Biguanides Associate with Decreased Early Mortality and Risk of Acute Kidney Injury In Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: a nationwide retrospective cohort study in Japan
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.07.20.24310736, Jul 2024
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 168,370 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes in Japan showing lower mortality and reduced risk of acute kidney injury with biguanide (likely primarily or only metformin) use. Authors hypothesize that metformin's activation of AMPK in renal tubular epithelium may provide a protective effect against COVID-19-induced kidney damage.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
Japan, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
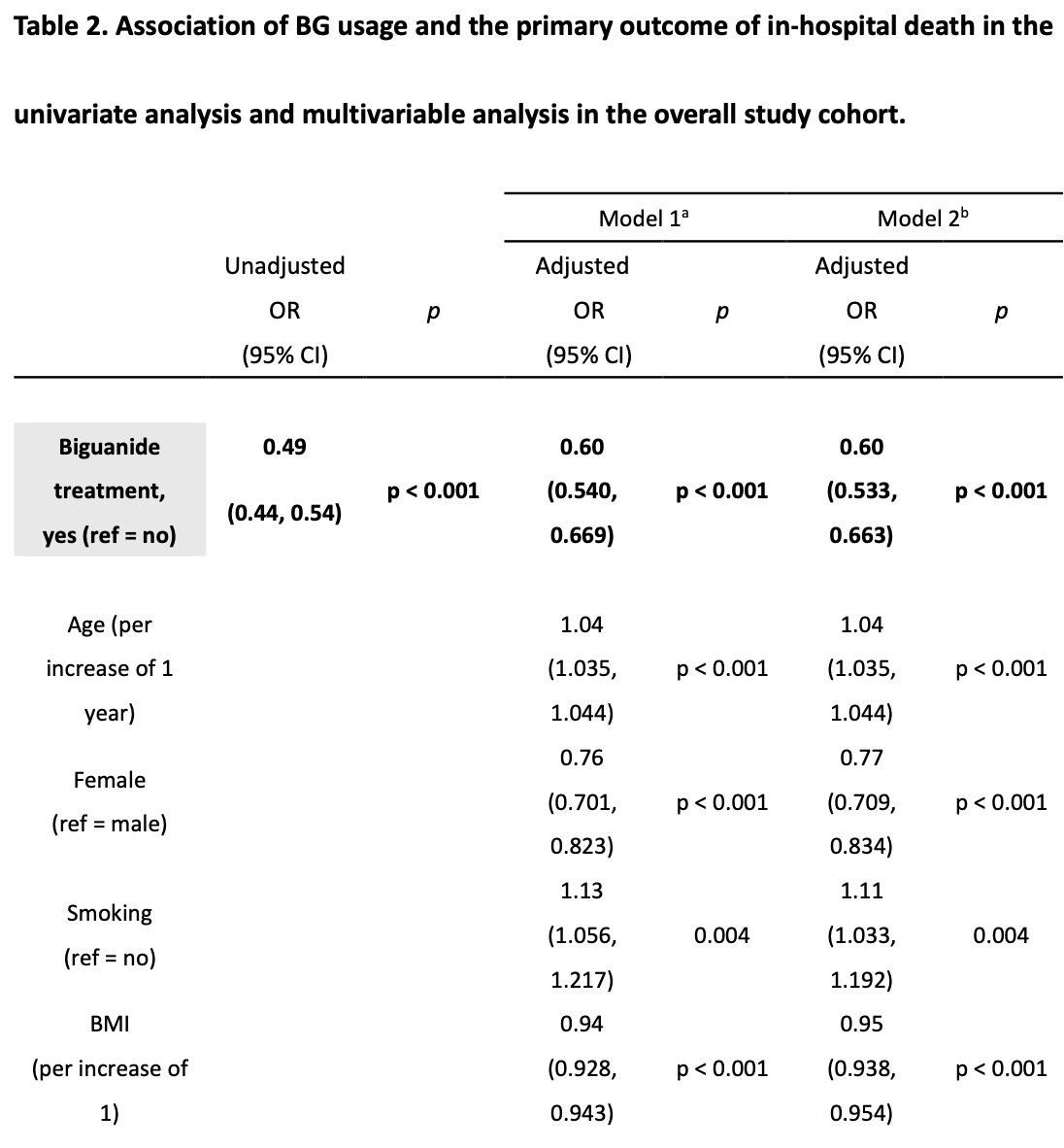
risk of death, 40.0% lower, HR 0.60, p < 0.001, treatment 30,908, control 137,642, adjusted per study, multivariable, day 100, model 2.
|
|
AKI, 41.0% lower, HR 0.59, p < 0.001, treatment 30,908, control 137,642, adjusted per study, multivariable, model 2.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sugimoto et al., 21 Jul 2024, retrospective, Japan, preprint, 12 authors, study period September 2021 - March 2023.
Contact: hiroaki.k1114@gmail.com.
Biguanides Associate with Decreased Early Mortality and Risk of Acute Kidney Injury In Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: a nationwide retrospective cohort study in Japan
doi:10.1101/2024.07.20.24310736
Background: Biguanide (BG) is the most-prescribed oral glucose-lowering medication worldwide and has potential for further therapeutic applications. The Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is a global public health emergency. Nevertheless, there are still no established low-cost treatments against COVID-19, of which the morbidity and mortality rates varing from country to country. Therefore, a nationwide study of the COVID-19 affected population is essential to explore therapeutic effect of BG against COVID-19. Methods: From the inpatient databases in Japan, covering the period from September 2021 to March 2023, which encompasses the era following the development of COVID-19 vaccines, we extracted data of 168,370 COVID-19 patients aged 20 to under 80 years who were suffered from diabetes mellitus treated with oral antidiabetic agents. The primary outcome was 100-day in-hospital mortality, and secondary outcome was the incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) during hospitalization. We compared outcomes in patients who received BG with those in patients who did not, using a logistic regression analysis and Cox proportional hazards under both propensity score-unmatched and matched cohorts.
Results: The incidence of in-hospital death was significantly lower in the BG group
Disclosure The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author contributions
References
Bailey, Metformin: Historical overview, Diabetologia
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Buse, Liebovitz et al., Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for covid-19. [Electronic version, N Engl J Med
De Broe, Kajbaf, Lalau, Renoprotective effects of metformin, Nephron
De Lusignan, Dorward, Correa, Jones, Akinyemi et al., Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 among patients in the oxford royal college of general practitioners research and surveillance centre primary care network: A cross-sectional study, Lancet Infect Dis
Defronzo, Fleming, Chen, Bicsak, Metformin-associated lactic acidosis: Current perspectives on causes and risk, Metabolism
Drew, Jenkin, Metabolic activity of trypanosoma lewisi cultured in vitro in the presence of normal or ablastinic rat serum. [Electronic version, Comp Biochem Physiol B
Fisher, Neugarten, Bellin, Yunes, Stahl et al., AKI in hospitalized patients with and without COVID-19: A comparison study, J Am Soc Nephrol
Foretz, Guigas, Bertrand, Pollak, Viollet, Metformin: From mechanisms of action to therapies, Cell Metab
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Liu, Zhou et al., Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: A preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci
Ge, Tian, Huang, Li, Li et al., An integrative drug repositioning framework discovered a potential therapeutic agent targeting COVID-19, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Zucker, Baldwin et al., Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with covid-19. [Electronic version, N Engl J Med
Hallows, Mount, Pastor-Soler, Power, Role of the energy sensor AMPactivated protein kinase in renal physiology and disease. [Electronic version, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol
Hayashida, Murakami, Matsuda, Fushimi, History and profile of diagnosis procedure combination (DPC): Development of a real data collection system for acute inpatient care in japan. [Electronic version], J Epidemiol
Karam, Morris, Bramante, Puskarich, Zolfaghari et al., mTOR inhibition in COVID-19: A commentary and review of efficacy in RNA viruses. [Electronic version, J Med Virol
Khalatbari-Soltani, Cumming, Delpierre, Kelly-Irving, Importance of collecting data on socioeconomic determinants from the early stage of the COVID-19 outbreak onwards. [Electronic version], J Epidemiol Community Health
Kikuchi, Sasaki, Nomura, Mori, Minamishima et al., Failure to sense energy depletion may be a novel therapeutic target in chronic kidney disease. [Electronic version, Kidney Int
Lancet, The COVID-19 pandemic in 2023: Far from over, Lancet
Li, Wang, Li, Yang, Zhang et al., Metformin-induced reduction of CD39 and CD73 blocks myeloid-derived suppressor cell activity in patients with ovarian cancer, Cancer Res
Li, Yang, Yan, Sun, Zeng et al., Metformin in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Med
Liao, Identification of potential new COVID-19 treatments via RWD-driven drug repurposing, Sci Rep
Limbutara, Chou, Knepper, Quantitative proteomics of all 14 renal tubule segments in rat. [Electronic version], J Am Soc Nephrol
Liu, Li, Lu, Ren, Sun et al., AMPK: A balancer of the renin-angiotensin system, Biosci Rep, doi:10.1042/BSR20181994
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, Zheng et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Malaekeh-Nikouei, Shokri-Naei, Karbasforoushan, Bahari, Rahimi et al., Metformin beyond an anti-diabetic agent: A comprehensive and mechanistic review on its effects against natural and chemical toxins, Biomed Pharmacother
Meizlish, Goshua, Liu, Fine, Amin et al., Intermediate-dose anticoagulation, aspirin, and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19: A propensity scorematched analysis, Am J Hematol
Ng, Salim, Chu, Drug repurposing for COVID-19: Approaches, challenges and promising candidates, Pharmacol Ther
Oakhill, Steel, Chen, Scott, Ling et al., AMPK is a direct adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. [Electronic version, Science
Ogedegbe, Ravenell, Adhikari, Butler, Cook et al., Assessment of racial/ethnic disparities in hospitalization and mortality in patients with COVID-19 in new york city, JAMA Netw Open
Postler, Peng, Bhatt, Ghosh, Metformin selectively dampens the acute inflammatory response through an AMPK-dependent mechanism, Sci Rep
Pryor, Cabreiro, Repurposing metformin: An old drug with new tricks in its binding pockets. [Electronic version], Biochem J
Reis, Santos, Silva, Silva, Thabane et al., Effect of early treatment with metformin on risk of emergency care and hospitalization among patients with COVID-19: The TOGETHER randomized platform clinical trial, Lancet Reg Health Am
Ruan, Likelihood of survival of coronavirus disease 2019, Lancet Infect Dis
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: A possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Sturmer, Wyss, Glynn, Brookhart, Propensity scores for confounder adjustment when assessing the effects of medical interventions using nonexperimental study designs. [Electronic version], J Intern Med
Vander Heiden, Cantley, Thompson, Understanding the warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation, Science
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in wuhan, china, Jama
Wang, Wu, Yang, Dong, Chen et al., Global, regional, and national estimates of target population sizes for covid-19 vaccination: Descriptive study, Bmj
Yanagi, Kikuchi, Susa, Takahashi, Bamba et al., Absence of ULK1 decreases AMPK activity in the kidney, leading to chronic kidney disease progression, Genes Cells
Zhang, Jackson, Mou, Ojha, Peng et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein D614G mutation increases virion spike density and infectivity, Nat Commun
Zhou, Myers, Li, Chen, Shen et al., Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. [Electronic version, J Clin Invest
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song et al., A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in china, 2019, N Engl J Med
