The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
et al., Open Medicine, doi:10.1515/med-2022-0569, Aug 2022
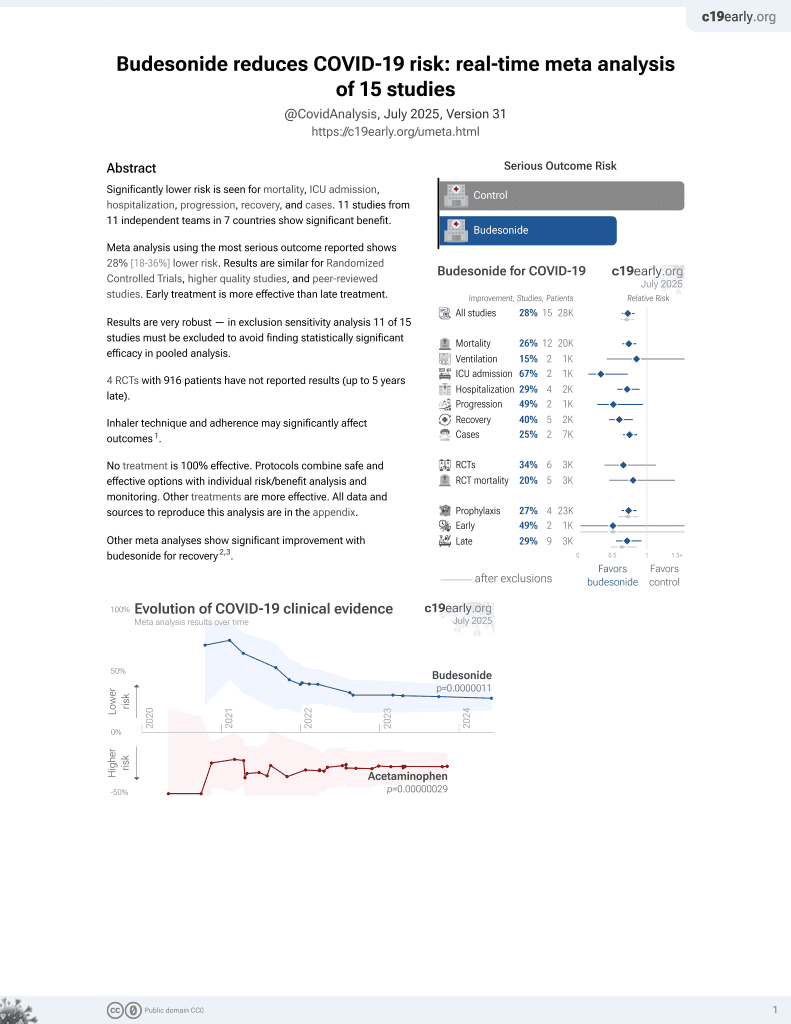
Budesonide for COVID-19
28th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2021, now with p = 0.0000042 from 14 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
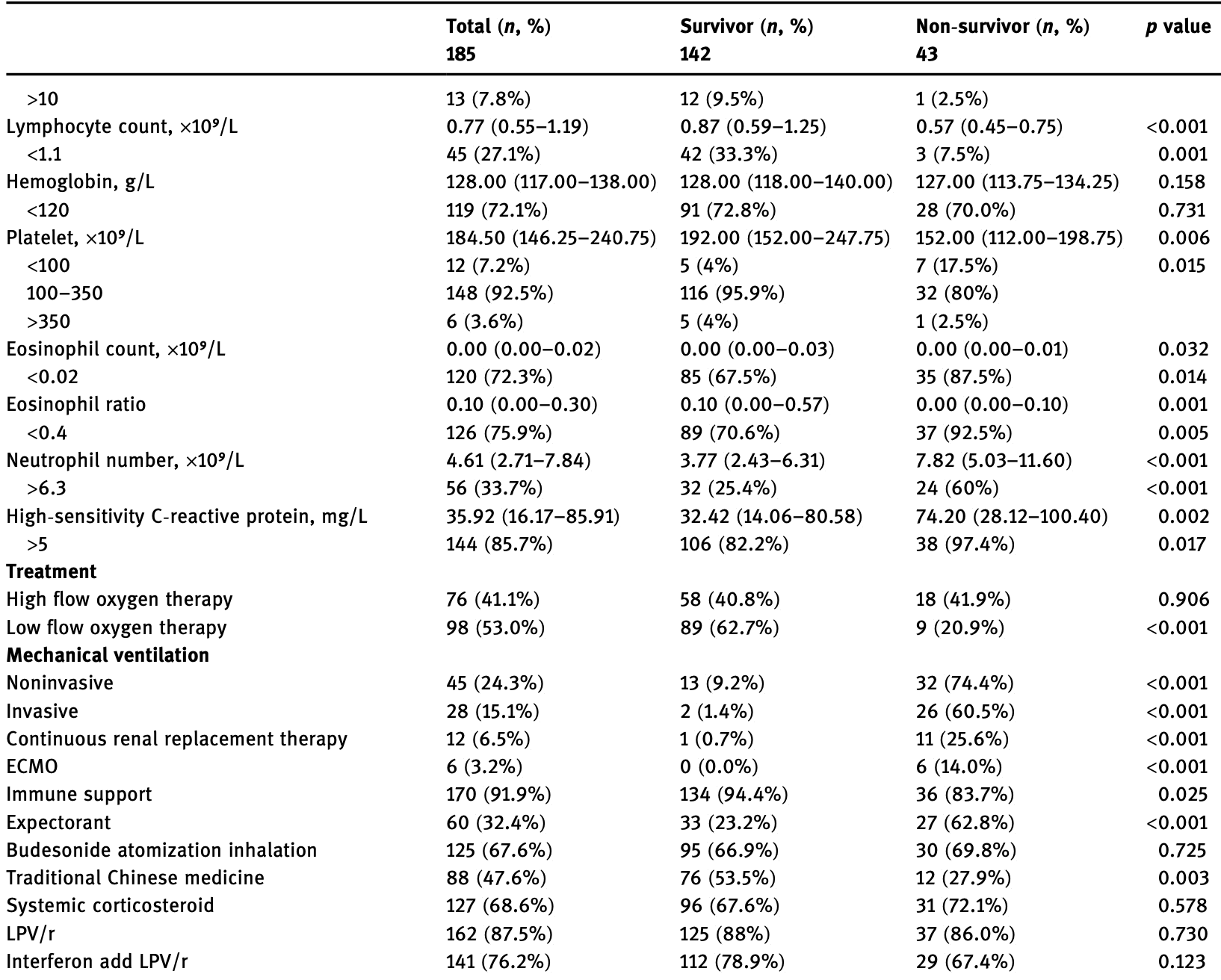
Retrospective 185 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China, showing no significant difference in mortality with budesonide use in unadjusted results.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of death, 10.8% higher, RR 1.11, p = 0.85, treatment 30 of 125 (24.0%), control 13 of 60 (21.7%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Yang et al., 31 Aug 2022, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, median age 62.0, 12 authors, study period 1 January, 2020 - 29 February, 2020.
Contact: 2205603@tongji.edu.cn, 1220775601@qq.com, 29553185@qq.com.
The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
Open Medicine, doi:10.1515/med-2022-0569
Since December, 2019, Wuhan, China, has experienced an outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 . We conducted a retrospective study of COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital (Wuhan, China) from January 1 to February 29, 2020. The subjects were divided into four groups due to different treatment regimes. We used the Kaplan-Meier method to determine the cumulative rates of in-hospital death and the Cox proportional hazard model to calculate the risk factors and corresponding hazard ratios. A total of 185 patients were included in this study. The median age of the patients was 62 years, including 94 men and 91 women. Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that mortality was higher in older patients, higher in men, and lower in the low-flow oxygen therapy group. Body mass index (BMI) had no influence on mortality, as well as high flow oxygen therapy, Lopinavir-ritonavir (LPV/r) therapy, and the interferon-alpha add LPV/r therapy. Cox proportional hazard regression confirmed that the low flow oxygen therapy was independent protective factor for in-hospital death after adjusting for age, gender, and BMI. In conclusion, the mortality was higher in older patients, higher in men, and lower in the low-flow oxygen therapy group. BMI had no influence on mortality, as well as high flow oxygen therapy, LPV/r therapy, and interferon-alpha add LPV/r therapy.
Abbreviations
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
References
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282.Epub2020
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lofy, Wiesman et al., First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001191.Epub2020
Li, Guan, Wu, Wang, Zhou et al., Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirusinfected pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316.Epub2020
Mo, Xing, Xiao, Deng, Zhao et al., Clinical characteristics of refractory COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa270
Wang, Pan, Tan, Xu, Ho, Immediate psychological responses and associated factors during the initial stage of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic among the general population in China, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17051729
Wenham, Smith, Morgan, COVID-19: the gendered impacts of the outbreak, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30526-2.Epub2020
Wu, Liu, Zhao, Liu, Wang, Clinical characteristics of imported cases of COVID-19 in Jiangsu Province: a multicenter descriptive study, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa199
Zeng, Xu, He, Tang, Li et al., Comparative effectiveness and safety of ribavirin plus interferon-alpha, lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alpha and ribavirin plus lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alphain in patients with mild to moderate novel coronavirus pneumonia, Chin Med J, doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000790
Zhao, Cao, Chong, Gao, Lou et al., The timevarying serial interval of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and its gender-specific difference: A data-driven analysis using public surveillance data in Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China from January 10 to, Infect Control Hospital Epidemiol, doi:10.1017/ice.2020.64
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017.Epub2020
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1515/med-2022-0569",
"ISSN": [
"2391-5463"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/med-2022-0569",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Since December, 2019, Wuhan, China, has experienced an outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We conducted a retrospective study of COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital (Wuhan, China) from January 1 to February 29, 2020. The subjects were divided into four groups due to different treatment regimes. We used the Kaplan–Meier method to determine the cumulative rates of in-hospital death and the Cox proportional hazard model to calculate the risk factors and corresponding hazard ratios. A total of 185 patients were included in this study. The median age of the patients was 62 years, including 94 men and 91 women. Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated that mortality was higher in older patients, higher in men, and lower in the low-flow oxygen therapy group. Body mass index (BMI) had no influence on mortality, as well as high flow oxygen therapy, Lopinavir–ritonavir (LPV/r) therapy, and the interferon-alpha add LPV/r therapy. Cox proportional hazard regression confirmed that the low flow oxygen therapy was independent protective factor for in-hospital death after adjusting for age, gender, and BMI. In conclusion, the mortality was higher in older patients, higher in men, and lower in the low-flow oxygen therapy group. BMI had no influence on mortality, as well as high flow oxygen therapy, LPV/r therapy, and interferon-alpha add LPV/r therapy.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1515/med-2022-0569"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Shanghai Fourth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University , Shanghai , China"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Ling",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tuberculosis department, Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Guoxi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Public Health, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine , Shanghai , China"
}
],
"family": "Cai",
"given": "Yuyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Xinhua Hospital , Shanghai , China"
}
],
"family": "An",
"given": "Ye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pudong Institute of Preventive Medicine, Fudan University , Shanghai , China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xiaopan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Xinhua Hospital , Shanghai , China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Xinhua Hospital , Shanghai , China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Cheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Warwick Clinical Trials Unit, Warwick Medical School , Warwick , Great Britain"
}
],
"family": "Ji",
"given": "Chen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tuberculosis department, Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Lan",
"given": "Xing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tuberculosis department, Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yaling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tuberculosis department, Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital , Wuhan , China"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Hai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Xinhua Hospital , Shanghai , China"
}
],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Open Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-22T14:25:57Z",
"timestamp": 1669127157000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-06T22:53:26Z",
"timestamp": 1670367206000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-07T06:01:23Z",
"timestamp": 1670392883193
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640995200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/med-2022-0569/xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/med-2022-0569/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "374",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1833-1839",
"prefix": "10.1515",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Walter de Gruyter GmbH",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_001",
"unstructured": "Chinese researchers reveal draft genome of virus implicated in Wuhan pneumonia outbreak. (https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2020/01/chinese-researchers-reveal-draft-genome-virus-implicated-wuhan-pneumonia-outbreak)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_002",
"unstructured": "Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:727–33. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017.Epub2020."
},
{
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_003",
"unstructured": "WHO Director-General’s Remarks at the Media Briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. (https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-2019-ncov-on-11-february-2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001316",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_004",
"unstructured": "Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(13):1199–207. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316.Epub2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_005",
"unstructured": "Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, et al. First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(10):929–36. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001191.Epub2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000790",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_006",
"unstructured": "Zeng YM, Xu XL, He XQ, Tang SQ, Li Y, Huang YQ, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of ribavirin plus interferon-alpha, lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alpha and ribavirin plus lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alphain in patients with mild to moderate novel coronavirus pneumonia. Chin Med J. 2020;133(9):1132–4. 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000790."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2008043",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_007",
"unstructured": "Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, et al. A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(19):1787–99. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282.Epub2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa270",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_008",
"unstructured": "Mo P, Xing Y, Xiao Y, Deng L, Zhao Q, Wang H, et al. Clinical characteristics of refractory COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;73(11):e4208–213. 10.1093/cid/ciaa270."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph17051729",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_009",
"unstructured": "Wang C, Pan R, Wan X, Tan Y, Xu L, Ho C, et al. Immediate psychological responses and associated factors during the initial stage of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic among the general population in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1729. 10.3390/ijerph17051729."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30526-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_010",
"unstructured": "Wenham C, Smith J, Morgan R. COVID-19: the gendered impacts of the outbreak. Lancet (London, Engl). 2020;395:846–8. 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30526-2.Epub2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/ice.2020.64",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_011",
"unstructured": "Zhao S, Cao P, Chong MK, Gao D, Lou Y, Ran J, et al. The time-varying serial interval of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and its gender-specific difference: A data-driven analysis using public surveillance data in Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China from January 10 to February 15, 2020. Infect Control Hospital Epidemiol. 2020;10(5):1–8. 10.1017/ice.2020.64."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa199",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022120618374797156_j_med-2022-0569_ref_012",
"unstructured": "Wu J, Liu J, Zhao X, Liu C, Wang W, Wang D, et al. Clinical characteristics of imported cases of COVID-19 in Jiangsu Province: a multicenter descriptive study. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(15):706–12. 10.1093/cid/ciaa199."
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/med-2022-0569/html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}