Virological Traits of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.87.1 Lineage
et al., Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines12050487, May 2024
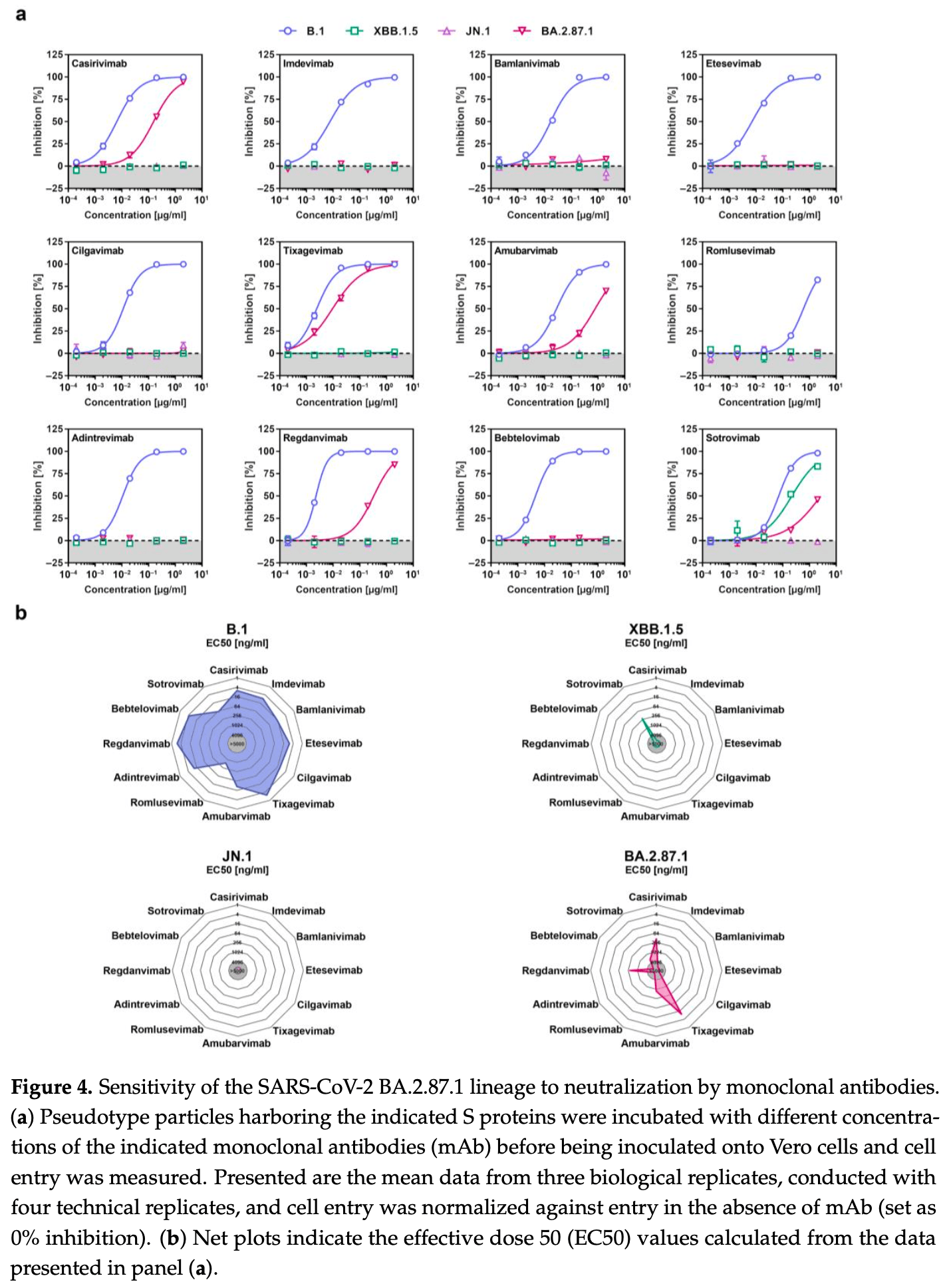
In vitro study showing that the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.87.1 lineage efficiently enters human cells but is more sensitive to neutralization by antibodies compared to the JN.1 variant. BA.2.87.1 pseudovirus particles robustly entered human cell lines, although entry into Calu-3 lung cells was reduced compared to JN.1. Notably, BA.2.87.1 showed high dependence on the cellular serine protease TMPRSS2 for Calu-3 lung cell entry, unlike other omicron sublineages that have reduced TMPRSS2 usage. This suggests BA.2.87.1 may have regained some TMPRSS2 dependence, potentially impacting its tissue tropism and disease severity. Despite the FDA previously suspending emergency use authorization for several monoclonal antibodies due to lack of efficacy against recent variants, this study found that BA.2.87.1 was neutralized by casirivimab, tixagevimab, amubarvimab, regdanvimab, and sotrovimab. In contrast, only sotrovimab neutralized XBB.1.5, and none were effective against JN.1.
Zhang et al., 1 May 2024, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Contact: mhoffmann@dpz.eu (corresponding author), luzhang@dpz.eu, inehlmeier@dpz.eu, akempf@dpz.eu, lgraichen@dpz.eu, spoehlmann@dpz.eu, jablonka.alexandra@mh-hannover.de, calderonhampel.noemi@mh-hannover.de, cossmann.anne@mh-hannover.de, stankov.metodi@mh-hannover.de, morillasramos.gema@mh-hannover.de, behrens.georg@mh-hannover.de, hans-martin.jaeck@fau.de.
Virological Traits of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.87.1 Lineage
Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines12050487
Transmissibility and immune evasion of the recently emerged, highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.87.1 are unknown. Here, we report that BA.2.87.1 efficiently enters human cells but is more sensitive to antibody-mediated neutralization than the currently dominating JN.1 variant. Acquisition of adaptive mutations might thus be needed for efficient spread in the population.
), the European Regional Development Fund Getting AIR (ZW7-85151373), and the Ministry for Science and Culture of Lower Saxony (Niedersächsisches Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Kultur; 14-76103-184, CO-FONI Network, project 4LZF23). The funding sources had no role in the design and execution of the study, the writing of the manuscript and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The authors did not receive payment by a pharmaceutical company or other agency to write the publication. The authors were not precluded from accessing data in the study, and they accept responsibility to submit for publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Internal Review Board of Hannover Medical School (institutional review board no. 8973_BO-K_2020, last amendment September 2023).
Informed Consent Statement: All study participants provided written informed consent and received no compensation. Conflicts of Interest: S.P. and M.H. performed contract research (testing of vaccinee sera for neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2) for Valneva unrelated to this work. A.D-J. served as advisor for Pfizer, unrelated to this work. G.M.N.B. served as advisor for Moderna, unrelated to this work. S.P. served as advisor for BioNTech, unrelated to this work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
References
Berger Rentsch, Zimmer, A vesicular stomatitis virus replicon-based bioassay for the rapid and sensitive determination of multi-species type i interferon, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025858
Braga, Ali, Secco, Chiavacci, Neves et al., Drugs that inhibit tmem16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6
Bussani, Schneider, Zentilin, Collesi, Ali et al., Persistence of viral rna, pneumocyte syncytia and thrombosis are hallmarks of advanced COVID-19 pathology, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103104
Cerutti, Guo, Zhou, Gorman, Lee et al., Potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies directed against spike n-terminal domain target a single supersite, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2021.03.005
Frenck, Jr, Klein, Kitchin, Gurtman et al., Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107456
Gayed, Diya, Lowry, Xu, Bangad et al., Safety and immunogenicity of the monovalent omicron xbb.1.5-adapted bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in individuals >/=12 years old: A phase 2/3 trial, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines12020118
Guo, Li, Lin, Liu, Chen et al., The glycan-binding trait of the sarbecovirus spike n-terminal domain reveals an evolutionary footprint, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.00958-22
Harvey, Carabelli, Jackson, Gupta, Thomson et al., Sars-cov-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0
Hoffmann, Arora, Nehlmeier, Kempf, Cossmann et al., Profound neutralization evasion and augmented host cell entry are hallmarks of the fast-spreading SARS-CoV-2 lineage xbb.1.5, Cell. Mol. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-023-00988-0
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., Sars-cov-2 cell entry depends on ace2 and tmprss2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hoffmann, Kruger, Schulz, Cossmann, Rocha et al., The omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032
Hui, Ho, Cheung, Ng, Ching et al., Sars-cov-2 omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04479-6
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ace2 receptor, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5
Lee, Cosgrove, Moore, Bethune, Nally et al., Omicron ba.1-containing mrna-1273 boosters compared with the original COVID-19 vaccine in the uk: A randomised, observer-blind, active-controlled trial, Lancet. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00295-5
Mccallum, De Marco, Lempp, Tortorici, Pinto et al., N-terminal domain antigenic mapping reveals a site of vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.028
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Goonawardane, Saito et al., Altered tmprss2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x
Moghadas, Vilches, Zhang, Wells, Shoukat et al., The impact of vaccination on coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) outbreaks in the united states, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab079
Moreira, Jr, Kitchin, Xu, Dychter et al., Safety and efficacy of a third dose of bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2200674
Munoz, Sher, Sabharwal, Gurtman, Xu et al., Evaluation of bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in children younger than 5 years of age, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2211031
Polack, Thomas, Kitchin, Absalon, Gurtman et al., Safety and efficacy of the bnt162b2 mrna COVID-19 vaccine, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
Qu, Xu, Faraone, Goodarzi, Zheng et al., Immune evasion, infectivity, and fusogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 ba.2.86 and flip variants, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.026
Rajah, Bernier, Buchrieser, Schwartz, The mechanism and consequences of SARS-CoV-2 spike-mediated fusion and syncytia formation, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167280
Schmidt, Weisblum, Muecksch, Hoffmann, Michailidis et al., Measuring SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity using pseudotyped and chimeric viruses, J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20201181
Shang, Ye, Shi, Wan, Luo et al., Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y
Shuai, Chan, Hu, Chai, Yuen et al., Attenuated replication and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 b.1.1.529 omicron, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5
Suryadevara, Shrihari, Gilchuk, Vanblargan, Binshtein et al., Neutralizing and protective human monoclonal antibodies recognizing the n-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.029
Tomris, Unione, Nguyen, Zaree, Bouwman et al., Sars-cov-2 spike n-terminal domain engages 9-o-acetylated alpha2-8-linked sialic acids, ACS Chem. Biol, doi:10.1021/acschembio.3c00066
Usdan, Patel, Rodriguez, Xu, Lee et al., A bivalent omicron-ba.4/ba.5-adapted bnt162b2 booster in >/=12-year-olds, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad718
Walsh, Frenck, Jr, Falsey, Kitchin et al., Safety and immunogenicity of two rna-based COVID-19 vaccine candidates, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2027906
Wang, Qiu, Hou, Deng, Xu et al., Axl is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y
Zhang, Kempf, Nehlmeier, Cossmann, Richter et al., Sars-cov-2 ba.2.86 enters lung cells and evades neutralizing antibodies with high efficiency, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.025
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines12050487",
"ISSN": [
"2076-393X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12050487",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Transmissibility and immune evasion of the recently emerged, highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.87.1 are unknown. Here, we report that BA.2.87.1 efficiently enters human cells but is more sensitive to antibody-mediated neutralization than the currently dominating JN.1 variant. Acquisition of adaptive mutations might thus be needed for efficient spread in the population.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"vaccines12050487"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, 37077 Göttingen, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Biology and Psychology, Georg-August-University Göttingen, 37073 Göttingen, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7129-100X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hannover Medical School, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
},
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), Partner Site Hannover-Braunschweig, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dopfer-Jablonka",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, 37077 Göttingen, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Nehlmeier",
"given": "Inga",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, 37077 Göttingen, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Biology and Psychology, Georg-August-University Göttingen, 37073 Göttingen, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Kempf",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, 37077 Göttingen, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Biology and Psychology, Georg-August-University Göttingen, 37073 Göttingen, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Graichen",
"given": "Luise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hannover Medical School, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Calderón Hampel",
"given": "Noemí",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hannover Medical School, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Cossmann",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hannover Medical School, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Stankov",
"given": "Metodi V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4835-5172",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hannover Medical School, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Morillas Ramos",
"given": "Gema",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6554-3346",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Molecular Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine 3, Friedrich-Alexander University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, 91054 Erlangen, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schulz",
"given": "Sebastian R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6332-8463",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Molecular Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine 3, Friedrich-Alexander University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, 91054 Erlangen, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jäck",
"given": "Hans-Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3111-621X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hannover Medical School, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
},
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), Partner Site Hannover-Braunschweig, 30625 Hannover, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Center for Individualized Infection Medicine (CiiM), 30625 Hannover, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Behrens",
"given": "Georg M. N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6086-9136",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, 37077 Göttingen, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Biology and Psychology, Georg-August-University Göttingen, 37073 Göttingen, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pöhlmann",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4603-7696",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, 37077 Göttingen, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Biology and Psychology, Georg-August-University Göttingen, 37073 Göttingen, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hoffmann",
"given": "Markus",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Vaccines",
"container-title-short": "Vaccines",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T12:59:39Z",
"timestamp": 1714568379000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T14:14:50Z",
"timestamp": 1714572890000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000780",
"award": [
"101057100"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "EU project UNDINE"
},
{
"award": [
"14-76103-184"
],
"name": "Ministry of Science and Culture of Lower Saxony in Germany"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001659",
"award": [
"PO 716/11-1"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "German Research Foundation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004543",
"award": [
"202006270031"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "China Scholarship Council"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000780",
"award": [
"ZAM5-87006761"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "European Social Fund"
},
{
"award": [
"14-76103-184"
],
"name": "Ministry for Science and Culture of Lower Saxony"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002347",
"award": [
"01KI2043"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "BMBF"
},
{
"award": [
"01KX2021"
],
"name": "NaFoUniMedCovid19-COVIM"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004563",
"award": [
"RTG1660",
"TRR130"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Bavarian State Ministry for Science and the Arts and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft"
},
{
"name": "Bayerische Forschungsstiftung"
},
{
"name": "Kastner Foundation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100009139",
"award": [
"80018019238"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "German Center for Infection Research"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000780",
"award": [
"ZW7-85151373"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "European Regional Development Fund Getting AIR"
},
{
"award": [
"14-76103-184"
],
"name": "Ministry for Science and Culture of Lower Saxony"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-02T00:35:34Z",
"timestamp": 1714610134809
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/12/5/487/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "487",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107456",
"article-title": "Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents",
"author": "Frenck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "239",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2200674",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of a third dose of bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine",
"author": "Moreira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1910",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2211031",
"article-title": "Evaluation of bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in children younger than 5 years of age",
"author": "Munoz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "621",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "388",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2034577",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of the bnt162b2 mrna COVID-19 vaccine",
"author": "Polack",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2603",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2027906",
"article-title": "Safety and immunogenicity of two rna-based COVID-19 vaccine candidates",
"author": "Walsh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2439",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab079",
"article-title": "The impact of vaccination on coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) outbreaks in the united states",
"author": "Moghadas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2257",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "The WHO European Respiratory Surveillance Network (2024). Estimated number of lives directly saved by COVID-19 vaccination programs in the who european region, december 2020 to march 2023. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad718",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_8",
"unstructured": "Usdan, L., Patel, S., Rodriguez, H., Xu, X., Lee, D.Y., Finn, D., Wyper, H., Sci, B.B., Lowry, F.S., and Mensa, F.J. (2023). A bivalent omicron-ba.4/ba.5-adapted bnt162b2 booster in >/=12-year-olds. Clin. Infect. Dis., advance online publication."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00295-5",
"article-title": "Omicron ba.1-containing mrna-1273 boosters compared with the original COVID-19 vaccine in the uk: A randomised, observer-blind, active-controlled trial",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1007",
"journal-title": "Lancet. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202401.0670.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Gayed, J., Diya, O., Lowry, F.S., Xu, X., Bangad, V., Mensa, F., Zou, J., Xie, X., Hu, Y., and Lu, C. (2024). Safety and immunogenicity of the monovalent omicron xbb.1.5-adapted bnt162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in individuals >/=12 years old: A phase 2/3 trial. Vaccines, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschembio.3c00066",
"article-title": "Sars-cov-2 spike n-terminal domain engages 9-o-acetylated alpha2-8-linked sialic acids",
"author": "Tomris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1180",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem. Biol.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.00958-22",
"article-title": "The glycan-binding trait of the sarbecovirus spike n-terminal domain reveals an evolutionary footprint",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0095822",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y",
"article-title": "Axl is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.028",
"article-title": "N-terminal domain antigenic mapping reveals a site of vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "McCallum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2332",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.029",
"article-title": "Neutralizing and protective human monoclonal antibodies recognizing the n-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Suryadevara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2316",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2021.03.005",
"article-title": "Potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies directed against spike n-terminal domain target a single supersite",
"author": "Cerutti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "819",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"article-title": "Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ace2 receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"article-title": "Sars-cov-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape",
"author": "Harvey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20201181",
"article-title": "Measuring SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity using pseudotyped and chimeric viruses",
"author": "Schmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e20201181",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "217",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "Sars-cov-2 cell entry depends on ace2 and tmprss2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032",
"article-title": "The omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "447",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-023-00988-0",
"article-title": "Profound neutralization evasion and augmented host cell entry are hallmarks of the fast-spreading SARS-CoV-2 lineage xbb.1.5",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "419",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0025858",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Berger Rentsch, M., and Zimmer, G. (2011). A vesicular stomatitis virus replicon-based bioassay for the rapid and sensitive determination of multi-species type i interferon. PLoS ONE, 6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103104",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Bussani, R., Schneider, E., Zentilin, L., Collesi, C., Ali, H., Braga, L., Volpe, M.C., Colliva, A., Zanconati, F., and Berlot, G. (2020). Persistence of viral rna, pneumocyte syncytia and thrombosis are hallmarks of advanced COVID-19 pathology. EBioMedicine, 61."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6",
"article-title": "Drugs that inhibit tmem16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia",
"author": "Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "88",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "594",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167280",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_28",
"unstructured": "Rajah, M.M., Bernier, A., Buchrieser, J., and Schwartz, O. (2022). The mechanism and consequences of SARS-CoV-2 spike-mediated fusion and syncytia formation. J. Mol. Biol., 434."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04479-6",
"article-title": "Sars-cov-2 omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo",
"author": "Hui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5",
"article-title": "Attenuated replication and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 b.1.1.529 omicron",
"author": "Shuai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"article-title": "Altered tmprss2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity",
"author": "Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.025",
"article-title": "Sars-cov-2 ba.2.86 enters lung cells and evades neutralizing antibodies with high efficiency",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "596",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "187",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.026",
"article-title": "Immune evasion, infectivity, and fusogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 ba.2.86 and flip variants",
"author": "Qu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "585",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "187",
"year": "2024"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/12/5/487"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Virological Traits of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.87.1 Lineage",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}