Efficacy and Safety of Obeldesivir in High-Risk Nonhospitalized Patients with COVID-19 (BIRCH): a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaf406, BIRCH, NCT05603143, Jul 2025
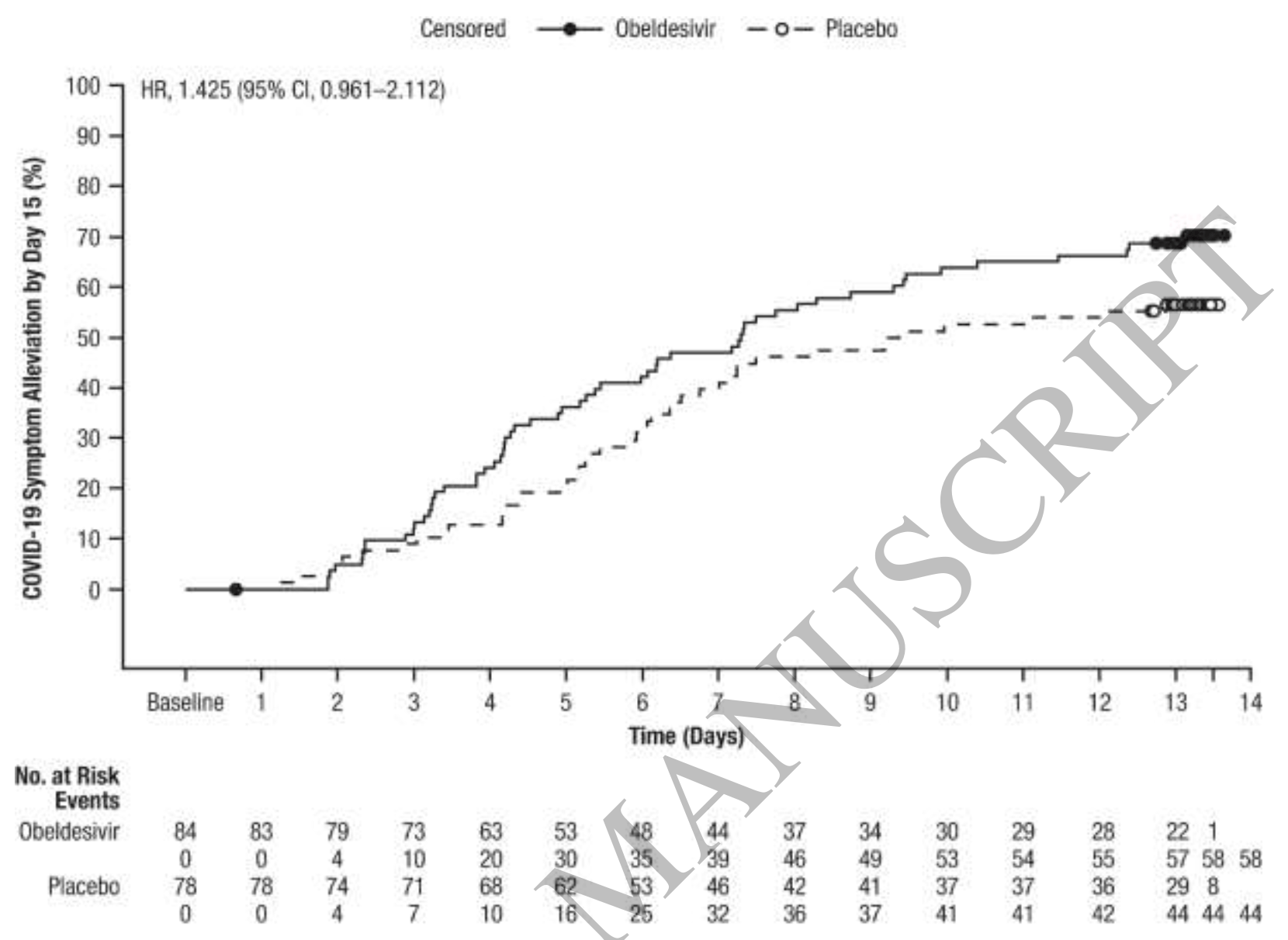
RCT 465 high-risk nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients showing 2-day shorter median time to symptom alleviation (7.3 vs 9.3 days) and significantly reduced viral RNA and infectious viral titers compared to placebo. There was no significant difference for hospitalization or death.
|
risk of death, 66.9% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.50, treatment 0 of 211 (0.0%), control 1 of 207 (0.5%), NNT 207, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 198.1% higher, RR 2.98, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 211 (0.5%), control 0 of 207 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
MAV, 194.3% higher, RR 2.94, p = 0.62, treatment 3 of 211 (1.4%), control 1 of 207 (0.5%).
|
|
risk of no recovery, 29.8% lower, HR 0.70, p = 0.08, treatment 84, control 78, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment.
|
|
viral load, 20.7% lower, relative load 0.79, p < 0.001, treatment mean 2.8 (±1.27) n=192, control mean 2.22 (±1.27) n=192, relative change from baseline, day 5.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Streinu-Cercel et al., 22 Jul 2025, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, median age 56.0, 24 authors, study period 5 November, 2022 - 6 October, 2023, trial NCT05603143 (history) (BIRCH).
Contact: juanmaria.gonzalezdel@salud.madrid.org.
Efficacy and Safety of Obeldesivir in High-Risk Nonhospitalized Patients with COVID-19 (BIRCH): a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
doi:10.1093/cid/ciaf4061
Background: Obeldesivir is an oral nucleoside analog prodrug inhibitor of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Methods: Nonhospitalized adults with risk factors for developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) were enrolled ≤5 days from COVID-19 symptom onset and randomized 1:1 to receive obeldesivir 350 mg or placebo twice daily for 5 days. The primary endpoint was COVID-19-related hospitalization or all-cause death by Day 29. Other endpoints included time to symptom alleviation by Day 15, change in SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA copy number and infectious viral titer, and incidence of adverse events and laboratory abnormalities. Results: 465 participants were randomized and received ≥1 dose of study drug. Baseline characteristics were generally balanced between groups. Overall, 58% had received ≥1 COVID-19 vaccination and 92% were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. COVID-19-related hospitalization or all-cause death by Day 29 was reported in 0/211 (0%) participants with obeldesivir and 1/207 (0.5%) participants with placebo (log-rank P=0.32). Time to COVID-19 symptom alleviation was numerically shorter with obeldesivir versus placebo. Obeldesivir reduced viral RNA copy number at Day 5 and infectious titer at Days 3 and 5 versus placebo. The safety profile was generally comparable across arms. Conclusions: Although underpowered in the context of a changing COVID-19 landscape, obeldesivir in nonhospitalized adults with targeted risk factors did not improve COVID-19related hospitalization or all-cause death. Obeldesivir reduced viral RNA copy number and infectious titer, demonstrating its ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication, and resulted in numerically faster symptom alleviation.
References
Amini, Shelton, Raut, Drug-drug interaction profiling of obeldesivir, a promising oral treatment for COVID-19, Open Forum Infect Dis
Anoshchenko, Abdelghany, Lichtman, Pharmacokinetics, mass balance, safety, and tolerability of obeldesivir in healthy participants, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Arroyo-Marioli, Bullano, Kucinskas, Moreno, Tracking ℛ of COVID-19: A new real-time estimation using the Kalman filter, PLoS One
Bhimraj, Morgan, Nadig, IDSA Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19
Cross, Woolsey, Chu, Oral administration of obeldesivir protects nonhuman primates against Sudan ebolavirus, Science
Cross, Woolsey, Prasad, Oral obeldesivir provides postexposure protection against Marburg virus in nonhuman primates, Nat Med
Dessie, Zewotir, Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients, BMC Infect Dis
Gebhard, Regitz-Zagrosek, Neuhauser, Morgan, Klein, Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe, Biol Sex Differ
Gomez, Du-Fay-De-Lavallaz, Fugar, Sex differences in COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality, J Womens Health (Larchmt)
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients, N Engl J Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Jin, Bai, He, Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: Focus on severity and mortality, Front Public Health
Kompaniyets, Pennington, Goodman, Underlying medical conditions and severe illness among 540,667 adults hospitalized with COVID-19, March 2020, Prev Chronic Dis
Lin, Huang, Milinovich, Duggal, Wang, Effectiveness of XBB.1.5 vaccines and antiviral drugs against severe outcomes of Omicron infection in the USA, Lancet Infect Dis
Mackman, Hui, Perron, Prodrugs of a 1'-CN-4-Aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine Cnucleoside leading to the discovery of remdesivir (GS-5734) as a potent inhibitor of respiratory syncytial virus with efficacy in the African green monkey model of RSV, J Med Chem
Mackman, Kalla, Babusis, Discovery of GS-5245 (obeldesivir), an oral prodrug of nucleoside GS-441524 that exhibits antiviral efficacy in SARS-CoV-2-infected African green monkeys, J Med Chem
Mathieu, Rodés-Guirao, What are the sources for Our World in Data's population estimates? Available at
Moline, Whitaker, Deng, Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in preventing hospitalization among adults aged ≥65 years -COVID-NET, 13 states, February-April 2021, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Ogbuagu, Goldman, Gottlieb, Obeldesivir for treatment of COVID-19 in adults and adolescents without risk factors for progression to severe disease: the OAKTREE study, Open Forum Infect Dis
Parienti, De Grooth, Clinical relevance of nasopharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 viral load reduction in outpatients with COVID-19, J Antimicrob Chemother
Parise, Ramesh, Ren, A scientific perspective of how and why Omicron is less severe than SARS-CoV-2, Emerg Crit Care Med
Peng, Humeniuk, Raut, Clinical evaluation of drug-drug interactions with obeldesivir, an orally administered antiviral agent, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Rodriguez, Zamora, Han, Remdesivir and obeldesivir retain potent antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants, Viruses
Tchesnokov, Gordon, Woolner, Template-dependent inhibition of coronavirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by remdesivir reveals a second mechanism of action, J Biol Chem
Yin, Mao, Luan, Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir, Science
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaf406",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaf406",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Obeldesivir is an oral nucleoside analog prodrug inhibitor of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Nonhospitalized adults with risk factors for developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) were enrolled ≤5 days from COVID-19 symptom onset and randomized 1:1 to receive obeldesivir 350 mg or placebo twice daily for 5 days. The primary endpoint was COVID-19–related hospitalization or all-cause death by Day 29. Other endpoints included time to symptom alleviation by Day 15, change in SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA copy number and infectious viral titer, and incidence of adverse events and laboratory abnormalities.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>465 participants were randomized and received ≥1 dose of study drug. Baseline characteristics were generally balanced between groups. Overall, 58% had received ≥1 COVID-19 vaccination and 92% were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. COVID-19–related hospitalization or all-cause death by Day 29 was reported in 0/211 (0%) participants with obeldesivir and 1/207 (0.5%) participants with placebo (log-rank P=0.32). Time to COVID-19 symptom alleviation was numerically shorter with obeldesivir versus placebo. Obeldesivir reduced viral RNA copy number at Day 5 and infectious titer at Days 3 and 5 versus placebo. The safety profile was generally comparable across arms.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Although underpowered in the context of a changing COVID-19 landscape, obeldesivir in nonhospitalized adults with targeted risk factors did not improve COVID-19-related hospitalization or all-cause death. Obeldesivir reduced viral RNA copy number and infectious titer, demonstrating its ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication, and resulted in numerically faster symptom alleviation.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trials Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>https://ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05603143; EudraCT 2022-002741-18.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"article-number": "ciaf406",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2794-6720",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy , Bucharest ,",
"place": [
"Romania"
]
},
{
"name": "National Institute of Infectious Diseases “Prof. Dr. Matei Bals” , Bucharest ,",
"place": [
"Romania"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Streinu-Cercel",
"given": "Anca",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8338-9714",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases Clinic, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University , Milan ,",
"place": [
"Italy"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Castagna",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6505-4139",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Taiwan University College of Medicine , Taipei ,",
"place": [
"Taiwan"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Shan-Chwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital , Kaohsiung ,",
"place": [
"Taiwan"
]
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yao-Shen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7764-1741",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Koullias",
"given": "Yiannis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Mozaffarian",
"given": "Afsaneh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8473-8285",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hyland",
"given": "Robert H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1573-793X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Humeniuk",
"given": "Rita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2275-8771",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Caro",
"given": "Luzelena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Santosh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0009-9124-4652",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rodriguez",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0512-7767",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hedskog",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Shuguang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Etchevers",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences Europe Ltd , Uxbridge ,",
"place": [
"UK"
]
}
],
"family": "Behenna-Renton",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Llewellyn",
"given": "Joe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Osinusi",
"given": "Anu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Foster City, CA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Duff",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "FAICIC Clinical Research , Veracruz ,",
"place": [
"Mexico"
]
}
],
"family": "Barrat Hernández",
"given": "Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ormeau Clinical Trials , Belfast ,",
"place": [
"UK"
]
}
],
"family": "McNally",
"given": "Damien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9630-7792",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Köhler & Milstein Research , Mérida ,",
"place": [
"Mexico"
]
},
{
"name": "Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán , Mérida ,",
"place": [
"Mexico"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Simon-Campos",
"given": "Jesus Abraham",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1986-3765",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brazilian National Cancer Institute , Rio de Janeiro ,",
"place": [
"Brazil"
]
},
{
"name": "Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade Municipal de São Caetano do Sul , São Paulo ,",
"place": [
"Brazil"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Leal",
"given": "Fabio Eudes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6297-9328",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Limpopo Clinical Research Initiative , Thabazimbi ,",
"place": [
"South Africa"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fouche",
"given": "Leon F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4329-9802",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Hospital Clínico Universitario San Carlos , Madrid ,",
"place": [
"Spain"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "González Del Castillo",
"given": "Juan Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Clinical Infectious Diseases"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-22T18:04:42Z",
"timestamp": 1753207482000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-22T18:04:42Z",
"timestamp": 1753207482000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-23T00:08:15Z",
"timestamp": 1753229295776,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1058-4838"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1537-6591"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
22
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1753142400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf406/63823996/ciaf406.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf406/63823996/ciaf406.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf406/8210547"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Efficacy and Safety of Obeldesivir in High-Risk Nonhospitalized Patients with COVID-19 (BIRCH): a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}