Safety and practicality of high dose inhaled nitric oxide in emergency department COVID-19 patients
et al., The American Journal of Emergency Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052, May 2022
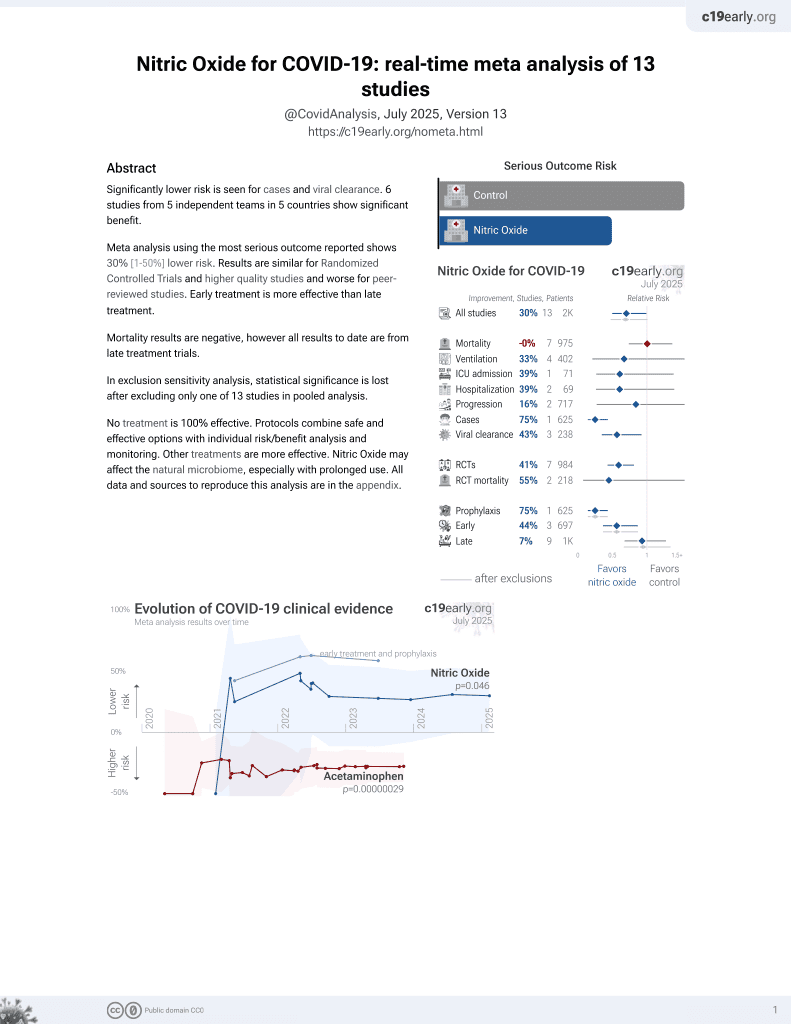
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Early terminated RCT with 47 ER patients in the USA, less than 12 days of symptoms, showing no significant difference in outcomes with a single high-dose administration of inhaled nitric oxide by mask, 250ppm for 30 min.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
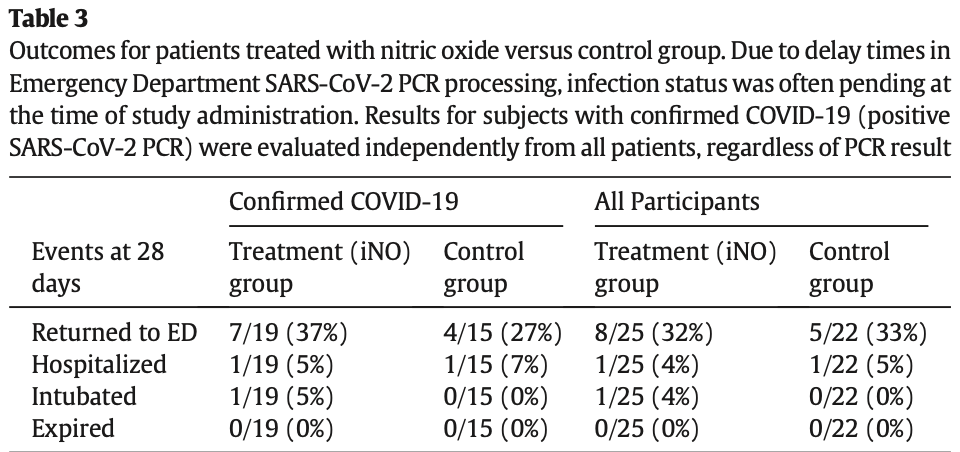
risk of mechanical ventilation, 178.9% higher, RR 2.79, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 19 (5.3%), control 0 of 15 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 21.1% lower, RR 0.79, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 19 (5.3%), control 1 of 15 (6.7%), NNT 71.
|
|
return to ER, 38.2% higher, RR 1.38, p = 0.72, treatment 7 of 19 (36.8%), control 4 of 15 (26.7%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Strickland et al., 4 May 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: brian.strickland@cuanschutz.edu.
Safety and practicality of high dose inhaled nitric oxide in emergency department COVID-19 patients
The American Journal of Emergency Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052
Background: Inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) is a selective pulmonary vasodilator and mild bronchodilator that has been shown to improve systemic oxygenation, but has rarely been administered in the Emergency Department (ED). In addition to its favorable pulmonary vascular effects, in-vitro studies report that NO donors can inhibit replication of viruses, including SARS Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). This study evaluated the administration of high-dose iNO by mask in spontaneously breathing emergency department (ED) patients with respiratory symptoms attributed to Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Methods: We designed a randomized clinical trial to determine whether 30 min of high dose iNO (250 ppm) could be safely and practically administered by emergency physicians in the ED to spontaneously-breathing patients with respiratory symptoms attributed to COVID-19. Our secondary goal was to learn if iNO could prevent the progression of mild COVID-19 to a more severe state. Findings: We enrolled 47 ED patients with acute respiratory symptoms most likely due to COVID-19: 25 of 47 (53%) were randomized to the iNO treatment group; 22 of 47 (46%) to the control group (supportive care only). All patients tolerated the administration of high-dose iNO in the ED without significant complications or symptoms. Five patients receiving iNO (16%) experienced asymptomatic methemoglobinemia (MetHb) > 5%. Thirty-four of 47 (72%) subjects tested positive for SARS-CoV-2: 19 of 34 were randomized to the iNO treatment group and 15 of 34 subjects to the control group. Seven of 19 (38%) iNO patients returned to the ED, while 4 of 15 (27%) control patients did. One patient in each study arm was hospitalized: 5% in iNO treatment and 7% in controls. One patient was intubated in the iNO group. No patients in either group died. The differences between these groups were not significant. Conclusion: A single dose of iNO at 250 ppm was practical and not associated with any significant adverse effects when administered in the ED by emergency physicians. Local disease control led to early study closure and prevented complete testing of COVID-19 safety and treatment outcomes measures.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors of this study have no conflicts of interest.
References
Akaberi, Krambrich, Ling, Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro, Redox Biol
Akerström, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected, Virology
Anand, Prasad, Chugh, Rao, Cornfield et al., Effects of inhaled nitric oxide and oxygen in high-altitude pulmonary edema, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.cir.98.22.2441
Archer, Huang, Hampl, Nelson, Shultz et al., Nitric oxide and cGMP cause vasorelaxation by activation of a charybdotoxin-sensitive K channel by cGMPdependent protein kinase, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.91.16.7583
Chen, Liu, Gao, Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: a rescue trial in Beijing, Clin Infect Dis
Deppisch, Herrmann, Graepler-Mainka, Gaseous nitric oxide to treat antibiotic resistant bacterial and fungal lung infections in patients with cystic fibrosis: a phase I clinical study, Infection
Fakhr, Fenza, Gianni, Wiegand, Miyazaki et al., Nitric oxide study investigators. Inhaled high dose nitric oxide is a safe and effective respiratory treatment in spontaneous breathing hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Nitric Oxide
Fakhr, Wiegand, Pinciroli, Gianni, Morais et al., High concentrations of nitric oxide inhalation therapy in pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Obstet Gynecol
Gebistorf, Karam, Wetterslev, Afshari, Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Gianni, Morais, Larson, Ideation and assessment of a nitric oxide delivery system for spontaneously breathing subjects, Nitric Oxide
Ichinose, Roberts, Zapol, Inhaled nitric oxide: a selective pulmonary vasodilator: current uses and therapeutic potential, Circulation
Kacmarek, Ripple, Cockrill, Bloch, Zapol et al., Inhaled nitric oxide. A bronchodilator in mild asthmatics with methacholine-induced bronchospasm, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Keyaerts, Vijgen, Chen, Inhibition of SARS-coronavirus infection in vitro by S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine, a nitric oxide donor compound, Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis
Kline, Hall, Jones, Puskarich, Mastouri et al., Randomized trial of inhaled nitric oxide to treat acute pulmonary embolism: the iNOPE trial, Am Heart J, doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2017.01.011
Kline, Hernandez, Garrett, Jones, Pilot study of a protocol to administer inhaled nitric oxide to treat severe acute submassive pulmonary embolism, Emerg Med J
Kline, Puskarich, Pike, Zagorski, Alves, Inhaled nitric oxide to control platelet hyper-reactivity in patients with acute submassive pulmonary embolism, Nitric Oxide
Miller, Mcmullin, Ghaffari, Gaseous nitric oxide bactericidal activity retained during intermittent high-dose short duration exposure, Nitric Oxide
Pepke-Zaba, Higenbottam, Dinh-Xuan, Stone, Wallwork, Inhaled nitric oxide as a cause of selective pulmonary vasodilatation in pulmonary hypertension, Lancet, doi:10.1016/0140-6736(91)92033-x
Regev-Shoshani, Vimalanathan, Mcmullin, Gaseous nitric oxide reduces influenza infectivity in vitro, Nitric Oxide
Samama, Diaby, Fellahi, Inhibition of platelet aggregation by inhaled nitric oxide in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Anesthesiology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052",
"ISSN": [
"0735-6757"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052",
"alternative-id": [
"S0735675722002832"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Safety and practicality of high dose inhaled nitric oxide in emergency department COVID-19 patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The American Journal of Emergency Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strickland",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albala",
"given": "Lorenzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coffey",
"given": "El Centro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carroll",
"given": "Ryan W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zapol",
"given": "Warren M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ichinose",
"given": "Fumito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berra",
"given": "Lorenzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "N. Stuart",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The American Journal of Emergency Medicine",
"container-title-short": "The American Journal of Emergency Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-04T15:43:28Z",
"timestamp": 1651679008000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-14T11:59:40Z",
"timestamp": 1657799980000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-14T12:43:12Z",
"timestamp": 1657802592588
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659312000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0735675722002832?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0735675722002832?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "5-8",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide: a selective pulmonary vasodilator: current uses and therapeutic potential",
"author": "Ichinose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3106",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0005",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0140-6736(91)92033-X",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide as a cause of selective pulmonary vasodilatation in pulmonary hypertension",
"author": "Pepke-Zaba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1173",
"issue": "8776",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0010",
"volume": "338",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.91.16.7583",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide and cGMP cause vasorelaxation by activation of a charybdotoxin-sensitive K channel by cGMP-dependent protein kinase",
"author": "Archer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7583",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0015",
"volume": "91",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.153.1.8542105",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide. A bronchodilator in mild asthmatics with methacholine-induced bronchospasm",
"author": "Kacmarek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0020",
"volume": "153",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults",
"author": "Gebistorf",
"first-page": "CD002787",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0025",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00000542-199507000-00007",
"article-title": "Inhibition of platelet aggregation by inhaled nitric oxide in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Samama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "Anesthesiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0030",
"volume": "83",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-coronavirus infection in vitro by S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine, a nitric oxide donor compound",
"author": "Keyaerts",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0035",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2013.03.007",
"article-title": "Gaseous nitric oxide reduces influenza infectivity in vitro",
"author": "Regev-Shoshani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0040",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/425357",
"article-title": "Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: a rescue trial in Beijing",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0045",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734",
"article-title": "Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro",
"author": "Akaberi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0050",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"article-title": "Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected",
"author": "Akerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0055",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-016-0879-x",
"article-title": "Gaseous nitric oxide to treat antibiotic resistant bacterial and fungal lung infections in patients with cystic fibrosis: a phase I clinical study",
"author": "Deppisch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "513",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0060",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2008.08.002",
"article-title": "Gaseous nitric oxide bactericidal activity retained during intermittent high-dose short duration exposure",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0065",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ahj.2017.01.011",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of inhaled nitric oxide to treat acute pulmonary embolism: the iNOPE trial",
"author": "Kline",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "Am Heart J",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0070",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/emermed-2013-202426",
"article-title": "Pilot study of a protocol to administer inhaled nitric oxide to treat severe acute submassive pulmonary embolism",
"author": "Kline",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Emerg Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0075",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.01.004",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide to control platelet hyper-reactivity in patients with acute submassive pulmonary embolism",
"author": "Kline",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0080",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.08.004",
"article-title": "Ideation and assessment of a nitric oxide delivery system for spontaneously breathing subjects",
"author": "Gianni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0085",
"volume": "104–105",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2021.08.003",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide study investigators. Inhaled high dose nitric oxide is a safe and effective respiratory treatment in spontaneous breathing hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Safaee Fakhr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0090",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/AOG.0000000000004128",
"article-title": "High concentrations of nitric oxide inhalation therapy in pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Safaee Fakhr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Obstet Gynecol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0095",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0100",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidance. Massachusetts General Hospitalhttps://www.massgeneral.org/news/coronavirus/treatment-guidance."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0105",
"unstructured": "ED COVID Updates. Massachusetts General Hospitalhttps://edcovidupdates.wixsite.com/mysite-1/md."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.98.22.2441",
"article-title": "Effects of inhaled nitric oxide and oxygen in high-altitude pulmonary edema",
"author": "Anand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2441",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Circulation.",
"key": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.052_bb0110",
"volume": "98",
"year": "1998"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0735675722002832"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Emergency Medicine",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety and practicality of high dose inhaled nitric oxide in emergency department COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "58"
}