Efficacy and safety of short-wave diathermy treatment for moderate COVID-19 patients: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled clinical study
et al., European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, doi:10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1, Mar 2022
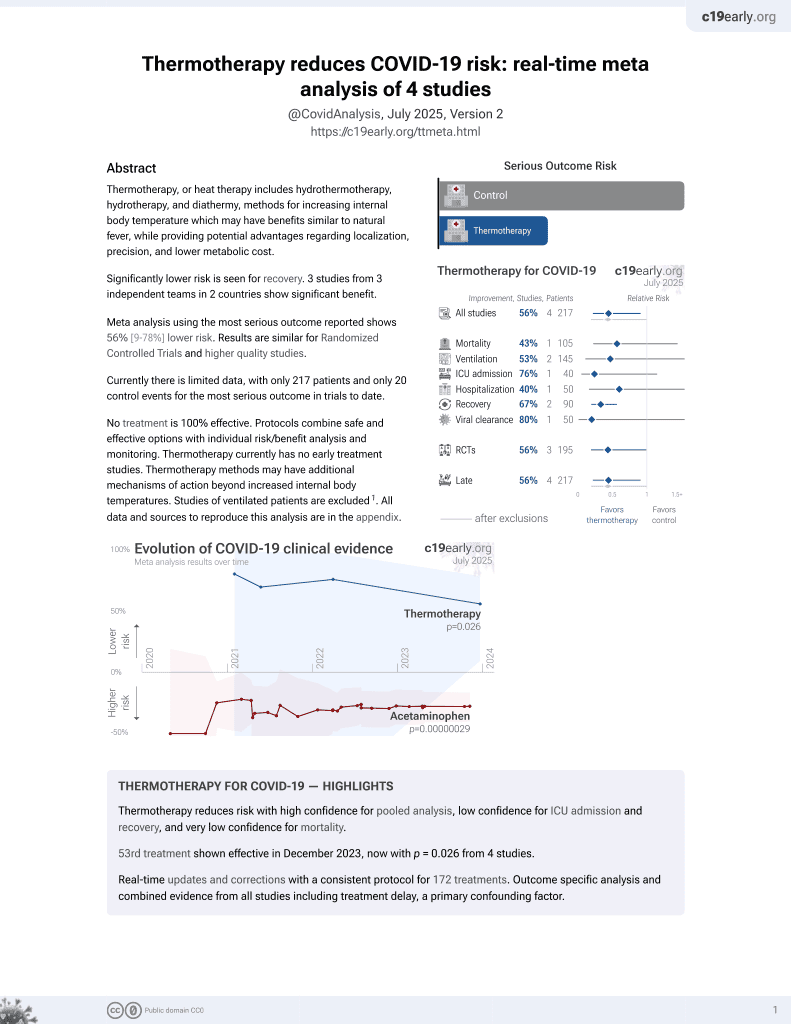
54th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2023, now with p = 0.026 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
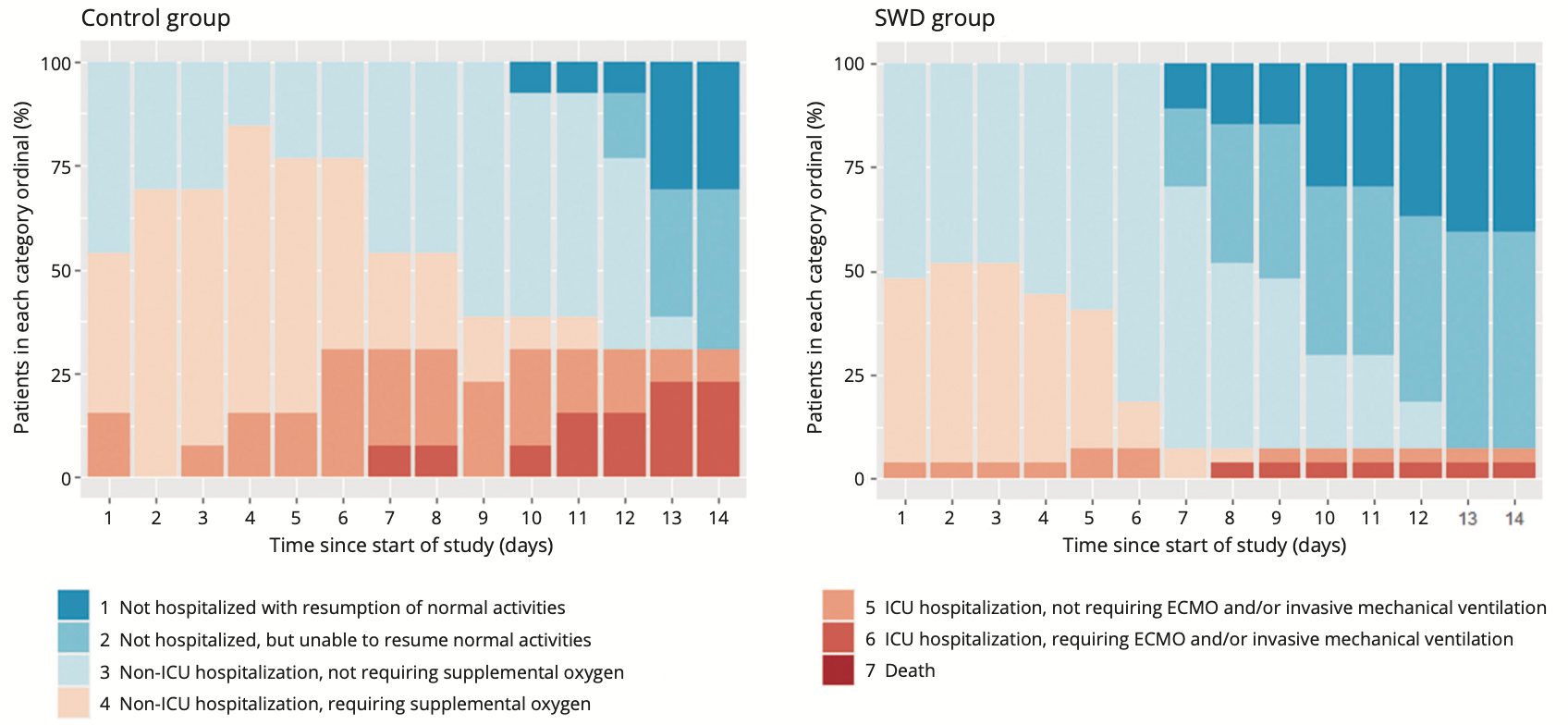
RCT 42 moderate COVID-19 inpatients showing significantly faster clinical and CT scan improvement with short-wave diathermy (SWD) treatment added to standard care, compared to placebo SWD plus standard care. 92.6% of the SWD group had clinical improvement at 14 days, compared to 69.2% in the control group. The SWD group also had significantly faster CT scan improvement. There was no significant difference in adverse events between groups, with only minor side effects like headache and dizziness reported.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 84.0% lower, RR 0.16, p = 0.09, treatment 1 of 27 (3.7%), control 3 of 13 (23.1%), NNT 5.2.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 75.9% lower, RR 0.24, p = 0.07, treatment 2 of 27 (7.4%), control 4 of 13 (30.8%), NNT 4.3.
|
|
clinical improvement, 67.2% lower, HR 0.33, p = 0.005, treatment 27, control 13, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
CT improvement, 73.1% lower, HR 0.27, p = 0.005, treatment 27, control 13, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tian et al., 31 Mar 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, China, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 5 April, 2020, diathermy.
Contact: yuanhuafmmu@foxmail.com.
Efficacy and safety of short-wave diathermy treatment for moderate COVID-19 patients: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled clinical study
doi:10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1)
BACKGROUND: Millions of human beings have suffered in the epidemic of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), but until now the effective treatment methods have been limited. AIM: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of short-wave diathermy (SWD) treatment for moderate COVID-19 patients. DESIGN: A prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled clinical study. SETTING: Inpatients Unit of a COVID-19 specialized hospital. POPULATION: Forty-two patients with moderate COVID-19 were randomly allocated at a 2:1 ratio to two groups: the SWD group and the control group. METHODS: Participants of the SWD group received SWD treatment, and participants of the control group received placebo SWD treatment for one session per day, 10 minutes per session, for no more than 14 days. Both groups were given standard care treatment. Primary outcome was the rate of clinical improvement according to a seven-category ordinal scale. Secondary outcomes included the rate of computed tomography (CT) improvement and the rate of potential adverse events. RESULTS: Clinical improvement occurred in 92.6% of patients in the SWD group by day 14 compared with 69.2% of patients in the control group (P=0.001). The Cox model indicated that the SWD group had a higher clinical improvement probability than the control group (hazard ratio: 3.045; 95% CI: 1.391-6.666; P=0.005). Similarly, CT improvement occurred in 85.2% of patients in the SWD group and 46.2% of patients in the control group respectively by day 14 (P=0.001). The Cox model indicated SWD group had a higher CT improvement probability than control group (hazard ratio: 3.720; 95% CI: 1.486-9.311; P=0.005). There was no significant difference in adverse events between the SWD group and the control group (2 of 27 [7.4%] SWD vs. 1 of 13 [7.7%] control, P=1.000), the most frequent of which were headache (1 of 27 [3.7%] SWD vs. 1 of 13 [7.7%] control patients) and dizziness (1 of 27 [3.7%] SWD vs. 0 of 13 [0%] control patients). CONCLUSIONS: SWD is a valid and reliable adjuvant therapy with a favorable safety profile for moderate COVID-19 patients. CLINICAL REHABILITATION IMPACT: Clinically relevant information is lacking regarding the efficacy and safety of SWD for patients with COVID-19. This study provides the first evidence that SWD is a promising adjuvant therapy for COVID-19.
References
Babaei-Ghazani, Shahrami, Fallah, Ahadi, Forough et al., Continuous shortwave diathermy with exercise reduces pain and improves function in Lateral Epicondylitis more than sham diathermy: A randomized controlled trial, J Bodyw Mov Ther
Baricich, Borg, Cuneo, Cadario, Azzolina et al., position paper for the state-of-the-art application of respiratory support in Patients with COVID-19, Respiration
Cao, Wei, Zou, Jiang, Wang et al., Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Goats, Continuous short-wave (radio-frequency) diathermy, Br J Sports Med
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
He, Ruan, Chang, Zhu, Changes of serum cytokines in children with bronchopneumonia treated with ultrashort wave diathermy, Zhonghua Shiyong Erke Linchuang Zazhi
Hill, Lewis, Mills, Kielty, Pulsed short-wave diathermy effects on human fibroblast proliferation, Arch Phys Med Rehabil
Hirayama, Masui, Murayama, Fujita, Okamoto et al., The characteristics and clinical course of patients with COVID-19 who received invasive mechanical ventilation in Osaka, Japan, Int J Infect Dis
Jan, Chai, Wang, Lin, Tsai, Effects of repetitive shortwave diathermy for reducing synovitis in patients with knee osteoarthritis: an ultrasonographic study, Phys Ther
Laufer, Dar, Effectiveness of thermal and athermal short-wave diathermy for the management of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Osteoarthritis Cartilage
Liu, Zhou, Chen, Ye, Liu et al., Efficacy and safety of antiviral treatment for COVID-19 from evidence in studies of SARS-CoV-2 and other acute viral infections: a systematic review and metaanalysis, CMAJ
Ma, Li, Liu, Short wave diathermy for small spontaneous pneumothorax, Thorax
Million, Lagier, Gautret, Colson, Fournier et al., Early treatment of COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: A retrospective analysis of 1061 cases in Marseille, France, Travel Med Infect Dis
Nicola, Neill, Sohrabi, Khan, Agha et al., Evidence based management guideline for the COVID-19 pandemic -Review article, Int J Surg
Oyelade, Alqahtani, Canciani, Prognosis of COVID-19 in Patients with Liver and Kidney Diseases: An Early Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Trop Med Infect Dis
Poston, Patel, Davis, Management of Critically Ill Adults With COVID-19, JAMA
Torgerson, Torgerson, Unequal Randomisation
Ugurov, Popevski, Gramosli, Neziri, Vuckova et al., Early Initiation of Extracorporeal Blood Purification Using the AN69ST (oXiris ® ) Hemofilter as a Treatment Modality for COVID-19 Patients: a Single-Centre Case Series, Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc
Wang, Fan, Horby, Hayden, Li et al., CAP-China Network. Comparative Outcomes of Adults Hospitalized With Seasonal Influenza A or B Virus Infection: Application of the 7-Category Ordinal Scale, Open Forum Infect Dis
Wang, Hajizadeh, Moore, Mcintyre, Moore et al., Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) treatment for COVID-19 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): A case series, J Thromb Haemost
Wang, Sun, Xu, Liu, Clinical study of ultrashort-wave therapy on airway inflammation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Chin J Phys Med Rehabil
Watson, The thermal and nonthermal effects of high and low doses of pulsed short wave therapy (PSWT), Physiother Res Int
Ye, Wang, Colunga-Lozano, Prasad, Tangamornsuksan et al., Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids in COVID-19 based on evidence for COVID-19, other coronavirus infections, influenza, community-acquired pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis, CMAJ
Yu, Jones, Dean, Laakso, Ultra-shortwave diathermy -a new purported treatment for management of patients with COVID-19, Physiother Theory Pract
Yu, Peng, Biological effects and mechanisms of shortwave radiation: a review, Mil Med Res
Zhang, Sun, Wang, Xu, Wang et al., Effects of ultrashort wave therapy on the clinical efficacy of noninvasive ventilation in patients with type II respiratory failure caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Chin J Phys Med Rehabil
Zhang, Zheng, Liu, Application of ultrashort wave diathermy in treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome, Chin J Phys Med Rehabil
Zheng, Lu, Lure, Jaeger, Lu, Clinical and radiological features of novel coronavirus pneumonia, J XRay Sci Technol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.23736/s1973-9087.21.06892-1",
"ISSN": [
"1973-9087",
"1973-9095"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "TIAN",
"given": "Fei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "WANG",
"given": "Jin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "XI",
"given": "Xiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "SUN",
"given": "Xiaolong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "HE",
"given": "Miao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "ZHAO",
"given": "Chenguang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "FENG",
"given": "Feng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "WANG",
"given": "Hongbin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "SUN",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MAO",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "HU",
"given": "Xu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "YUAN",
"given": "Hua",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Eur J Phys Rehabil Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-20T08:29:16Z",
"timestamp": 1642667356000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-18T14:28:42Z",
"timestamp": 1647613722000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-02T12:21:06Z",
"timestamp": 1704198066177
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1"
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.minervamedica.it/pdf.php?cod=R33Y2022N01A0137",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "17149",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.23736",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Edizioni Minerva Medica",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06699-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0403",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.200647",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000819",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ptj/86.2.236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref007"
},
{
"article-title": "Application of ultrashort wave diathermy in treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Zhang LF",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Chin J Phys Med Rehabil",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref008",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09593985.2020.1757264",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4914",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.joca.2012.05.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofz053",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/XST-200687",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40779-017-0133-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbmt.2019.05.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsm.23.2.123",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pri.460",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref018"
},
{
"article-title": "Changes of serum cytokines in children with bronchopneumonia treated with ultrashort wave diathermy",
"author": "He YG",
"first-page": "220",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Shiyong Erke Linchuang Zazhi",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref019",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thx.52.6.561",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical study of ultrashort-wave therapy on airway inflammation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"author": "Wang W",
"first-page": "477",
"journal-title": "Chin J Phys Med Rehabil",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref021",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of ultrashort wave therapy on the clinical efficacy of noninvasive ventilation in patients with type II respiratory failure caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"author": "Zhang Y",
"first-page": "838",
"journal-title": "Chin J Phys Med Rehabil",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref022",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101738",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.200645",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000509104",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref026"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/apmr.2002.32823",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref027"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14828",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref028"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1057/9780230583993_10",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref029",
"unstructured": "Torgerson DJ, Torgerson CJ. Unequal Randomisation. In: Designing Randomised Trials in Health, Education and the Social Sciences. London: Palgrave Macmillan; 2008. p.108-13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/tropicalmed5020080",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1_ref030"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.minervamedica.it/index2.php?show=R33Y2022N01A0137"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Rehabilitation",
"Physical Therapy, Sports Therapy and Rehabilitation"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and safety of short-wave diathermy treatment for moderate COVID-19 patients: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled clinical study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "58"
}