Beyond Stress Granules: G3BP1 and G3BP2 Redundantly Suppress SARS-CoV-2 Infection
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17070912, Jun 2025
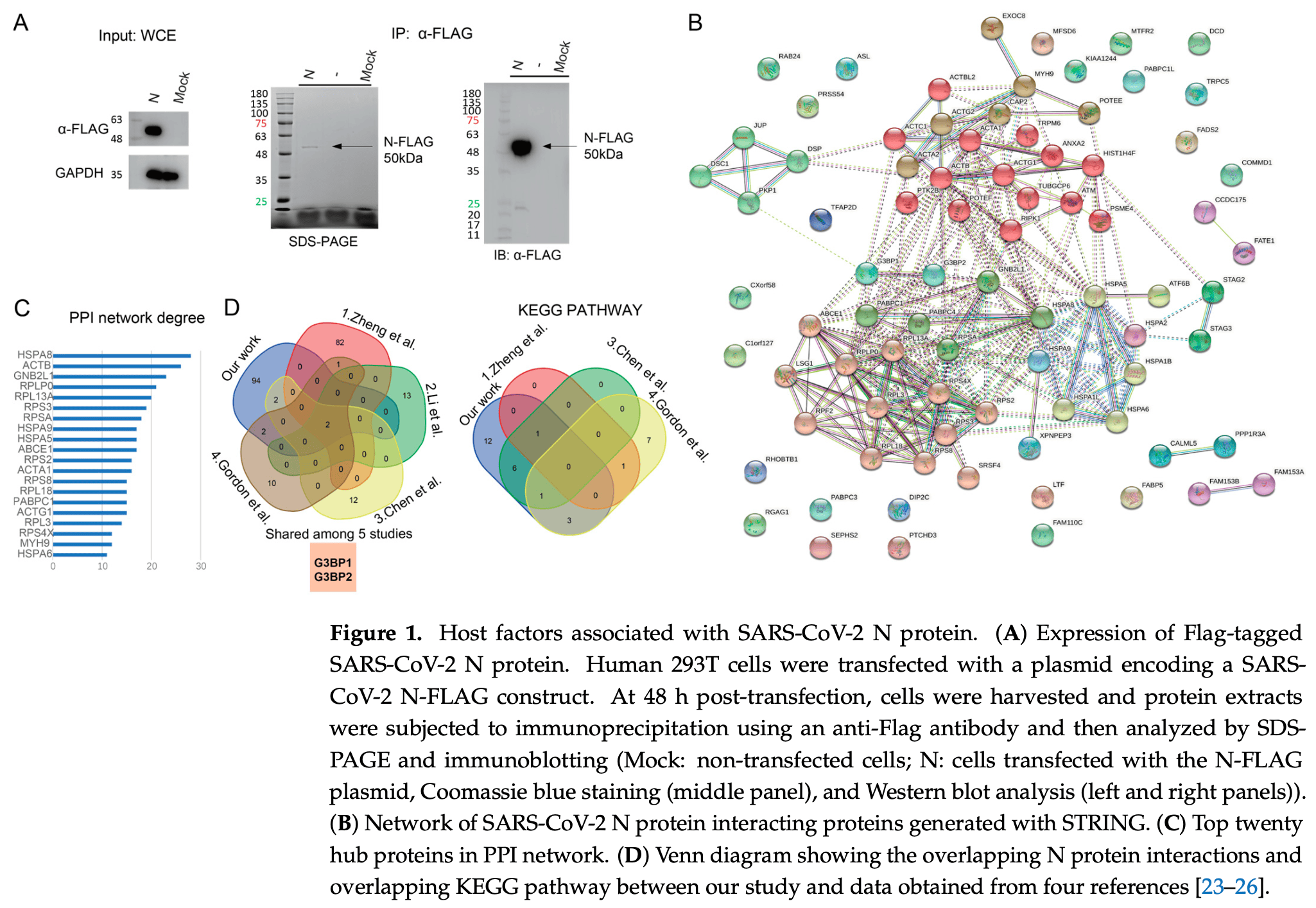
In vitro study showing that G3BP1 and G3BP2 proteins redundantly suppress SARS-CoV-2 infection by inhibiting viral replication beyond their roles in stress granule formation. Authors identified G3BP1/2 as key host factors that interact with the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein through a comparative analysis of multiple proteomic datasets.
Xu et al., 27 Jun 2025, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: ronghai@ucr.edu (corresponding author), duox@ucr.edu, christine.light@email.ucr.edu, ywu548@ucr.edu, mbisw002@ucr.edu, jikuis@ucr.edu, quanqinz@ucr.edu, chenjinye@txbiomed.org, lmartinez@txbiomed.org.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Beyond Stress Granules: G3BP1 and G3BP2 Redundantly Suppress SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17070912
The global pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has posed unprecedented challenges to public health and economic stability. Central to SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis is its ability to evade the host immune response by hijacking host pathways via the interaction between viral and host proteins. We identified Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 1/2 (G3BP1/G3BP2) as a critical host factor that interacts with the viral nucleocapsid (N) protein, emerging from a comparative analysis of proteomic data from multiple studies. We revisited the underlying molecular mechanisms by confirming the residues required for the interaction between G3BP1/G3BP2 and SARS-CoV-2 N protein and showed that this interaction disrupts stress granule formation. Intriguingly, we observed that the ablation of both G3BP1 and G3BP2 enhanced SARS-CoV-2 replication. Our data collectively supports the notion that G3BP1 and G3BP2 play a critical role in modulating the host-virus interface during SARS-CoV-2 infection, and that their multifaceted function in cellular defense extends beyond the stress granule pathway.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v17070912/s1 , Figure S1 : Linear representation of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein, highlighting peptides identified by LC-MS analysis. The full-length protein sequence is shown, with tryptic digestion sites indicated in green. Red indicates the peptides that were successfully identified in our LC-MS analysis; Figure S2 : Coomassie blue-stained protein gel of pull-down assays using SARS-CoV-2 N protein versus mock samples, prepared for LC-MS analysis to compare interacting proteins; Figure S3 : Schematic of specific mutations in genes induced by CRISPR-Cas9 in A549 Cell Lines; Table S1 -1: The SARS-CoV-2 N protein associated host proteins obtained by MS data search; Table S1 -2: The selected SARS-CoV-2 N associated host proteins after intensity comparison; Table S2 -1: The Protein IDs summary and Venn results from our analysis and previously studies; Table S2 -2: The KEGG pathway summary and Venn results from our analysis and previously studies; Table S3 -1: The result of QIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis: Table S3
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Aloise, Schipper, Van Vliet, Oymans, Donselaar et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein inhibits the PKR-mediated integrated stress response through RNA-binding domain N2b, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1011582
Anderson, Kedersha, RNA granules: Post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/nrm2694
Anderson, Kedersha, Stress granules: The Tao of RNA triage, Trends Biochem. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2007.12.003
Biswal, Lu, Song, SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Targets a Conserved Surface Groove of the NTF2-like Domain of G3BP1, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167516
Brown, Storey, Treatment of allergy of the respiratory tract with beclomethasone dipropionate steroid aerosol, Postgrad. Med. J
Burd, Dreyfuss, Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins, Science, doi:10.1126/science.8036511
Cai, Zhang, Zhuang, Zhang, Ma et al., Phase-separated nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 suppresses cGAS-DNA recognition by disrupting cGAS-G3BP1 complex, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01420-9
Chen, Xiao, Hu, Ge, Tian et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Interacts with RIG-I and Represses RIG-Mediated IFN-β Production, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13010047
Ciccosanti, Di Rienzo, Romagnoli, Colavita, Refolo et al., Proteomic analysis identifies the RNA helicase DDX3X as a host target against SARS-CoV-2 infection, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105064
Dinesh, Chalupska, Silhan, Koutna, Nencka et al., Structural basis of RNA recognition by the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009100
Gerassimovich, Miladinovski-Bangall, Bridges, Boateng, Ball et al., Proximity-dependent biotinylation detects associations between SARS coronavirus nonstructural protein 1 and stress granule-associated proteins, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101399
Ghisolfi, Dutt, Mcconkey, Ebert, Anderson, Stress granules contribute to α-globin homeostasis in differentiating erythroid cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.070
Gordon, Hiatt, Bouhaddou, Rezelj, Ulferts et al., Comparative host-coronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abe9403
He, Gou, Zhou, Wu, Ren et al., The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein suppresses innate immunity by remodeling stress granules to atypical foci, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202201973RR
Huang, Ju, Tian, Li, Yu et al., Molecular determinants for regulation of G3BP1/2 phase separation by the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, Cell Discov, doi:10.1038/s41421-021-00306-w
Jiang, Zhang, Meng, Xie, Li et al., SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b suppresses type I interferon responses by targeting TOM70, Cell. Mol. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0514-8
Kang, Wang, Yang, Zhang, Zheng et al., Research Progress on the Structure and Function of G3BP, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.718548
Katsafanas, Moss, Vaccinia virus intermediate stage transcription is complemented by Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein (G3BP) and cytoplasmic activation/proliferation-associated protein (p137) individually or as a heterodimer, J. Biol. Chem
Kedersha, Ivanov, Anderson, Stress granules and cell signaling: More than just a passing phase?, Trends Biochem. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2013.07.004
Kennedy, French, Guitard, Ru, Tocque et al., Characterization of G3BPs: Tissue specific expression, chromosomal localisation and rasGAP(120) binding studies, J. Cell Biochem, doi:10.1002/jcb.1277
Kim, Maharjan, Kang, Kim, Park et al., Differential effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on stress granule formation in Vero and Calu-3 cells, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.997539
Korn, Dhamotharan, Jeffries, Schlundt, The preference signature of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid NTD for its 5 ′ -genomic RNA elements, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-38882-y
Kruse, Benz, Garvanska, Lindqvist, Mihalic et al., Large scale discovery of coronavirus-host factor protein interaction motifs reveals SARS-CoV-2 specific mechanisms and vulnerabilities, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26498-z
Leblanc, Lynch, Layne, Vendramelli, Sloan et al., The Nucleocapsid Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Close Relative Bat Coronavirus RaTG13 Are Capable of Inhibiting PKR-and RNase L-Mediated Antiviral Pathways, Microbiol. Spectr, doi:10.1128/spectrum.00994-23
Leblanc, Tocque, Delumeau, Ras-GAP controls Rho-mediated cytoskeletal reorganization through its SH3 domain, Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1128/MCB.18.9.5567
Lee, Klein, Fon Tacer, Lord, Oatley et al., Translational Repression of G3BP in Cancer and Germ Cells Suppresses Stress Granules and Enhances Stress Tolerance, Mol. Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.037
Li, Guo, Tian, Wang, Yang et al., Virus-Host Interactome and Proteomic Survey Reveal Potential Virulence Factors Influencing SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis, Med, doi:10.1016/j.medj.2020.07.002
Liu, Bai, Zhang, Gao, Liu et al., SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Antagonizes Stress Granule Assembly and IFN Production by Interacting with G3BPs to Facilitate Viral Replication, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.00412-22
Lu, Ye, Singh, Cao, Diedrich et al., The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein forms mutually exclusive condensates with RNA and the membrane-associated M protein, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20768-y
Luo, Li, Zhao, Ju, Ma et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein phase separates with G3BPs to disassemble stress granules and facilitate viral production, Sci. Bull, doi:10.1016/j.scib.2021.01.013
Matsuki, Takahashi, Higuchi, Makokha, Oie et al., Both G3BP1 and G3BP2 contribute to stress granule formation, Genes. Cells, doi:10.1111/gtc.12023
Mccormick, Khaperskyy, Translation inhibition and stress granules in the antiviral immune response, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri.2017.63
Murigneux, Softic, Aubé, Grandi, Judith et al., Proteomic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 particles unveils a key role of G3BP proteins in viral assembly, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-44958-0
Nabeel-Shah, Lee, Ahmed, Burke, Farhangmehr et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein binds host mRNAs and attenuates stress granules to impair host stress response, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.103562
Parker, Maurier, Delumeau, Duchesne, Faucher et al., A Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3-domain-binding protein, Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1128/MCB.16.6.2561
Reineke, Dougherty, Pierre, Lloyd, Large G3BP-induced granules trigger eIF2α phosphorylation, Mol. Biol. Cell, doi:10.1091/mbc.e12-05-0385
Thompson, Simons, Wilkins, Cheng, Del Valle et al., Molecular states during acute COVID-19 reveal distinct etiologies of long-term sequelae, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-022-02107-4
Valiente-Echeverría, Melnychuk, Vyboh, Ajamian, Gallouzi et al., eEF2 and Ras-GAP SH3 domain-binding protein (G3BP1) modulate stress granule assembly during HIV-1 infection, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/ncomms5819
Wong, Perlman, Immune dysregulation and immunopathology induced by SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses-Are we our own worst enemy?, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00656-2
Yang, Johnson, Meliopoulos, Ju, Zhang et al., Interaction between host G3BP and viral nucleocapsid protein regulates SARS-CoV-2 replication and pathogenicity, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113965
Yang, Mathieu, Kolaitis, Zhang, Messing et al., G3BP1 Is a Tunable Switch that Triggers Phase Separation to Assemble Stress Granules, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.046
Ye, West, Silletti, Corbett, Architecture and self-assembly of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, Protein Sci, doi:10.1002/pro.3909
Zheng, Sun, Yu, Shi, Zhu et al., Interactome Analysis of the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Virus, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10091155
Zheng, Wang, Xu, Fu, Wang, SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein impairs stress granule formation to promote viral replication, Cell Discov, doi:10.1038/s41421-021-00275-0
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v17070912",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v17070912",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The global pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has posed unprecedented challenges to public health and economic stability. Central to SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis is its ability to evade the host immune response by hijacking host pathways via the interaction between viral and host proteins. We identified Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 1/2 (G3BP1/G3BP2) as a critical host factor that interacts with the viral nucleocapsid (N) protein, emerging from a comparative analysis of proteomic data from multiple studies. We revisited the underlying molecular mechanisms by confirming the residues required for the interaction between G3BP1/G3BP2 and SARS-CoV-2 N protein and showed that this interaction disrupts stress granule formation. Intriguingly, we observed that the ablation of both G3BP1 and G3BP2 enhanced SARS-CoV-2 replication. Our data collectively supports the notion that G3BP1 and G3BP2 play a critical role in modulating the host–virus interface during SARS-CoV-2 infection, and that their multifaceted function in cellular defense extends beyond the stress granule pathway.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v17070912"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2554-3602",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology and Plant Pathology, University of California-Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Duo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry, University of California-Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA"
}
],
"family": "Biswal",
"given": "Mahamaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for Integrative Genome Biology, Proteomics Core, University of California-Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Quanqing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology and Plant Pathology, University of California-Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA"
}
],
"family": "Light",
"given": "Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology and Plant Pathology, University of California-Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA"
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Yijie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Texas Biomedical Research Institute, San Antonio, TX 78227, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ye",
"given": "Chenjin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7084-0804",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Texas Biomedical Research Institute, San Antonio, TX 78227, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Martínez-Sobrido",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry, University of California-Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Jikui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology and Plant Pathology, University of California-Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hai",
"given": "Rong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-02T11:55:43Z",
"timestamp": 1751457343000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-02T11:59:55Z",
"timestamp": 1751457595000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"1R21AI147057",
"R01AI153419"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "NIAID"
},
{
"award": [
"T32 ES018827"
],
"name": "NRSA T32"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-02T12:40:04Z",
"timestamp": 1751460004211,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1750982400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/7/912/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "912",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-02107-4",
"article-title": "Molecular states during acute COVID-19 reveal distinct etiologies of long-term sequelae",
"author": "Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00656-2",
"article-title": "Immune dysregulation and immunopathology induced by SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses—Are we our own worst enemy?",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0514-8",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b suppresses type I interferon responses by targeting TOM70",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "998",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pro.3909",
"article-title": "Architecture and self-assembly of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1890",
"journal-title": "Protein Sci.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.02.022194",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "Dinesh, D.C., Chalupska, D., Silhan, J., Koutna, E., Nencka, R., Veverka, V., and Boura, E. (2020). Structural basis of RNA recognition by the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein. PLoS Pathog., 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-38882-y",
"article-title": "The preference signature of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid NTD for its 5′-genomic RNA elements",
"author": "Korn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3331",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-021-00306-w",
"article-title": "Molecular determinants for regulation of G3BP1/2 phase separation by the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Cell Discov.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113965",
"article-title": "Interaction between host G3BP and viral nucleocapsid protein regulates SARS-CoV-2 replication and pathogenicity",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113965",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-44958-0",
"article-title": "Proteomic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 particles unveils a key role of G3BP proteins in viral assembly",
"author": "Murigneux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "640",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/spectrum.00994-23",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "LeBlanc, K., Lynch, J., Layne, C., Vendramelli, R., Sloan, A., Tailor, N., Deschambault, Y., Zhang, F., Kobasa, D., and Safronetz, D. (2023). The Nucleocapsid Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Close Relative Bat Coronavirus RaTG13 Are Capable of Inhibiting PKR- and RNase L-Mediated Antiviral Pathways. Microbiol. Spectr., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202201973RR",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein suppresses innate immunity by remodeling stress granules to atypical foci",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e23269",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-023-01420-9",
"article-title": "Phase-separated nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 suppresses cGAS-DNA recognition by disrupting cGAS-G3BP1 complex",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "170",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.09.02.506332",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Aloise, C., Schipper, J.G., van Vliet, A., Oymans, J., Donselaar, T., Hurdiss, D.L., de Groot, R.J., and van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein inhibits the PKR-mediated integrated stress response through RNA-binding domain N2b. PLoS Pathog., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.103562",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein binds host mRNAs and attenuates stress granules to impair host stress response",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103562",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.00412-22",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Antagonizes Stress Granule Assembly and IFN Production by Interacting with G3BPs to Facilitate Viral Replication",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0041222",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.997539",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Kim, D., Maharjan, S., Kang, M., Kim, J., Park, S., Kim, M., Baek, K., Kim, S., Suh, J.G., and Lee, Y. (2022). Differential effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on stress granule formation in Vero and Calu-3 cells. Front. Microbiol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167516",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Biswal, M., Lu, J., and Song, J. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Targets a Conserved Surface Groove of the NTF2-like Domain of G3BP1. J. Mol. Biol., 434."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-021-00275-0",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein impairs stress granule formation to promote viral replication",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Cell Discov.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scib.2021.01.013",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein phase separates with G3BPs to disassemble stress granules and facilitate viral production",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1194",
"journal-title": "Sci. Bull.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20768-y",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein forms mutually exclusive condensates with RNA and the membrane-associated M protein",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "502",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26498-z",
"article-title": "Large scale discovery of coronavirus-host factor protein interaction motifs reveals SARS-CoV-2 specific mechanisms and vulnerabilities",
"author": "Kruse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6761",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101399",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Gerassimovich, Y.A., Miladinovski-Bangall, S.J., Bridges, K.M., Boateng, L., Ball, L.E., Valafar, H., and Nag, A. (2021). Proximity-dependent biotinylation detects associations between SARS coronavirus nonstructural protein 1 and stress granule-associated proteins. J. Biol. Chem., 297."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10091155",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Zheng, X., Sun, Z., Yu, L., Shi, D., Zhu, M., Yao, H., and Li, L. (2021). Interactome Analysis of the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Pathogens, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medj.2020.07.002",
"article-title": "Virus-Host Interactome and Proteomic Survey Reveal Potential Virulence Factors Influencing SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Med",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13010047",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Chen, K., Xiao, F., Hu, D., Ge, W., Tian, M., Wang, W., Pan, P., Wu, K., and Wu, J. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Interacts with RIG-I and Represses RIG-Mediated IFN-β Production. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe9403",
"article-title": "Comparative host-coronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabe9403",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2017.63",
"article-title": "Translation inhibition and stress granules in the antiviral immune response",
"author": "McCormick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.718548",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_28",
"unstructured": "Kang, W., Wang, Y., Yang, W., Zhang, J., Zheng, H., and Li, D. (2021). Research Progress on the Structure and Function of G3BP. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/gtc.12023",
"article-title": "Both G3BP1 and G3BP2 contribute to stress granule formation",
"author": "Matsuki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Genes. Cells",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105064",
"article-title": "Proteomic analysis identifies the RNA helicase DDX3X as a host target against SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Ciccosanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105064",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Treatment of allergy of the respiratory tract with beclomethasone dipropionate steroid aerosol",
"author": "Brown",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "51",
"year": "1975"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.8036511",
"article-title": "Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins",
"author": "Burd",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "615",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "265",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/MCB.16.6.2561",
"article-title": "A Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3-domain-binding protein",
"author": "Parker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2561",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "16",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/MCB.18.9.5567",
"article-title": "Ras-GAP controls Rho-mediated cytoskeletal reorganization through its SH3 domain",
"author": "Leblanc",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5567",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "18",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.070",
"article-title": "Stress granules contribute to α-globin homeostasis in differentiating erythroid cells",
"author": "Ghisolfi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "768",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "420",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.1277",
"article-title": "Characterization of G3BPs: Tissue specific expression, chromosomal localisation and rasGAP(120) binding studies",
"author": "Kennedy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biochem.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.046",
"article-title": "G3BP1 Is a Tunable Switch that Triggers Phase Separation to Assemble Stress Granules",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.037",
"article-title": "Translational Repression of G3BP in Cancer and Germ Cells Suppresses Stress Granules and Enhances Stress Tolerance",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "645",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e12-05-0385",
"article-title": "Large G3BP-induced granules trigger eIF2α phosphorylation",
"author": "Reineke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3499",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm2694",
"article-title": "RNA granules: Post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tibs.2007.12.003",
"article-title": "Stress granules: The Tao of RNA triage",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Trends Biochem. Sci.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tibs.2013.07.004",
"article-title": "Stress granules and cell signaling: More than just a passing phase?",
"author": "Kedersha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "494",
"journal-title": "Trends Biochem. Sci.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms5819",
"article-title": "eEF2 and Ras-GAP SH3 domain-binding protein (G3BP1) modulate stress granule assembly during HIV-1 infection",
"author": "Melnychuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4819",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M411033200",
"article-title": "Vaccinia virus intermediate stage transcription is complemented by Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein (G3BP) and cytoplasmic activation/proliferation-associated protein (p137) individually or as a heterodimer",
"author": "Katsafanas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "52210",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2004"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/7/912"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Beyond Stress Granules: G3BP1 and G3BP2 Redundantly Suppress SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}