Antibiotics and probiotics impact gut antimicrobial resistance gene reservoir in COVID-19 patients
et al., Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2022.2128603, NCT04581018, Oct 2022
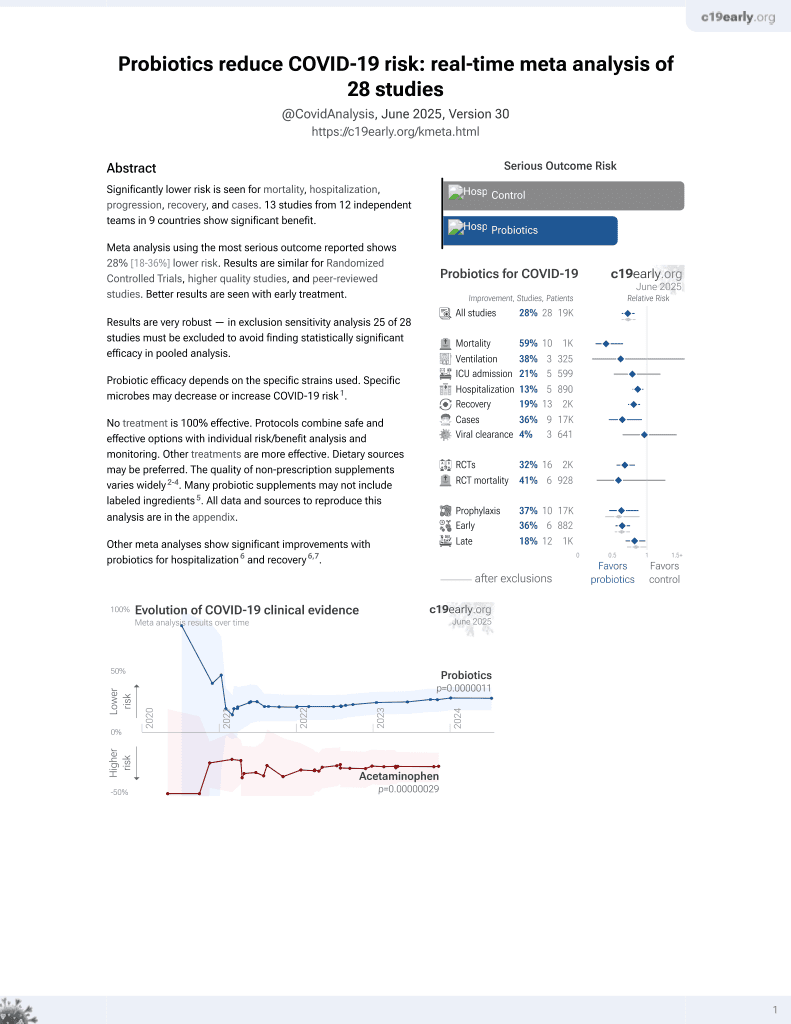
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of 142 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing antibiotics further expanded the gut antimicrobial resistance gene (AMR) reservoir while probiotics (synbiotic formula SIM01) reduced AMR genes. At admission, antibiotic-naive COVID-19 patients had higher AMR gene diversity and abundance compared to controls. AMR genes further increased during infection and persisted 6 months after viral clearance. Antibiotic treatment led to additional AMR gene expansion while SIM01 probiotics significantly reduced AMR genes during and after infection without rebound in 12 weeks. Expanded AMR genes were associated with increased Klebsiella prevalence and post-acute COVID-19 syndrome risk.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
Su et al., 6 Oct 2022, China, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, trial NCT04581018 (history).
Contact: siewchienng@cuhk.edu.hk.
Antibiotics and probiotics impact gut antimicrobial resistance gene reservoir in COVID-19 patients
Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2022.2128603
Dysbiosis of gut microbiota is well-described in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19), but the dynamics of antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) reservoir, known as resistome, is less known. Here, we performed longitudinal fecal metagenomic profiling of 142 patients with COVID-19, characterized the dynamics of resistome from diagnosis to 6 months after viral clearance, and reported the impact of antibiotics or probiotics on the ARGs reservoir. Antibiotic-naive patients with COVID-19 showed increased abundance and types, and higher prevalence of ARGs compared with non-COVID-19 controls at baseline. Expansion in resistome was mainly driven by tetracycline, vancomycin, and multidrug-resistant genes and persisted for at least 6 months after clearance of SARS-CoV-2. Patients with expanded resistome exhibited increased prevalence of Klebsiella sp. and post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Antibiotic treatment resulted in further increased abundance of ARGs whilst oral probiotics (synbiotic formula, SIM01) significantly reduced the ARGs reservoir in the gut microbiota of COVID-19 patients during the acute infection and recovery phase. Collectively, these findings shed new insights on the dynamic of ARGs reservoir in COVID-19 patients and the potential role of microbiota-directed therapies in reducing the burden of accumulated ARGs.
Disclosure statement FKLC and SCN are the scientific co-founders and sit on the board of Directors of GenieBiome Ltd. SCN, FKLC and ZX are inventors of patent applications related to SIM01. SCN has
References
Alcock, Raphenya, Lau, Tsang, Bouchard et al., CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkz935
Campbell, Sun, Patel, Sanz, Morgan et al., The microbiome and resistome of chimpanzees, gorillas, and humans across host lifestyle and geography, ISME J, doi:10.1038/s41396-020-0634-2
Cao, Wang, Zhang, Lei, Xu et al., Integrated gut virome and bacteriome dynamics in COVID-19 patients, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1887722
Chen, Chen, Haifeng, Shi, Guo et al., Six-month follow-up of gut microbiota richness in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324090
Chen, Hui, Yeoh, Wong, Chan et al., Impact of Preservation Method and 16S rRNA Hypervariable Region on Gut Microbiota Profiling, mSystems
Conwell, Daniels, Naughton, Dooley, Interspecies transfer of vancomycin, erythromycin and tetracycline resistance among Enterococcus species recovered from agrarian sources, BMC Microbiol, doi:10.1186/s12866-017-0928-3
Dell'annunziata, Donadio, Piaz, Izzo, Filippis et al., Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived from Klebsiella pneumoniae Are a Driving Force for Horizontal Gene Transfer, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22168732
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut microbiota and Covid-19possible link and implications, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018
Domingues, Rebelo, Dionisio, Botelho, Nogueira, The Social Distancing Imposed To Contain COVID-19 Can Affect Our Microbiome: a Double-Edged Sword in Human Health, mSphere, doi:10.1128/mSphere.00716-20
Feldgarden, Brover, Haft, Dh, Prasad et al., Validating the AMRFinder Tool and Resistance Gene Database by Using Antimicrobial Resistance Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in a Collection of Isolates, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Flanagan, Sutherland, Vaughn, Diekema, Doebbeling, Development and validation of measures to assess prevention and control of AMR in hospitals, Med Care, doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31803bb48b
Goren, Carmeli, Schwaber, Chmelnitsky, Schechner et al., Transfer of carbapenem-resistant plasmid from Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 to Escherichia coli in patient, Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid1606.091671
Gorrie, Mirceta, Wick, Edwards, Thomson et al., Gastrointestinal Carriage Is a Major Reservoir of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Intensive Care Patients, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/cix270
Gottig, Gruber, Stecher, Wichelhaus, Kempf, In vivo horizontal gene transfer of the carbapenemase OXA-48 during a nosocomial outbreak, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/civ191
Gu, Chen, Wu, Chen, Gao et al., Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 or H1N1 Influenza, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa709
Hegstad, Mylvaganam, Josefsen, Sivertsen, Skaare, Role of Horizontal Gene Transfer in the Development of Multidrug Resistance in Haemophilus influenzae, mSphere
Huemer, Shambat, Brugger, Zinkernagel, Antibiotic resistance and persistence-Implications for human health and treatment perspectives, EMBO Rep, doi:10.15252/embr.202051034
Kang, Chen, Chen, Tian, Wu et al., Alterations of fecal antibiotic resistome in COVID-19 patients after empirical antibiotic exposure, Int J Hyg Environ Health, doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113882
Kim, Joo, Lee, Ahn, Kim et al., Reversion of Gut Microbiota during the Recovery Phase in Patients with Asymptomatic or Mild COVID-19: longitudinal Study, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms9061237
Kwok, Wei, Ma, Ip, Cheung et al., Antibiotic use among COVID-19 patients in Hong Kong, January 2018 to, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.02.014
Langford, So, Raybardhan, Leung, Soucy et al., Antibiotic prescribing in patients with COVID-19: rapid review and meta-analysis, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.12.018
Lau, Ng, Yu, Targeting the Gut Microbiota in Coronavirus Disease 2019: hype or Hope?, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.009
Launay, Ballard, Johnson, Grayson, Lambert, Transfer of vancomycin resistance transposon Tn1549 from Clostridium symbiosum to Enterococcus spp. in the gut of gnotobiotic mice, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.50.3.1054-1062.2006
Li, Liu, Luo, Sadakane, Lam, MEGAHIT: an ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv033
Liu, Mak, Su, Yeoh, Lui et al., Gut microbiota dynamics in a prospective cohort of patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325989
Macpherson, Mathieu, Tremblay, Champagne, Nantel et al., Gut Bacterial Microbiota and its Resistome Rapidly Recover to Basal State Levels after Short-term Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid Treatment in Healthy Adults, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-29229-5
Mak, Chan, Ng, Probiotics and COVID-19: one size does not fit all, Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30122-9
Montassier, Valdés-Mas, Batard, Zmora, Bachash et al., Probiotics impact the antibiotic resistance gene reservoir along the human GI tract in a person-specific and antibiotic-dependent manner, Nat Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-021-00920-0
Nalbandian, Sehgal, Gupta, Madhavan, Mcgroder et al., Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Newsome, Gauthier, Hernandez, Abraham, Robinson et al., The gut microbiome of COVID-19 recovered patients returns to uninfected status in a minority-dominated United States cohort, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1926840
Partridge, Firth, Jensen, Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance, Clin Microbiol Rev, doi:10.1128/CMR.00088-17
Perl, The threat of vancomycin resistance, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(98)00354-4
Pfizer, Ferring, Ferring, Tillotts, Menarini et al., She has received research grants from Olympus, Ferring, and Abbvie. FKLC has served as an advisor and lecture speaker for Eisai
Rawson, Moore, Zhu, Ranganathan, Skolimowska et al., Bacterial and fungal coinfection in individuals with coronavirus: a rapid review to support COVID-19 antimicrobial prescribing, Clin Infect Dis
Ren, Wang, Cui, Lu, Wang et al., Alterations in the human oral and gut microbiomes and lipidomics in COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323826
Resistance, No time to Wait. Securing the future from drug-resistant infections
Schjorring, Struve, Krogfelt, Transfer of antimicrobial resistance plasmids from Klebsiella pneumoniae to Escherichia coli in the mouse intestine, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkn323
Selvin, Maity, Sajayan, Kiran, Revealing antibiotic resistance in therapeutic and dietary probiotic supplements, J Glob Antimicrob Resist, doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2020.02.007
Sharma, Tomar, Goswami, Sangwan, Singh, Antibiotic resistance among commercially available probiotics, Food Res J, doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.025
Sommer, Dantas, Church, Functional characterization of the antibiotic resistance reservoir in the human microflora, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1176950
Stecher, Denzler, Maier, Bernet, Sanders et al., Gut inflammation can boost horizontal gene transfer between pathogenic and commensal Enterobacteriaceae, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.1113246109
Su, Lau, Liu, Chan, Ng, Post-acute COVID-19. syndrome and gut dysbiosis linger beyond 1 year after SARS-CoV-2 clearance, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328319
Suez, Zmora, Segal, Elinav, The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0439-x
Sun, Patel, Santalucia, Roberts, Zhao et al., Measurement of Klebsiella Intestinal Colonization Density To Assess Infection Risk, mSphere, doi:10.1128/mSphere.00500-21
Tsigalou, Konstantinidis, Stavropoulou, Bezirtzoglou, Tsakris, Potential Elimination of Human Gut Resistome by Exploiting the Benefits of Functional Foods, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.00050
Wu, Xu, Cao, Pan, Zhu et al., The volatile and heterogeneous gut microbiota shifts of COVID-19 patients over the course of a probioticsassisted therapy, Clin Transl Med, doi:10.1002/ctm2.643
Yang, Jiang, Chai, Ma, Li et al., ARGs-OAP: online analysis pipeline for antibiotic resistance genes detection from metagenomic data using an integrated structured ARG-database, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btw136
Yeoh, Zuo, Lui, Zhang, Liu et al., Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020
Zhang, Ai, Yang, Zhou, He et al., Metatranscriptomic Characterization of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Identified a Host Transcriptional Classifier Associated With Immune Signaling, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa663
Zhang, Wan, Zuo, Yeoh, Liu et al., Prolonged Impairment of Short-Chain Fatty Acid and L-Isoleucine Biosynthesis in Gut Microbiome in Patients With COVID-19, Gastroenterology
Zhang, Xu, Mak, Chow, Lui et al., Gut microbiota-derived synbiotic formula (SIM01) as a novel adjuvant therapy for COVID-19: an open-label pilot study, J Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1111/jgh.15796
Zuo, Lui, Yeoh, Li, Zhan et al., Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization, Gastroenterology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2022.2128603",
"ISSN": [
"1949-0976",
"1949-0984"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2022.2128603",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/19490976.2022.2128603"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=kgmi20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=kgmi20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-05-24"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-09-20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-10-06"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9100-387X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Center for Gut Microbiota Research, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Su",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Center for Gut Microbiota Research, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Qin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Center for Gut Microbiota Research, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Center for Gut Microbiota Research, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Zhilu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Center for Gut Microbiota Research, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Chenyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Wenqi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Ching",
"given": "Jessica YL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Mak",
"given": "Joyce Wing Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Lui",
"given": "Grace Chung Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Stanley Ho Centre for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "Susanna So Shan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Chow",
"given": "Kai Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Stanley Ho Centre for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Hui",
"given": "David SC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Paul KS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Center for Gut Microbiota Research, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Francis Ka Leung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6850-4454",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Microbiota I-Center (Magic), Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, Institute of Digestive Disease, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
},
{
"name": "Center for Gut Microbiota Research, Faculty of Medicine, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ng",
"given": "Siew C",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Gut Microbes",
"container-title-short": "Gut Microbes",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-06T18:47:59Z",
"timestamp": 1665082079000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-08T23:40:51Z",
"timestamp": 1704757251000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "This work was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund, the Food and Health Bureau, and InnoHK, The Government of Hong Kong, Special Administrative Region of the People’s Republic of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-19T12:38:45Z",
"timestamp": 1705667925735
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1665014400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/19490976.2022.2128603",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_3_5_2_1",
"unstructured": "Resistance I.C.G.o.A. 2019. No time to Wait. Securing the future from drug-resistant infections."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.12.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_3_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Bacterial and fungal coinfection in individuals with coronavirus: a rapid review to support COVID-19 antimicrobial prescribing",
"author": "Rawson TM",
"first-page": "2459",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "e_1_3_5_4_1",
"unstructured": "Rawson TM, Moore LS, Zhu N, Ranganathan N, Skolimowska K, Gilchrist M, Satta G, Cooke G, Holmes A, et al. Bacterial and fungal coinfection in individuals with coronavirus: a rapid review to support COVID-19 antimicrobial prescribing. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2459–16.",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1176950",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-021-00920-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41396-020-0634-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1113246109",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.50.3.1054-1062.2006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/civ191",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid1606.091671",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_11_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization",
"author": "Tao Zuo FZ",
"issue": "944",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "e_1_3_5_12_1",
"unstructured": "Tao Zuo FZ, Lui GCY, Yeoh YK, Li AYL, Zhan H, Wan Y, Chung ACK, Cheung CP, Chen N, Lai CKC, et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:944–955.",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323826",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa709",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa663",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2021.1887722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_16_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Prolonged Impairment of Short-Chain Fatty Acid and L-Isoleucine Biosynthesis in Gut Microbiome in Patients With COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang F",
"first-page": "e544",
"issue": "548",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "e_1_3_5_17_1",
"unstructured": "Zhang F, Wan Y, Zuo T, Yeoh YK, Liu Q, Zhang L, Zhan H, Lu W, Xu W, Lui GCY, Li AYL, Cheung CP, Wong CK, Chan PKS, Chan FKL, Ng SC, et al. Prolonged Impairment of Short-Chain Fatty Acid and L-Isoleucine Biosynthesis in Gut Microbiome in Patients With COVID-19. Gastroenterology. 2022;162548–561:e544.",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325989",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328319",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113882",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.00050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30122-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctm2.643",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgh.15796",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSphere.00500-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/cix270",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.02.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSphere.00716-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00088-17",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkn323",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22168732",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms9061237",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2021.1926840",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-29229-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_38_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of Horizontal Gene Transfer in the Development of Multidrug Resistance in Haemophilus influenzae",
"author": "Hegstad K",
"journal-title": "mSphere",
"key": "e_1_3_5_39_1",
"unstructured": "Hegstad K, Mylvaganam H, Janice J, Josefsen E, Sivertsen, A, Skaare D. Role of Horizontal Gene Transfer in the Development of Multidrug Resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. mSphere. 2020;5(1):e00969-19.",
"volume": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-017-0928-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(98)00354-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embr.202051034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-019-0439-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jgar.2020.02.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MLR.0b013e31803bb48b",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_47_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Impact of Preservation Method and 16S rRNA Hypervariable Region on Gut Microbiota Profiling",
"author": "Zigui Chen PCH",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "mSystems",
"key": "e_1_3_5_48_1",
"unstructured": "Zigui Chen PCH, Hui M, Yeoh YK, Wong PY, Chan MCW, Wong MCS, Ng SC, Chan FKL, Chan PKS. Impact of Preservation Method and 16S rRNA Hypervariable Region on Gut Microbiota Profiling. mSystems. 4(1):e00271–18.",
"volume": "4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btw136",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btv033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkz935",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00483-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_52_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 51,
"references-count": 51,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19490976.2022.2128603"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Gastroenterology",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antibiotics and probiotics impact gut antimicrobial resistance gene reservoir in COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01",
"volume": "14"
}