Impact of corticosteroid doses on prognosis of severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection: a propensity score matching study
et al., Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0, Aug 2024
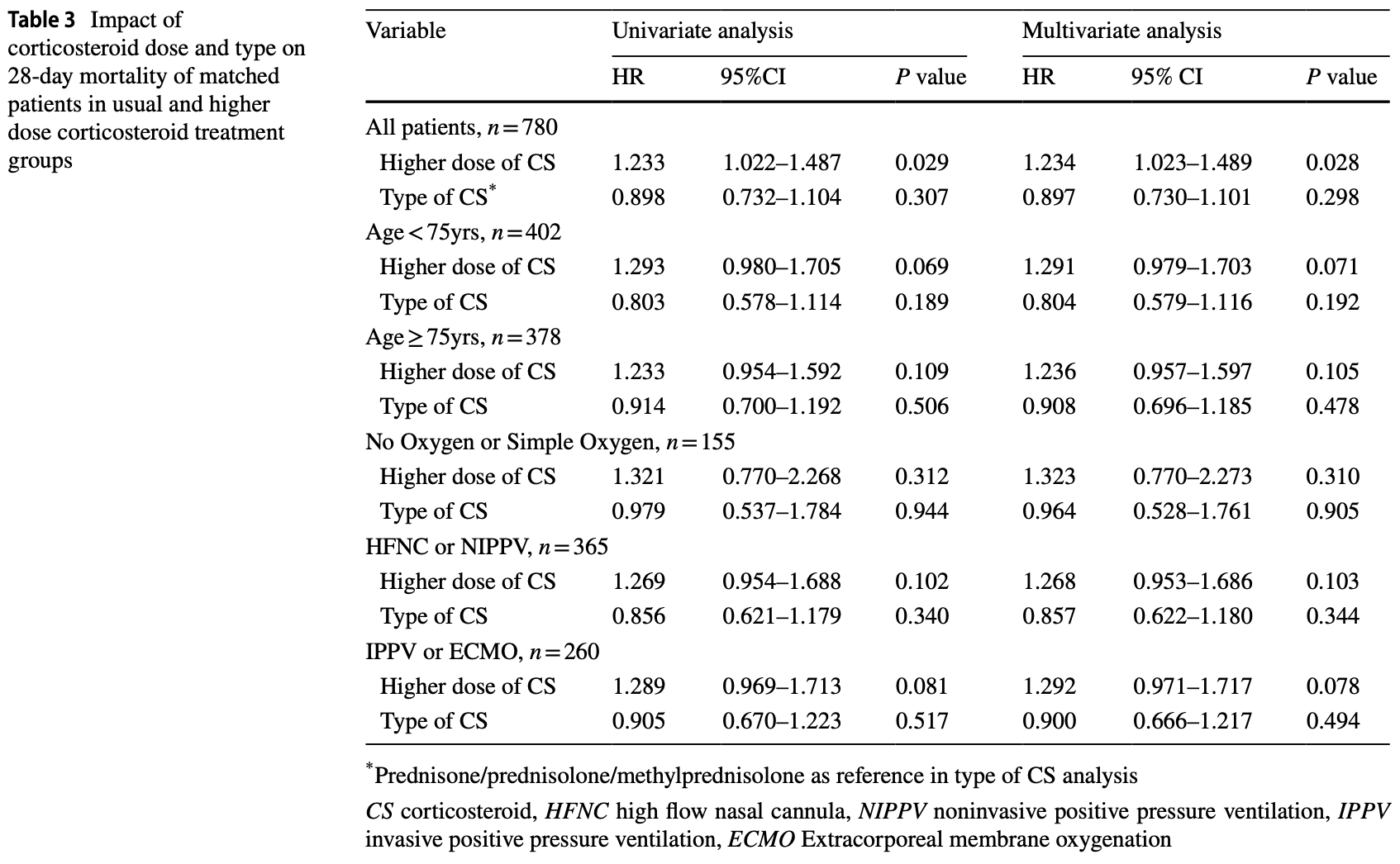
Retrospective 1,167 severe/critical COVID-19 patients in China showing higher 28-day mortality with higher doses of corticosteroids (>50mg/day prednisone equivalent) compared to usual doses (30-50mg/day). The type of corticosteroid used did not affect outcomes. Authors suggest that higher doses of corticosteroids may lead to poorer prognosis for severe/critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron infection in the ICU, possibly due to a milder inflammatory response with Omicron.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of death, 23.4% higher, HR 1.23, p = 0.03, treatment 260, control 520, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Wang et al., 9 Aug 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period 1 November, 2022 - 11 February, 2023.
Contact: drzhanqy@163.com.
Impact of corticosteroid doses on prognosis of severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection: a propensity score matching study
Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0
Background There is lack of research on corticosteroid use for severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection. Methods This multi-center retrospective cohort study involved 1167 patients from 59 ICUs across the mainland of China diagnosed with severe or critical SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection between November 1, 2022, and February 11, 2023. Patients were segregated into two groups based on their corticosteroid treatment-usual dose (equivalent prednisone dose 30-50 mg/day) and higher dose (equivalent prednisone dose > 50 mg/day). The primary outcome was 28-day ICU mortality. Propensity score matching was used to compare outcomes between cohorts. Results After propensity score matching, 520 patients in the usual dose corticosteroid group and 260 patients in the higher dose corticosteroid group were included in the analysis, respectively. The mortality was significantly higher in the higher dose corticosteroid group (67.3%, 175/260) compared to the usual dose group (56.0%, 291/520). Logistic regression showed that higher doses of corticosteroids were significantly associated with increased mortality at 28-day (OR = 1.62,95% CI 1.19-2.21, p = 0.002) and mortality in ICU stay (OR = 1.66,95% CI 1.21-2.28, p = 0.002). Different types of corticosteroids did not affect the effect. Conclusions The study suggests that higher-dose corticosteroids may lead to a poorer prognosis for severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection in the ICU. Further research is needed to determine the appropriate corticosteroid dosage for these patients.
Author contributions SW, ZC and QZ conceived of the study. SW, XW and QZ participated in the design of the study and coordination. LH, XC, YC, XH, JX, SG, and ML participated in the enrolment of the cases. SW, ZC, YW, and QZ participated in the data collection. SW, XZ performed the statistical analysis. SW drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations Ethics approval The study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Commission of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2019-79-K51-1) . This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Conflict of interests The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose. Consent to participate Written informed consent was waived.
Consent to publish Not applicable. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted..
References
Angus, Derde, Al-Beidh, Annane, Arabi et al., Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the remap-cap covid-19 corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Bojkova, Widera, Ciesek, Wass, Michaelis et al., Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in Omicron variant compared to Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 isolates, Cell Res
Bouzid, Visseaux, Kassasseya, Daoud, Fémy et al., Comparison of patients infected with delta versus omicron covid-19 variants presenting to paris emergency departments : a retrospective cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Català, Coma, Alonso, Andrés, Blanco et al., Transmissibility, hospitalization, and intensive care admissions due to omicron compared to delta variants of SARS-CoV-2 in Catalonia: a cohort study and ecological analysis, Front Public Health
China, Management protocol for COVID-19
De Prost, Audureau, Heming, Gault, Pham et al., Clinical phenotypes and outcomes associated with SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron in critically ill French patients with COVID-19, Nat Commun
Defilippis, Chapman, Mills, De Lemos, Arbab-Zadeh et al., Assessment and treatment of patients with type 2 myocardial infarction and acute nonischemic myocardial injury, Circulation
Do, Manabe, Vu, Nong, Fujikura et al., Clinical characteristics and mortality risk among critically ill patients with COVID-19 owing to the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant in Vietnam: a retrospective observational study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0279713
Du, Tang, Gao, Wu, Meng et al., Omicron adopts a different strategy from Delta and other variants to adapt to host, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Granholm, Kjaer, Munch, Myatra, Vijayaraghavan et al., Long-term outcomes of dexamethasone 12 mg versus 6 mg in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxaemia, Inten Care Med
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Albano, Antonelli et al., Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with covid-19 in intensive care units in lombardy, Italy JAMA Intern Med
Group, Higher dose corticosteroids in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 who are hypoxic but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet
Health, COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Iuliano, Brunkard, Boehmer, Peterson, Adjei et al., Trends in disease severity and health care utilization during the early omicron variant period compared with previous sars-cov-2 high transmission periods -united states, december 2020-january 2022, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Jung, Wernly, Fjølner, Bruno, Dudzinski et al., Steroid use in elderly critically ill COVID-19 patients, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00979-2021
Katz, Altshuler, Papadopoulos, Amoroso, Goldenberg et al., The use of high-dose corticosteroids versus low-dose corticosteroids with and without tocilizumab in covid-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Pharmacother
Kellum, Lameire, Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: a KDIGO summary (Part 1), Crit Care
Lamers, Haagmans, SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis, Nat Rev Microbiol
Lauring, Tenforde, Chappell, Gaglani, Ginde et al., Clinical severity of, and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against, covid-19 from omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: prospective observational study, BMJ
Munch, Myatra, Vijayaraghavan, Saseedharan, Benfield et al., Effect of 12 mg vs 6 mg of dexamethasone on the number of days alive without life support in adults with covid-19 and severe hypoxemia: the covid steroid 2 randomized trial, JAMA
Organization, Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline
Piralla, Mojoli, Pellegrinelli, Ceriotti, Valzano et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variants in patients requiring intensive care unit (ICU) admission for COVID-19, Northern Italy, December 2021 to, Respir Med Res
Rhodes, Evans, Alhazzani, Levy, Antonelli et al., Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016, Intensive Care Med
Salvarani, Massari, Costantini, Merlo, Mariani et al., Intravenous methylprednisolone pulses in hospitalised patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00025-2022
Shen, Liu, Shang, Xie, Li et al., Incidence and etiology of drug-induced liver injury in mainland China, Gastroenterology
Sterne, Murthy, Diaz, Slutsky, Villar et al., Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with covid-19: a meta-analysis, JAMA
Tomazini, Maia, Cavalcanti, Berwanger, Rosa et al., Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and covid-19: the codex randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Toroghi, Abbasian, Nourian, Davoudi-Monfared, Khalili et al., Comparing efficacy and safety of different doses of dexamethasone in the treatment of COVID-19: a three-arm randomized clinical trial, Pharmacol Rep
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China JAMA Intern Med
Yaqoob, Greenberg, Hwang, Lee, Vernik et al., Comparison of pulse-dose and high-dose corticosteroids with no corticosteroid treatment for COVID-19 pneumonia in the intensive care unit, J Med Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0",
"ISSN": [
"0925-4692",
"1568-5608"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>There is lack of research on corticosteroid use for severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This multi-center retrospective cohort study involved 1167 patients from 59 ICUs across the mainland of China diagnosed with severe or critical SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection between November 1, 2022, and February 11, 2023. Patients were segregated into two groups based on their corticosteroid treatment—usual dose (equivalent prednisone dose 30–50 mg/day) and higher dose (equivalent prednisone dose > 50 mg/day). The primary outcome was 28-day ICU mortality. Propensity score matching was used to compare outcomes between cohorts.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>After propensity score matching, 520 patients in the usual dose corticosteroid group and 260 patients in the higher dose corticosteroid group were included in the analysis, respectively. The mortality was significantly higher in the higher dose corticosteroid group (67.3%, 175/260) compared to the usual dose group (56.0%, 291/520). Logistic regression showed that higher doses of corticosteroids were significantly associated with increased mortality at 28-day (OR = 1.62,95% CI 1.19–2.21, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.002) and mortality in ICU stay (OR = 1.66,95% CI 1.21–2.28, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.002). Different types of corticosteroids did not affect the effect.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The study suggests that higher-dose corticosteroids may lead to a poorer prognosis for severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection in the ICU. Further research is needed to determine the appropriate corticosteroid dosage for these patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"1520"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "30 October 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "23 January 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "9 August 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Commission of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2019-79-K51-1). This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": " The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Written informed consent was waived."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent to publish",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 5,
"value": "Not applicable."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1066-4850",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Shiyao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Ziying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Xinran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Xiaojing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yuqiong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Linna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cui",
"given": "Xiaoyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cai",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Xu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Jingen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gu",
"given": "Sichao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0021-0270",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhan",
"given": "Qingyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Inflammopharmacol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-09T09:12:22Z",
"timestamp": 1723194742000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-21T16:08:12Z",
"timestamp": 1726934892000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"2022-NHLHCRF-LX-01-01"
],
"name": "National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-22T04:16:31Z",
"timestamp": 1726978591238
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1723161600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1723161600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3347-3356",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17022",
"author": "DC Angus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1317",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1520_CR1",
"unstructured": "Angus DC, Derde L, Al-Beidh F, Annane D, Arabi Y, Beane A et al (2020) Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the remap-cap covid-19 corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324(13):1317–1329",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00619-9",
"author": "D Bojkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "319",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "1520_CR2",
"unstructured": "Bojkova D, Widera M, Ciesek S, Wass MN, Michaelis M, Cinatl J Jr (2022) Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in Omicron variant compared to Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 isolates. Cell Res 32(3):319–321",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-0308",
"author": "D Bouzid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "831",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "1520_CR3",
"unstructured": "Bouzid D, Visseaux B, Kassasseya C, Daoud A, Fémy F, Hermand C et al (2022) Comparison of patients infected with delta versus omicron covid-19 variants presenting to paris emergency departments : a retrospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med 175(6):831–837",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.961030",
"author": "M Català",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "1520_CR4",
"unstructured": "Català M, Coma E, Alonso S, Andrés C, Blanco I, Antón A et al (2022) Transmissibility, hospitalization, and intensive care admissions due to omicron compared to delta variants of SARS-CoV-2 in Catalonia: a cohort study and ecological analysis. Front Public Health 10:961030",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "1520_CR5",
"unstructured": "China, N. H. C. o. t. P. s. R. o. (2023). Management protocol for COVID-19. Retrieved 5 January 2023, from https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2023-01/06/5735343/files/5844ce04246b431dbd322d8ba10afb48.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-33801-z",
"author": "N de Prost",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6025",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "1520_CR6",
"unstructured": "de Prost N, Audureau E, Heming N, Gault E, Pham T, Chaghouri A et al (2022) Clinical phenotypes and outcomes associated with SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron in critically ill French patients with COVID-19. Nat Commun 13(1):6025",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040631",
"author": "AP DeFilippis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1661",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "1520_CR7",
"unstructured": "DeFilippis AP, Chapman AR, Mills NL, de Lemos JA, Arbab-Zadeh A, Newby LK et al (2019) Assessment and treatment of patients with type 2 myocardial infarction and acute nonischemic myocardial injury. Circulation 140(20):1661–1678",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0279713",
"author": "TV Do",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "1520_CR8",
"unstructured": "Do TV, Manabe T, Vu GV, Nong VM, Fujikura Y, Phan D et al (2023) Clinical characteristics and mortality risk among critically ill patients with COVID-19 owing to the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant in Vietnam: a retrospective observational study. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279713",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00903-5",
"author": "X Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "1520_CR9",
"unstructured": "Du X, Tang H, Gao L, Wu Z, Meng F, Yan R et al (2022) Omicron adopts a different strategy from Delta and other variants to adapt to host. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1):45",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-022-06677-2",
"author": "A Granholm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "580",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Inten Care Med",
"key": "1520_CR10",
"unstructured": "Granholm A, Kjær MN, Munch MW, Myatra SN, Vijayaraghavan BKT, Cronhjort M et al (2022) Long-term outcomes of dexamethasone 12 mg versus 6 mg in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxaemia. Inten Care Med 48(5):580–589",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"author": "G Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1345",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Italy JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "1520_CR11",
"unstructured": "Grasselli G, Greco M, Zanella A, Albano G, Antonelli M, Bellani G et al (2020) Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with covid-19 in intensive care units in lombardy. Italy JAMA Intern Med 180(10):1345–1355",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00510-X",
"author": "R. C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1499",
"issue": "10387",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1520_CR12",
"unstructured": "Group, R. C (2023) Higher dose corticosteroids in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 who are hypoxic but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 401(10387):1499–1507",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "1520_CR13",
"unstructured": "Health, N. I. o. (2023). COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. Retrieved April 20, 2023, from https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/immunomodulators/corticosteroids/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"author": "P Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1520_CR14",
"unstructured": "Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, Mafham M, Bell JL, Linsell L et al (2021) Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19. N Engl J Med 384(8):693–704",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e4",
"author": "AD Iuliano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "146",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "1520_CR15",
"unstructured": "Iuliano AD, Brunkard JM, Boehmer TK, Peterson E, Adjei S, Binder AM et al (2022) Trends in disease severity and health care utilization during the early omicron variant period compared with previous sars-cov-2 high transmission periods - united states, december 2020-january 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 71(4):146–152",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00979-2021",
"author": "C Jung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "1520_CR16",
"unstructured": "Jung C, Wernly B, Fjølner J, Bruno RR, Dudzinski D, Artigas A et al (2021) Steroid use in elderly critically ill COVID-19 patients. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00979-2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10600280221094571",
"author": "A Katz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Pharmacother",
"key": "1520_CR17",
"unstructured": "Katz A, Altshuler D, Papadopoulos J, Amoroso N, Goldenberg R, Tarras E et al (2023) The use of high-dose corticosteroids versus low-dose corticosteroids with and without tocilizumab in covid-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann Pharmacother 57(1):5–15",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc11454",
"author": "JA Kellum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "204",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "1520_CR18",
"unstructured": "Kellum JA, Lameire N (2013) Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: a KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit Care 17(1):204",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00713-0",
"author": "MM Lamers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "270",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "1520_CR19",
"unstructured": "Lamers MM, Haagmans BL (2022) SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 20(5):270–284",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2021-069761",
"author": "AS Lauring",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "1520_CR20",
"unstructured": "Lauring AS, Tenforde MW, Chappell JD, Gaglani M, Ginde AA, McNeal T et al (2022) Clinical severity of, and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against, covid-19 from omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: prospective observational study. BMJ 376:e069761",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.18295",
"author": "MW Munch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1807",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1520_CR21",
"unstructured": "Munch MW, Myatra SN, Vijayaraghavan BKT, Saseedharan S, Benfield T, Wahlin RR et al (2021) Effect of 12 mg vs 6 mg of dexamethasone on the number of days alive without life support in adults with covid-19 and severe hypoxemia: the covid steroid 2 randomized trial. JAMA 326(18):1807–1817",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "1520_CR22",
"unstructured": "Organization, W. H. (2023). Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. Retrieved 13 January 2023, from https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1449398/retrieve"
},
{
"author": "A Piralla",
"journal-title": "Respir Med Res",
"key": "1520_CR23",
"unstructured": "Piralla A, Mojoli F, Pellegrinelli L, Ceriotti F, Valzano A, Grasselli G et al (2023) Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variants in patients requiring intensive care unit (ICU) admission for COVID-19, Northern Italy, December 2021 to January 2022. Respir Med Res 83:100990",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6",
"author": "A Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "304",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "1520_CR24",
"unstructured": "Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R et al (2017) Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med 43(3):304–377",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00025-2022",
"author": "C Salvarani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "1520_CR25",
"unstructured": "Salvarani C, Massari M, Costantini M, Merlo DF, Mariani GL, Viale P et al (2022) Intravenous methylprednisolone pulses in hospitalised patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00025-2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.002",
"author": "T Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2230",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "1520_CR26",
"unstructured": "Shen T, Liu Y, Shang J, Xie Q, Li J, Yan M et al (2019) Incidence and etiology of drug-induced liver injury in mainland China. Gastroenterology 156(8):2230-2241.e2211",
"volume": "156",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"author": "JAC Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1330",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1520_CR27",
"unstructured": "Sterne JAC, Murthy S, Diaz JV, Slutsky AS, Villar J, Angus DC et al (2020) Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with covid-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA 324(13):1330–1341",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17021",
"author": "BM Tomazini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1307",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1520_CR28",
"unstructured": "Tomazini BM, Maia IS, Cavalcanti AB, Berwanger O, Rosa RG, Veiga VC et al (2020) Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and covid-19: the codex randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324(13):1307–1316",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00341-0",
"author": "N Toroghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "229",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "1520_CR29",
"unstructured": "Toroghi N, Abbasian L, Nourian A, Davoudi-Monfared E, Khalili H, Hasannezhad M et al (2022) Comparing efficacy and safety of different doses of dexamethasone in the treatment of COVID-19: a three-arm randomized clinical trial. Pharmacol Rep 74(1):229–240",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"author": "C Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "934",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "China JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "1520_CR30",
"unstructured": "Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S et al (2020) Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan. China JAMA Intern Med 180(7):934–943",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27351",
"author": "H Yaqoob",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "349",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1520_CR31",
"unstructured": "Yaqoob H, Greenberg D, Hwang F, Lee C, Vernik D, Manglani R et al (2022) Comparison of pulse-dose and high-dose corticosteroids with no corticosteroid treatment for COVID-19 pneumonia in the intensive care unit. J Med Virol 94(1):349–356",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of corticosteroid doses on prognosis of severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection: a propensity score matching study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "32"
}