Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of COVID‐19: A multicenter, prospective, open‐label and randomized controlled trial
et al., Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7141, NCT04295551, May 2021
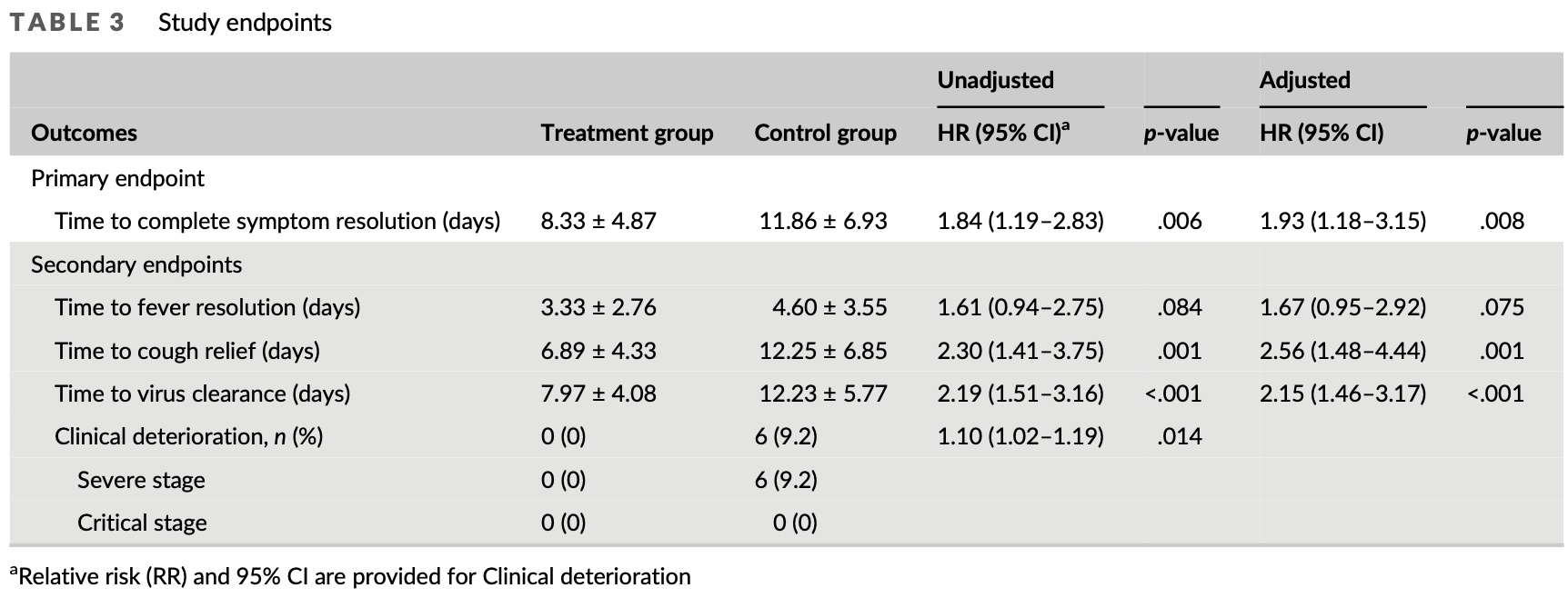
RCT 130 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China, showing lower progression and improved recovery with Xiyanping injection (9-dehydro-17-hydro-andrographolide and sodium 9-dehydro-17-hydro-andrographolide-19-yl sulfate, which are derived from andrographis).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of severe case, 92.3% lower, RR 0.08, p = 0.03, treatment 0 of 65 (0.0%), control 6 of 65 (9.2%), NNT 11, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of no recovery, 48.2% lower, HR 0.52, p = 0.008, treatment 65, control 65, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 40.1% lower, HR 0.60, p = 0.07, treatment 65, control 65, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, fever.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 60.9% lower, HR 0.39, p = 0.001, treatment 65, control 65, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, cough.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 53.5% lower, HR 0.47, p < 0.001, treatment 65, control 65, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zhang et al., 12 May 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, China, peer-reviewed, mean age 46.3, 12 authors, study period 27 January, 2020 - 20 February, 2020, trial NCT04295551 (history).
Contact: xqyencu@gmail.com.
Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of COVID ‐19: A multicenter, prospective, open‐label and randomized controlled trial
Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7141
Xiyanping (XYP) is a Chinese herbal medicine used in the clinic to treat respiratory infection and pneumonia. Recent evidence identified XYP as a potential inhibitor of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, implying XYP as a possible treatment for the coronavirus disease 2019 . Here, we conducted a prospective, multicenter, open-label and randomized controlled trial to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of XYP injection in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. We consecutively recruited 130 COVID-19 patients with mild to moderate symptoms from five study sites, and randomized them in 1:1 ratio to receive XYP injection in combination with standard therapy or receive standard supportive therapy alone. We found that XYP injection significantly reduced the time to cough relief, fever resolution and virus clearance. Less patients receiving XYP injection experienced disease progression to the severe stage during the treatment process. No severe adverse events were reported during the study. Taken together, XYP injection is safe and effective in improving the recovery of patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. However, further studies are warranted to evaluate the efficacy of XYP in an expanded cohort comprising COVID-19 patients at different disease stages.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Xiao-Qun Ye, Xin-Yi Zhang and Lang Lv: Designed the experiment. Xiao-Qun Ye, Xin-Yi Zhang, Lang Lv, Yu-Long Zhou and Liang-Dong Xie: Collected the data. Qin Xu, Xiao-Fan Zou, Yan Ding, Jie Tian, Jia-Liang Fan, Hai-Wei Fan and Yi-Xi Yang: Contributed to data analysis. All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
ETHICS STATEMENT The study on human participants was approved by the institutional review board or ethics committee at each participating site. Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Additional supporting information may be found online in the Supporting Information section at the end of this article.
References
Boulware, Pullen, Bangdiwala, Pastick, Lofgren et al., A randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19, The New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2016638
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, The New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Chandramohan, Kaphle, Chekuri, Gangarudraiah, Bychapur Siddaiah, Evaluating andrographolide as a potent inhibitor of NS3-4A protease and its drug-resistant mutants using in silico approaches, Advances in Virology, doi:10.1155/2015/972067
Chang, Ding, Chen, Pan, Zhao et al., Dehydroandrographolide succinic acid monoester as an inhibitor against the human immunodeficiency virus, doi:10.3181/00379727-197-43225
Chong, Chen, Luo, Jiang, Simultaneous determination of 9-dehydro-17-hydro-andrographolide and sodium 9-dehydro-17-hydro-andrographolide-19-yl sulfate in rat plasma by UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS after administration of xiyanping injection: Application to a pharmacokinetic study, Biomedical Chromatography, doi:10.1002/bmc.2866
Enmozhi, Raja, Sebastine, Joseph, Andrographolide as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: An in silico approach, Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1760136
Guo, Liu, Chen, Hong, Qian et al., Water-soluble andrographolide sulfonate exerts anti-sepsis action in mice through down-regulating p38 MAPK, STAT3 and NF-κB pathways, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2012.09.002
Gupta, Mishra, Ganju, Broad-spectrum antiviral properties of andrographolide, Archives of Virology, doi:10.1007/s00705-016-3166-3
Hu, Guan, Bi, Zhang, Li et al., Efficacy and safety of Lianhuaqingwen capsules, a repurposed Chinese herb, in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled trial, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153242
Huang, Bai, He, Xie, Zhou, Review on the potential action mechanisms of Chinese medicines in treating Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Pharmacological Research, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104939
Li, He, Tang, Ding, Chu et al., Andrographolide inhibits inflammatory cytokines secretion in LPSstimulated RAW264.7 cells through suppression of NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2017/8248142
Li, Li, Zhang, Guo, Xu et al., Xiyanping plus azithromycin chemotherapy in pediatric patients with mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: A systematic review and metaanalysis of efficacy and safety, Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2019/2346583
Li, Yang, Guan, Wen, Duan et al., Andrographolide sulfonate reduces mortality in Enterovirus 71 infected mice by modulating immunity, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.042
Lin, Chen, Duh, Chang, Liu, Inhibition of the epstein-barr virus lytic cycle by andrographolide, Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, doi:10.1248/bpb.31.2018
Peng, Zhou, Ding, Li, Yao, Modulation of lianbizi injection
Raja, Prabahar, Selvakumar, Raja, In silico analysis to compare the effectiveness of assorted drugs prescribed for swine flu in diverse medicine systems, Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Reddy, Reddy, Ravikanth, Krishnaiah, Goud et al., A new bis-andrographolide ether from Andrographis paniculata nees and evaluation of anti-HIV activity, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786410410001709197
Seubsasana, Pientong, Ekalaksananan, Thongchai, Aromdee, A potential andrographolide analogue against the replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 in vero cells, Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/157340611795564268
Sheeja, Kuttan, Activation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses and attenuation of tumor growth in vivo by Andrographis paniculata extract and andrographolide, Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology, doi:10.1080/08923970701282726
Sheeja, Kuttan, Modulation of natural killer cell activity, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and antibody-dependent complement-mediated cytotoxicity by andrographolide in normal and Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing mice, Integrative Cancer Therapies, doi:10.1177/1534735406298975
Shi, Guo, Zhu, Li, Ung et al., Cost-effectiveness analysis of Xiyanping injection (andrographolide sulfonate) for treatment of adult community acquired pneumonia: A retrospective, propensity score-matched cohort study, Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2019/4510591
Tang, Cao, Han, Wang, Chen et al., Hydroxychloroquine in patients with mainly mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019: Open label, randomised controlled trial, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1849
Wang, Xie, Adverse event case reports for Xiyanping injection based on literature], Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, doi:10.4268/cjcmm20121830
Wei, Diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 7), Chin Med J (Engl), doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000819
Xiong, Wang, Liu, Chen, Zheng et al., Effect of the combination of Xiyanping and Cefazolin on the function of neutrophils in mice], Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi
Yang, Li, Zhang, Xu, Yang et al., Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory and anaphylactic effects of andrographlide sulphonate E in Xiyanping, a traditional Chinese medicine injection, The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/jphp.13028
Zhang, Li, Li, Wong, Wang et al., Therapeutic options of TCM for organ injuries associated with COVID-19 and the underlying mechanism, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153297
Zheng, Shao, Chen, Luo, In vitro metabolism of sodium 9-dehydro-17-hydro-andrographolide-19-yl sulfate in rat liver S9 by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method, Pharmacognosy Magazine, doi:10.4103/0973-1296.182194
Zhuang, Fan, Chu, Wang, Yang et al., Chinese patent medicines in the treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01066
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7141",
"ISSN": [
"0951-418X",
"1099-1573"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7141",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/ptr.7141"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2020-11-02"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-04-11"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-05-12"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University Nanchang China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Xin‐Yi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Drug Research State Key Laboratory of Innovative Natural Medicine and TCM Injections Ganzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Lv",
"given": "Lang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang Nanchang China"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Yu‐Long",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine The Fifth People's Hospital of Ganzhou Ganzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Liang‐Dong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases Fengcheng People's Hospital Fengcheng China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Qin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases Ji'an Central People's Hospital Ji'an China"
}
],
"family": "Zou",
"given": "Xiao‐Fan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University Ganzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang Nanchang China"
}
],
"family": "Tian",
"given": "Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases Ji'an Central People's Hospital Ji'an China"
}
],
"family": "Fan",
"given": "Jia‐Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Drug Research State Key Laboratory of Innovative Natural Medicine and TCM Injections Ganzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Fan",
"given": "Hai‐Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Drug Research State Key Laboratory of Innovative Natural Medicine and TCM Injections Ganzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yi‐Xi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9682-3789",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Diseases The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University Nanchang China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ye",
"given": "Xiao‐Qun",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"container-title-short": "Phytotherapy Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-12T18:49:22Z",
"timestamp": 1620845362000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-02T19:34:09Z",
"timestamp": 1638473649000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-22T14:32:45Z",
"timestamp": 1692714765811
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 60,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1620777600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1620777600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ptr.7141",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/ptr.7141",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ptr.7141",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4401-4410",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2016638",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2015/972067",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3181/00379727-197-43225",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bmc.2866",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1760136",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2012.09.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-016-3166-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153242",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104939",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/2346583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_13_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Andrographolide inhibits inflammatory cytokines secretion in LPS‐stimulated RAW264.7 cells through suppression of NF‐κB/MAPK signaling pathway",
"author": "Li Y.",
"first-page": "8248142",
"journal-title": "Evidence‐based Complementary and Alternative Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_11_14_1",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1248/bpb.31.2018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_15_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Modulation of lianbizi injection (andrographolide) on some immune functions",
"author": "Peng G. Y.",
"first-page": "147",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi",
"key": "e_1_2_11_16_1",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"article-title": "In silico analysis to compare the effectiveness of assorted drugs prescribed for swine flu in diverse medicine systems",
"author": "Raja K.",
"first-page": "10",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_11_17_1",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14786410410001709197",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/157340611795564268",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08923970701282726",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1534735406298975",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/4510591",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1849",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_23_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Adverse event case reports for Xiyanping injection based on literature",
"author": "Wang Z. F.",
"first-page": "2792",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi",
"key": "e_1_2_11_24_1",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000819",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_25_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of the combination of Xiyanping and Cefazolin on the function of neutrophils in mice",
"author": "Xiong N.",
"first-page": "1079",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi",
"key": "e_1_2_11_26_1",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jphp.13028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153297",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_28_1"
},
{
"article-title": "In vitro metabolism of sodium 9‐dehydro‐17‐hydro‐andrographolide‐19‐yl sulfate in rat liver S9 by liquid chromatography‐mass spectrometry method",
"author": "Zheng D.",
"first-page": "S102",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Pharmacognosy Magazine",
"key": "e_1_2_11_29_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01066",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_30_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ptr.7141"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of\n <scp>COVID</scp>\n ‐19: A multicenter, prospective, open‐label and randomized controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "35"
}