ACE2-independent entry factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune activation
et al., mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01897-24, Dec 2025
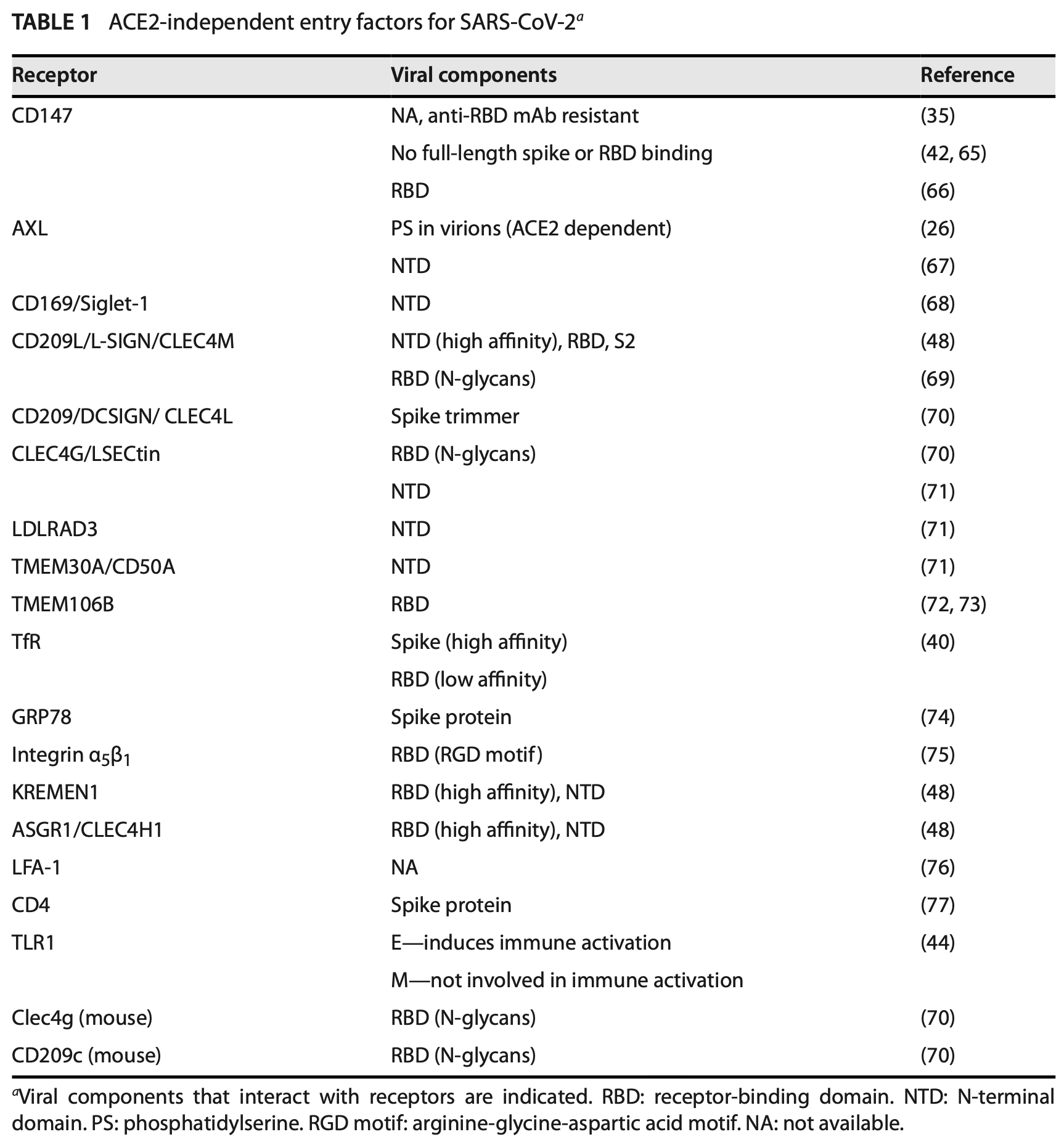
Review of ACE2-independent entry factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune activation. Authors identify multiple alternative receptors including CD147, AXL, C-type lectin receptors (CD209L, CD209, CLEC4G), I-type lectin receptors (CD169/Siglec-1), membrane proteins (LDLRAD3, TMEM30A, TMEM106B), transferrin receptor, GRP78, integrin α5β1, KREMEN1, ASGR1, LFA-1, and CD4 that enable SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells lacking detectable ACE2 expression.
Sun et al., 22 Dec 2025, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: theresa.chang@rutgers.edu.
ACE2-independent entry factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune activation
mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01897-24
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), remains a major public health threat, particularly in vulnerable populations. SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins interact with the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, together with accessory molecules that facilitate viral entry, through its spike receptor-binding domain (RBD). Although ACE2 is the primary receptor required for viral replication, its expression patterns do not fully correlate with viral distribution or tissue pathology. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to infect cells and tissues lacking detectable ACE2 expression. Viral entry via ACE2-independent pathways may also confer resistance to some monoclonal antibodies (Abs) targeting the spike RBD that block ACE2-mediated binding. These observations highlight the potential significance of ACE2-independent entry factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly in vaccinated individuals with Abs directed against ACE2-dependent viral entry. In this review, we discuss the emerging roles of ACE2-independent entry factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection and the immune responses. These factors include CD147, AXL, CD169/Siglec-1, CD209L, CD209, CLEC4G, ASGR1, LDLRAD3, TMEM30A, TMEM106B, transferrin receptor 1, GPR78, integrin α5β1, KREMEN1, LFA-1, and CD4. While ACE2 remains central to viral replication, ACE2-inde pendent entry appears sufficient to elicit immune responses. Therefore, future inves tigations are warranted to elucidate the roles of ACE2-independent mechanisms in immune-mediated pathology and viral evolution, independent of immune pressure targeting ACE2-mediated entry in previously infected or vaccinated individuals.
KEYWORDS SARS-CoV-2, alternative receptors T he coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, associated with more than 20 million deaths, was caused by severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and remains a threat due to the continuous evolution of new variants (1, 2). Vaccinated people remain susceptible to infection by emerging variants (3) (4) (5) (6) , and between 100 and 1,000 COVID-19-related deaths continue to occur each week in the United States in 2025 (7). Although current SARS-CoV-2 variants are less pathogenic than early strains, co-infection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus can have severe disease outcomes (8, 9). Additionally, the emergence of newly evolved strains with better transmissibility and enhanced immune escape poses an ongoing concern. Therefore, a deeper understand ing of the mechanisms underlying SARS-CoV-2 infection is essential for developing more effective preventive and therapeutic strategies to protect vulnerable populations. SARS-CoV-2 entry is primarily mediated by binding of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, the entry mechanism of which has been summarized in an excellent review (10). In virus-producing..
AUTHOR AFFILIATIONS Various domains on the spike proteins and E proteins are involved. The interaction of viruses and alternative receptors (e.g., TMEM106B may occur in endosomal compartments). These alternative receptors may play a crucial role in immune activation, particularly in myeloid cells. Additionally, they can act synergistically to facilitate entry of the SARS-CoV-2 E484D variant that is resistant to antibodies targeting RBD through ACE2-mediated viral entry. (B) Alternative receptors can enhance or inhibit ACE2-mediated SARS-CoV-2 entry. The enhancing effect of AXL on ACE2-mediated infection is absent in cells expressing TMPRSS2.
References
Ahn, Burnett, Pandey, Ghoshal, Singla et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein stimulates macropinocytosis in murine and human macrophages via PKC-NADPH oxidase signaling, Antioxidants (Basel), doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Akinyemi, Simpson, Oyelere, Nur, Ngule et al., Unveiling the dark side of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) in cancers and other human pathology: a systematic review, Pediatr Res, doi:10.1038/s41390-020-01177-9
Ali, Mirza, Naquiallah, Hassan, Masrur et al., CD147 levels in blood and adipose tissues correlate with vascular dysfunction in obese diabetic adults, J Cardiovasc Dev Dis
Amraei, Yin, Napoleon, Suder, Berrigan et al., CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN act as receptors for SARS-CoV-2, ACS Cent Sci, doi:10.1021/acscentsci.0c01537
Amruta, Engler-Chiurazzi, Ic, Gressett, Biose et al., In vivo protection from SARS-CoV-2 infection by ATN-161 in k18-hACE2 transgenic mice, Life Sci, doi:10.1038/ncb0702-e172
Arora, Kempf, Nehlmeier, Schulz, Cossmann et al., Augmented neutralisation resistance of emerging omicron subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00422-4
Arora, Zhang, Nehlmeier, Kempf, Graichen et al., Host cell lectins ASGR1 and DC-SIGN jointly with TMEM106B confer ACE2 independence and imdevimab resistance to SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus with spike mutation E484D, J Virol, doi:10.1101/2023.05.04.539267
Badeti, Jiang, Naghizadeh, Tseng, Bushkin et al., Development of a novel human CD147 knock-in NSG mouse model to test SARS-CoV-2 viral infection, Cell Biosci, doi:10.3390/v14112535
Baggen, Jacquemyn, Persoons, Vanstreels, Pye et al., TMEM106B is a receptor mediating ACE2-independent SARS-CoV-2 cell entry, Cell, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Baggen, Persoons, Vanstreels, Jansen, Van Looveren et al., Genome-wide CRISPR screening identifies TMEM106B as a proviral host factor for SARS-CoV-2, Nat Genet, doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c03296
Barrett, Bilaloglu, Cornwell, Burgess, Virginio et al., Platelets contribute to disease severity in COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01082-6
Bayati, Kumar, Francis, Mcpherson, SARS-CoV-2 infects cells after viral entry via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1128/JVI.00253-07
Bertolotti, Zhang, Hendershot, Harding, Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfoldedprotein response, Nat Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/35014014
Bestle, Heindl, Limburg, Lam Van T, Pilgram et al., TMPRSS2 and furin are both essential for proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 in human airway cells, Life Sci Alliance, doi:10.26508/lsa.202000786
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6
Biering, De Sousa, Tjang, Pahmeier, Zhu et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike triggers barrier dysfunction and vascular leak via integrins and TGF-β signaling, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34910-5
Blanco-Melo, Nilsson-Payant, Liu, Uhl, Hoagland et al., Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19, Cell, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Bohan, Van Ert, Ruggio, Rogers, Badreddine et al., Phosphatidylserine receptors enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Bozzo, Nchioua, Volcic, Koepke, Krüger et al., IFITM proteins promote SARS-CoV-2 infection and are targets for virus inhibition in vitro, Nat Commun, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Brady, Zheng, Murphy, Huang, Hu, The frontotempo ral lobar degeneration risk factor, TMEM106B, regulates lysosomal morphology and function, Hum Mol Genet, doi:10.1093/hmg/dds475
Brenig, Pop, Triantafyllou, Geng, Singanayagam et al., Expression of AXL receptor tyrosine kinase relates to monocyte dysfunction and severity of cirrhosis, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Brocchieri, De Macario, Macario, Hsp70 genes in the human genome: conservation and differentiation patterns predict a wide array of overlapping and specialized functions, BMC Evol Biol, doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-19
Brunetti, Davanzo, De Moraes, Ferrari, Souza et al., SARS-CoV-2 uses CD4 to infect T helper lymphocytes, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.84790
Callaway, Coronavirus variant XBB.1.5 rises in the United States -is it a global threat?, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-00014-3
Cantuti-Castelvetri, Ojha, Pedro, Djannatian, Franz et al., Neuropi lin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity, Science, doi:10.1128/JVI.00253-07
Carnevale, Cammisotto, Bartimoccia, Nocella, Castellani et al., Toll-like receptor 4-dependent platelet-related Minireview, mBio Month, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321541
Causeret, Sumia, Pierani, Kremen1 and Dickkopf1 control cell survival in a Wnt-independent manner, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.3390/ijms21144818
Choudhary, Calianese, Honnen, Kolloli, Dikdan et al., Broad-spectrum heavily mutated monoclonal antibody isolated from COVID-19 convalescent vaccinee with capacity to neutralize SARS-CoV2 variants ranging from B.1 to BQ, doi:10.1101/2023.05.04.539267
Christie, Tada, Yin, Bhardwaj, Landau et al., Single-virus tracking reveals variant SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins induce ACE2-independent membrane interactions, Sci Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abo3977
Chu, Chan, Zhang, Wang, Yuan et al., Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus and bat coronavirus HKU9 both can utilize GRP78 for attachment onto host cells, Journal of Biological Chemistry, doi:10.1074/jbc.RA118.001897
Clausen, Sandoval, Spliid, Pihl, Perrett et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection depends on cellular heparan sulfate and ACE2, Cell, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Cong, Deng, Wang, Li, The role of respiratory co-infection with influenza or respiratory syncytial virus in the clinical severity of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Glob Health, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Daly, Simonetti, Klein, Chen, Williamson et al., Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Science, doi:10.1128/JVI.00253-07
Den Dunnen, Gringhuis, Geijtenbeek, Innate signaling by the C-type lectin DC-SIGN dictates immune responses, Cancer Immunol Immunother, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Desautels, Arrildt, Zemla, Lau, Zhu et al., 130.156.56. potency of a clinical antibody against Omicron, mBio Month, doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07385-1
Destras, Bal, Simon, Lina, Josset, Sotrovimab drives SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant evolution in immunocompromised patients, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Dominguez-Soto, Aragoneses-Fenoll, Gayo, Martinez-Prats, Colmenares et al., The DC-SIGN-related lectin LSECtin mediates antigen capture and pathogen binding by human myeloid cells, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2006-09-048058
Duan, Xing, Chu, Deng, Du et al., ACE2-dependent and -independent SARS-CoV-2 entries dictate viral replication and inflammatory response during infection, Nat Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41556-024-01388-w
Felordi, Memarnejadian, Najimi, Vosough, Is there any alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2?, Cell J, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Feng, Lacrampe, Hu, Physiological and pathological functions of TMEM106B: a gene associated with brain aging and multiple brain disorders, Acta Neuropathol, doi:10.1007/s00401-020-02246-3
Gay, Balaji, Byers, Giving AXL the axe: targeting AXL in human malignancy, Br J Cancer, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Grabowska, Lopez-Venegas, Affandi, Den Haan, CD169+ macrophages capture and dendritic cells instruct: the interplay of the gatekeeper and the general of the immune system, Front Immunol, doi:10.3892/br.2020.1402
Gramberg, Hofmann, Möller, Lalor, Marzi et al., LSECtin interacts with filovirus glycoproteins and the spike protein of SARS coronavirus, Virology (Auckland), doi:10.3892/br.2020.1402
Grass, Toole, How, with whom and when: an overview of CD147-mediated regulatory networks influencing matrix metallopro teinase activity, Biosci Rep, doi:10.1042/BSR20150256
Gressett, Nader, Robles, Buranda, Kerrigan et al., Integrins as therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-99893-7
Grodzki, Bluhm, Schaefer, Tagmount, Russo et al., Genome-scale CRISPR screens identify host factors that promote human coronavirus infection, Genome Med, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Gu, Cao, Zhang, Gao, Wang et al., Receptome profiling identifies KREMEN1 and ASGR1 as alternative functional receptors of SARS-CoV-2, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-021-00595-6
Han, Lv, Moser, Zhou, Woehrle et al., ACE2-independent SARS-CoV-2 virus entry through cell surface GRP78 on monocytes, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104869
Hansen, Baum, Pascal, Russo, Giordano et al., Studies in humanized mice and convalescent humans yield a SARS-CoV-2 antibody cocktail, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd0827
Herzog, Fragkou, Arneth, Mkhlof, Skevaki, Myeloid CD169/Siglec1: an immunoregulatory biomarker in viral disease, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.979373
Hikmet, Méar, Edvinsson, Micke, Uhlén et al., The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues, Mol Syst Biol, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Pöhlmann, A multibasic cleavage site in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is essential for infection of human lung cells, Mol Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1128/JVI.00253-07
Hoffmann, Mereiter, Oh, Monteil, Elder et al., Identification of lectin receptors for conserved SARS-CoV-2 glycosylation sites, EMBO J, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Hoffmann, Sidarovich, Arora, Krüger, Nehlmeier et al., Evidence for an ACE2-independent entry pathway that can protect from neutralization by an antibody used for covid-19 therapy, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Hsu, Laurent-Rolle, Pawlak, Wilen, Cresswell, Translational shutdown and evasion of the innate immune response by SARS-CoV-2 NSP14 protein, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2101161118
Hunt, Kolokoltsov, Davey, The Tyro3 receptor kinase Axl enhances macropinocytosis of zaire ebolavirus, J Virol, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Iacono, Brown, Greene, Saouaf, CD147 immunoglo bulin superfamily receptor function and role in pathology, Exp Mol Pathol, doi:10.3390/ijms151017411
Ibrahim, Abdelmalek, Elfiky, GRP78: a cell's response to stress, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022
Inoue, Tanaka, Tanaka, Inoue, Morita et al., Clathrin-dependent entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus into target cells expressing ACE2 with the cytoplasmic tail deleted, J Virol
Iwata-Yoshikawa, Kakizaki, Shiwa-Sudo, Okura, Tahara et al., Essential role of TMPRSS2 in SARS-CoV-2 infection in murine airways, Nat Commun, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Jalloh, Olejnik, Berrigan, Suder, Akiyama et al., CD169-mediated restrictive SARS-CoV-2 infection of macrophages induces pro inflammatory responses, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Janssen, Schulz, Steenvoorden, Schmidberger, Strehl et al., A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor with oncogenic potential, Oncogene, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Jefferysmith, Rowland, Patel, Whitaker, Iyanger et al., Reinfection with new variants of SARS-CoV-2 after natural infection, Lancet Healthy Longev, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Jin, Taguwa, Hirano, Uemura, Ono et al., SFTSV utilizes AXL/GAS6 for entry via PI3K-PLC-dependent macropinocytosis activated by AXLkinase, J Virol, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Kim, Jang, Lee, Kim, Seon et al., Trypsin enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection by facilitating viral entry, Arch Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00253-07
Kinoshita, Watanabe, Sakurai, Nishi, Yoshikawa et al., Co-infection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus causes more severe and prolonged pneumonia in hamsters, Sci Rep, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Kuklina, T lymphocytes as targets for SARS-CoV-2, Biochemis try Moscow, doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjac021
Lancet, The COVID-19 pandemic in 2023: far from over, Lancet, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Landras, De Moura, Jouenne, Lebbe, Menashi et al., CD147 is a promising target of tumor progression and a prognostic biomarker, Cancers, doi:10.3390/cancers11111803
Leibel, Mcvicar, Murad, Kwong, Clark et al., A therapy for suppressing canonical and noncanonical SARS-CoV-2 viral entry and an intrinsic intrapulmonary inflammatory response, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Lemke, Biology of the TAM receptors, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Lempp, Soriaga, Montiel-Ruiz, Benigni, Noack et al., Lectins enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection and influence neutralizing antibodies, Nature, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Li, Yang, Liang, Qiu, Pan et al., Tmem30a plays critical roles in ensuring the survival of hematopoietic cells and leukemia cells in mice, Am J Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.02.015
Li, Zhang, Guo, Jia, Han et al., RNA interference targeting CD147 inhibits metastasis and invasion of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells by downregulating MMP-9/VEGF expression, Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, doi:10.1093/abbs/gmy062
Liao, Wang, Tang, Yang, Duan et al., Human transferrin receptor can mediate SARS-CoV-2 infection, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.3390/v14112535
Lim, Zhang, Chang, ACE2-independent alternative receptors for SARS-CoV-2, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14112535
Liu, Lu, Chen, Plow, Qin, Integrin mediates cell entry of the SARS-CoV-2 virus independent of cellular receptor ACE2, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1038/ncb0702-e172
Liu, Xia, Qiu, Functions of CD169 positive macrophages in human diseases (Review), Biomed Rep, doi:10.3892/br.2020.1402
Lopez-Marques, Theorin, Palmgren, Pomorski, P4-ATPases: lipid flippases in cell membranes, Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol, doi:10.1007/s00424-013-1363-4
Ma, Kim, Kafai, Earnest, Shah et al., LDLRAD3 is a receptor for Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus
Maginnis, Virus-receptor interactions: the key to cellular invasion, J Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2018.06.024
Masre, Jufri, Ibrahim, Raub, Classical and alternative receptors for SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic strategy, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.3390/v14112535
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Goonawardane, Saito et al., Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Mercer, Helenius, Virus entry by macropinocytosis, Nat Cell Biol, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Metzdorf, Jacobsen, Mc, Hoffmann, Lüddecke et al., TMPRSS2 is essential for SARS-CoV-2 beta and Omicron infection, Viruses, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Miura, Travanty, Oko, Bielefeldt-Ohmann, Weiss et al., The spike glycoprotein of murine coronavirus MHV-JHM mediates receptor-independent infection and spread in the central nervous systems of Ceacam1a -/-mice, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01851-07
Nchioua, Schundner, Kmiec, Bozzo, Zech et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern hijack IFITM2 for efficient replication in human lung cells, J Virol, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Nehlmeier, Kempf, Arora, Cossmann, Dopfer-Jablonka et al., Host cell entry and neutralisation sensitivity of the SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1.16 lineage, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Nguyen, Houhamdi, Hoang, Delerce, Delorme et al., SARS-CoV-2 reinfection and COVID-19 severity, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Nguyen, Mccord, Bui, Bouwman, Kitova et al., Sialic acid-containing glycolipids mediate binding and viral entry of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Chem Biol, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Niemeyer, Stenzel, Veith, Schroeder, Friedmann et al., SARS-CoV-2 variant Alpha has a spike-dependent replication advantage over the ancestral B.1 strain in human cells with low ACE2 expression, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3001871
Noyes, Hampton, Migliorini, Strickland, Regulation of Itch and Nedd4 E3 ligase activity and degradation by LRAD3, Biochemistry, doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01218
Osada, Ito, Fermin, Vazquez-Cintron, Venkatesh et al., The Wnt signaling antagonist kremen1 is required for development of thymic architecture, J Immunol Res, doi:10.1080/17402520600935097
Pak, Adegboye, Adekunle, Rahman, Mcbryde et al., Economic consequences of the COVID-19 outbreak: the need for epidemic preparedness, Front Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Palmulli, Machesky, Bielecka, Poświata, Kozik et al., The GAS6-AXL signaling pathway triggers actin remodeling that drives membrane ruffling, macropinocytosis, and cancer-cell invasion, Curr Opin Cell Biol, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Park, Myint, Ito, Appiah, Darkwah et al., Integrin-ligand interactions in inflammation, cancer, and metabolic disease: insights into the multifaceted roles of an emerging ligand irisin, Front Cell Dev Biol, doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.588066
Partridge, Urwin, Nicklin, James, Green et al., ACE2-independent interaction of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with human epithelial cells is inhibited by unfractionated heparin, Cells
Paulusma, Folmer, Ho-Mok, De Waart, Hilarius et al., ATP8B1 requires an accessory protein for endoplasmic reticulum exit and plasma membrane lipid flippase activity, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.21950
Peacock, Brown, Zhou, Thakur, Sukhova et al., The altered entry pathway and antigenic distance of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant map to separate domains of spike protein, bioRxiv, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Perez-Zsolt, Martinez-Picado, Izquierdo-Useros, When dendritic cells go viral: the role of Siglec-1 in host defense and dissemination of enveloped viruses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12010008
Perez-Zsolt, Muñoz-Basagoiti, Rodon, Elosua-Bayes, Raïch-Regué et al., SARS-CoV-2 interaction with Siglec-1 mediates trans-infection by dendritic cells, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-021-00794-6
Pfaffenbach, Lee, The critical role of GRP78 in physiologic and pathologic stress, Curr Opin Cell Biol, doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2010.09.007
Pia, Jones, Omicron entry route, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Pontelli, Castro, Martins, Serra, Veras et al., SARS-CoV-2 productively infects primary human immune system cells in vitro and in COVID-19 patients, J Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjac021
Raaben, Jae, Herbert, Kuehne, Stubbs et al., NRP2 and CD63 are host factors for lujo virus cell entry, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.002
Ragotte, Pulido, Donnellan, Hill, Gorini et al., Human basigin (CD147) does not directly interact with SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, mSphere e, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Rahimi, C-type lectin CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN: cell adhesion molecules turned to pathogen recognition receptors, Biology (Basel), doi:10.3390/biology10010001
Rahman, Rahman, Miah, Begum, Sarmin et al., COVID-19 reinfections among naturally infected and vaccinated individuals, Sci Rep, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Robles, Zamora, Castro, Siqueiros-Marquez, De La Escalera et al., The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces endothelial inflammation through integrin α5β1 and NF-κB signaling, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1038/ncb0702-e172
Root, Merino, Nuckols, Johnson, Kukar, Lysosome dysfunction as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases: lessons from frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Neurobiol Dis, doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105360
Rothbächer, Lemaire, Crème de la Kremen of Wnt signalling inhibition, Nat Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/ncb0702-e172
Sandgren, Wilkinson, Miranda-Saksena, Mcinerney, Byth-Wilson et al., A differential role for macropinocytosis in mediating entry of the two forms of vaccinia virus into dendritic cells, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000866
Schweighauser, Arseni, Bacioglu, Huang, Lövestam et al., Age-dependent formation of TMEM106B amyloid filaments in human brains, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04650-z
Shah, Woo, Omicron: a heavily mutated SARS-CoV-2 variant exhibits stronger binding to ACE2 and potently escapes approved COVID-19 therapeutic antibodies, Front Immunol, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Shen, Geng, Li, Chen, Li et al., ACE2-independent infection of T lymphocytes by SARS-CoV-2, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00919-x
Shen, Zhang, Fang, Lu, Wu et al., SARS-CoV-2 interacts with platelets and megakaryocytes via ACE2-independent mechanism, J Hematol Oncol, doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01082-6
Shi, Kenney, Kudryashova, Zani, Zhang et al., Opposing activities of IFITM proteins in SARS-CoV-2 infection, EMBO J, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Shilts, Crozier, Greenwood, Lehner, Wright, No evidence for basigin/CD147 as a direct SARS-CoV-2 spike binding receptor, Sci Rep, doi:10.3390/v14112535
Simons, Rinaldi, Bondu, Kell, Bradfute et al., Integrin activation is an essential component of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-99893-7
Singh, Bansal, Feschotte, A single-cell RNA expression map of human coronavirus entry factors, Cell Rep, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Stewart, Nemerow, Cell integrins: commonly used receptors for diverse viral pathogens, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2007.10.001
Sun, Cui, Garcia, Wang, Zhang et al., Comparative transcriptomic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 infected cell model systems reveals differential innate immune responses, Sci Rep, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Sungnak, Huang, Bécavin, Berg, Queen et al., SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes, Nat Med, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Tachibana, Nakamura, Do, Kihara, Kawada et al., Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins affected the ACE2-binding affinity during the development of Omicron pandemic variants, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150120
Tang, Xu, Tan, Shi, Li et al., CD36 mediates SARS-CoV-2-envelopeprotein-induced platelet activation and thrombosis, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40824-7
Tang, Yang, Liu, Tang, Chen et al., Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell lectin, LSECtin, negatively regulates hepatic T-cell immune response, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.051
Tang, Yang, Tang, Ying, Qian et al., The DC-SIGN family member LSECtin is a novel ligand of CD44 on activated T cells, Eur J Immunol, doi:10.3892/br.2020.1402
Uraki, Ito, Furusawa, Yamayoshi, Iwatsuki-Horimoto et al., Humoral immune evasion of the omicron subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Van Der Mark, Elferink, Paulusma, P4 ATPases: flippases in health and disease, IJMS, doi:10.3390/ijms14047897
Vanarsdall, Pritchard, Wisner, Liu, Jardetzky et al., CD147 promotes entry of pentamer-expressing human cytomegalovirus into epithelial and endothelial cells, mBio, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Vanblargan, Errico, Halfmann, Zost, Crowe et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, Nat Med, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Wang, Chao, Wei, Li, Liu et al., CD147 promotes collective invasion through cathepsin B in hepatocellular carcinoma, J Exp Clin Cancer Res, doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01647-2
Wang, Chen, Zhang, Deng, Lian et al., CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Wang, Qiu, Hou, Deng, Xu et al., AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells, Cell Res, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Wang, Simoneau, Kulsuptrakul, Bouhaddou, Travisano et al., Genetic screens identify host factors for SARS-CoV-2 and common cold coronaviruses, doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01218
Wang, Wells, Wu, Macropinocytosis and cytoskeleton contribute to dendritic cell-mediated HIV-1 transmission to CD4+ T cells, Virology (Auckland), doi:10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.028
Weigang, Fuchs, Zimmer, Schnepf, Kern et al., Within-host evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in an immunosuppressed COVID-19 patient as a source of immune escape variants, Nat Commun, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00422-4
Wessling-Resnick, Crossing the iron gate: why and how transferrin receptors mediate viral entry, Annu Rev Nutr, doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-082117-051749
Willett, Grove, Maclean, Wilkie, Lorenzo et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron is an immune escape variant with an altered cell entry pathway, Nat Microbiol, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108375
Williamson, Donaldson, Arf6, JIP3, and dynein shape and mediate macropinocytosis, Mol Biol Cell, doi:10.1091/mbc.E19-01-0022
Wium, Ajayi-Smith, Paccez, Zerbini, The role of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl in carcinogenesis and development of therapeutic resistance: an overview of molecular mechanisms and future applications, Cancers, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Xin, Zeng, Gu, Li, Tan et al., CD147/EMMPRIN overexpression and prognosis in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/srep32804
Xiong, Edwards, Zhou, The biological function and clinical utilization of CD147 in human diseases: a review of the current scientific literature, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms151017411
Xu, Wang, Geng, Honnen, Wang et al., Human immunodeficiency viruses pseudotyped with SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins infect a broad spectrum of human cell lines through multiple entry mechanisms, Viruses, doi:10.1128/mbio.00364-22
Yan, Dumenil, Stewart, Bishop, Tang et al., TMEM106B-mediated SARS-CoV-2 infection allows for robust ACE2-independent infection in vitro but not in vivo, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114921
Yang, Chen, CD147 in ovarian and other cancers, Int J Gynecol Cancer, doi:10.1093/abbs/gmy062
Yu, Zhang, Huang, Chen, Wu et al., COVID-19 serum drives spike-mediated SARS-CoV-2 variation, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16050763
Zang, Castro, Mccune, Zeng, Rothlauf et al., TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes, Sci Immunol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00253-07
Zhang, Liang, Wang, Ye, Wang et al., SARS-CoV-2 hijacks macropinocytosis to facilitate its entry and promote viral spikemediated cell-to-cell fusion, J Biol Chem, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Zhang, Liu, Wang, Yang, Li et al., SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19, J Hematol Oncol, doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01082-6
Zhang, Ren, Zuo, DC-SIGN, DC-SIGNR and LSECtin: C-type lectins for infection, Int Rev Immunol, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Zhang, Tian, Wen, Zhang, Qi et al., Asialoglycoprotein receptor facilitates infection of PLC/PRF/5 cells by HEV through interaction with ORF2, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.24570
Zhang, Wang, Nguyen, Watson, Lao et al., Integrin α(5)β(1) contributes to cell fusion and inflammation mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike via RGD-independent interaction, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1038/ncb0702-e172
Zhao, Gao, Novel Omicron Variants enhance anchored recognition of TMEM106B: a new pathway for SARS-CoV-2 cellular invasion, J Phys Chem Lett, doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c03296
Zhou, Wang, Wang, Cui, Zhao et al., SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus enters the host cells through spike protein-CD147 in an Arf6-dependent manner, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.3109/08830185.2013.834897
Zhu, Liu, Zhou, Zhang, Xiao et al., Genome-wide CRISPR activation screen identifies candidate receptors for SARS-CoV-2 entry, Sci China Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s11427-021-1990-5
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01897-24",
"ISSN": [
"2150-7511"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01897-24",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title/>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), remains a major public health threat, particularly in vulnerable populations. SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins interact with the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, together with accessory molecules that facilitate viral entry, through its spike receptor-binding domain (RBD). Although ACE2 is the primary receptor required for viral replication, its expression patterns do not fully correlate with viral distribution or tissue pathology. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to infect cells and tissues lacking detectable ACE2 expression. Viral entry via ACE2-independent pathways may also confer resistance to some monoclonal antibodies (Abs) targeting the spike RBD that block ACE2-mediated binding. These observations highlight the potential significance of ACE2-independent entry factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly in vaccinated individuals with Abs directed against ACE2-dependent viral entry. In this review, we discuss the emerging roles of ACE2-independent entry factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection and the immune responses. These factors include CD147, AXL, CD169/Siglec-1, CD209L, CD209, CLEC4G, ASGR1, LDLRAD3, TMEM30A, TMEM106B, transferrin receptor 1, GPR78, integrin α5β1, KREMEN1, LFA-1, and CD4. While ACE2 remains central to viral replication, ACE2-independent entry appears sufficient to elicit immune responses. Therefore, future investigations are warranted to elucidate the roles of ACE2-independent mechanisms in immune-mediated pathology and viral evolution, independent of immune pressure targeting ACE2-mediated entry in previously infected or vaccinated individuals.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/mbio.01897-24"
],
"article-number": "e01897-24",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-12-22"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0005-5467-8655",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Rutgers School of Graduate Studies",
"place": [
"Newark, USA"
]
},
{
"name": "Public Health Research Institute",
"place": [
"Newark, USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Yiyu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0727-8289",
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/014ye1258",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School",
"place": [
"Newark, USA"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/014ye1258",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Center for Virus-Host Innate Immunity, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School",
"place": [
"Newark, USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Lok-Yin Roy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0696-9755",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health Research Institute",
"place": [
"Newark, USA"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/014ye1258",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School",
"place": [
"Newark, USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Theresa L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "mBio",
"container-title-short": "mBio",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-22T14:00:32Z",
"timestamp": 1766412032000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-22T14:00:35Z",
"timestamp": 1766412035000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasad",
"given": "Vinayaka R.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"R01AI136948"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"R01AI136948"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000072",
"award": [
"R21DE033170"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"R21DE033170"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000072",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"R00AI170966"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"R00AI170966"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-22T14:03:59Z",
"timestamp": 1766412239933,
"version": "3.48.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1766361600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1766361600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01897-24",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01897-24",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-023-00014-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00050-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.00241",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-05325-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00253-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2052358",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_7_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_2_8_2",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. 2025. Weekly confirmed COVID-19 deaths. Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/weekly-covid-deaths"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-00809-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.12.05040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd0827",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26508/lsa.202000786",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abc3582",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-021-05343-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd3072",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd2985",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100306",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00253-07",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41589-021-00924-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24817-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.00594-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13073-022-01013-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009743",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2020106501",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-96462-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.20209610",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03925-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13060953",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22074/cellj.2021.7977",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.00364-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2207",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2317026121",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13578-022-00822-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-80464-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14112535",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41556-024-01388-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abo3977",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3001871",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_48_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00595-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_49_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01230-24",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_50_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.05.04.539267",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_51_2",
"unstructured": "Choudhary AK Calianese D Honnen W Kolloli A Dikdan RJ Jaijyan D Song G Capozzola T Akkaraju V Mattappallil A Rosania A Khan S Lerman M Afzal N Subbian S Chou TC Andrabi R Burton D Pinter A. 2023. Broad-spectrum heavily mutated monoclonal antibody isolated from COVID-19 convalescent vaccinee with capacity to neutralize SARS-CoV2 variants ranging from B.1 to BQ.1.1. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2023.05.04.539267"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26602-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_52_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00422-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_53_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-024-07385-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_54_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00816-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_55_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_56_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(22)00120-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_57_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.830527",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_58_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-023-01030-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_59_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_60_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-022-01143-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_61_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-022-00681-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_62_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.12.31.474653:2021.12.31.474653",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_63_2",
"unstructured": "Peacock TP Brown JC Zhou J Thakur N Sukhova K Newman J Kugathasan R Yan AWC Furnon W Lorenzo G Cowton VM Reuss D et al.. 2022. The altered entry pathway and antigenic distance of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant map to separate domains of spike protein. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.12.31.474653:2021.12.31.474653"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15020271",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_64_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-33911-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_65_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSphere.00647-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_66_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_67_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_68_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1010479",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_69_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscentsci.0c01537",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_70_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2021108375",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_71_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-021-1990-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_72_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-021-00805-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_73_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c03296",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_74_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104869",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_75_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-34910-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_76_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00919-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_77_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.84790",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_78_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20150256",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_79_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_2_80_2",
"unstructured": "The Human Protein Atlas. 2005. BSG – tissue expression. Available from: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000172270-BSG/tissue"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers11111803",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_81_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep32804",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_82_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13046-020-01647-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_83_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/IGC.0b013e3182749139",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_84_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/abbs/gmy062",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_85_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.yexmp.2007.08.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_86_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms151017411",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_87_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcdd9010007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_88_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.E19-01-0022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_89_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncb0509-510",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_90_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2408109121",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_91_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102511",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_92_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00781-18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_93_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2059403",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_94_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox13020175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_95_2"
},
{
"article-title": "A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor with oncogenic potential",
"author": "Janssen JW",
"first-page": "2113",
"journal-title": "Oncogene",
"key": "e_1_3_2_96_2",
"unstructured": "Janssen JW, Schulz AS, Steenvoorden AC, Schmidberger M, Strehl S, Ambros PF, Bartram CR. 1991. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor with oncogenic potential. Oncogene 6:2113–2120.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers13071521",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_97_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a009076",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_98_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/bjc.2016.428",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_99_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26508/lsa.201900465",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_100_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.V84.6.1931.1931",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_101_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_2_102_2",
"unstructured": "The Human Protein Atlas. 2005. AXL – tissue expression. Available from: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000167601-AXL/tissue"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ceb.2025.102513",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_103_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2024596118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_104_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01278-09",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_105_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.00221-25",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_106_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00262-008-0615-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_107_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biology10010001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_108_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/08830185.2013.834897",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_109_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2006-09-048058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_110_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_111_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.979373",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_112_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000866",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_113_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_114_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.200939936",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_115_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2005.06.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_116_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02472",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_117_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/br.2020.1402",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_118_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12010008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_119_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-021-00794-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_120_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2101161118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_121_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_122_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_2_123_2",
"unstructured": "The Human Protein Atlas. 2025. LRAD3 – tissue expression. Available from: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000179241-LDLRAD3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01218",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_124_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2915-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_125_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_2_126_2",
"unstructured": "The Human Protein Atlas. 2025. TMEM30A – tissue expression. Available from: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000112697-TMEM30A/tissue"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00424-013-1363-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_127_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms14047897",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_128_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.21950",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_129_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.02.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_130_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_131_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00401-020-02246-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_132_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04650-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_133_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/dds475",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_134_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105360",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_135_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v16050763",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_136_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114921",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_137_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-nutr-082117-051749",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_138_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2148-8-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_139_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ceb.2010.09.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_140_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/35014014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_141_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA118.001897",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_142_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_143_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s10020-023-00706-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_144_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41390-020-01177-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_145_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.588066",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_146_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2018.06.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_147_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2007.10.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_148_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2022.892323",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_149_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-99893-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_150_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119881",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_151_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101695",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_152_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2311913120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_153_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101710",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_154_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncb0702-e172",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_155_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17402520600935097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_156_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cdd.2015.100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_157_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21144818",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_158_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.24570",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_159_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1134/S0006297922060086",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_160_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jmcb/mjac021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_161_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.15534",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_162_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-020-00954-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_163_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-021-01082-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_164_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321541",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_165_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-40824-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_166_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01851-07",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_167_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10061419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_168_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 167,
"references-count": 167,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mbio.01897-24"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "ACE2-independent entry factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune activation",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page"
}