Use of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees and risk of pneumonia in hospitalised patients with mild coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.947373, Aug 2022
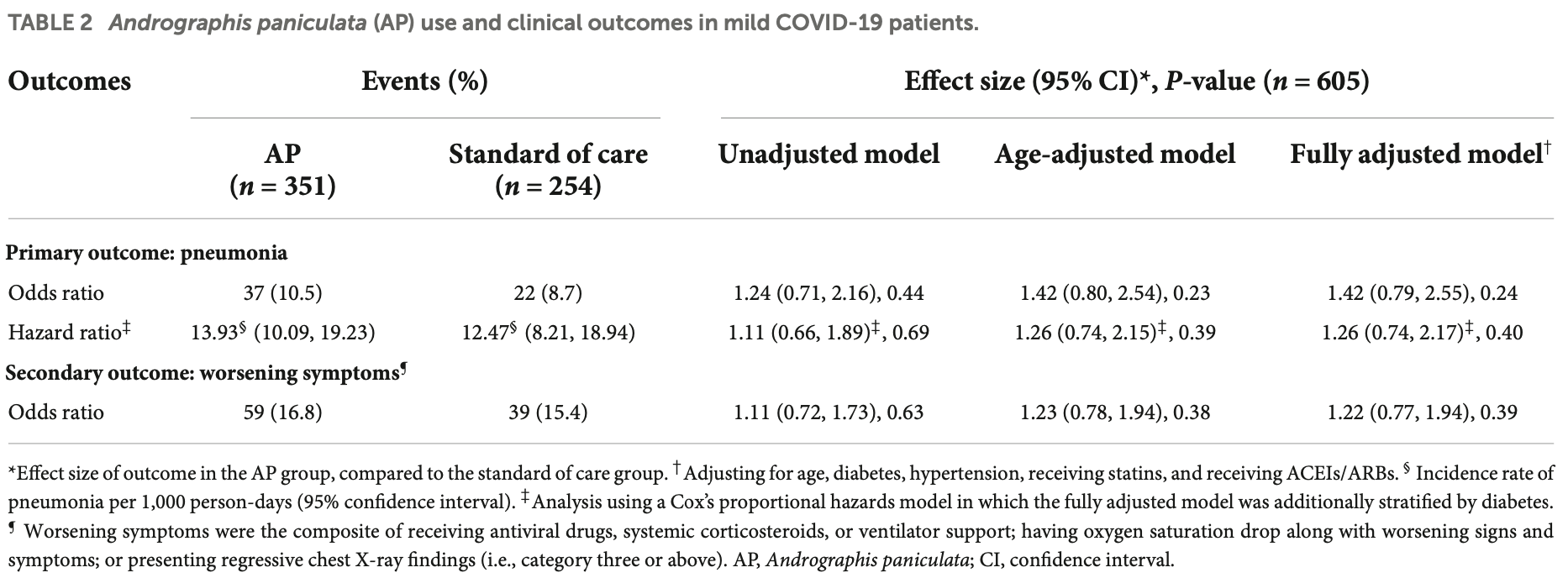
Retrospective 605 hospitalized patients in Thailand, showing higher progression with andrographis, without statistical significance.
|
risk of progression, 26.0% higher, HR 1.26, p = 0.40, treatment 37 of 351 (10.5%), control 22 of 254 (8.7%), Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tanwettiyanont et al., 10 Aug 2022, retrospective, Thailand, peer-reviewed, mean age 35.4, 8 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 31 August, 2021.
Contact: nat.na@up.ac.th, sukrit.ka@up.ac.th.
Use of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees and risk of pneumonia in hospitalised patients with mild coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.947373
Background: Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees (AP) has been widely used in Thailand to treat mild COVID-19 infections since early 2020; however, supporting evidence is scarce and ambiguous. Thus, this study aimed to examine whether the use of AP is associated with a decreased risk of pneumonia in hospitalised mild COVID-19 patients.
Materials and methods: We collected data between March 2020 and August 2021 from COVID-19 patients admitted to one hospital in Thailand. Patients whose infection was confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction, had normal chest radiography and did not receive favipiravir at admission were included and categorised as either AP (deriving from a dried and ground aerial part of the plant), given as capsules with a total daily dose of 180 mg andrographolide for 5 days or standard of care. They were followed for pneumonia confirmed by chest radiography. Multiple logistic regression was used for the analysis controlling for age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, statin use, and antihypertensive drug use.
Ethics statement The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee for clinical research of Phrae Hospital approved this study (no. 70/2564). Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions JT, SK, and NN-E conceptualised the study objectives, designed and collected the data, contributed to the literature review, data cleaning, data analyses, and interpretation of the findings. JT prepared an initial manuscript. NN-E further developed subsequent manuscripts. SK, PT, NP, LS, BB, and CS critically revised the initial manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/..
References
Dai, Chen, Chai, Zhao, Wang et al., Overview of pharmacological activities of Andrographis paniculata and its major compound andrographolide, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1501657
Enmozhi, Raja, Sebastine, Joseph, Andrographolide as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: an in silico approach, J Biomol Struct Dyn, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1760136
Hossain, Urbi, Karuniawati, Mohiuddin, Qrimida et al., Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) wall. ex nees: an updated review of phytochemistry, antimicrobial pharmacology, and clinical safety and efficacy, Life, doi:10.3390/life11040348
Hossain, Urbi, Sule, Rahman, None
Jara, Undurraga, González, Paredes, Fontecilla et al., Effectiveness of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in Chile, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107715
Karbwang, Bangchang, Repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment, J Thai Trad Alt Med
Phumiamorn, Sapsutthipas, Pruksakorn, Trisiriwanich, In vitro Study on Antiviral Activity of Andrographis paniculata against COVID-19
Rajagopal, Varakumar, Baliwada, Byran, Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Futur J Pharm Sci, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x
Rattanaraksa, Khempetch, Poolwiwatchaikool, Nimitvilai, Loatrakul et al., The efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract for treatment of COVID-19 patients with mild symptoms, Nakhonpathom hospital. Reg 4-5 Med J
Sa-Ngiamsuntorn, Suksatu, Pewkliang, Thongsri, Kanjanasirirat et al., Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of Andrographis paniculata extract and its major component andrographolide in human lung epithelial cells and cytotoxicity evaluation in major organ cell representatives, J Nat Prod, doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01324
Schumann, Heigl, Rohrbach, Sheriff, Wagner et al., A report on the first 7 sequential patients treated within the C-reactive protein apheresis in COVID (CACOV) registry, Am J Case Rep, doi:10.12659/AJCR.935263
Vandenbroucke, Elm, Altman, Gøtzsche, Mulrow et al., Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration, PLoS Med, doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.014
Wanaratna, Leethong, Inchai, Chueawiang, Sriraksa et al., Efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract in patients with mild COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial (version 3). medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.07.08.21259912
Worakunphanich, Thavorncharoensap, Youngkong, Thadanipon, Thakkinstian, Safety of Andrographis paniculata: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf, doi:10.1002/pds.5190
Zeng, Wei, Zhou, Yuan, Lei et al., Andrographolide: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches, Phyther Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7324
Zhang, Lv, Zhou, Xie, Xu et al., Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of COVID-19: a multicenter, prospective, open-label and randomized controlled trial, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7141
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.947373",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.947373",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p><jats:italic>Andrographis paniculata</jats:italic> (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees (AP) has been widely used in Thailand to treat mild COVID-19 infections since early 2020; however, supporting evidence is scarce and ambiguous. Thus, this study aimed to examine whether the use of AP is associated with a decreased risk of pneumonia in hospitalised mild COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Materials and methods</jats:title><jats:p>We collected data between March 2020 and August 2021 from COVID-19 patients admitted to one hospital in Thailand. Patients whose infection was confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction, had normal chest radiography and did not receive favipiravir at admission were included and categorised as either AP (deriving from a dried and ground aerial part of the plant), given as capsules with a total daily dose of 180 mg andrographolide for 5 days or standard of care. They were followed for pneumonia confirmed by chest radiography. Multiple logistic regression was used for the analysis controlling for age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, statin use, and antihypertensive drug use.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 605 out of 1,054 patients (mostly unvaccinated) were included in the analysis. Of these, 59 patients (9.8%) developed pneumonia during the median follow-up of 7 days. The incidence rates of pneumonia were 13.93 (95% CI 10.09, 19.23) and 12.47 (95% CI 8.21, 18.94) per 1,000 person-days in the AP and standard of care groups, respectively. Compared to the standard of care group, the odds ratios of having pneumonia in the AP group were 1.24 (95% CI 0.71, 2.16; unadjusted model) and 1.42 (95% CI 0.79, 2.55; fully adjusted model). All sensitivity analyses were consistent with the main results.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>The use of AP was not significantly associated with a decreased risk of pneumonia in mild COVID-19 patients. While waiting for insights from ongoing trials, AP’s use in COVID-19 should be done with caution.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2022.947373"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanwettiyanont",
"given": "Jeeranan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piriyachananusorn",
"given": "Napacha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sangsoi",
"given": "Lilit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boonsong",
"given": "Benjawan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sunpapoa",
"given": "Chamlong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanamatayarat",
"given": "Patcharawan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Na-Ek",
"given": "Nat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kanchanasurakit",
"given": "Sukrit",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T05:25:20Z",
"timestamp": 1660109120000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T05:25:24Z",
"timestamp": 1660109124000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100011093",
"award": [
"UoE62010"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "University of Phayao"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-22T14:30:11Z",
"timestamp": 1692714611888
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1660089600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.947373/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment.",
"author": "Karbwang",
"first-page": "285",
"journal-title": "J Thai Trad Alt Med.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2018.1501657",
"article-title": "Overview of pharmacological activities of Andrographis paniculata and its major compound andrographolide.",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S17",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/274905",
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) wall. ex nees: a review of ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology.",
"author": "Hossain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci World J.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life11040348",
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) wall. ex nees: an updated review of phytochemistry, antimicrobial pharmacology, and clinical safety and efficacy.",
"author": "Hossain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Life.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x",
"article-title": "Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach.",
"author": "Rajagopal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Futur J Pharm Sci.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1760136",
"article-title": "Andrographolide as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: an in silico approach.",
"author": "Enmozhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3092",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Phumiamorn",
"journal-title": "In vitro Study on Antiviral Activity of Andrographis paniculata against COVID-19.",
"key": "B7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01324",
"article-title": "Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of Andrographis paniculata extract and its major component andrographolide in human lung epithelial cells and cytotoxicity evaluation in major organ cell representatives.",
"author": "Sa-ngiamsuntorn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1261",
"journal-title": "J Nat Prod.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract for treatment of COVID-19 patients with mild symptoms, Nakhonpathom hospital.",
"author": "Rattanaraksa",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Reg 4-5 Med J.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.07.08.21259912",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract in patients with mild COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial (version 3).",
"author": "Wanaratna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv[Preprint].",
"key": "B10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7141",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of COVID-19: a multicenter, prospective, open-label and randomized controlled trial.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4401",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.014",
"article-title": "Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration.",
"author": "Vandenbroucke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"journal-title": "Clinical Management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) when COVID-19 Disease is Suspected: Interim Guidance.",
"key": "B13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"journal-title": "Identifier TCTR20210809004 - Comparison Efficacy and Safety of Andrographis paniculata Extract Capsules and Placebo in COVID-19 Patients: Double Blind Randomized Control Trial.",
"key": "B14",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"journal-title": "Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with Higher Risk for Severe COVID-19: Information for Healthcare Providers.",
"key": "B15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"journal-title": "Science Brief: Evidence Used to Update the List of Underlying Medical Conditions that Increase a Person’s Risk of Severe Illness from COVID-19.",
"key": "B16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7324",
"article-title": "Andrographolide: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches.",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "336",
"journal-title": "Phyther Res.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/AJCR.935263",
"article-title": "A report on the first 7 sequential patients treated within the C-reactive protein apheresis in COVID (CACOV) registry.",
"author": "Schumann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Case Rep.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107715",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in Chile.",
"author": "Jara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.5190",
"article-title": "Safety of Andrographis paniculata: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Worakunphanich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.947373/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Use of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees and risk of pneumonia in hospitalised patients with mild coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "9"
}