Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Adults With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Trial
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab732, NCT04579393, Aug 2021
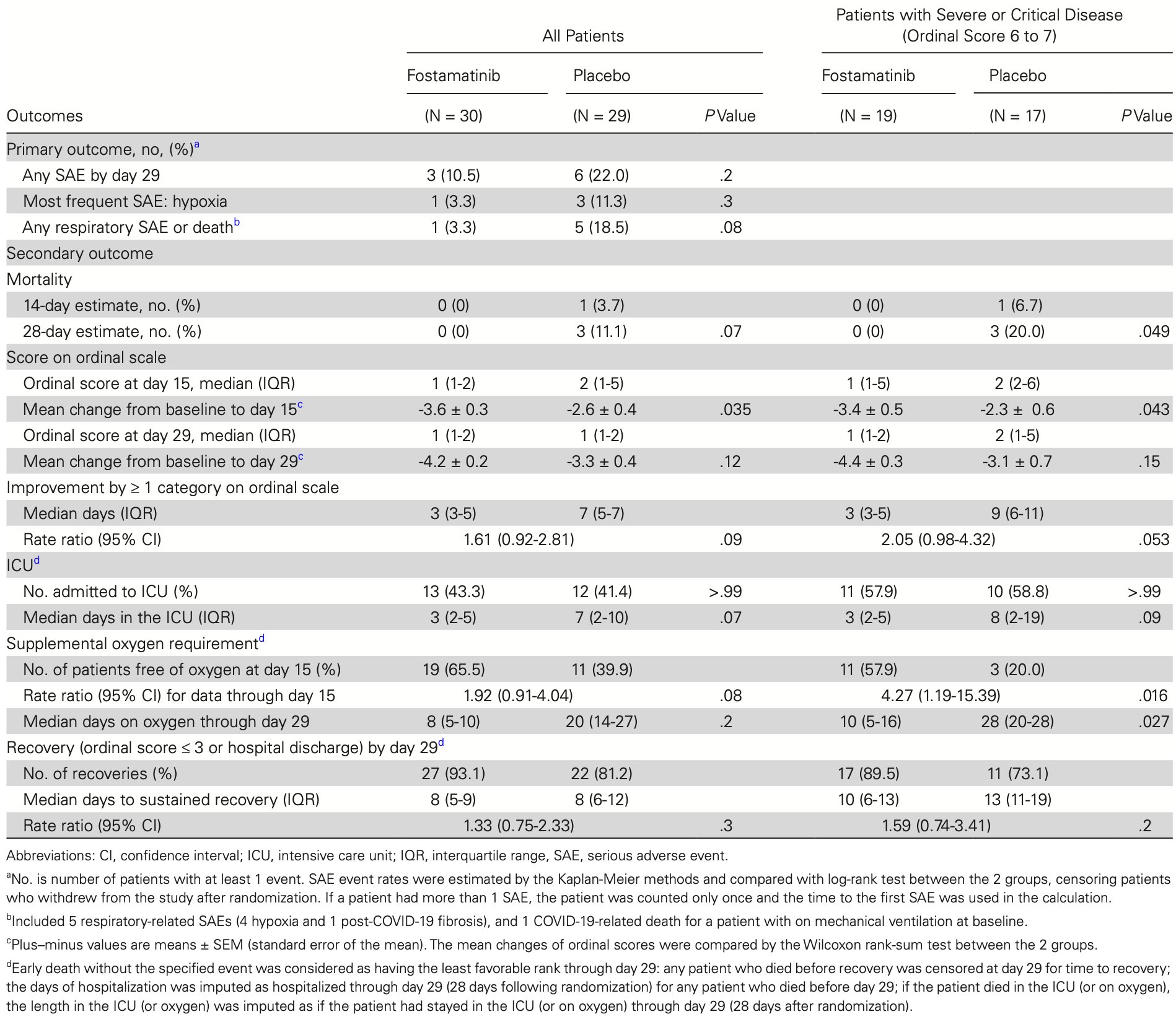
Double-blind RCT with 59 hospitalized COVID-19 patients requiring oxygen showing that adding fostamatinib to standard of care was safe and resulted in improved clinical outcomes compared to placebo, including faster recovery, fewer days in the ICU, and less supplemental oxygen needed, especially for those with severe or critical disease.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 67.8% lower, RR 0.32, p = 0.35, treatment 1 of 30 (3.3%), control 3 of 29 (10.3%), NNT 14, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 85.9% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.11, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 3 of 29 (10.3%), NNT 9.7, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Strich et al., 28 Aug 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 55.6, 34 authors, study period 8 October, 2020 - 2 March, 2021, trial NCT04579393 (history).
Contact: jeffrey.strich@nih.gov.
Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Adults With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Trial
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab732
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) requiring hospitalization is characterized by robust antibody production, dysregulated immune response, and immunothrombosis. Fostamatinib is a novel spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor that we hypothesize will ameliorate Fc activation and attenuate harmful effects of the anti-COVID-19 immune response. Methods: We conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in hospitalized adults requiring oxygen with COVID-19 where patients receiving standard of care were randomized to receive fostamatinib or placebo. The primary outcome was serious adverse events by day 29. Results: A total of 59 patients underwent randomization (30 to fostamatinib and 29 to placebo). Serious adverse events occurred in 10.5% of patients in the fostamatinib group compared with 22% in placebo (P = .2). Three deaths occurred by day 29, all receiving placebo. The mean change in ordinal score at day 15 was greater in the fostamatinib group (-3.6 ± 0.3 vs -2.6 ± 0.4, P = .035) and the median length in the intensive care unit was 3 days in the fostamatinib group vs 7 days in placebo (P = .07). Differences in clinical improvement were most evident in patients with severe or critical disease (median days on oxygen, 10 vs 28, P = .027). There were trends toward more rapid reductions in C-reactive protein, D-dimer, fibrinogen, and ferritin levels in the fostamatinib group.
Conclusion: For COVID-19 requiring hospitalization, the addition of fostamatinib to standard of care was safe and patients were observed to have improved clinical outcomes compared with placebo. These results warrant further validation in larger confirmatory trials. NCT04579393.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at Clinical Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
Notes for this publication data collection and reporting. The authors also thank Henry Masur, MD (NIH Critical Care Medicine Department), for his support of this trial and thoughtful review of manuscript during preparation. Last, the authors thank the NHLBI's Division of Intramural Research (DIR), including the DIR's Office of the Clinical Director and Office of Biostatistical Research for providing the comprehensive support, oversight, and analysis needed to conduct this trial. The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, NHLBI, NIAID, or National Institutes of Health Clinical Center. Financial support.
References
Alimova, Sidhom, Satyam, A high content screen for mucin-1reducing compounds identifies fostamatinib as a candidate for rapid repurposing for acute lung injury during the COVID-19 pandemic, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.30.180380
Angus, Derde, Al-Beidh, Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators. Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, ACTT-1 Study Group Members. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Bonaventura, Vecchié, Dagna, Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol
Bye, Hoepel, Mitchell, Aberrant glycosylation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG is a pro-thrombotic stimulus for platelets, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2021011871
Garcia-Beltran, Lam, Astudillo, COVID-19-neutralizing antibodies predict disease severity and survival, Cell
Hoepel, Chen, Geyer, High titers and low fucosylation of early human anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG promote inflammation by alveolar macrophages, Sci Transl Med
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kalil, Patterson, Mehta, ACTT-2 Study Group Members. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kaneko, Esmail, Voss, System-wide hematopoietic and immune signaling aberrations in COVID-19 revealed by deep proteome and phosphoproteome analysis, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.19.21253675
Liao, Zhou, Luo, Haematological characteristics and risk factors in the classification and prognosis evaluation of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Haematol
Middleton, He, Denorme, Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immunothrombosis in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome, Blood
Mócsai, Ruland, Tybulewicz, The SYK tyrosine kinase: a crucial player in diverse biological functions, Nat Rev Immunol
Papayannopoulos, Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease, Nat Rev Immunol
Rosas, Bräu, Waters, Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with severe Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Sarma, Christenson, COVID-19 ARDS is characterized by a dysregulated host response that differs from cytokine storm and is modified by dexamethasone, Res Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-141578/v1
Sharifpour, Rangaraju, Liu, C-Reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, PLoS One
Strich, Ramos-Benitez, Randazzo, Fostamatinib inhibits neutrophils extracellular traps induced by COVID-19 patient plasma: a potential therapeutic, J Infect Dis
Veras, Pontelli, Silva, SARS-CoV-2-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps mediate COVID-19 pathology, J Exp Med
Woodruff, Ramonell, Nguyen, Extrafollicular B cell responses correlate with neutralizing antibodies and morbidity in COVID-19, Nat Immunol
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zuo, Yalavarthi, Shi, Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, JCI Insight
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab732",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab732",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) requiring hospitalization is characterized by robust antibody production, dysregulated immune response, and immunothrombosis. Fostamatinib is a novel spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor that we hypothesize will ameliorate Fc activation and attenuate harmful effects of the anti-COVID-19 immune response.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in hospitalized adults requiring oxygen with COVID-19 where patients receiving standard of care were randomized to receive fostamatinib or placebo. The primary outcome was serious adverse events by day 29.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 59 patients underwent randomization (30 to fostamatinib and 29 to placebo). Serious adverse events occurred in 10.5% of patients in the fostamatinib group compared with 22% in placebo (P = .2). Three deaths occurred by day 29, all receiving placebo. The mean change in ordinal score at day 15 was greater in the fostamatinib group (-3.6 ± 0.3 vs -2.6 ± 0.4, P = .035) and the median length in the intensive care unit was 3 days in the fostamatinib group vs 7 days in placebo (P = .07). Differences in clinical improvement were most evident in patients with severe or critical disease (median days on oxygen, 10 vs 28, P = .027). There were trends toward more rapid reductions in C-reactive protein, D-dimer, fibrinogen, and ferritin levels in the fostamatinib group.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>For COVID-19 requiring hospitalization, the addition of fostamatinib to standard of care was safe and patients were observed to have improved clinical outcomes compared with placebo. These results warrant further validation in larger confirmatory trials.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trials Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Clinicaltrials.gov, NCT04579393.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine Department, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Strich",
"given": "Jeffrey R",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Tian",
"given": "Xin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Samour",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "King",
"given": "Christopher S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Shlobin",
"given": "Oksana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Reger",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Adventist Healthcare Shady Grove Medical Center , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "Kareem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "A Whitney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Khangoora",
"given": "Vikramjit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Aryal",
"given": "Shambhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Migdady",
"given": "Yazan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kyte",
"given": "Jennifer Jo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Joo",
"given": "Jungnam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hays",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "A Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Battle",
"given": "Edwinia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Valdez",
"given": "Janet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Rivero",
"given": "Josef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Ick Ho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Erb-Alvarez",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Shalhoub",
"given": "Ruba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Chakraborty",
"given": "Mala",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacy Department, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Colton",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine Department, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "Postdoctoral Research Associate Training Program, National Institute of General Medical Sciences , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Ramos-Benitez",
"given": "Marcos J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine Department, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Warner",
"given": "Seth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine Department, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Chertow",
"given": "Daniel S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Olivier",
"given": "Kenneth N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Aue",
"given": "Georg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Davey",
"given": "Richard T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Critical Care Medicine Department, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Suffredini",
"given": "Anthony F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Childs",
"given": "Richard W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program, Inova Fairfax Hospital , Falls Church, Virginia , USA"
}
],
"family": "Nathan",
"given": "Steven D",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-01T05:10:42Z",
"timestamp": 1630473042000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-01T21:55:31Z",
"timestamp": 1675288531000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100017540",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100017540",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Division of Intramural Research (DIR) of the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000002",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"name": "Cooperative Research and Development Agreement"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-15T17:08:30Z",
"timestamp": 1726420110731
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 33,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
28
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab732/40833871/ciab732.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/75/1/e491/49017925/ciab732.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/75/1/e491/49017925/ciab732.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e491-e498",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
28
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0001",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00536-9",
"article-title": "Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19",
"author": "Bonaventura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0002",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0003",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0004",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031994",
"article-title": "Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Kalil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "795",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0005",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028700",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with severe Covid-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Rosas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1503",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0006",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0007",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.015",
"article-title": "COVID-19-neutralizing antibodies predict disease severity and survival",
"author": "Garcia-Beltran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "476",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0008",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.19.21253675",
"article-title": "System-wide hematopoietic and immune signaling aberrations in COVID-19 revealed by deep proteome and phosphoproteome analysis",
"author": "Kaneko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0009",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-141578/v1",
"article-title": "COVID-19 ARDS is characterized by a dysregulated host response that differs from cytokine storm and is modified by dexamethasone",
"author": "Sarma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Res Sq",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0010",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-00814-z",
"article-title": "Extrafollicular B cell responses correlate with neutralizing antibodies and morbidity in COVID-19",
"author": "Woodruff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1506",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0011",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri2765",
"article-title": "The SYK tyrosine kinase: a crucial player in diverse biological functions",
"author": "Mócsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "387",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0012",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abf8654",
"article-title": "High titers and low fucosylation of early human anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG promote inflammation by alveolar macrophages",
"author": "Hoepel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0013",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2021011871",
"article-title": "Aberrant glycosylation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG is a pro-thrombotic stimulus for platelets",
"author": "Bye",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0014",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa789",
"article-title": "Fostamatinib inhibits neutrophils extracellular traps induced by COVID-19 patient plasma: a potential therapeutic",
"author": "Strich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "981",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0015",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007008",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immunothrombosis in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Middleton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1169",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0016",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2017.105",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease",
"author": "Papayannopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0017",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20201129",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps mediate COVID-19 pathology",
"author": "Veras",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e20201129",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0018",
"volume": "217",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19",
"author": "Zuo",
"first-page": "e138999",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0019",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.30.180380",
"article-title": "A high content screen for mucin-1-reducing compounds identifies fostamatinib as a candidate for rapid repurposing for acute lung injury during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Alimova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17022",
"article-title": "Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Angus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1317",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0022",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0242400",
"article-title": "C-Reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Sharifpour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0242400",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0023",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30217-9",
"article-title": "Haematological characteristics and risk factors in the classification and prognosis evaluation of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Liao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e671",
"journal-title": "Lancet Haematol",
"key": "2023020110331268900_CIT0024",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/75/1/e491/6358811"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Adults With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "75"
}