Baseline serum vitamin A and vitamin C levels and their association with disease severity in COVID-19 patients
et al., Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis, doi:10.23750/abm.v94i1.13655, Feb 2023
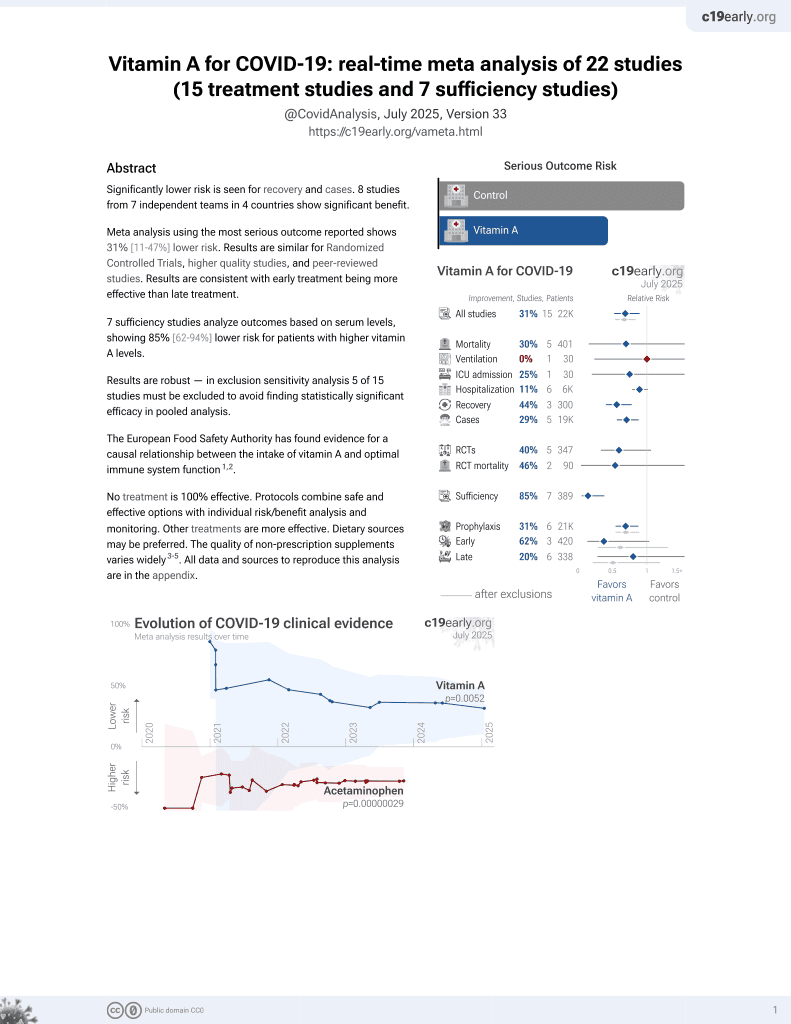
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
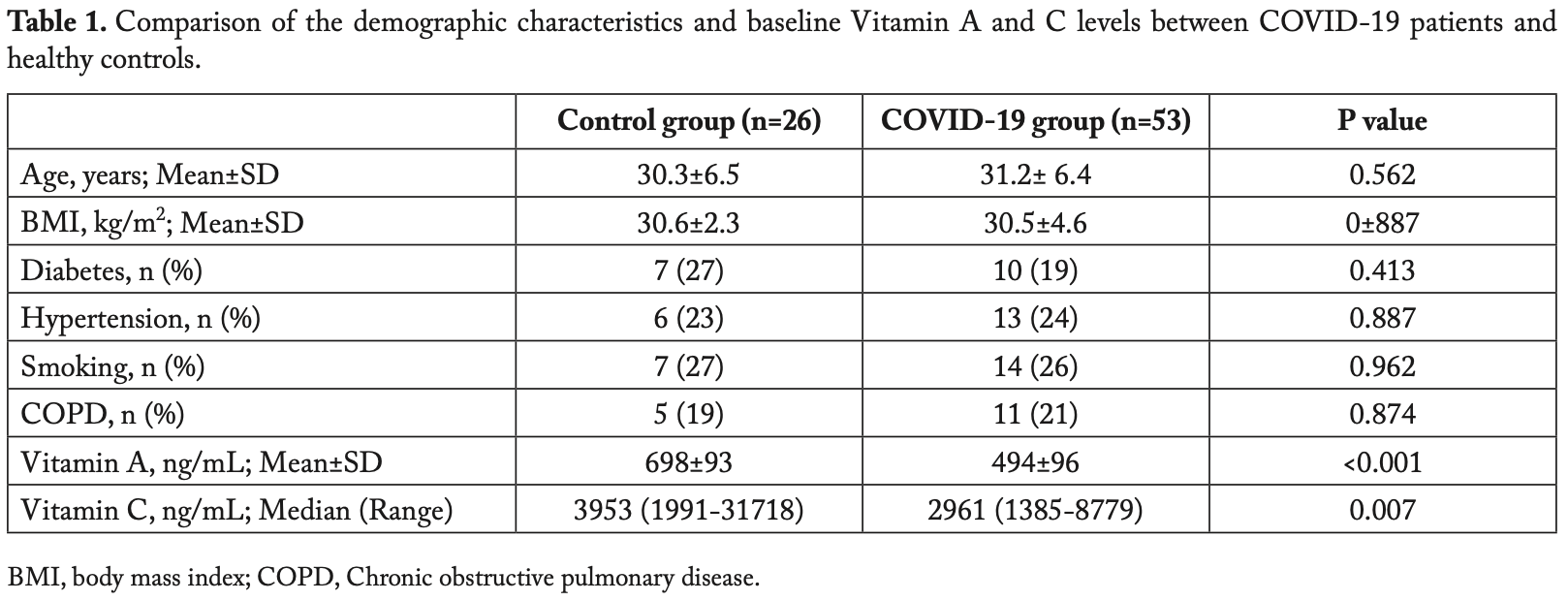
Analysis of 53 consecutive hospitalized COVID-19 patients and 26 matched controls, showing significantly lower vitamin A and vitamin C levels in COVID-19 patients, and a negative correlation between vitamin A and vitamin C levels and CT scores and length of hospitalization.
Study covers vitamin C and vitamin A.
Yilmaz et al., 13 Feb 2023, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period May 2020 - July 2020.
Baseline serum vitamin A and vitamin C levels and their association with disease severity in COVID-19 patients
doi:10.23750/abm.v94i1.13655
Aim: We aimed to investigate the association between the serum concentrations of Vitamin A and Vitamin C and the severity of the COVID-19. Methods: Fifty-three consecutive PCR (+) COVID-19 patients admitted to a dedicated ward were enrolled in this study. Blood samples for serum Vitamin A and C measurements were drawn from all participants upon admission. All subjects underwent thoracic CT imaging prior to hospitalization. CT severity score (CT-SS) was then calculated for determining the extent of pulmonary involvement. A group of healthy volunteers, in whom COVID-19 was ruled out, were assigned to the control group (n=26). These groups were compared by demographic features and serum vitamin A and C levels. The relationship between serum concentrations of these vitamins and pre-defined outcome measures, CT-SS and length of hospitalization (LOH), was also assessed. Results: In COVID-19 patients, serum Vitamin A (ng/ml, 494±96 vs. 698±93; p<0.001) and Vitamin C (ng/ml, 2961 [1991-31718] vs. 3953 [1385-8779]; p=0.007) levels were significantly lower with respect to healthy controls. According to the results of correlation analyses, there was a significant negative association between Vitamin A level and outcome measures (LOH, p=0.010). The negative correlations between Vitamin C level and those measures were even more prominent (LOH, r=-0.478; p<0.001 and CT-SS, r=-0.734: p<0.001). Conclusion: COVID-19 patients had lower baseline serum Vitamin A and Vitamin C levels as compared to healthy controls. In subjects with COVID-19, Vitamin A and Vitamin C levels were negatively correlated with CT-SS and LOH. (www.actabiomedica.it)
References
Arraes, Freitas, Da Silva, De, Neto et al., Impaired neutrophil chemotaxis in sepsis associates with GRK expression and inhibition of actin assembly and tyrosine phosphorylation, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2006-05-024638
Coppock, Violet, Vasquez, Pharmacologic Ascorbic Acid as Early Therapy for Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Life, doi:10.3390/life12030453
Demaret, Venet, Friggeri, Marked alterations of neutrophil functions during sepsis-induced immunosuppression, J Leukoc Biol, doi:10.1189/jlb.4A0415-168RR
Derya Ozden Omaygenc, Istanbul, Training, & Research Hospital, Department of Anesthesiology, Ugur Mumcu
Farjana, Moni, Sohag, Repositioning Vitamin C as a Promising Option to Alleviate Complications associated with COVID-19, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2020.52.4.461
Fisher, Kraskauskas, Martin, Mechanisms of attenuation of abdominal sepsis induced acute lung injury by ascorbic acid, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00300.2011
Heuser, Vojdani, Enhancement of natural killer cell activity and T and B cell function by buffered vitamin C in patients exposed to toxic chemicals: the role of protein kinase-C, Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, doi:10.3109/08923979709046977
Hummel, Whitcroft, Rueter, Haehner, Intranasal vitamin A is beneficial in post-infectious olfactory loss, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1007/s00405-017-4576-x
Hunt, Chakravorty, Annan, Habibzadeh, Schorah, The clinical effects of vitamin C supplementation in elderly hospitalised patients with acute respiratory infections, Int J Vitam Nutr Res
Jamal, Bangash, Habiba, Immune dysregulation and system pathology in COVID-19, Virulence, doi:10.1080/21505594.2021.1898790
Jimenez, Watson, Parodo, Dysregulated expression of neutrophil apoptosis in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome, Arch Surg, doi:10.1001/archsurg.1997.01430360009002
Kim, Kim, Bae, Vitamin C Is an Essential Factor on the Anti-viral Immune Responses through the Production of Interferon-α/β at the Initial Stage of Influenza A Virus (H3N2) Infection, Immune Netw, doi:10.4110/in.2013.13.2.70
Kiss, Rühl, Szegezdi, Retinoid receptor-activating ligands are produced within the mouse thymus during postnatal development, Eur J Immunol, doi:10.1002/eji.200737342
Koo, Jetten, Belloni, Yoon, Kim et al., Role of retinoid receptors in the regulation of mucin gene expression by retinoic acid in human tracheobronchial epithelial cells, Biochem J
Kuwata, Wang, Tamura, Vitamin A deficiency in mice causes a systemic expansion of myeloid cells, Blood
Li, Wu, Li, Revealing the targets and mechanisms of vitamin A in the treatment of COVID-19, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103888
Mccullough, Clewes, Thurnham, The effect of vitamin A on epithelial integrity, Proc Nutr Soc, doi:10.1017/s0029665199000403
Mochalkin, Askorbinovaia kislota v kompleksnoĭ terapii bol'nykh ostroĭ pnevmonieĭ [Ascorbic acid in the complex therapy of acute pneumonia
Mohammed, Fisher, Kraskauskas, Vitamin C promotes wound healing through novel pleiotropic mechanisms, Int Wound J, doi:10.1111/iwj.12484
Murni, Prawirohartono, Triasih, Potential Role of Vitamins and Zinc on Acute Respiratory Infections Including Covid-19, Glob Pediatr Health, doi:10.1177/2333794X211021739
Odegaard, Chawla, Connecting type 1 and type 2 diabetes through innate immunity. Cold Spring Harb Per, spect Med, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a007724
Pecoraro, Crescenzi, Galdiero, Immunosuppressive therapy with rituximab in common variable immunodeficiency, Clin Mol Allergy, doi:10.1186/s12948-019-0113-3
Pereira, Mohan, Cohen, COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: Initial report from the US epicenter, Am J Transplant, doi:10.1111/ajt.15941
Qi, Niu, Zhu, Zhao, Yang et al., Relationship between deficiencies in vitamin A and E and occurrence of infectious diseases among children, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Riva, Conti, Bernacchia, Darunavir does not prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in HIV patients, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104826
Shiau, Krause, Valera, Swaminathan, Halkitis, The Burden of COVID-19 in People Living with HIV: A Syndemic Perspective, AIDS Behav, doi:10.1007/s10461-020-02871-9
Stephensen, Lietz, Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114521000246
Sulaiman, Aljuhani, Saleh, Ascorbic acid as an adjunctive therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a propensity score matched study, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-96703-y.Correspondence:Received:5
Sultangazi, None
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Tian, Yuan, Xiao, Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with COVID-19 disease severity in patients with cancer in Wuhan, China: a multicentre, retrospective, cohort study, Lancet Oncol, doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30309-0
Van Bennekum, Wong, Kong, Gijbels, Mitogen response of B cells, but not T cells, is impaired in adult vitamin A-deficient rats, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/121.12.1960
Wang, Swartz-Basile, Rubin, Levin, Retinoic acid stimulates early cellular proliferation in the adapting remnant rat small intestine after partial resection, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/127.7.1297
Wang, Yu, Kane, Moise, Modulation of retinoid signaling: therapeutic opportunities in organ fibrosis and repair, Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107415
Yang, Li, Liu, Zhen, Zhang et al., Chest CT Severity Score: An Imaging Tool for Assessing Severe COVID-19, Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging, doi:10.1148/ryct.2020200047
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.23750/abm.v94i1.13655",
"ISSN": "2531-6745, 0392-4203",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v94i1.13655",
"abstract": "Aim: We aimed to investigate the association between the serum concentrations of Vitamin A and Vitamin C and the severity of the COVID-19. Methods: Fifty-three consecutive PCR (+) COVID-19 patients admitted to a dedicated ward were enrolled in this study. Blood samples for serum Vitamin A and C measurements were drawn from all participants upon admission. All subjects underwent thoracic CT imaging prior to hospitalization. CT severity score (CT-SS) was then calculated for determining the extent of pulmonary involvement. A group of healthy volunteers, in whom COVID-19 was ruled out, were assigned to the control group (n=26). These groups were compared by demographic features and serum vitamin A and C levels. The relationship between serum concentrations of these vitamins and pre-defined outcome measures, CT-SS and length of hospitalization (LOH), was also assessed. Results: In COVID-19 patients, serum Vitamin A (ng/ml, 494±96 vs. 698±93; p<0.001) and Vitamin C (ng/ml, 2961 [1991-31718] vs. 3953 [1385-8779]; p=0.007) levels were significantly lower with respect to healthy controls. According to the results of correlation analyses, there was a significant negative association between Vitamin A level and outcome measures (LOH, r=-0.293; p=0.009 and CT-SS, r=-0.289; p=0.010). The negative correlations between Vitamin C level and those measures were even more prominent (LOH, r=-0.478; p<0.001 and CT-SS, r=-0.734: p<0.001). Conclusion: COVID-19 patients had lower baseline serum Vitamin A and Vitamin C levels as compared to healthy controls. In subjects with COVID-19, Vitamin A and Vitamin C levels were negatively correlated with CT-SS and LOH.",
"author": [
{
"family": "Yilmaz",
"given": "Gulseren"
},
{
"family": "Bulut",
"given": "Huri"
},
{
"family": "Ozden Omaygenc",
"given": "Derya"
},
{
"family": "Akca",
"given": "Aysu"
},
{
"family": "Can",
"given": "Esra"
},
{
"family": "Tuten",
"given": "Nevin"
},
{
"family": "Bestel",
"given": "Aysegul"
},
{
"family": "Erdem",
"given": "Baki"
},
{
"family": "Atmaca",
"given": "Uygar Ozan"
},
{
"family": "Kara",
"given": "Yasin"
},
{
"family": "Kaya",
"given": "Ebru"
},
{
"family": "Unsel",
"given": "Murat"
},
{
"family": "Sahin",
"given": "Ayca Sultan"
},
{
"family": "Salihoglu",
"given": "Ziya"
}
],
"container-title": "Acta Biomedica Atenei Parmensis",
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
13
]
]
},
"language": "eng",
"medium": "JB",
"page": "e2023007",
"page-first": "e2023007",
"publisher": "Mattioli 1885 srl",
"publisher-place": "IT",
"title": "Baseline serum vitamin A and vitamin C levels and their association with disease severity in COVID-19 patients: Serum Vitamin A and C levels and COVID-19 severity",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "94"
}