chmichailidis@gmail.com, katsikastheodoros@gmail.com, fotiosbarkas@gmail.com, vaglimp@yahoo.com, vkotsis@auth.gr, kostento1@yahoo.com, peggigrigo@yahoo.gr, atetoka@yahoo.gr, dimitris.bassoulis@gmail.com, z_alexiou@yahoo.gr, mdaganou@hotmail.com, medp2011815@med.uoc.gr, akoutsou@med.uoa.gr, pefan1@otenet.gr, ioannisbaraboutis@yahoo.gr, eleni_agelonidou@yahoo.com.
COVID-19 Outcomes and Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study
Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11061416
The link between type 2 diabetes (T2D) and the severe outcomes of COVID-19 has raised concerns about the optimal management of patients with T2D. This study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics and outcomes of T2D patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and explore the potential associations between chronic T2D treatments and adverse outcomes. This was a multicenter prospective cohort study of T2D patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Greece during the third wave of the pandemic (February-June 2021). Among the 354 T2D patients included in this study, 63 (18.6%) died during hospitalization, and 16.4% required ICU admission. The use of DPP4 inhibitors for the chronic management of T2D was associated with an increased risk of in-hospital death (adjusted odds ratio (adj. OR) 2.639, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.148-6.068, p = 0.022), ICU admission (adj. OR = 2.524, 95% CI: 1.217-5.232, p = 0.013), and progression to ARDS (adj. OR = 2.507, 95% CI: 1.278-4.916, p = 0.007). Furthermore, the use of DPP4 inhibitors was significantly associated with an increased risk of thromboembolic events (adjusted OR of 2.249, 95% CI: 1.073-4.713, p = 0.032) during hospitalization. These findings highlight the importance of considering the potential impact of chronic T2D treatment regiments on COVID-19 and the need for further studies to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, N.T.; formal analysis, K.A. and G.S.; data curation, K.A., G.S., E.B., M.B., L.L., C.M., T.K., F.B., E.L., V.K., K.T., P.G., A.F., D.B., Z.A., M.D., C.B., V.D., A.K., A.P., I.G.B. and E.A.; writing-original draft preparation, K.A. and G.S., writing-review and editing, K.A. and N.T.; visualization, K.A. and G.S.; supervision, N.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
References
Abdi, Jalilian, Sarbarzeh, Vlaisavljevic, Diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review on the current evidences, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347
Agarwal, Schechter, Southern, Crandall, Tomer, Preadmission Diabetes-Specific Risk Factors for Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes and Coronavirus Disease 2019, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1543
Akinosoglou, Kapsokosta, Mouktaroudi, Rovina, Kaldis et al., Diabetes on sepsis outcomes in non-ICU patients: A cohort study and review of the literature, J. Diabetes Complicat, doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107765
Al Mahmeed, Al-Rasadi, Banerjee, Ceriello, Cosentino et al., Promoting a Syndemic Approach for Cardiometabolic Disease Management During COVID-19: The CAPISCO International Expert Panel, Front. Cardiovasc. Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.787761
Aubert, Henderson, Kerr, Holleman, Klamerus et al., Type 2 Diabetes Management, Control and Outcomes During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Older US Veterans: An Observational Study, J. Gen. Intern. Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-07301-7
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Weaver, Bradley et al., Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: A whole-population study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2
Berbudi, Rahmadika, Tjahjadi, Ruslami, Type 2 Diabetes and its Impact on the Immune System, Curr. Diabetes Rev, doi:10.2174/1573399815666191024085838
Bonora, Avogaro, Fadini, Disentangling conflicting evidence on DPP-4 inhibitors and outcomes of COVID-19: Narrative review and meta-analysis, J. Endocrinol. Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01515-6
Ceconi, Barbi, Tornese, Glycemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 lockdown: What comes after a "quarantine, J. Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13110
Chao, Tseng, Wu, Shih, Yi et al., Higher glycemic variability within the first day of ICU admission is associated with increased 30-day mortality in ICU patients with sepsis, Ann. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-0635-3
Codo, Davanzo, Monteiro, De Souza, Muraro et al., Elevated Glucose Levels Favor SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Monocyte Response through a HIF-1alpha/Glycolysis-Dependent Axis, Cell. Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.015
Corona, Pizzocaro, Vena, Rastrelli, Semeraro et al., Diabetes is most important cause for mortality in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-021-09630-8
Corrao, Pinelli, Vacca, Raspanti, Argano, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: A Narrative Review, Front. Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.609470
Dalan, Ang, Tan, Fong, Tay et al., The association of hypertension and diabetes pharmacotherapy with COVID-19 severity and immune signatures: An observational study, Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother, doi:10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa098
Dallavalasa, Tulimilli, Prakash, Ramachandra, Madhunapantula et al., COVID-19: Diabetes Perspective-Pathophysiology and Management, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12020184
Deng, Yang, Xu, Empagliflozin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus-related diabetic nephropathy via altering the gut microbiota, Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids, doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159234
Emami, Javanmardi, Pirbonyeh, Akbari, Prevalence of Underlying Diseases in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med
Etoom, Alwardat, Alwardat, Issues for conducting meta-analyses in COVID-19. Commentary on "Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104389
Faruqi, Balasubramanyam, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: A review of the incidence, pathophysiology and management of diabetes during the pandemic, Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1080/17446651.2023.2176300
French, Hulse, Nguyen, Sobotka, Webster et al., Impact of Hospital Strain on Excess Deaths During the COVID-19 Pandemic-United States, July 2020, MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7046a5
Gangopadhyay, Does having diabetes increase chances of contracting COVID-19 infection?, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.048
Gregory, Slaughter, Duffus, Smith, Lestourgeon et al., COVID-19 Severity Is Tripled in the Diabetes Community: A Prospective Analysis of the Pandemic's Impact in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-2260
Gupta, Ghosh, Singh, Misra, Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002
Gupta, Gupta, Katoch, Garg, Garg, A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diabetes Associated Mortality in Patients with COVID-19, Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.5812/ijem.113220
Halvatsiotis, Kotanidou, Tzannis, Jahaj, Magira et al., Demographic and clinical features of critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Greece: The burden of diabetes and obesity, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108331
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor and outcome from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in diabetic patients: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, J. Diabetes Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s40200-021-00777-4
Holman, Knighton, Kar, O'keefe, Curley et al., Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: A population-based cohort study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0
Holman, Wild, Gregg, Valabhji, Sattar et al., Comparison of mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes by age of diagnosis: An incident population-based study in England and Wales, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00293-X
Hsieh, Hu, How, Seak, Hsieh et al., Hospital outcomes and cumulative burden from complications in type 2 diabetic sepsis patients: A cohort study using administrative and hospital-based databases, Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1177/2042018819875406
Hu, Sun, Dai, Deng, Li et al., Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371
Huang, Lim, Pranata, Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia-A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Hussain, Bhowmik, Do Vale Moreira, COVID-19 and diabetes: Knowledge in progress, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108142
Iacobellis, COVID-19 and diabetes: Can DPP4 inhibition play a role?, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108125
Jafar, Edriss, Nugent, The Effect of Short-Term Hyperglycemia on the Innate Immune System, Am. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2015.11.011
Khunti, Del Prato, Mathieu, Kahn, Gabbay et al., COVID-19, Hyperglycemia, and New-Onset Diabetes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc21-1318
Khunti, Knighton, Zaccardi, Bakhai, Barron et al., Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide observational study in England, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00050-4
Krejner-Bienias, Grzela, Grzela, DPP4 Inhibitors and COVID-19-Holy Grail or Another Dead End?, Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp, doi:10.1007/s00005-020-00602-5
Li, Shen, Yang, Fairley, Chai et al., Global Diabetes Prevalence in COVID-19 Patients and Contribution to COVID-19-Related Severity and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc22-1943
Li, Yang, Zhao, Zhi, Wang et al., Prevalence and impact of cardiovascular metabolic diseases on COVID-19 in China, Clin. Res. Cardiol, doi:10.1007/s00392-020-01626-9
Lim, Bae, Kwon, Nauck, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: From pathophysiology to clinical management, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4
Lima-Martinez, Carrera Boada, Madera-Silva, Marin, Contreras, COVID-19 and diabetes: A bidirectional relationship, Clin. Investig. Arterioscler, doi:10.1016/j.artere.2021.04.004
Mahamat-Saleh, Fiolet, Rebeaud, Mulot, Guihur et al., Diabetes, hypertension, body mass index, smoking and COVID-19-related mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052777
Matias, Manique, Sabino, Rego, Mihon et al., Absolute Hyperglycemia versus Stress Hyperglycemia Ratio for the Prognosis of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in the First Months of the Pandemic: A Retrospective Study, Diabetes Ther, doi:10.1007/s13300-022-01347-4
Matsubara, Sugiyama, Akiyama, Iwashita, Kurokawa et al., Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, improves endothelial dysfunction in association with its anti-inflammatory effects in patients with coronary artery disease and uncontrolled diabetes, Circ. J, doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-12-1168
Montastruc, Romano, Montastruc, Silva, Seguin et al., Pharmacological characteristics of patients infected with SARS-Cov-2 admitted to Intensive Care Unit in South of France, Therapie, doi:10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.005
Nassar, Abosheaishaa, Singh, Misra, Bloomgarden, Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359
Nowotny, Jung, Hohn, Weber, Grune, Advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom5010194
Patel, Mccoy, Barnett, Shah, Mehrotra, Diabetes Care and Glycemic Control During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United States, JAMA Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3047
Pedrosa, Martins, Rizzo, Silva-Nunes, Metformin in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A hidden path-from altered inflammation to reduced mortality. A review from the literature, J. Diabetes Complicat, doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108391
Popovic, Papanas, Koufakis, Kotsa, Mahmeed et al., Glucometabolic Perturbations in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronavirus Disease 2019: Causes, Consequences, and How to Counter Them Using Novel Antidiabetic Drugs-The CAPISCO International Expert Panel, Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes
Rakhmat, Kusmala, Handayani, Juliastuti, Nawangsih et al., Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027
Reinhold, Brocke, DPP4-directed therapeutic strategies for MERS-CoV, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70696-0
Rhee, Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19, Diabetes Metab. J, doi:10.4093/dmj.2021.0118
Rizvi, Kathuria, Al Mahmeed, Al-Rasadi, Al-Alawi et al., Post-COVID syndrome, inflammation, and diabetes, J. Diabetes Complicat, doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108336
Roncon, Zuin, Rigatelli, Zuliani, Diabetic patients with COVID-19 infection are at higher risk of ICU admission and poor short-term outcome, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104354
Sardu, D'onofrio, Balestrieri, Barbieri, Rizzo et al., Outcomes in Patients With Hyperglycemia Affected by COVID-19: Can We Do More on Glycemic Control?, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0723
Satoh-Asahara, Sasaki, Wada, Tochiya, Iguchi et al., A dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in type 2 diabetic patients, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2012.09.004
Scheen, DPP-4 inhibition and COVID-19: From initial concerns to recent expectations, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.11.005
Sheetz, King, Molecular understanding of hyperglycemia's adverse effects for diabetic complications, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.288.20.2579
Shenoy, Ismaily, Bajaj, Diabetes and COVID-19: A global health challenge, BMJ Open. Diabetes Res. Care, doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001450
Shi, Zhang, Jiang, Zhang, Hu et al., Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors for Mortality of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes in Wuhan, China: A Two-Center, Retrospective Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0598
Singh, Khunti, COVID-19 and Diabetes, Annu. Rev. Med, doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042220-011857
Solerte, ; D'addio, Trevisan, Lovati, Rossi et al., Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1521
Stoian, Banerjee, Rizvi, Rizzo, Diabetes and the COVID-19 Pandemic: How Insights from Recent Experience Might Guide Future Management, Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord, doi:10.1089/met.2020.0037
Tilg, Moschen, Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance, Mol. Med, doi:10.2119/2007-00119.Tilg
Tomas, Lin, Dagher, Saha, Luo et al., Hyperglycemia and insulin resistance: Possible mechanisms, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04262.x
Tomovic, Lazarevic, Kocic, Deljanin-Ilic, Anderluh et al., Mechanisms and pathways of antiinflammatory activity of DPP-4 inhibitors in cardiovascular and renal protection, Med. Res. Rev, doi:10.1002/med.21513
Trzaskalski, Fadzeyeva, Mulvihill, Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 at the Interface Between Inflammation and Metabolism, Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes, doi:10.1177/1179551420912972
Unnikrishnan, Misra, Diabetes and COVID19: A bidirectional relationship, Nutr. Diabetes, doi:10.1038/s41387-021-00163-2
Van Niekerk, Christowitz, Conradie, Engelbrecht, Insulin as an immunomodulatory hormone, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.11.006
Vankadari, Wilce, Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: Glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565
Wang, Li, Lu, Huang, Does comorbidity increase the risk of patients with COVID-19: Evidence from meta-analysis, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103000
Wargny, Potier, Gourdy, Pichelin, Amadou et al., Predictors of hospital discharge and mortality in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: Updated results from the nationwide CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Wu, Tang, Cheng, Diabetes increases the mortality of patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis, Acta Diabetol, doi:10.1007/s00592-020-01546-0
Yang, Cai, Zhang, Hyperglycemia at admission is a strong predictor of mortality and severe/critical complications in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis, Biosci. Rep, doi:10.1042/BSR20203584
Yang, Yang, Zhang, Ling, Ge, Risks factors for death among COVID-19 patients combined with hypertension, coronary heart disease or diabetes, Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, doi:10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.004
Yang, Yu, Xu, Shu, Xia et al., Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
Yang, Zhong, Tian, Xie, Fu et al., The effect of diabetes on mortality of COVID-19: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000020913
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11061416",
"ISSN": [
"2076-2607"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061416",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The link between type 2 diabetes (T2D) and the severe outcomes of COVID-19 has raised concerns about the optimal management of patients with T2D. This study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics and outcomes of T2D patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and explore the potential associations between chronic T2D treatments and adverse outcomes. This was a multicenter prospective cohort study of T2D patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Greece during the third wave of the pandemic (February–June 2021). Among the 354 T2D patients included in this study, 63 (18.6%) died during hospitalization, and 16.4% required ICU admission. The use of DPP4 inhibitors for the chronic management of T2D was associated with an increased risk of in-hospital death (adjusted odds ratio (adj. OR) 2.639, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.148–6.068, p = 0.022), ICU admission (adj. OR = 2.524, 95% CI: 1.217–5.232, p = 0.013), and progression to ARDS (adj. OR = 2.507, 95% CI: 1.278–4.916, p = 0.007). Furthermore, the use of DPP4 inhibitors was significantly associated with an increased risk of thromboembolic events (adjusted OR of 2.249, 95% CI: 1.073–4.713, p = 0.032) during hospitalization. These findings highlight the importance of considering the potential impact of chronic T2D treatment regiments on COVID-19 and the need for further studies to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"microorganisms11061416"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4289-9494",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Patras, University Hospital of Patras, 265 04 Patras, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Akinosoglou",
"given": "Karolina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7963-1865",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Patras, University Hospital of Patras, 265 04 Patras, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schinas",
"given": "Georgios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3680-859X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Lamia, 351 00 Lamia, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bletsa",
"given": "Evanthia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Lamia, 351 00 Lamia, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Bristianou",
"given": "Magdaline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Lamia, 351 00 Lamia, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Lanaras",
"given": "Leonidas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1st Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Athens “G. Gennimatas”, 115 27 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Michailides",
"given": "Charalambos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1st Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Athens “G. Gennimatas”, 115 27 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Katsikas",
"given": "Theodoros",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5940-6895",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "2nd Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences, University of Ioannina, 451 10 Ioannina, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Barkas",
"given": "Fotios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7162-3323",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "2nd Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences, University of Ioannina, 451 10 Ioannina, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liberopoulos",
"given": "Evangelos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "3rd Department of Internal Medicine, Medical School, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, General Hospital of Thessaloniki “Papageorgiou”, 564 29 Thessaloniki, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Kotsis",
"given": "Vasileios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Athens “Elpis”, 115 22 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Tentolouris",
"given": "Konstantinos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Athens “Elpis”, 115 22 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Grigoropoulou",
"given": "Pinelopi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Athens “Elpis”, 115 22 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Frangou",
"given": "Archontoula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0686-872X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1st Department of Internal Medicine, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Laiko General Hospital, 11527 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Basoulis",
"given": "Dimitrios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "General Hospital of Eleusis “Thriasio”, 196 00 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Alexiou",
"given": "Zoi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0001-1726-5086",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care Unit, General Hospital for Thoracic Diseases “Sotiria”, 115 27 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Daganou",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care Unit, General Hospital for Thoracic Diseases “Sotiria”, 115 27 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Bostantzoglou",
"given": "Clementine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Patras, University Hospital of Patras, 265 04 Patras, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Dimakopoulou",
"given": "Vasiliki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1st University Pulmonology Clinic and ICU, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, General Hospital for Thoracic Diseases “Sotiria”, 115 27 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Koutsoukou",
"given": "Antonia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and 1st Department of Infectious Diseases, General Hospital for Thoracic Diseases “Sotiria”, 115 27 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Pefanis",
"given": "Angelos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, “Pammakaristos” Hospital, 111 44 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Baraboutis",
"given": "Ioannis G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, “Pammakaristos” Hospital, 111 44 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Agelonidou",
"given": "Eleni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1st Department of Internal Medicine, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Laiko General Hospital, 11527 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Tentolouris",
"given": "Nikolaos",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Microorganisms",
"container-title-short": "Microorganisms",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-27T20:10:53Z",
"timestamp": 1685218253000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-29T13:42:01Z",
"timestamp": 1685367721000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-30T04:25:52Z",
"timestamp": 1685420752263
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685145600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/6/1416/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1416",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000020913",
"article-title": "The effect of diabetes on mortality of COVID-19: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e20913",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-042220-011857",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Diabetes",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Med.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104354",
"article-title": "Diabetic patients with COVID-19 infection are at higher risk of ICU admission and poor short-term outcome",
"author": "Roncon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104354",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/ijem.113220",
"article-title": "A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diabetes Associated Mortality in Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e113220",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc22-1943",
"article-title": "Global Diabetes Prevalence in COVID-19 Patients and Contribution to COVID-19-Related Severity and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "890",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-020-01546-0",
"article-title": "Diabetes increases the mortality of patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002",
"article-title": "Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review on the current evidences",
"author": "Abdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108347",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/met.2020.0037",
"article-title": "Diabetes and the COVID-19 Pandemic: How Insights from Recent Experience Might Guide Future Management",
"author": "Stoian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens12020184",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Dallavalasa, S., Tulimilli, S.V., Prakash, J., Ramachandra, R., Madhunapantula, S.V., and Veeranna, R.P. (2023). COVID-19: Diabetes Perspective-Pathophysiology and Management. Pathogens, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17446651.2023.2176300",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: A review of the incidence, pathophysiology and management of diabetes during the pandemic",
"author": "Faruqi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.015",
"article-title": "Elevated Glucose Levels Favor SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Monocyte Response through a HIF-1alpha/Glycolysis-Dependent Axis",
"author": "Codo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Cell. Metab.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Type 2 Diabetes and its Impact on the Immune System",
"author": "Berbudi",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "Curr. Diabetes Rev.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.288.20.2579",
"article-title": "Molecular understanding of hyperglycemia’s adverse effects for diabetic complications",
"author": "Sheetz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2579",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2015.11.011",
"article-title": "The Effect of Short-Term Hyperglycemia on the Innate Immune System",
"author": "Jafar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "351",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20203584",
"article-title": "Hyperglycemia at admission is a strong predictor of mortality and severe/critical complications in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "BSR20203584",
"journal-title": "Biosci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13300-022-01347-4",
"article-title": "Absolute Hyperglycemia versus Stress Hyperglycemia Ratio for the Prognosis of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in the First Months of the Pandemic: A Retrospective Study",
"author": "Matias",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "335",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Ther.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-1318",
"article-title": "COVID-19, Hyperglycemia, and New-Onset Diabetes",
"author": "Khunti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2645",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2119/2007-00119.Tilg",
"article-title": "Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance",
"author": "Tilg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom5010194",
"article-title": "Advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Nowotny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04262.x",
"article-title": "Hyperglycemia and insulin resistance: Possible mechanisms",
"author": "Tomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "967",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108142",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: Knowledge in progress",
"author": "Hussain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108142",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Risks factors for death among COVID-19 patients combined with hypertension, coronary heart disease or diabetes",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "420",
"journal-title": "Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107765",
"article-title": "Diabetes on sepsis outcomes in non-ICU patients: A cohort study and review of the literature",
"author": "Akinosoglou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107765",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Complicat.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0723",
"article-title": "Outcomes in Patients With Hyperglycemia Affected by COVID-19: Can We Do More on Glycemic Control?",
"author": "Sardu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1408",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41387-021-00163-2",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID19: A bidirectional relationship",
"author": "Unnikrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.11.006",
"article-title": "Insulin as an immunomodulatory hormone",
"author": "Christowitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Empagliflozin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus-related diabetic nephropathy via altering the gut microbiota",
"author": "Deng",
"first-page": "159234",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "1867",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-2260",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Severity Is Tripled in the Diabetes Community: A Prospective Analysis of the Pandemic’s Impact in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Gregory",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "526",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052777",
"article-title": "Diabetes, hypertension, body mass index, smoking and COVID-19-related mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Fiolet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e052777",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001450",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19: A global health challenge",
"author": "Shenoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e001450",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open. Diabetes Res. Care",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"article-title": "Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2",
"article-title": "Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: A whole-population study",
"author": "Barron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.048",
"article-title": "Does having diabetes increase chances of contracting COVID-19 infection?",
"author": "Gangopadhyay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "765",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108331",
"article-title": "Demographic and clinical features of critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Greece: The burden of diabetes and obesity",
"author": "Halvatsiotis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108331",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-021-09630-8",
"article-title": "Diabetes is most important cause for mortality in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Corona",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "275",
"journal-title": "Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevalence of Underlying Diseases in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Emami",
"first-page": "e35",
"journal-title": "Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104389",
"article-title": "Issues for conducting meta-analyses in COVID-19. Commentary on “Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis”",
"author": "Etoom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104389",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371",
"article-title": "Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104371",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00392-020-01626-9",
"article-title": "Prevalence and impact of cardiovascular metabolic diseases on COVID-19 in China",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Clin. Res. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018",
"article-title": "Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia—A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "395",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103000",
"article-title": "Does comorbidity increase the risk of patients with COVID-19: Evidence from meta-analysis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6049",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: From pathophysiology to clinical management",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00293-X",
"article-title": "Comparison of mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes by age of diagnosis: An incident population-based study in England and Wales",
"author": "Holman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0598",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors for Mortality of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes in Wuhan, China: A Two-Center, Retrospective Study",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0",
"article-title": "Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: A population-based cohort study",
"author": "Holman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "823",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1543",
"article-title": "Preadmission Diabetes-Specific Risk Factors for Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes and Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2339",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-0635-3",
"article-title": "Higher glycemic variability within the first day of ICU admission is associated with increased 30-day mortality in ICU patients with sepsis",
"author": "Chao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2042018819875406",
"article-title": "Hospital outcomes and cumulative burden from complications in type 2 diabetic sepsis patients: A cohort study using administrative and hospital-based databases",
"author": "Hsieh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2042018819875406",
"journal-title": "Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.11.005",
"article-title": "DPP-4 inhibition and COVID-19: From initial concerns to recent expectations",
"author": "Scheen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101213",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00005-020-00602-5",
"article-title": "DPP4 Inhibitors and COVID-19-Holy Grail or Another Dead End?",
"author": "Grzela",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565",
"article-title": "Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: Glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26",
"author": "Vankadari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1179551420912972",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 at the Interface Between Inflammation and Metabolism",
"author": "Trzaskalski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1179551420912972",
"journal-title": "Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/med.21513",
"article-title": "Mechanisms and pathways of anti-inflammatory activity of DPP-4 inhibitors in cardiovascular and renal protection",
"author": "Tomovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "404",
"journal-title": "Med. Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1253/circj.CJ-12-1168",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, improves endothelial dysfunction in association with its anti-inflammatory effects in patients with coronary artery disease and uncontrolled diabetes",
"author": "Matsubara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1337",
"journal-title": "Circ. J.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2012.09.004",
"article-title": "A dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in type 2 diabetic patients",
"author": "Sasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "347",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.005",
"article-title": "Pharmacological characteristics of patients infected with SARS-Cov-2 admitted to Intensive Care Unit in South of France",
"author": "Montastruc",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Therapie",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2021.0118",
"article-title": "Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19",
"author": "Rhee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. J.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1521",
"article-title": "Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study",
"author": "Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2999",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w",
"article-title": "Predictors of hospital discharge and mortality in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: Updated results from the nationwide CORONADO study",
"author": "Wargny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "778",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)—A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression",
"author": "Rakhmat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "777",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70696-0",
"article-title": "DPP4-directed therapeutic strategies for MERS-CoV",
"author": "Reinhold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108125",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: Can DPP4 inhibition play a role?",
"author": "Iacobellis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108125",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa098",
"article-title": "The association of hypertension and diabetes pharmacotherapy with COVID-19 severity and immune signatures: An observational study",
"author": "Dalan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e48",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00050-4",
"article-title": "Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide observational study in England",
"author": "Khunti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13359",
"article-title": "Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Nassar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "86",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01515-6",
"article-title": "Disentangling conflicting evidence on DPP-4 inhibitors and outcomes of COVID-19: Narrative review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bonora",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1379",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Invest",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40200-021-00777-4",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor and outcome from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in diabetic patients: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "543",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Metab. Disord.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: A bidirectional relationship",
"author": "Marin",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "Clin. Investig. Arterioscler.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108391",
"article-title": "Metformin in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A hidden path-from altered inflammation to reduced mortality. A review from the literature",
"author": "Pedrosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108391",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Complicat.",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.609470",
"article-title": "Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: A Narrative Review",
"author": "Corrao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "609470",
"journal-title": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7046a5",
"article-title": "Impact of Hospital Strain on Excess Deaths During the COVID-19 Pandemic-United States, July 2020–July 2021",
"author": "French",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1613",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep.",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-021-07301-7",
"article-title": "Type 2 Diabetes Management, Control and Outcomes During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Older US Veterans: An Observational Study",
"author": "Aubert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3047",
"article-title": "Diabetes Care and Glycemic Control During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United States",
"author": "Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1412",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13110",
"article-title": "Glycemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 lockdown: What comes after a “quarantine”?",
"author": "Ceconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "946",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_77",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2021.787761",
"article-title": "Promoting a Syndemic Approach for Cardiometabolic Disease Management During COVID-19: The CAPISCO International Expert Panel",
"author": "Banerjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "787761",
"journal-title": "Front. Cardiovasc. Med.",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108336",
"article-title": "Post-COVID syndrome, inflammation, and diabetes",
"author": "Rizvi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108336",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Complicat.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-2019-1111",
"article-title": "Glucometabolic Perturbations in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronavirus Disease 2019: Causes, Consequences, and How to Counter Them Using Novel Antidiabetic Drugs-The CAPISCO International Expert Panel",
"author": "Popovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "260",
"journal-title": "Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 80,
"references-count": 80,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/6/1416"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 Outcomes and Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}
