A retrospective cohort study of the efficacy and safety of oral azvudine versus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients aged over 60 years
et al., Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032, Dec 2024
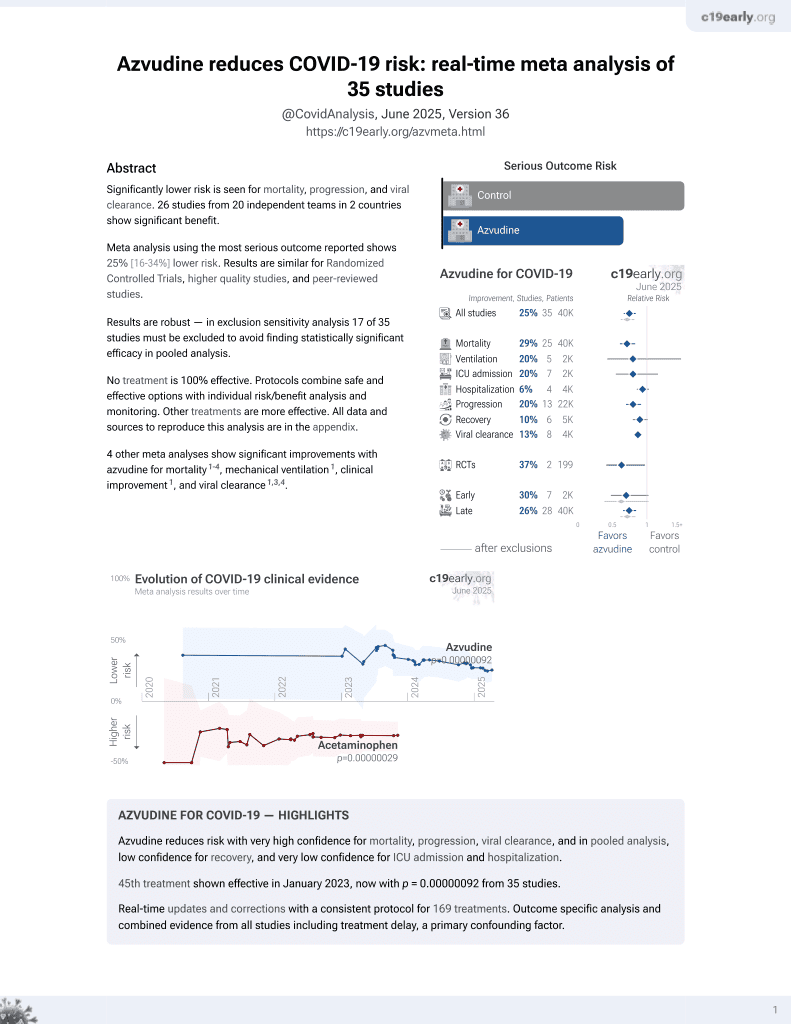
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
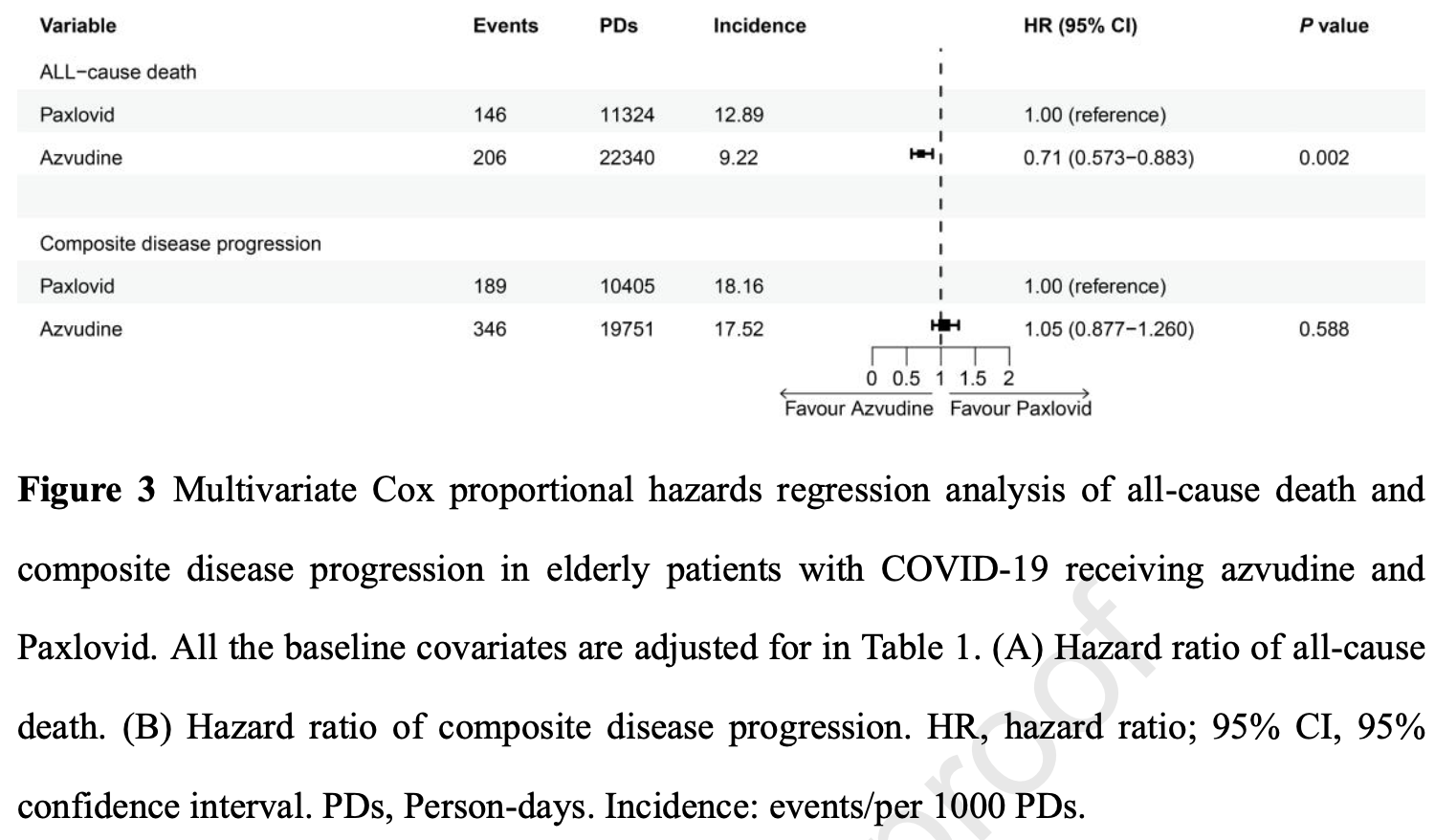
Retrospective 5,131 elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower mortality with azvudine compared to paxlovid. There was no significant difference in composite disease progression. Safety analysis showed azvudine had a lower incidence of adverse events. Authors hypothesize that azvudine's benefits may be due to its ability to protect thymic function and enhance immune response in elderly patients.
Study covers azvudine and paxlovid.
Yu et al., 31 Dec 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 18 authors, study period 5 December, 2022 - 31 January, 2023.
Contact: kanqc@zzu.edu.cn, jiang.jdong@163.com, fccrenzg@zzu.edu.cn.
A retrospective cohort study of the efficacy and safety of oral azvudine versus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients aged over 60 years
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032
Azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) are recommended for COVID-19 treatment in China, but their safety and efficacy in the elderly population are not fully known. In this multicenter, retrospective, cohort study, we identified 5131 elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients from 32,864 COVID-19 patients admitted to nine hospitals in Henan Province, China, from December 5, 2022, to January 31, 2023. The primary outcome was all-cause death, and the secondary outcome was composite disease progression. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed to control for confounding factors, including demographics, vaccination status, comorbidities, and laboratory tests. After 2:1 PSM, 1786 elderly patients receiving azvudine and 893 elderly patients receiving Paxlovid were included. Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses revealed that compared with Paxlovid group, azvudine could significantly reduce the risk of all-cause death (log-rank P=0.002; HR: 0.71, 95% CI: 0.573-0.883, P=0.002), but there was no difference in composite disease progression (log-rank P=0.52; HR: 1.05, 95% CI: 0.877-1.260, P=0.588). Four sensitivity analyses verified the robustness of above results. Subgroup analysis suggested that a greater benefit of azvudine over Paxlovid was observed in elderly patients with primary malignant tumors (P for interaction = 0.005, HR: 0.32, 95% CI: 0.18-0.57) compared to patients without primary J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f malignant tumors. Safety analysis revealed that azvudine treatment had a lower incidence of adverse events and higher lymphocyte levels than Paxlovid treatment. In conclusion, azvudine treatment is not inferior to Paxlovid treatment in terms of all-cause death, composite disease progression and adverse events in elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Author contributions Bo Yu, Haiyu Wang, Guangming Li, Junyi Sun, and Hong Luo contributed equally to this work. Quancheng Kan, Jiandong Jiang and Zhigang Ren conceived and designed the study; Zhigang Ren, Guangming Li, Guotao Li, Shixi Zhang, Ling Wang, Hong Luo, Donghua Zhang, Silin Li and Guowu Qian managed the patients; Haiyu Wang, Mengzhao Yang, Ming Cheng, Ling Wang, Junyi Sun, Yanyang Zhang and Ruihan Liu collected the data; Bo Yu, Junyi Sun, Mengzhao Yang, and Haiyu Wang analyzed the data; Bo Yu and Haiyu Wang wrote the manuscript; All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Conflicts of interests The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Brunner, Herndler-Brandstetter, Weinberger, Grubeck-Loebenstein, Persistent viral infections and immune aging, Ageing Res Rev
Cdc, Team, Severe outcomes among patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-United States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Chen, Guo, Deng, Wang, Gao et al., All-cause mortality in moderate and severe COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury receiving versus not receiving azvudine: a propensity score-matched analysis, Cardiol Plus
Department, Of Health And Human Services. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) version 5.0
Gandhi, Hirsch, Treating acute Covid-19-final chapters still unwritten, N Engl J Med
Garg, Kim, Whitaker, 'halloran, Cummings et al., Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019-COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1-30, 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Fleishaker, Almas, Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hu, Li, Xing, Gao, Zhao et al., The effect of age on the clinical and immune characteristics of critically ill patients with COVID-19: a preliminary report, PLoS One
J O U R N A L P R E, None
Liu, Wang, Li, Han, Xia et al., Decreased T cell populations contribute to the increased severity of COVID-19, Clin Chim Acta J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
Marzi, Vakil, Bahmanyar, Zarenezhad, Paxlovid: mechanism of action, synthesis, and in silico study, Biomed Res Int
Marzolini, Kuritzkes, Marra, Boyle, Gibbons et al., Recommendations for the management of drug-drug interactions between the COVID-19 antiviral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) and comedications, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Mobinizadeh, Akbarisari, Olyaeemanesh, Mohammadshahi, Ahmadnezhad et al., Safety and efficacy of paxlovid in COVID-19 treatment: a rapid review, Health Tech Asmnt Act, doi:10.18502/htaa.v6i1.11131
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Khoury, Amar et al., Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients, Clin Infect Dis
Osan, Talukdar, Feldmann, Demontigny, Jerome et al., Goblet cell hyperplasia increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Microbiol Spectr
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study, Adv Sci (Weinh)
Sheng, Li, Li, Wang, Wang et al., Selectively T cell phosphorylation activation of azvudine in the thymus tissue with immune protection effect, Acta Pharm Sin B
Sun, Dian, Shen, Zeng, Chen, Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine
Tisminetzky, Delude, Hebert, Carr, Goldberg et al., Age, multiple chronic conditions, and COVID-19: a literature review, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci
Tokarczyk, Kaliszewski, Kopszak, Nowak, Sutkowska-Stępień et al., Liver function tests in COVID-19: assessment of the actual prognostic value, J Clin Med
Vafadar Moradi, Teimouri, Rezaee, Morovatdar, Foroughian et al., Increased age, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and white blood cells count are associated with higher COVID-19 mortality, Am J Emerg Med
Vuorio, Kovanen, Raal, Cholesterol-lowering drugs for high-risk hypercholesterolemia patients with COVID-19 while on Paxlovid™ therapy, Future Virol
Wang, Sun, Zhang, Li, Qin et al., Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study, EClinicalMedicine
Wang, Thomas, Oh, Su, Thymic aging may be associated with COVID-19 pathophysiology in the elderly, Cells
Wang, Yang, Luo, Peng, Dai et al., Azvudine, a novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro, PLoS One
Worldometers, Coronavirus Worldwide Graphs
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Zhao, Cheng, Zhang, Qianda, Zhouma et al., Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in Tibet: a retrospective study, Infect Drug Resist
Zhu, Efficacy and safety evaluation of azvudine in the prospective treatment of COVID-19 based on four phase III clinical trials, Front Pharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032",
"ISSN": [
"2211-3835"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032",
"alternative-id": [
"S2211383524004891"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "A retrospective cohort study of the efficacy and safety of oral azvudine versus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients aged over 60 years"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Haiyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Guangming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Junyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Hong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Mengzhao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yanyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Ruihan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Shixi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Guotao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qian",
"given": "Guowu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Donghua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Silin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kan",
"given": "Quancheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Jiandong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0798-3444",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ren",
"given": "Zhigang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"container-title-short": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-01T00:13:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735690380000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-01T00:13:14Z",
"timestamp": 1735690394000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-01T00:40:23Z",
"timestamp": 1735692023035,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1733011200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1733011200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 27,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735344000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2211383524004891?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2211383524004891?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib1",
"unstructured": "Worldometers. Coronavirus Worldwide Graphs. Published [2024-04-13]. Accessed [2024-04-13]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/worldwide-graphs/#google_vignette."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3",
"article-title": "Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019—COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1-30, 2020",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "458",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib2",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2",
"article-title": "Severe outcomes among patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)—United States, February 12-March 16, 2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib3",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of age on the clinical and immune characteristics of critically ill patients with COVID-19: a preliminary report",
"author": "Hu",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib4",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib5",
"unstructured": "The State Council the People's Republic of China. Notice on the issuance of the diagnosis and treatment protocol for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Trial Tenth Edition). Published [2023-01-05]. Accessed [2024-04-15]. Available from: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2023-01/06/content_5735343.htm."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S423725",
"article-title": "Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in Tibet: a retrospective study",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6053",
"journal-title": "Infect Drug Resist",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib6",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e342",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib7",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/7341493",
"article-title": "Paxlovid: mechanism of action, synthesis, and in silico study",
"author": "Marzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib8",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib9",
"unstructured": "National Medical Products Administration. China grants conditional approval for Pfizer's oral COVID-19 drug. Published [2022-02-14]. Accessed [2024-04-13]. Available from: https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2022-02/14/c_707085.htm."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468",
"article-title": "Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib10",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib11",
"unstructured": "National Medical Products Administration. Domestically developed drug joins virus battle. Published [2022-08-15]. Accessed [2024-04-15]. Available from: http://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2022-08/15/c_797867.htm."
},
{
"article-title": "Azvudine, a novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib12",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety evaluation of azvudine in the prospective treatment of COVID-19 based on four phase III clinical trials",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib13",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib14",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.03.032",
"article-title": "Selectively T cell phosphorylation activation of azvudine in the thymus tissue with immune protection effect",
"author": "Sheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3140",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin B",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib15",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study",
"author": "Ren",
"journal-title": "Adv Sci (Weinh)",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib16",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "All-cause mortality in moderate and severe COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury receiving versus not receiving azvudine: a propensity score-matched analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Cardiol Plus",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib17",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib18",
"unstructured": "The State Council the People's Republic of China. Notice on the issuance of the Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Trial Ninth Edition). Published [2022-03-14]. Accessed [2024-04-15]. Available from: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-03/15/content_5679257.htm. (Accessed 2024-04-15)"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib19",
"unstructured": "U.S. Department Of Health And Human Services. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) version 5.0. Published [2017-11-27]. Accessed [2024-04-15]. Available from: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcae_v5_quick_reference_5x7.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib20",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.003",
"article-title": "Increased age, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and white blood cells count are associated with higher COVID-19 mortality",
"author": "Vafadar Moradi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib21",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11154490",
"article-title": "Liver function tests in COVID-19: assessment of the actual prognostic value",
"author": "Tokarczyk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4490",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib22",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/spectrum.00459-22",
"article-title": "Goblet cell hyperplasia increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"author": "Osan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Microbiol Spectr",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib23",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2010.08.003",
"article-title": "Persistent viral infections and immune aging",
"author": "Brunner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "362",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib24",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10030628",
"article-title": "Thymic aging may be associated with COVID-19 pathophysiology in the elderly",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "628",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib25",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2020.05.019",
"article-title": "Decreased T cell populations contribute to the increased severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Clin Chim Acta",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib26",
"volume": "508",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib27",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2309003",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1186",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib28",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2402224",
"article-title": "Treating acute Covid-19—final chapters still unwritten",
"author": "Gandhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1234",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib29",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of paxlovid in COVID-19 treatment: a rapid review",
"author": "Mobinizadeh",
"journal-title": "Health Tech Asmnt Act",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib30",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2646",
"article-title": "Recommendations for the management of drug–drug interactions between the COVID-19 antiviral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) and comedications",
"author": "Marzolini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1191",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib31",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glaa320",
"article-title": "Age, multiple chronic conditions, and COVID-19: a literature review",
"author": "Tisminetzky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "872",
"journal-title": "J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib32",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2022-0060",
"article-title": "Cholesterol-lowering drugs for high-risk hypercholesterolemia patients with COVID-19 while on Paxlovid™ therapy",
"author": "Vuorio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Future Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032_bib34",
"unstructured": "Drugs-Price Guide. Paxlovid prices, coupons, copay cards & patient assistance. Published [2024-12-22]. Accessed [2024-12-26]. Available from: https://www.drugs.com/price-guide/paxlovid."
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2211383524004891"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A retrospective cohort study of the efficacy and safety of oral azvudine versus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients aged over 60 years",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}