Role of high dose oral liposomal vitamin C in reducing mortality in patients with COVID-19
et al., Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research, doi:10.36848/IJBAMR/2020/29215.55599 , Jun 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
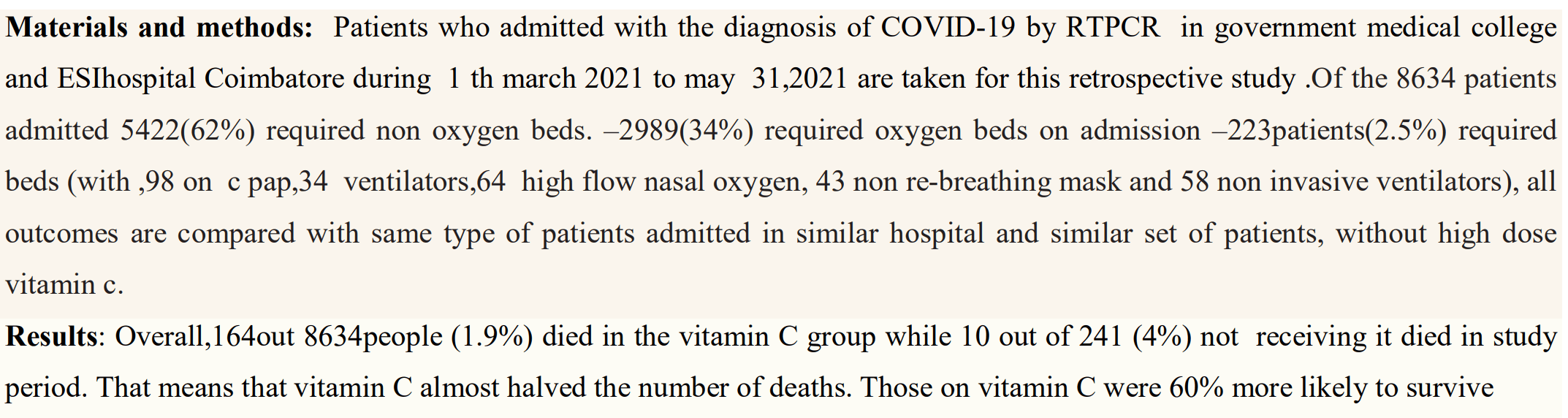
Retrospective 8,634 hospitalized patients in India, showing lower mortality with high-dose vitamin C in unadjusted results. No group details are provided, the text and table appear to show different results, and some numbers do not match.
This is the 29th of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
21 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0012.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details; minimal details of groups provided.
|
risk of death, 54.2% lower, RR 0.46, p = 0.03, treatment 164 of 8,634 (1.9%), control 10 of 241 (4.1%), NNT 44.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Vishnuram et al., 30 Jun 2021, retrospective, India, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, dosage 4000mg days 1-10.
ROLE OF HIGH DOSE ORAL LIPOSOMAL VITAMIN -C IN REDUCING MORTALITY IN PATIENTS WITH COVID-19
doi:10.36848/IJBAMR/2020/29215.55599
Introduction: Severe cases of COVID-19 are associated with hypoxemic respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), septic shock, cardiac dysfunction, elevation in multiple inflammatory cytokines, thrombo embolic disease, and/or exacerbation of underlying co morbidities. In addition to pulmonary disease, patients with COVID-19 may also experience cardiac, hepatic, renal, and central nervous system disease. AIM OF THE STUDY ;To describe the role and outcome, of highdose of oral liposomal vitamin C treatment in reducing mortality in Covid-19 patients admitted in Government Medical College
References
Arvinte, Singh, Marik, Serum Levels of Vitamin C and Vitamin D in a Cohort of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients of a North American Community Hospital Intensive Care Unit in May 2020: A Pilot Study. Medicine in Drug Discovery
Chiscano-Camón, Ruiz-Rodriguez, Ruiz-Sanmartin, Roca, Ferrer, Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Critical Care
Dr, Ravi Kumar. Dr, gowri sankar indian journal of basic and applied medical research
Holford, Vitamin C for the Prevention and Treatment of Coronavirus, Orthomolecular Medicine News Service
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19 -Preliminary Report, N Engl J Med
Rasmussen, Vitamin C Evidence for Treating Complications of COVID-19 and other Viral Infections, Orthomolecular Medicine News Service
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., High-dose vitamin C infusion for the treatment of critically ill COVID-19, Pulmonology
