Sep 8 2024 |
et al., Journal of Cellular and Molecular Anesthesia, doi:10.5812/jcma-149015 | Effects of Spirulina platensis Supplementation on COVID-19 Severity in Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
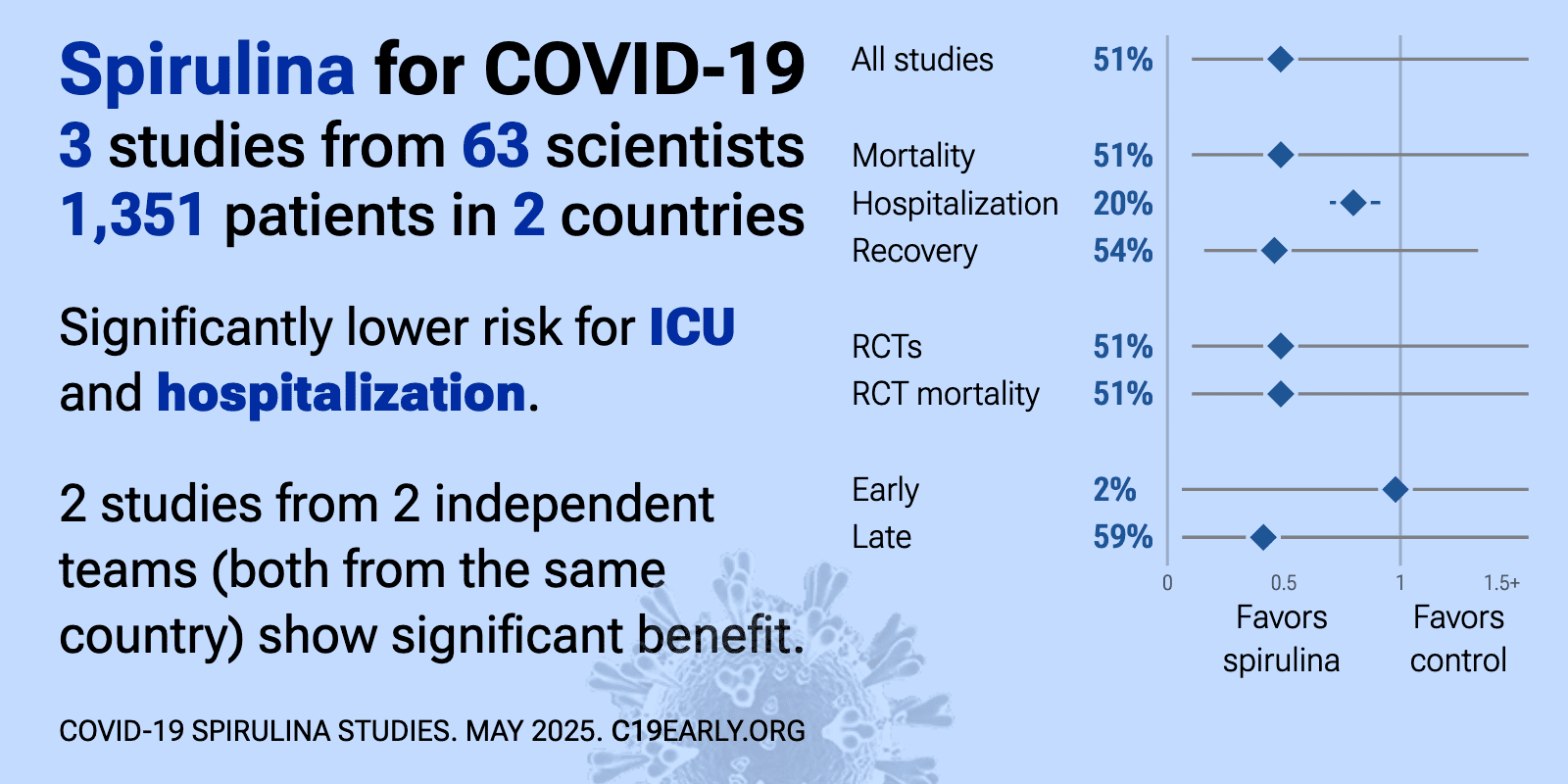
| 3% higher mortality (p=0.93), 26% shorter ICU admission (p=0.007), 17% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.64), and 20% shorter hospitalization (p=0.001). RCT 192 critically ill COVID-19 ICU patients showing reduced SOFA score, hospital stay and ICU stay with spirulina supplementation (5g/day), but no significant difference in mortality, NEWS2 score, APACHE score, NUTRIC score, or respirato.. | ||
Aug 15 2024 |
et al., The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.06.016 | Effect of spirulina on risk of hospitalization among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomized trial |
| 21% higher progression (p=0.29). RCT 1,126 patients in Brazil showing no significant differences with low dose spirulina. The dose used was 7.6 times lower than the dose used by [Aghasadeghi] which shows significantly lower mortality. eFigure 1 shows 12 events in the tr.. | ||
Apr 8 2024 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425 | Effect of high-dose Spirulina supplementation on hospitalized adults with COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial |
| 85% lower mortality (p=0.0002) and 75% higher hospital discharge (p=0.003). RCT 189 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality and faster recovery with spirulina. Spirulina treatment also resulted in greater reductions in inflammatory markers such as IL-6, TNF-a, IP-10, CRP, ESR, and ferritin. All pat.. | ||
Jul 31 2023 |
et al., Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030039 | Algae Polysaccharides (Carrageenan and Alginate)—A Treasure-Trove of Antiviral Compounds: An In Silico Approach to Identify Potential Candidates for Inhibition of S1-RBD Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 |
| In silico study showing the potential antiviral activity of algal polysaccharides alginate and carrageenan against SARS-CoV-2. Molecular docking analyses predict that alginate and carrageenan can bind to and inhibit the viral S1-RBD spike.. | ||
Jul 3 2023 |
et al., Journal of Personalized Medicine, doi:10.3390/jpm13071093 | A Hypertonic Seawater Nasal Irrigation Solution Containing Algal and Herbal Natural Ingredients Reduces Viral Load and SARS-CoV-2 Detection Time in the Nasal Cavity |
| 42% improved viral clearance (p=0.06). RCT 56 severe COVID-19 patients, showing significantly decreased viral load with Sinomarin Plus Algae nasal irrigation. Sinomarin Plus Algae is a hypertonic seawater solution with algal and herbal natural ingredients with a pH of 7.5-8.. | ||
May 30 2022 |
et al., European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, doi:10.24018/ejmed.2022.4.3.1355 | The Contribution of Spirulina Platensis Supplementation on COVID-19 Prevention and Hospitalization |
| 90% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001) and 81% fewer symptomatic cases (p<0.0001). Analysis of 186 adults in Greece showing a significant reduction in COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations with 6 g/day spirulina treatment for 6 months. Authors do not provide baseline details for each group. | ||
Oct 25 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19031172 (date from preprint) | Effect of a Nutritional Support System to Increase Survival and Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Stage III and Comorbidities: A Blinded Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial |
| 86% lower mortality (p=0.03) and 57% lower ventilation (p=0.31). 80 patient RCT with 40 patients treated with a comprehensive regimen of nutritional support, showing significantly lower mortality with treatment. Treatment contained cholecalciferol, vitamin C, zinc, spirulina maxima, folic acid, glutami.. | ||