Probiotics Intake as Adjunct Therapy for Infected Health-Care with SARS COV-2
et al., Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology, 15:2, Jun 2021
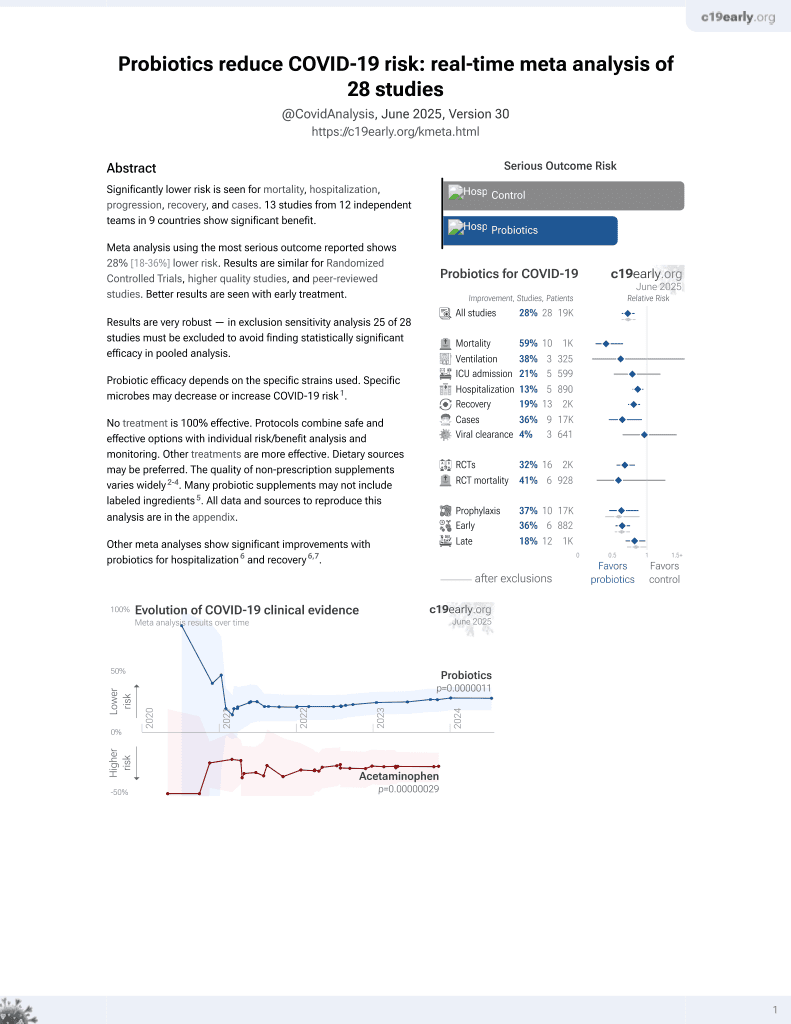
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Small case control analysis with 15 probiotics patients and 15 contol patients, showing no significant differences. PCR tests were only done weekly. Dosage is unknown. 115/LOE/301.4.2/IX/2020.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
the observered difference in duration could be caused by the baseline difference in Ct values.
|
time to viral-, 29.0% lower, relative time 0.71, p = 0.22, treatment 15, control 15.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Veterini et al., 30 Jun 2021, retrospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Probiotics Intake as Adjunct Therapy for Infected Health-Care with SARS COV-2
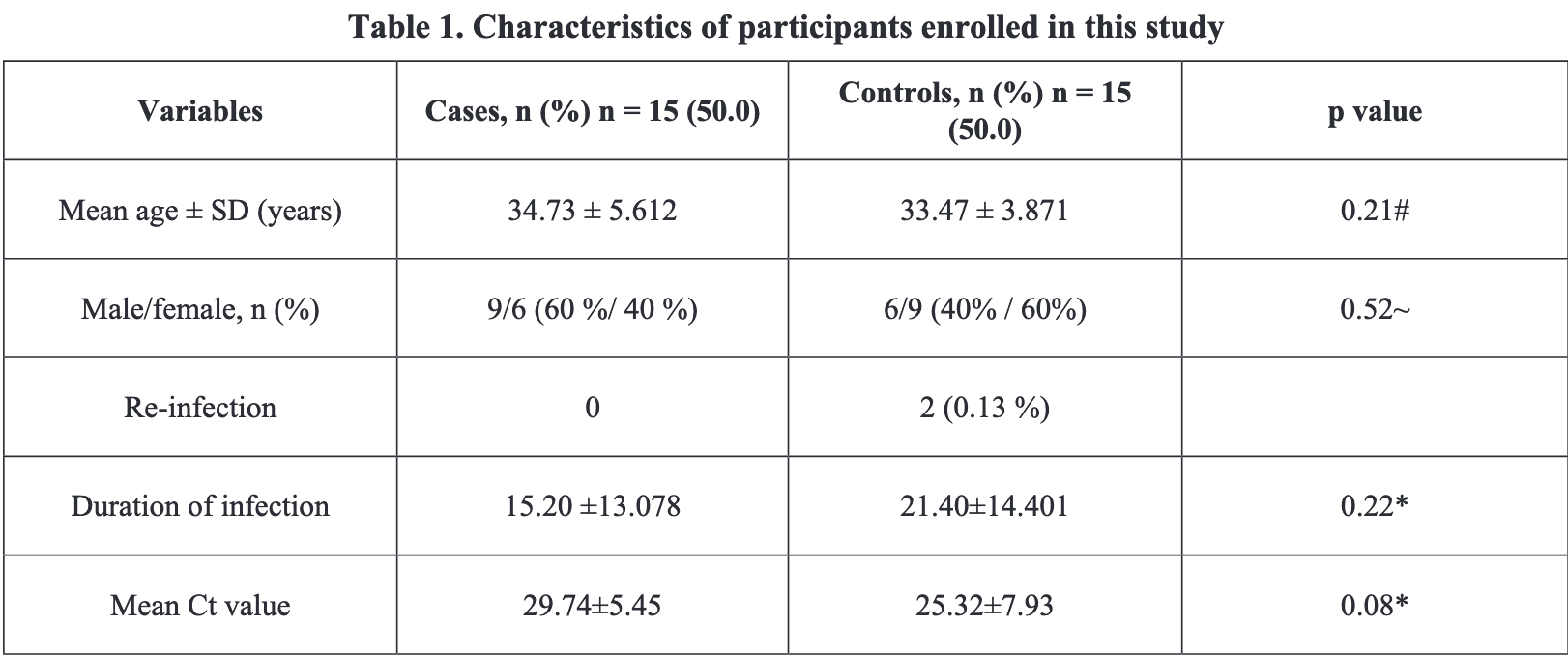
Objectives: We performed this case-control observational study to evaluate the comparison of the length of duration of SARS COV-2 infection and the cycle threshold (Ct) value of reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) nasopharynx swab between the probiotics intake (case) group and the nonprobiotics intake (control) group.
Materials and Methods: Our study was a case-control study involving 15 cases and 15 controls match for RT-PCR positive results. The participants were healthcare consisted of registrars, consultants, and nurses. Each participant was interviewed by google forms using a structured questionnaire to collect sociodemographic characteristics, diet, therapy from a pulmonologist, and adjunct therapy.
Results: The total participants consisted of 15 males and 15 females. 4 participants in the case group had febrile, 1 participant with anosmia, 1 participant with febrile, nausea, and vomit before they consumed probiotics, and 9 participants without clinical complaints. One participant in the control group had fevered and cough, 14 participants without clinical complaints-1 participant with co-morbidities in the control group. The data of age, duration of infection, and cycle threshold (Ct) value were in the normal distribution. Analysis results using SPSS 21.00 show no significant differences in the course of disease between the case group and the control group. We found 2 participants in the control group had re-infection, while there was no re-infection in the case group.
Conclusion: The present study's finding may imply future care for the viral infection through the immunomodulation mechanism by probiotics consumption.
Conflict of Interests: All authors have no conflict of interest.
References
Baud, Agri, Gibson, Reid, Giannoni, Using Probiotics to Flatten the Curve of Coronavirus Disease COVID-2019 Pandemic, Front Public Heal
Didari, Solki, Mozaffari, Nikfar, Abdollahi, A systematic review of the safety of probiotics, Expert Opin Drug Saf
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lofy, Wiesman et al., First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Infusino, Marazzato, Mancone, Fedele, Mastroianni et al., Diet Supplementation, Probiotics, and Nutraceuticals in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Scoping Review, Nutrients
Jin, Lian, Hu, Gao, Zheng et al., Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of 74 cases of coronavirus-infected disease
Kaijin, Hongliu, Yihong, Qin, Yu et al., Management of corona virus disease-19 (COVID-19): the Zhejiang experience, J Zhejiang Univ
Lin, Jiang, Zhang, Huang, Zhang et al., Gastrointestinal symptoms of 95 cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Gut
Ng, Tilg, COVID-19 and the gastrointestinal tract: more than meets the eye, Gut
Pan, Zhang, Yang, Poon, Wang, Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30113-4
Wu, Xiao, Zhang, Gu, Lee et al., SARS-CoV-2 titers in wastewater are higher than expected from clinically confirmed cases, medRxiv