No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
et al., Open Medicine, doi:10.1515/med-2021-0361, Sep 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 397 severe COVID-19 patients in China, showing worse outcomes with vitamin C treatment, without statistical significance. IV vitamin C 2-4g/day. Subject to confounding by indication and immortal time bias. Exclusion criteria were (a) the duration of hospitalization was less than 3 days; (b) vitamin C treatment started before admission; and (c) the length of vitamin C use was less than 3 days. Includes vitamin C use started at any time during hospitalization, for many patients this was >15 days later (Figure A2). Duration of treatment varied widely (Figure A1). Treatment was determined by clinicians according to the condition of each patient.
This is the 33rd of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
21 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0012.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
substantial unadjusted confounding by indication likely; immortal time bias may significantly affect results; treatment start times unknown, treatment may not have started at baseline.
|
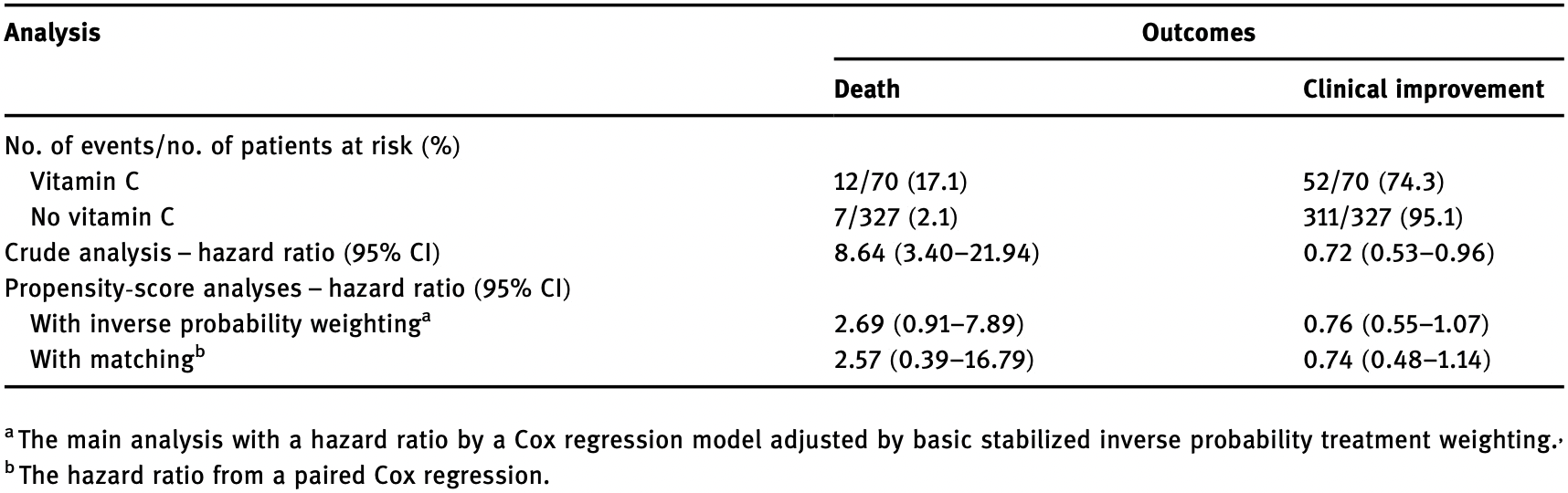
risk of death, 157.0% higher, HR 2.57, p = 0.33, treatment 12 of 70 (17.1%), control 7 of 327 (2.1%), adjusted per study, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death, 169.0% higher, HR 2.69, p = 0.07, treatment 12 of 70 (17.1%), control 7 of 327 (2.1%), adjusted per study, IPTW.
|
|
clinical improvement ≥ 2 points, 35.1% worse, HR 1.35, p = 0.17, treatment 18 of 70 (25.7%), control 16 of 327 (4.9%), adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, propensity score matching.
|
|
clinical improvement ≥ 2 points, 31.6% worse, HR 1.32, p = 0.11, treatment 18 of 70 (25.7%), control 16 of 327 (4.9%), adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, IPTW.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zheng et al., 22 Sep 2021, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 13 February, 2020 - 29 February, 2020, dosage 3000mg days 1-5.
No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
Open Medicine, doi:10.1515/med-2021-0361
There is no specific drug for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We aimed to investigate the possible clinical efficacy of moderate-dose vitamin C infusion among inpatients with severe COVID-19. Data of 397 adult patients with severe COVID-19 admitted to a designated clinical center of Wuhan Union Hospital (China) between February 13 and February 29, 2020, were collected. Besides standard therapies, patients were treated with vitamin C (2-4 g/day) or not. The primary outcome was all-cause death. Secondary outcome was clinical improvement of 2 points on a 6-point ordinal scale. About 70 participants were treated with intravenous vitamin C, and 327 did not receive it. No significant association was found between vitamin C use and death on inverse probability treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 2.69; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91-7.89). Clinical improvement occurred in 74.3% (52/70) of patients in the vitamin C group and 95.1% (311/327) in the no vitamin C group. No significant difference was observed between the two groups on IPTW analysis (weighted HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.55-1.07). Our findings revealed that in patients with severe COVID-19, treatment with moderate dose of intravenous vitamin C had no significant benefit on reducing the risk of death and obtaining clinical improvement.
Conflict of interest: The authors report no conflict of interest.
Appendix
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2015432
Carr, Rosengrave, Bayer, Chambers, Mehrtens et al., Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes, Crit Care
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
China, Guidelines of the diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 8)
De Grooth, Manubulu-Choo, Zandvliet, Spoelstra-De Man, Girbes et al., Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in critically Ill patients: a randomized trial of four IV regimens, Chest
Fowler Aa 3rd, Truwit, Hite, Morris, Dewilde et al., Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Grein, Ohmagari, Shin, Diaz, Asperges et al., Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hecker, Mechanisms and consequences of oxidative stress in lung disease: therapeutic implications for an aging populace, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00275.2017
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C as a possible therapy for COVID-19, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.222
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: a meta-analysis, Nutrients
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C may reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients: a metaregression analysis, J Intensive Care
Hiedra, Lo, Elbashabsheh, Gul, Wright et al., The use of IV vitamin C for patients with COVID-19: a case series, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther
Hunt, Chakravorty, Annan, Habibzadeh, Schorah, The clinical effects of vitamin C supplementation in elderly hospitalised patients with acute respiratory infections, Int J Vitam Nutr Res
Iii, Kim, Lepler, Malhotra, Debesa et al., Intravenous vitamin C as adjunctive therapy for enterovirus/rhinovirus induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, World J Crit Care Med
Kim, Yeom, Reply: vitamin C as a possible therapy for COVID-19, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.224
Mousavi, Bereswill, Heimesaat, Immunomodulatory and antimicrobial effects of vitamin C, Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp)
Nabzdyk, Bittner, Vitamin C in the critically ill -indications and controversies, World J Crit Care Med
Patel, Dial, Wu, Gauthier, Wu et al., Dietary antioxidants significantly attenuate hyperoxia-induced acute inflammatory lung injury by enhancing macrophage function via reducing the accumulation of airway HMGB1, Int J Mol Sci
Stuart, Lee, Leacy, Prognostic score-based balance measures can be a useful diagnostic for propensity score methods in comparative effectiveness research, J Clin Epidemiol
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott, Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA
Yan, Fu, Jia, Ma, Tao et al., Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling mediated an antioxidative protection of human placental mesenchymal stem cells of fetal origin in alveolar epithelial cells, Oxid Med Cell Longev
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1515/med-2021-0361",
"ISSN": [
"2391-5463"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/med-2021-0361",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>There is no specific drug for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We aimed to investigate the possible clinical efficacy of moderate-dose vitamin C infusion among inpatients with severe COVID-19. Data of 397 adult patients with severe COVID-19 admitted to a designated clinical center of Wuhan Union Hospital (China) between February 13 and February 29, 2020, were collected. Besides standard therapies, patients were treated with vitamin C (2–4 g/day) or not. The primary outcome was all-cause death. Secondary outcome was clinical improvement of 2 points on a 6-point ordinal scale. About 70 participants were treated with intravenous vitamin C, and 327 did not receive it. No significant association was found between vitamin C use and death on inverse probability treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 2.69; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91–7.89). Clinical improvement occurred in 74.3% (52/70) of patients in the vitamin C group and 95.1% (311/327) in the no vitamin C group. No significant difference was observed between the two groups on IPTW analysis (weighted HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.55–1.07). Our findings revealed that in patients with severe COVID-19, treatment with moderate dose of intravenous vitamin C had no significant benefit on reducing the risk of death and obtaining clinical improvement.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1515/med-2021-0361"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ultrasound, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Shaoping",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University , Guangzhou , China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Qiaosen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University , Guangzhou , China"
}
],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Hongbo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Chunxia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Jinzhuo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Sumeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Hua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Huadong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
},
{
"name": "Joint International Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Xin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
},
{
"name": "Joint International Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Huazhong University of Science and Technology , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Weng",
"given": "Zhihong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Open Medicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-22T21:20:40Z",
"timestamp": 1632345640000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-10T05:30:54Z",
"timestamp": 1639114254000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-16T00:12:03Z",
"timestamp": 1639613523854
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2391-5463"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/med-2021-0361/xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/med-2021-0361/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "374",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1403-1414",
"prefix": "10.1515",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
22
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Walter de Gruyter GmbH",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_001",
"unstructured": "Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;324(8):782–93."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.85",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_002",
"unstructured": "Fowler Iii AA, Kim C, Lepler L, Malhotra R, Debesa O, Natarajan R, et al. Intravenous vitamin C as adjunctive therapy for enterovirus/rhinovirus induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. World J Crit Care Med. 2017;6(1):85–90."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1556/1886.2019.00016",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_003",
"unstructured": "Mousavi S, Bereswill S, Heimesaat MM. Immunomodulatory and antimicrobial effects of vitamin C. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2019;9(3):73–9."
},
{
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_004",
"unstructured": "Hunt C, Chakravorty NK, Annan G, Habibzadeh N, Schorah CJ. The clinical effects of vitamin C supplementation in elderly hospitalised patients with acute respiratory infections. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1994;64(3):212–9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-017-1891-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_005",
"unstructured": "Carr AC, Rosengrave PC, Bayer S, Chambers S, Mehrtens J, Shaw GM. Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes. Crit Care. 2017;21(1):300."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2018.02.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_006",
"unstructured": "de Grooth HJ, Manubulu-Choo WP, Zandvliet AS, Spoelstra-de Man AME, Girbes AR, Swart EL, et al. Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in critically Ill patients: a randomized trial of four IV regimens. Chest. 2018;153(6):1368–77."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11040708",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_007",
"unstructured": "Hemilä H, Chalker E. Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: a meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2019;11(4):708."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40560-020-0432-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_008",
"unstructured": "Hemilä H, Chalker E. Vitamin C may reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients: a meta-regression analysis. J Intensive Care. 2020;8:15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.222",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_009",
"unstructured": "Hemilä H, Chalker E. Vitamin C as a possible therapy for COVID-19. Infect Chemother. 2020;52(2):222–3. 10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.222."
},
{
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_010",
"unstructured": "China NHC. Guidelines of the diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 8). (in Chinese). Available from: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202008/0a7bdf12bd4b46e5bd28ca7f9a7f5e5a.shtml"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2015312",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_011",
"unstructured": "Grein J, Ohmagari N, Shin D, Diaz G, Asperges E, Castagna A, et al. Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(24):2327–36."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.01.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_012",
"unstructured": "Stuart EA, Lee BK, Leacy FP. Prognostic score-based balance measures can be a useful diagnostic for propensity score methods in comparative effectiveness research. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66(8 Suppl):S84–90e1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.224",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_013",
"unstructured": "Kim SB, Yeom JS. Reply: vitamin C as a possible therapy for COVID-19. Infect Chemother. 2020;52(2):224–5. 10.3947/ic.2020.52.2.224."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/2654910",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_014",
"unstructured": "Yan X, Fu X, Jia Y, Ma X, Tao J, Yang T, et al. Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling mediated an antioxidative protection of human placental mesenchymal stem cells of fetal origin in alveolar epithelial cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:2654910."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00275.2017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_015",
"unstructured": "Hecker L. Mechanisms and consequences of oxidative stress in lung disease: therapeutic implications for an aging populace. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018;314(4):L642–53. 10.1152/ajplung.00275.2017."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_016",
"unstructured": "Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–13. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015432",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_017",
"unstructured": "Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(2):120–8. 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5492/wjccm.v7.i5.52",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_018",
"unstructured": "Nabzdyk CS, Bittner EA. Vitamin C in the critically ill – indications and controversies. World J Crit Care Med. 2018;7(5):52–61."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21030977",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_019",
"unstructured": "Patel V, Dial K, Wu J, Gauthier AG, Wu W, Lin M, et al. Dietary antioxidants significantly attenuate hyperoxia-induced acute inflammatory lung injury by enhancing macrophage function via reducing the accumulation of airway HMGB1. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):977."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.11825",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_020",
"unstructured": "Fowler AA 3rd, Truwit JD, Hite RD, Morris PE, DeWilde C, Priday A, et al. Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;322(13):1261–70."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2020.1794819",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_021",
"unstructured": "Hiedra R, Lo KB, Elbashabsheh M, Gul F, Wright RM, Albano J, et al. The use of IV vitamin C for patients with COVID-19: a case series. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020;18(12):1259–61."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_022",
"unstructured": "Hemilä H, Chalker E. Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;1:CD000980."
},
{
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_023",
"unstructured": "High-dose vitamin C (PDQ(r)) – health professional version – National Cancer Institute. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/hp/vitamin-c-pdq"
},
{
"key": "2021121004381567292_j_med-2021-0361_ref_024",
"unstructured": "U.S. National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov is a database of privately and publicly funded clinical studies conducted around the world. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}
