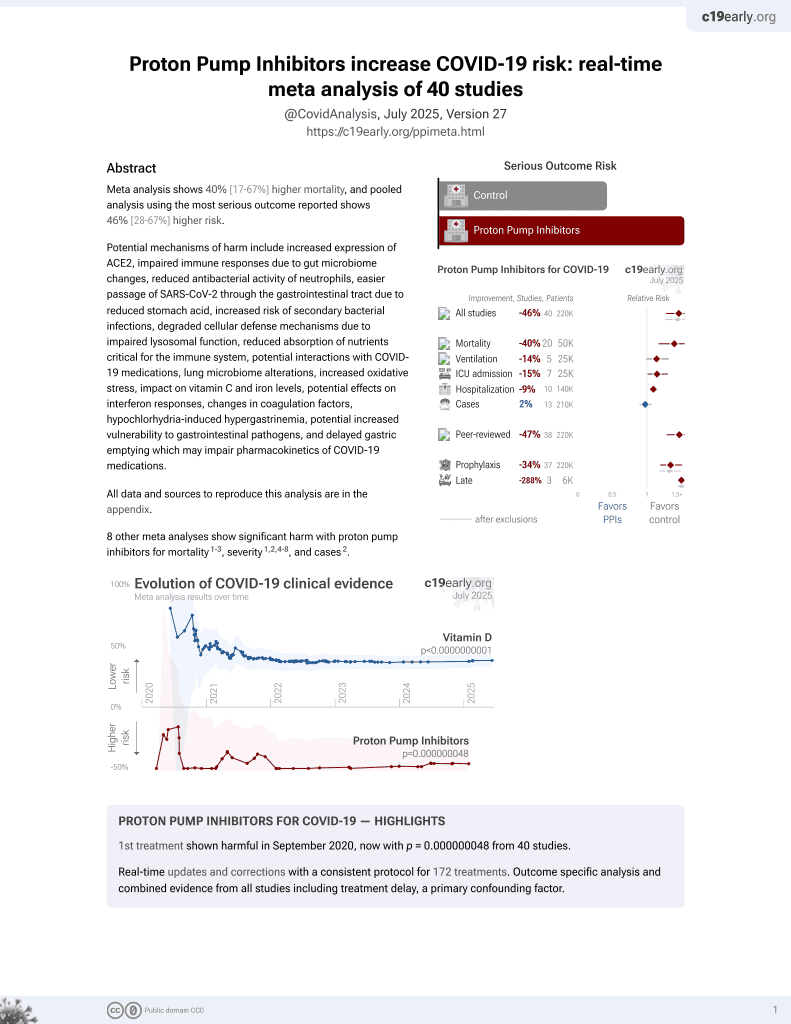
Impact of proton pump inhibitors on the in-hospital outcome of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study
et al., Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology, doi:10.1177/17562848221104365, Jan 2022
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 3,024 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing increased risk of the composite outcome of ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use. Intravenous administration was significantly worse than oral. Authors hypothesize that PPIs may lead to worse COVID-19 outcomes by increasing the risk of secondary infections, cardiac damage, renal damage, and liver complications.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
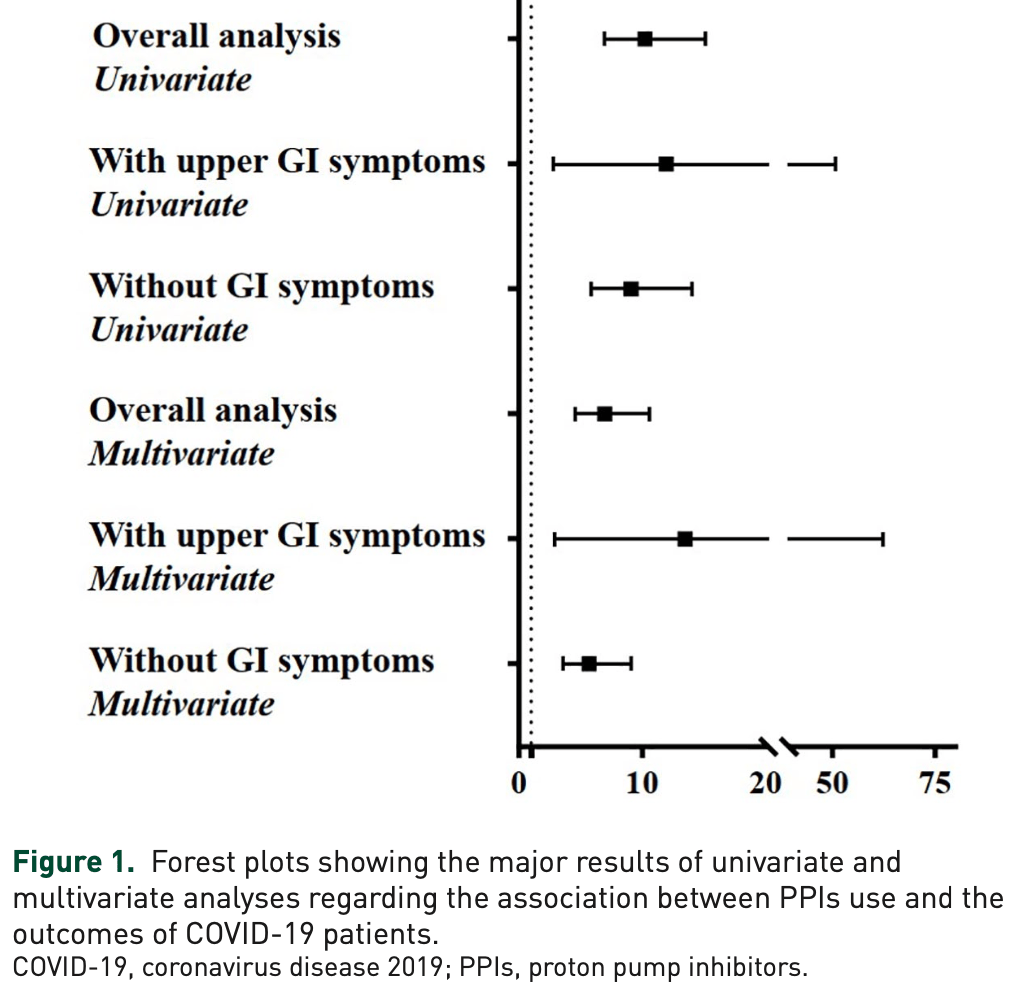
risk of severe case, 600.0% higher, OR 7.00, p < 0.001, treatment 694, control 2,330, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of severe case, 2501.0% higher, OR 26.01, p < 0.001, treatment 82, control 2,330, adjusted per study, intravenous, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of severe case, 95.0% higher, OR 1.95, p = 0.02, treatment 537, control 2,330, oral, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Yao et al., 31 Jan 2022, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, median age 60.0, 17 authors, study period February 2020 - April 2020.
Contact: xingshunqi@126.com, chloe212@live.cn, notherntheater@126.com.
Impact of proton pump inhibitors on the in-hospital outcome of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology, doi:10.1177/17562848221104365
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has triggered a global public health crisis. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are one of the most commonly prescribed drugs. However, the effect of PPIs on the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients remains unclear. Methods: All COVID-19 patients admitted to the Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital from February 2020 to April 2020 were retrospectively collected. Patients were divided into PPIs and non-PPIs groups. Logistic regression analyses were performed to explore the effects of PPIs on the outcomes of COVID-19 patients, including transfer to intensive care unit, mechanical ventilation, and death. Subgroup analyses were performed according to the presence of upper gastrointestinal symptoms potentially associated with acid and the routes, types, median total dosage, and duration of PPIs. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. Results: Of the 3024 COVID-19 patients included, 694 and 2330 were in PPIs and non-PPIs groups, respectively. Univariate logistic regression analysis showed that PPIs significantly increased the risk of reaching the composite endpoint in COVID-19 patients (OR = 10.23, 95% CI = 6.90-15.16, p < 0.001). After adjusting for age, sex, comorbidities, other medications, and severe/critical COVID-19, PPIs were independently associated with an increased risk of reaching the composite endpoint (OR = 7.00, 95% CI = 4.57-10.71, p < 0.001). This association remained significant in patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms and those who received an intravenous omeprazole alone, but not those who received oral lansoprazole or rabeprazole alone. It was not influenced by dosage or duration of PPIs.
Conclusion: The use of intravenous PPIs alone during hospitalization may be associated with worse clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients.
Authors' Note The abstract of the paper has been presented by two major authors as a poster at the 21st Congress of Gastroenterology China (CGC), which was published in 2021 in the Journal of Digestive Diseases (doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.13053).
Author contributions
ORCID iD Xingshun Qi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9448-6739
Conflict of interest statement The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Availability of data and material The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Supplemental material Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
Almario, Chey, Spiegel, Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors, Am J Gastroenterol
Barletta, Sclar, Use of proton pump inhibitors for the provision of stress ulcer prophylaxis: clinical and economic consequences, Pharmacoeconomics
Benlabed, Mena, Gaudy, Analysis of particulate exposure during continuous drug infusion in critically ill adult patients: a preliminary proof-of-concept in vitro study, Intensive Care Med Exp
Blank, Parkin, Paul, A nationwide nested case-control study indicates an increased risk of acute interstitial nephritis with proton pump inhibitor use, Kidney Int
Brooks, Intravenous cannula site management, Nurs Stand
Ca, Benea, Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, J Gastrointestin Liver Dis
Chen, Tong, Ma, Gastrointestinal bleeding, but not other gastrointestinal symptoms, is associated with worse outcomes in COVID-19 patients, Front Med
Cyriac, Switch over from intravenous to oral therapy: a concise overview, J Pharmacol Pharmacother
Dam, Vilstrup, Watson, Proton pump inhibitors as a risk factor for hepatic encephalopathy and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis with ascites, Hepatology
Feng, Wang, Ma, Dynamic change of serum albumin level can predict the prognosis of COVID-19 patients with hypoalbuminemia, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27439
Haastrup, Thompson, Søndergaard, Side effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor use: a review, Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol
Ho, Maddox, Wang, Risk of adverse outcomes associated with concomitant use of clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors following acute coronary syndrome, JAMA
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Hunt, East, Lanas, COVID-19 and gastrointestinal disease: implications for the gastroenterologist, Dig Dis
Hunt, The protective role of gastric acid, Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl
Jackson, Goodrich, Maxan, Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota, Gut
Kow, Hasan, Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of adverse clinical outcomes from COVID-19: a meta-analysis, J Intern Med
Liu, Tao, Liu, GI symptoms and fever increase the risk of severe illness and death in patients with COVID-19, Gut
Luxenburger, Sturm, Biever, Treatment with proton pump inhibitors increases the risk of secondary infections and ARDS in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: coincidence or underestimated risk factor?, J Intern Med
Malfertheiner, Kandulski, Venerito, Proton-pump inhibitors: understanding the complications and risks, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol
Martinsen, Bergh, Waldum, Gastric juice: a barrier against infectious diseases, Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol
Martinsen, Fossmark, Waldum, The phylogeny and biological function of gastric juice-microbiological consequences of removing gastric acid, Int J Mol Sci
Moledina, Perazella, PPIs and kidney disease: from AIN to CKD, J Nephrol
Nehra, Alexander, Loftus, Proton pump inhibitors: review of emerging concerns, Mayo Clin Proc
Shin, Sachs, Pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors, Curr Gastroenterol Rep
Siller-Matula, Jilma, Schrör, Effect of proton pump inhibitors on clinical outcome in patients treated with clopidogrel: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Thromb Haemost
Tantai, Yang, Wei, Association of proton pump inhibitors with risk of hepatic encephalopathy in advanced liver disease: a meta-analysis, World J Gastroenterol
Tzotzos, Fischer, Fischer, Incidence of ARDS and outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a global literature survey, Crit Care
Van Boxel, Van Oijen, Hagenaars, Cardiovascular and gastrointestinal outcomes in clopidogrel users on proton pump inhibitors: results of a large Dutch cohort study, Am J Gastroenterol
Von Elm, Altman, Egger, The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies, Lancet
Who, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic
Wong, Lui, Sung, Covid-19 and the digestive system, J Gastroenterol Hepatol
Wu, Ma, Guo, Characteristics and in-hospital outcomes of COVID-19 patients with abnormal liver biochemical tests, Ann Hepatol
Wu, Ma, Guo, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 patients with hypoxic hepatitis, Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol
Ye, Wang, Zhang, The mechanism and treatment of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with COVID-19, Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol
Yibirin, Oliveira, Valera, Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitor use, Cureus
Zhang, Guo, Ma, Characteristics and in-hospital outcomes of COVID-19 patients with acute or subacute liver failure, Dig Liver Dis
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zhu, Qi, Yu, Association of proton pump inhibitors with the risk of hepatic encephalopathy during hospitalization for liver cirrhosis, United European Gastroenterol J
Zhu, Yu, Mancuso, Proton pump inhibitors in liver cirrhosis: a review of benefits and harms, Immunity
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/17562848221104365",
"ISSN": [
"1756-2848",
"1756-2848"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/17562848221104365",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background:</jats:title><jats:p>Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has triggered a global public health crisis. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are one of the most commonly prescribed drugs. However, the effect of PPIs on the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients remains unclear.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods:</jats:title><jats:p>All COVID-19 patients admitted to the Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital from February 2020 to April 2020 were retrospectively collected. Patients were divided into PPIs and non-PPIs groups. Logistic regression analyses were performed to explore the effects of PPIs on the outcomes of COVID-19 patients, including transfer to intensive care unit, mechanical ventilation, and death. Subgroup analyses were performed according to the presence of upper gastrointestinal symptoms potentially associated with acid and the routes, types, median total dosage, and duration of PPIs. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results:</jats:title><jats:p>Of the 3024 COVID-19 patients included, 694 and 2330 were in PPIs and non-PPIs groups, respectively. Univariate logistic regression analysis showed that PPIs significantly increased the risk of reaching the composite endpoint in COVID-19 patients (OR = 10.23, 95% CI = 6.90–15.16, p < 0.001). After adjusting for age, sex, comorbidities, other medications, and severe/critical COVID-19, PPIs were independently associated with an increased risk of reaching the composite endpoint (OR = 7.00, 95% CI = 4.57–10.71, p < 0.001). This association remained significant in patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms and those who received an intravenous omeprazole alone, but not those who received oral lansoprazole or rabeprazole alone. It was not influenced by dosage or duration of PPIs.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion:</jats:title><jats:p>The use of intravenous PPIs alone during hospitalization may be associated with worse clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/17562848221104365"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Postgraduate College, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Yao",
"given": "Haijuan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Hongyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Medicine, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Zhuang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Yanyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Yufu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Meng",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Chengfei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Teng",
"given": "Yue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Quanyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Medicine, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "No.7 Department of Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Tianyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Medicine, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Section of Medical Service, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Haitao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Information Section of Medical Security Center, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Chu",
"given": "Guiyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Section of Medical Service, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Zhenhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, No. 83 Wenhua Road, Shenyang, Liaoning Province 110840, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Section of Medical Service, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110840, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, No. 83 Wenhua Road, Shenyang, Liaoning Province 110840, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9448-6739",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "COVID-19 Study Group, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110840, P.R. China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, No. 83 Wenhua Road, Shenyang, Liaoning Province 110840, P.R. China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Qi",
"given": "Xingshun",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology",
"container-title-short": "Therap Adv Gastroenterol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-14T10:00:48Z",
"timestamp": 1655200848000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-08T04:20:11Z",
"timestamp": 1675830011000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-09T05:15:59Z",
"timestamp": 1675919759954
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640995200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/17562848221104365",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/17562848221104365",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/17562848221104365",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "175628482211043",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr1-17562848221104365"
},
{
"key": "bibr2-17562848221104365",
"unstructured": "WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed 13 April 2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgh.15047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000512152",
"author": "Hunt RH",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis",
"key": "bibr5-17562848221104365",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.759152",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40273-013-0119-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2017.10.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto960202.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20236031",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-17562848221104365"
},
{
"author": "Yibirin M",
"first-page": "e12759",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "bibr11-17562848221104365",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrgastro.2017.117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dld.2021.05.027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27439.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aohep.2021.100349",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101665",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-17562848221104365"
},
{
"author": "General Office of National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China",
"first-page": "801",
"journal-title": "China Med",
"key": "bibr18-17562848221104365",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/00365528809099128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11894-008-0098-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310861",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-17562848221104365"
},
{
"author": "Liu J",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "bibr23-17562848221104365",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpgi.00148.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcpt.13023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13121",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03240-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2009.261",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ajg.2010.334",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04049.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40620-016-0309-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ki.2014.74",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-17562848221104365"
},
{
"author": "Căruntu FA",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "J Gastrointestin Liver Dis",
"key": "bibr33-17562848221104365",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.28737",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v25.i21.2683",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr35-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2050640618773564",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr36-17562848221104365"
},
{
"author": "Zhu J",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "bibr37-17562848221104365",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40635-018-0205-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr38-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0976-500X.130042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr39-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7748/ns.2016.e10315",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr40-17562848221104365"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr41-17562848221104365"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/17562848221104365"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of proton pump inhibitors on the in-hospital outcome of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "15"
}