Efficacy of diammonium glycyrrhizinate combined with vitamin C for treating hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a retrospective, observational study
et al., QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab184 , Jul 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
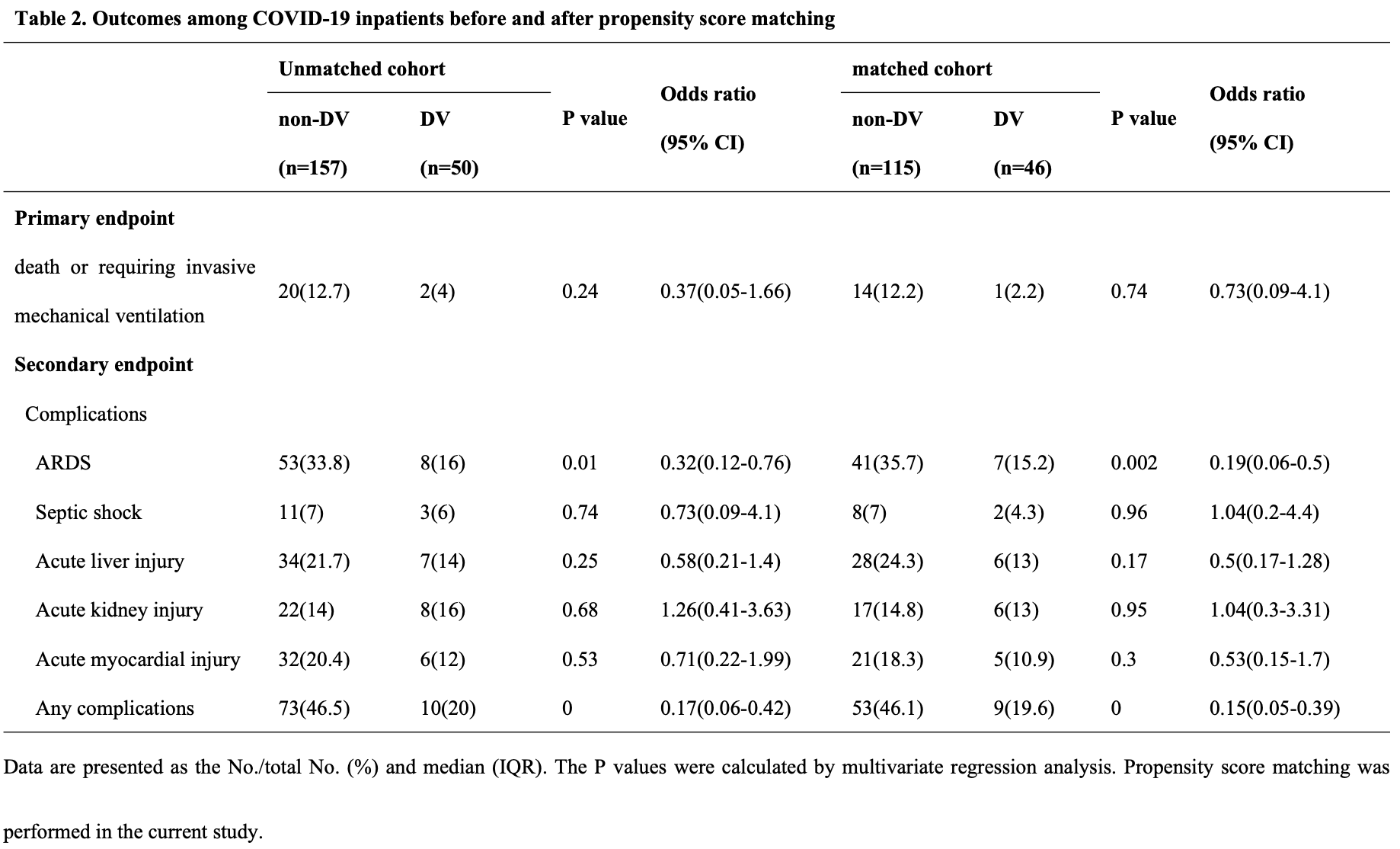
PSM retrospective 207 hospitalized patients in China, 46 treated with diammonium glycyrrhizinate and vitamin C, showing lower risk of ARDS with treatment.
This is the 30th of 73 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000076.
20 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0016.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of death/intubation, 24.5% lower, RR 0.75, p = 0.74, treatment 1 of 46 (2.2%), control 14 of 115 (12.2%), NNT 10.0, odds ratio converted to relative risk, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of ARDS, 73.3% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.002, treatment 7 of 46 (15.2%), control 41 of 115 (35.7%), NNT 4.9, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tan et al., 26 Jul 2021, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, dosage 500mg tid days 1-7, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with diammonium glycyrrhizinate) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Efficacy of diammonium glycyrrhizinate combined with vitamin C for treating hospitalized 2 COVID-19 patients: a retrospective, observational study 3 4
doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab184/6329274
Aims: To observe the effect of combination treatment of giammonium glycyrrhizinate and vitamin 36 C (DV)on the prognoses of patients with COVID-19. 37 Methods: This retrospective observational study recruited 207 COVID-19 patients from Tongji 38 Hospital,patients were assigned to DV and non-DV groups on the basis of the DV treatment. To 39 make the results more credible, a propensity-score matching (PSM) approach was adopted at a 1:3 40 ratio to determine the participants. Logistic analysis was used to assess the effect of DV therapy in 41 the progress of COVID-19. 42 Results: In the DV group, the new onset incidence rate of acute respiratory distress syndrome 43 (ARDS) after admission was clearly lower than that in the non-DV group (DV vs non-DV groups, 44 15.2% vs 35.7%; P=0.002). Compared with the non-DV group, the DV group showed fewer new 45 onset of complications (such as ARDS, acute liver injury and acute myocardial injury) (DV vs non-46 DV groups,19.6% vs 46.1%; P=0.000). Moreover, DG+VC may help to recover the count of NK 47 cells and decrease the level of sIL-2R. 48 Conclusions: DG+VC might be a promising candidate for preventing the deterioration of COVID-49 19 patients, which is worthy to be studied in large and perspective cohort. 50
Authors' contributions
300 LJL and HPQ contributed to study concept and design. RMT and XGX contributed to the literature
References
Biancatelli, Mmarik, The antiviral properties of vitamin C, Expert Rev 333 Anti Infect Ther
Chen, Hu, Hood, Zhang, Zhang et al., A Novel Combination of Vitamin C, 376 Curcumin and Glycyrrhizic Acid Potentially Regulates Immune and Inflammatory Response 377 Associated with Coronavirus Infections: A Perspective from System Biology Analysis, Nutrients
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical 365 characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive 366 study, Lancet
Chiscano-Camon, Ruiz-Rodriguez, Ruiz-Sanmartin, Oferrer, Vitamin C levels 368 in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care
Cvergoten, Glycyrrhizin: An alternative drug for the treatment of COVID-19 infection 327 and the associated respiratory syndrome?, Pharmacol Ther
Ding, Deng, Ding, Ye, Shuang, Glycyrrhetinic acid and its derivatives as 373 potential alternative medicine to relieve symptoms in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med
Du, Liang, Yang, Wang, Cao et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection complicated 362 by inflammatory syndrome. Could high-dose human immunoglobulin for intravenous use (IVIG) 363 be beneficial?, Autoimmun Rev
Force, Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition, JAMA
Gabarre, Dumas, Dupont, Darmon, Ezafrani, Acute kidney injury in 348 critically ill patients with COVID-19, Intensive Care Med
Hiedra, Lo, Elbashabsheh, Gul, Wright et al., The use of IV vitamin 371 C for patients with COVID-19: a case series, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther
Holford, Carr, Jovic, Ali, Whitaker et al., Vitamin C-An Adjunctive
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 320 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 343 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Kwo, Smlim, ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver 341 Chemistries, Am J Gastroenterol
Li, Sun, Liu, Natural products in licorice for the therapy of liver diseases: Progress and 329 future opportunities, Pharmacol Res
Li, Wu, Li, Liang, Kpchen, Integrative pharmacological mechanism of vitamin 322 C combined with glycyrrhizic acid against COVID-19: findings of bioinformatics analyses, Bioinform
Luo, Liu, Li, Pharmacological perspective: glycyrrhizin may be an efficacious therapeutic 325 agent for COVID-19, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Riva, Yuan, Yin, Martin-Sancho, Matsunaga et al., SARS-CoV-2 was associated with organ dysfunction such as ARDS, acute heart injury, acute 238 kidney injury, shock and acute liver injury,significant cases progressed rapidly to severe forms 239
Singer, Deutschman, Seymour, Shankar-Hari, Annane et al., The 345 Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3), JAMA
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk Factors Associated With Acute 350 Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia 351 in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., Harm of IV High-Dose 337 Vitamin C Therapy in Adult Patients: A Scoping Review, Ann Intensive Care
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab184",
"ISSN": [
"1460-2725",
"1460-2393"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcab184",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Summary</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The current global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has shown limited responses to medical treatments.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Aims</jats:title><jats:p>To observe the effect of combination treatment of giammonium glycyrrhizinate and vitamin C (DV) on the prognoses of patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This retrospective observational study recruited 207 COVID-19 patients from Tongji Hospital, patients were assigned to DV and non-DV groups on the basis of the DV treatment. To make the results more credible, a propensity score matching (PSM) approach was adopted at a 1:3 ratio to determine the participants. Logistic analysis was used to assess the effect of DV therapy in the progress of COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In the DV group, the new-onset incidence rate of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) after admission was clearly lower than that in the non-DV group (DV vs. non-DV groups, 15.2% vs. 35.7%; P = 0.002). Compared with the non-DV group, the DV group showed fewer new onset of complications (such as ARDS, acute liver injury and acute myocardial injury) (DV vs. non-DV groups, 19.6% vs. 46.1%; P = 0.000). Moreover, DG+VC may help to recover the count of NK cells and decrease the level of sIL-2R.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>DG+VC might be a promising candidate for preventing the deterioration of COVID-19 patients, which is worthy to be studied in large and perspective cohort.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Department of Critical Care Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China"
}
],
"family": "Xiang",
"given": "X",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Surgery, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Department of Critical Care Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China"
}
],
"family": "Qu",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Department of Critical Care Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "QJM: An International Journal of Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-23T11:11:31Z",
"timestamp": 1627038691000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-06T11:18:07Z",
"timestamp": 1699269487000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"YG2020YQ30"
],
"name": "Medical-engineering Cross Foundation of Shanghai Jiao Tong University"
},
{
"award": [
"GWV-10.2-XD03"
],
"name": "Three-year Plan For Developing a Public Health System of Shanghai, Talent Training"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81770005",
"81970005"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-07T00:35:24Z",
"timestamp": 1699317324792
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
21
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1627344000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/qjmed/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/qjmed/hcab184/40664592/hcab184.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/qjmed/article-pdf/115/2/77/42568425/hcab184.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/qjmed/article-pdf/115/2/77/42568425/hcab184.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "77-83",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1",
"article-title": "Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing",
"author": "Riva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B1",
"volume": "586",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bib/bbaa141",
"article-title": "Integrative pharmacological mechanism of vitamin C combined with glycyrrhizic acid against COVID-19: findings of bioinformatics analyses",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1161",
"journal-title": "Brief Bioinform",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B3",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105995",
"article-title": "Pharmacological perspective: glycyrrhizin may be an efficacious therapeutic agent for COVID-19",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105995",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B4",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107618",
"article-title": "Glycyrrhizin: an alternative drug for the treatment of COVID-19 infection and the associated respiratory syndrome?",
"author": "Bailly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107618",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B5",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2019.04.025",
"article-title": "Natural products in licorice for the therapy of liver diseases: progress and future opportunities",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "210",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B6",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123760",
"article-title": "Vitamin C-an adjunctive therapy for respiratory infection, sepsis and COVID-19",
"author": "Holford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3760",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2020.1706483",
"article-title": "The antiviral properties of vitamin C",
"author": "Colunga Biancatelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B8",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3",
"article-title": "Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B9",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004396",
"article-title": "Harm of IV high-dose vitamin C therapy in adult patients: a scoping review",
"author": "Yanase",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e620",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B10",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition",
"author": "Force",
"first-page": "2526",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B11",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ajg.2016.517",
"article-title": "ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries",
"author": "Kwo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B12",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2016.0287",
"article-title": "The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3)",
"author": "Singer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "801",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B13",
"volume": "315",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06153-9",
"article-title": "Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gabarre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1339",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B14",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B15",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B16",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00524-2020",
"article-title": "Predictors of mortality for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2000524",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B17",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-0158-2",
"article-title": "A retrospective cohort study of methylprednisolone therapy in severe patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B18",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102559",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection complicated by inflammatory syndrome. Could high-dose human immunoglobulin for intravenous use (IVIG) be beneficial?",
"author": "Prete",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102559",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B19",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B20",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Chiscano-Camón",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "522",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B21",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2020.1794819",
"article-title": "The use of IV vitamin C for patients with COVID-19: a case series",
"author": "Hiedra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1259",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B22",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26064",
"article-title": "Glycyrrhetinic acid and its derivatives as potential alternative medicine to relieve symptoms in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2200",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B23",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041193",
"article-title": "A novel combination of vitamin C, curcumin and glycyrrhizic acid potentially regulates immune and inflammatory response associated with coronavirus infections: a perspective from system biology analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1193",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2022022115094689500_hcab184-B24",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/qjmed/article/115/2/77/6329274"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of diammonium glycyrrhizinate combined with vitamin C for treating hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a retrospective, observational study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "115"
}
