Jan 10 2025 |
et al., Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.4274/tjps.galenos.2024.49768 | In silico Evaluation of H1-Antihistamine as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase: Repurposing Study of COVID-19 Therapy |
| In silico study showing that H1RA antihistamines, including bilastine, fexofenadine, mizolastine, rupatadine, terfenadine, and the leukotriene receptor antagonists montelukast and zafirlukast, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA poly.. | ||
Dec 31 2022 |
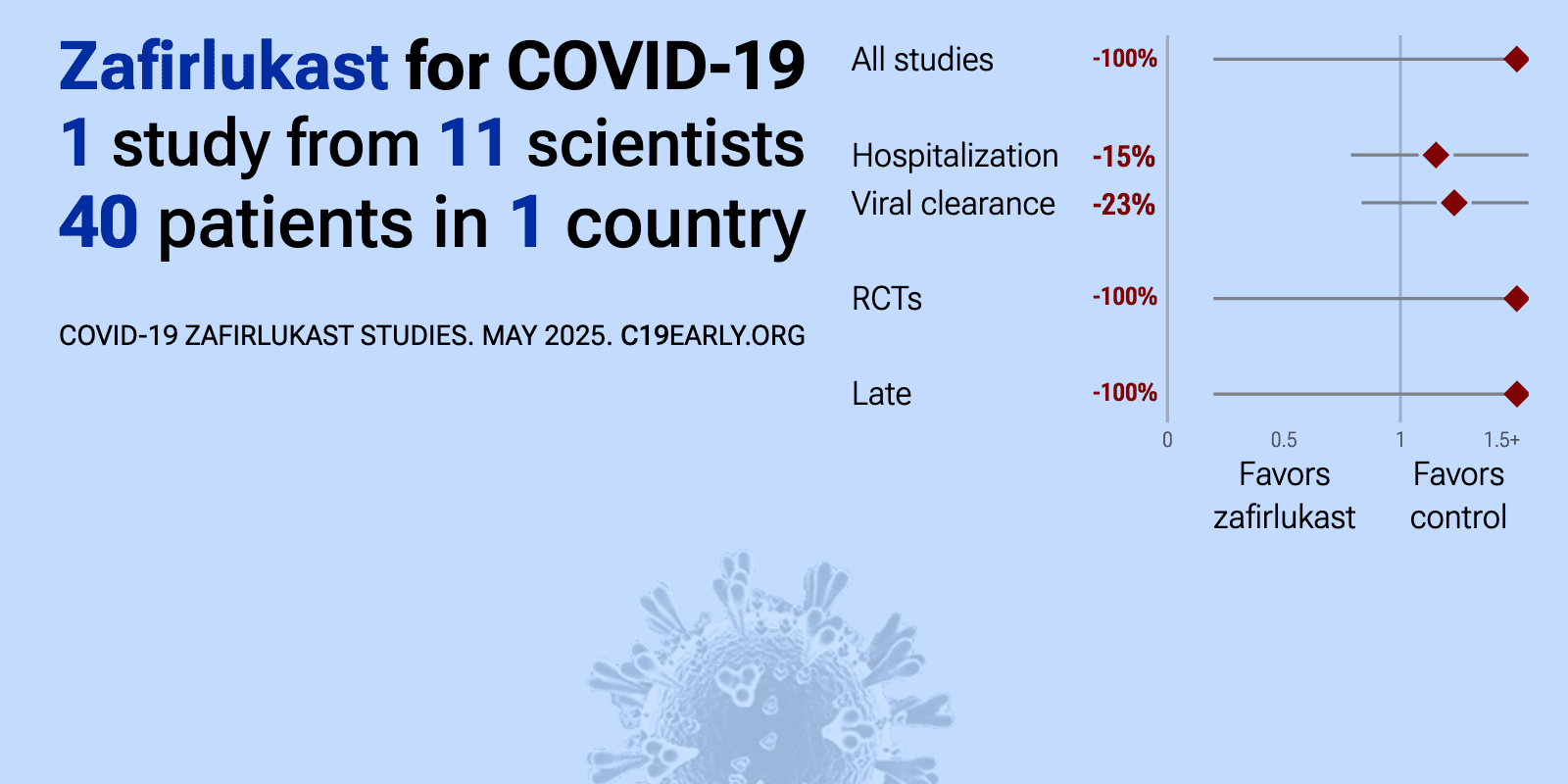
et al., Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2022.11.016 | The efficacy of Zafirlukast as a SARS-CoV-2 helicase inhibitor in adult patients with moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia (pilot randomized clinical trial) |
| 100% higher ICU admission (p=1), 9% worse 7-point scale results (p=0.48), 15% longer hospitalization (p=0.47), and 23% worse viral clearance (p=0.48). RCT 40 hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 pneumonia showing no significant difference with zafirlukast treatment compared to placebo. Authors suggest that the lack of efficacy might be related to timing of drug administration re.. | ||