Real-World Effectiveness and Tolerability of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Ambulatory Patients with Early COVID-19
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab331, Jun 2021
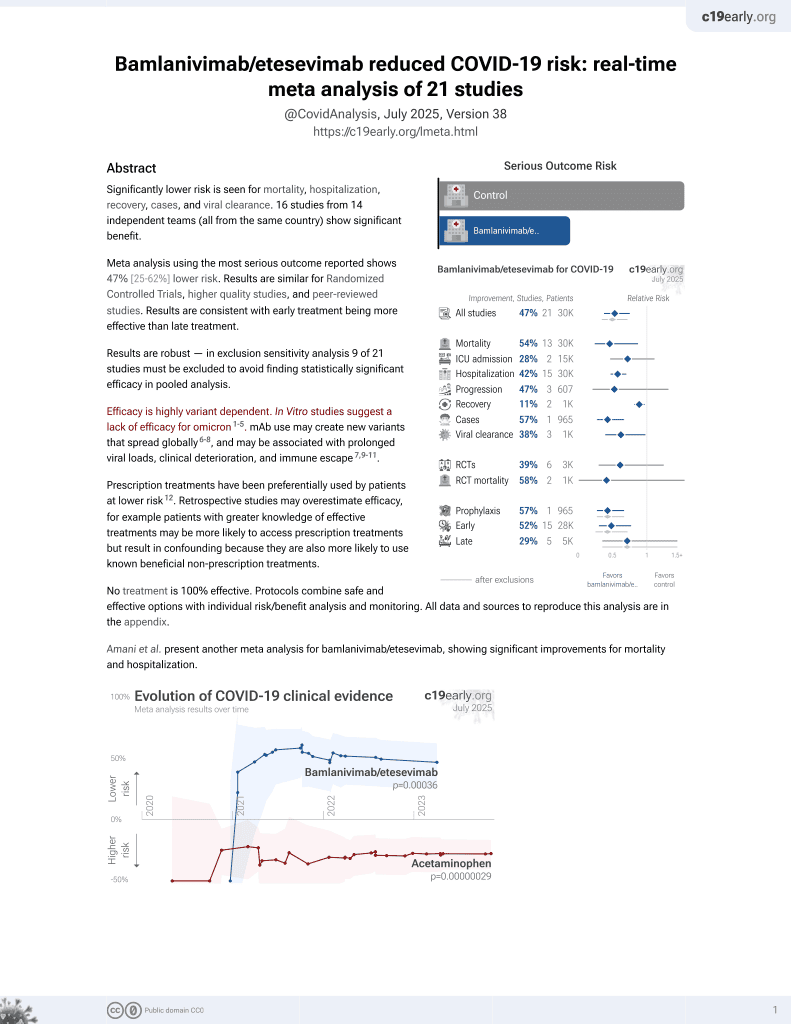
25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 479 patients treated with bamlanivimab showing lower mortality, hospital admission, and emergency department visits with treatment. Authors incorrectly state that "no other COVID-19 therapies for ambulatory patients have proven effective".
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments6.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers casirivimab/imdevimab and bamlanivimab/etesevimab.
|
risk of death, 79.7% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.09, treatment 1 of 479 (0.2%), control 57 of 5,536 (1.0%), NNT 122.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 52.7% lower, RR 0.47, p < 0.001, treatment 22 of 479 (4.6%), control 538 of 5,536 (9.7%), NNT 20.
|
|
risk of hospitalization/ER, 26.8% lower, RR 0.73, p < 0.001, treatment 65 of 479 (13.6%), control 1,018 of 5,536 (18.4%), NNT 21, odds ratio converted to relative risk, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Webb et al., 23 Jun 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Real-world Effectiveness and Tolerability of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Ambulatory Patients With Early COVID-19
Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab331
Background. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are a promising therapy for early coronavirus disease 2019 , but their effectiveness has not been confirmed in a real-world setting. Methods. In this quasi-experimental pre-/postimplementation study, we estimated the effectiveness of MAb treatment within 7 days of symptom onset in high-risk ambulatory adults with COVID-19. The primary outcome was a composite of emergency department visits or hospitalizations within 14 days of positive test. Secondary outcomes included adverse events and 14-day mortality. The average treatment effect in the treated for MAb therapy was estimated using inverse probability of treatment weighting and the impact of MAb implementation using propensity-weighted interrupted time series analysis. Results. Pre-implementation (July-November 2020), 7404 qualifying patients were identified. Postimplementation (December 2020-January 2021), 594 patients received MAb treatment and 5536 did not. The primary outcome occurred in 75 (12.6%) MAb recipients, 1018 (18.4%) contemporaneous controls, and 1525 (20.6%) historical controls. MAb treatment was associated with decreased likelihood of emergency care or hospitalization (odds ratio, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.60-0.79). After implementation, the weighted probability that a given patient would require an emergency department visit or hospitalization decreased significantly (0.7% per day; 95% CI, 0.03%-0.10%). Mortality was 0.2% (n = 1) in the MAb group compared with 1.0% (n = 71) and 1.0% (n = 57) in pre-and postimplementation controls, respectively. Adverse events occurred in 7 (1.2%); 2 (0.3%) were considered serious. Conclusions. MAb treatment of high-risk ambulatory patients with early COVID-19 was well tolerated and likely effective at preventing the need for subsequent emergency department or hospital care.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at Open Forum Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
References
Austin, Stuart, Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies, Stat Med
Cevik, Tate, Lloyd, SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Microbe
Charlson, Pompei, Ales, Mackenzie, A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation, J Chronic Dis
Chatellier, Zapletal, Lemaitre, The number needed to treat: a clinically useful nomogram in its proper context, BMJ
Chen, Nirula, Heller, BLAZE-1 Investigators. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Elixhauser, Steiner, Harris, Coffey, Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data, Med Care
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Fundación INFANT-COVID-19 Group. Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med
Rubin, Estimating causal effects from large data sets using propensity scores, Ann Intern Med
Wagner, Soumerai, Zhang, Ross-Degnan, Segmented regression analysis of interrupted time series studies in medication use research, J Clin Pharm Ther
Webb, Levin, Grisel, Simple scoring tool to estimate risk of hospitalization and mortality in ambulatory and emergency department patients with COVID-19, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.02.22.21252171
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Trial Investigators. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab331",
"ISSN": [
"2328-8957"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab331",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are a promising therapy for early coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), but their effectiveness has not been confirmed in a real-world setting.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this quasi-experimental pre-/postimplementation study, we estimated the effectiveness of MAb treatment within 7 days of symptom onset in high-risk ambulatory adults with COVID-19. The primary outcome was a composite of emergency department visits or hospitalizations within 14 days of positive test. Secondary outcomes included adverse events and 14-day mortality. The average treatment effect in the treated for MAb therapy was estimated using inverse probability of treatment weighting and the impact of MAb implementation using propensity-weighted interrupted time series analysis.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Pre-implementation (July–November 2020), 7404 qualifying patients were identified. Postimplementation (December 2020–January 2021), 594 patients received MAb treatment and 5536 did not. The primary outcome occurred in 75 (12.6%) MAb recipients, 1018 (18.4%) contemporaneous controls, and 1525 (20.6%) historical controls. MAb treatment was associated with decreased likelihood of emergency care or hospitalization (odds ratio, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.60–0.79). After implementation, the weighted probability that a given patient would require an emergency department visit or hospitalization decreased significantly (0.7% per day; 95% CI, 0.03%–0.10%). Mortality was 0.2% (n = 1) in the MAb group compared with 1.0% (n = 71) and 1.0% (n = 57) in pre- and postimplementation controls, respectively. Adverse events occurred in 7 (1.2%); 2 (0.3%) were considered serious.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>MAb treatment of high-risk ambulatory patients with early COVID-19 was well tolerated and likely effective at preventing the need for subsequent emergency department or hospital care.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1799-3315",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Epidemiology, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
},
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine, Stanford Medicine, Palo Alto, California, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Webb",
"given": "Brandon J",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacy Services, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Buckel",
"given": "Whitney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Epidemiology, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Vento",
"given": "Todd",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Enterprise Analytics, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "Allison M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Enterprise Analytics, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Grisel",
"given": "Nancy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Intermountain Medical Center and University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Samuel M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Intermountain Medical Center and University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Peltan",
"given": "Ithan D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Spivak",
"given": "Emily S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Urgent Care Service Line, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Sakata",
"given": "Theadora",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Urgent Care Service Line, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Wallin",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Epidemiology, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
},
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine, Stanford Medicine, Palo Alto, California, USA"
},
{
"name": "Office of Patient Experience, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Stenehjem",
"given": "Eddie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Executive Leadership Team, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
}
],
"family": "Poulsen",
"given": "Greg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Stanford Medicine, Palo Alto, California, USA"
}
],
"family": "Bledsoe",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Open Forum Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-23T01:00:39Z",
"timestamp": 1624410039000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-27T12:52:09Z",
"timestamp": 1627390329000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-11T21:07:10Z",
"timestamp": 1710191230929
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 42,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1624406400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ofid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofab331/38814041/ofab331.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/8/7/ofab331/39337375/ofab331.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/8/7/ofab331/39337375/ofab331.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24415",
"article-title": "An EUA for bamlanivimab—a monoclonal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "880",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0001",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "An EUA for casirivimab and imdevimab for COVID-19",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "Med Lett Drugs Ther",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0002",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0003",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"article-title": "Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0004",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0005",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation",
"author": "Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "J Chronic Dis",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0006",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005650-199801000-00004",
"article-title": "Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data",
"author": "Elixhauser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Med Care",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0007",
"volume": "36",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0008",
"volume-title": "Utah Department of Health and Utah Hospital Association"
},
{
"article-title": "Simple scoring tool to estimate risk of hospitalization and mortality in ambulatory and emergency department patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Webb",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0009",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-127-8_Part_2-199710151-00064",
"article-title": "Estimating causal effects from large data sets using propensity scores",
"author": "Rubin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "757",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0010",
"volume": "127",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.6607",
"article-title": "Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3661",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0011",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.312.7028.426",
"article-title": "The number needed to treat: a clinically useful nomogram in its proper context",
"author": "Chatellier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "426",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0012",
"volume": "312",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2710.2002.00430.x",
"article-title": "Segmented regression analysis of interrupted time series studies in medication use research",
"author": "Wagner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "299",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pharm Ther",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0013",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"article-title": "Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults",
"author": "Libster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "610",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0014",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30172-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cevik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "2021072712513475600_CIT0015",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 15,
"references-count": 15,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2021.03.15.21253646",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofab331/6308074"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Oncology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world Effectiveness and Tolerability of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Ambulatory Patients With Early COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "8"
}