The Effect of Vitamin B12, Magnesium and Vitamin D in COVID-19 among Geriatric Patients
et al., International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 14:5, Apr 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
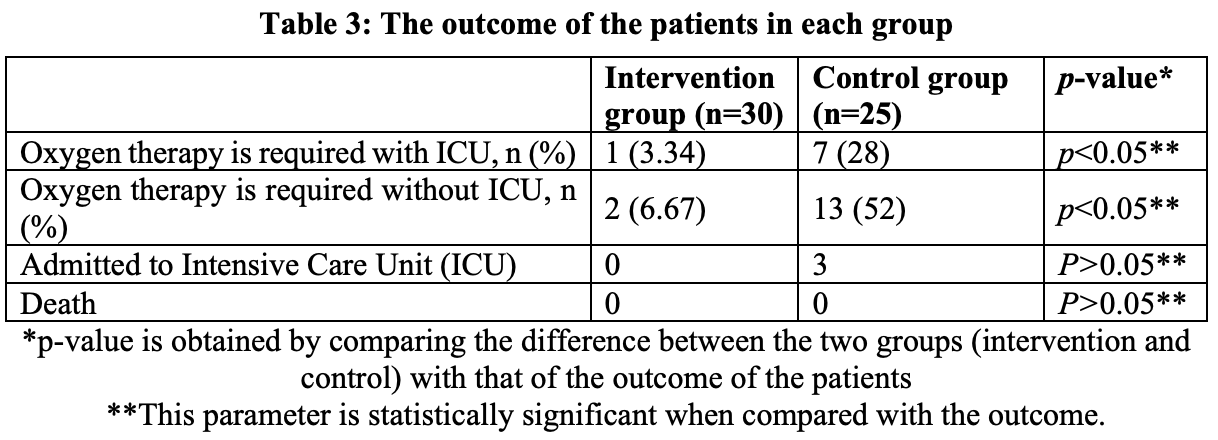
Prospective study of 30 patients treated with vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12, and 25 control patients, showing shorter hospitalization and lower oxygen and ICU requirements with treatment. Cholecalciferol 1000IU, magnesium oxide 150mg, vitamin B12 500μg.
This is the 79th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
Study covers vitamin B12 and vitamin D.
|
risk of ICU admission, 86.8% lower, RR 0.13, p = 0.09, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 3 of 25 (12.0%), NNT 8.3, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
hospitalization time, 38.5% lower, relative time 0.62, p < 0.001, treatment mean 11.2 (±2.8) n=30, control mean 18.2 (±1.21) n=25.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Valecha et al., 26 Apr 2022, prospective, India, peer-reviewed, 1 author, average treatment delay 3.7 days, dosage 1,000IU daily, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with magnesium and vitamin B12) - results of individual treatments may vary.
The Effect of Vitamin B12, Magnesium and Vitamin D in COVID-19 among Geriatric Patients
Introduction: The pandemic hit caused a high prevalence of COVID-19 and fatalities globally. This disease has affected various organ systems and caused systemic inflammation, other than respiratory symptoms. The pathophysiological mechanism also showed that lower levels of vitamin B12 caused disruption in gut microbiota and increased oxidative stress. Reduced levels of vitamins and magnesium, which resulted from the infection of this disease, have led to further deterioration of the health status. Aims and Objectives: This study is intended to evaluate the effect of combination therapy of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in COVID-19 patients by analyzing the outcomes of the disease when this combination therapy is applied. Materials and Methods: This current study is a cohort observational prospective, in which 30 patients were given a combination of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) of 1000 IU, magnesium oxide at 150 mg dose and methylcobalamin (Vitamin B12) of 500 µg, referred to as Intervention group. Another 25 patients were taken for comparison and referred to as the Control group. The baseline data was collected and the outcomes were observed and compared between the two groups.
Results: The study also found that the duration required to run the management of COVID-19 is significantly less in the Intervention group than the control group (p<0.05). The study further added that the group which received the combination therapy required less oxygen therapy with or without ICU support (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The study concluded that this combination therapy can improve the health status of COVID-19 patients by decreasing the probability to require oxygen therapy and ICU support. The study also concluded that this combined therapy can reduce the duration of hospitalization of COVID-19 patients.
References
Aguilar, Fatigue symptom and oximetry sign in a patient with a positive Covid-19 antigen test for Sars-Cov-2, Journal of Medical Research and Health Sciences
Baykal, Ülger, Correlation of vitamin D level with the clinicalradiological severity of COVID-19 in geriatric patients, J Health Sci Med
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut microbiota and Covid-19-possible link and implications, Virus Res
Dinicolantonio, Keefe, Magnesium and Vitamin D Deficiency as a Potential Cause of Immune Dysfunction, Cytokine Storm and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Covid-19 Patients, Mo Med
Dofitas, Philippine COVID-19 Living clinical practice guidelines. Should protective physical barriers be used to prevent COVID-19?, Philippine Soc Microbiol Infect Dis-PSMID
Eskander, Razzaque, Can maintaining optimal magnesium balance reduce the disease severity of COVID-19 patients?, Frontiers in Endocrinology
Grant, Vitamin D's role in reducing risk of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 incidence, severity, and death, Nutrients
Mikkelsen, Stojanovska, Prakash, Apostolopoulos, The effects of vitamin B on the immune/cytokine network and their involvement in depression, Maturitas
Negi, Das, Pahari, Nadeem, Agrewala, Potential role of gut microbiota in induction and regulation of innate immune memory, Front Immunol
Pan, Mu, Yang, Sun, Wang et al., Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study, Am J Gastroenterology
Shakoor, Feehan, Mikkelsen, Dhaheri, Ali et al., Be well: A potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19, Maturitas
Tan, Ho, Kalimuddin, Cherng, Teh et al., Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19), Nutrition
Trapani, Rosanoff, Baniasadi, Barbagallo, Castiglioni et al., The relevance of magnesium homeostasis in COVID-19, Eur J Nutr
Van Kempen, Deixler, SARS-CoV-2: influence of phosphate and magnesium, moderated by vitamin D, on energy (ATP) metabolism and on severity of COVID-19, American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Wiskill, Whittaker et al., Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis, Lancet Infect Dis
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Yeoh, Li et al., Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization, Gastroenterology
