Multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof of concept study of LSALT peptide as prevention of acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute kidney injury in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076142, NCT04402957, Mar 2024
RCT 61 hospitalised moderate/severe COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in clinical outcomes with intravenous LSALT peptide treatment.
|
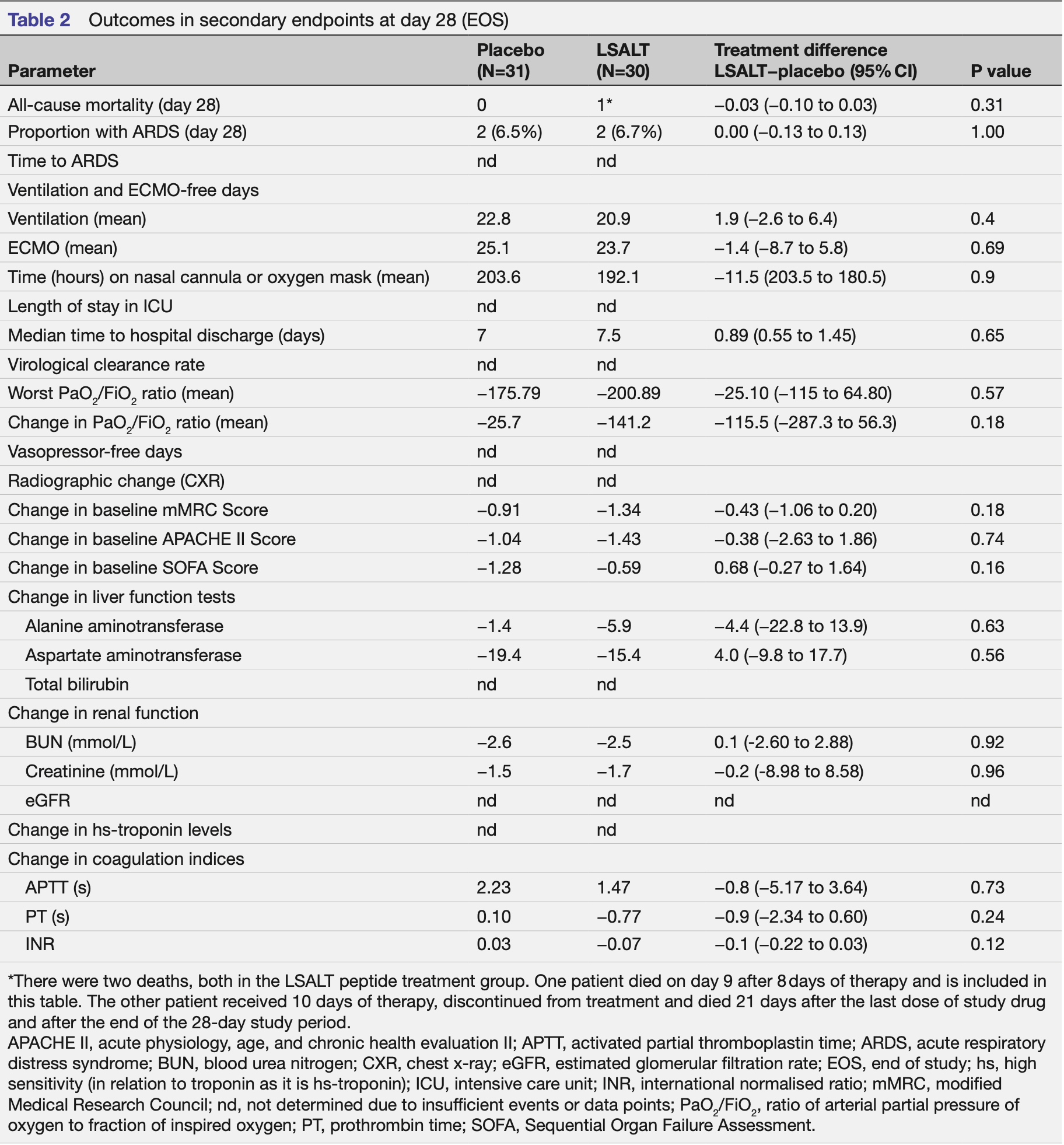
risk of death, 406.7% higher, RR 5.07, p = 0.24, treatment 2 of 30 (6.7%), control 0 of 31 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), in-hospital.
|
|
risk of death, 203.3% higher, RR 3.03, p = 0.49, treatment 1 of 30 (3.3%), control 0 of 31 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of ARDS, 3.3% higher, RR 1.03, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 30 (6.7%), control 2 of 31 (6.5%), day 28.
|
|
hospitalization time, 7.1% higher, relative time 1.07, p = 0.65, treatment 30, control 31.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Somayaji et al., 15 Mar 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, mean age 59.8, 19 authors, study period 13 October, 2020 - 28 April, 2021, trial NCT04402957 (history).
Contact: somayaj@ucalgary.ca.
Multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof of concept study of LSALT peptide as prevention of acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute kidney injury in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076142
Objective Dipeptidase-1 (DPEP-1) is a recently discovered leucocyte adhesion receptor for neutrophils and monocytes in the lungs and kidneys and serves as a potential therapeutic target to attenuate inflammation in moderateto-severe COVID-19. We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the DPEP-1 inhibitor, LSALT peptide, to prevent specific organ dysfunction in patients hospitalised with COVID-19. Design Phase 2a randomised, placebo-controlled, doubleblinded, trial. Setting Hospitals in Canada, Turkey and the USA. Participants A total of 61 subjects with moderate-tosevere COVID-19. Interventions Randomisation to LSALT peptide 5 mg intravenously daily or placebo for up to 14 days. Primary and secondary outcome measures The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects alive and free of respiratory failure and/or the need for renal replacement therapy (RRT). Numerous secondary and exploratory endpoints were assessed including ventilationfree days, and changes in kidney function or serum biomarkers. Results At 28 days, 27 (90.3%) and 28 (93.3%) of subjects in the placebo and LSALT groups were free of respiratory failure and the need for RRT (p=0.86). On days 14 and 28, the number of patients still requiring more intensive respiratory support (O 2 ≥6 L/minute, non-invasive or invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) was 6 (19.4%) and 3 (9.7%) in the placebo group versus 2 (6.7%) and 2 (6.7%) in the LSALT group, respectively (p=0.14; p=0.67). Unadjusted analysis of ventilation-free days demonstrated 22.8 days for the LSALT group compared with 20.9 in the placebo group (p=0.4). LSALT-treated subjects had a significant reduction in the fold expression from baseline to end of treatment of serum CXCL10 compared with placebo (p=0.02). Treatmentemergent adverse events were similar between groups.
Conclusion In a Phase 2 study, LSALT peptide was demonstrated to be safe and tolerated in patients hospitalised with moderate-to-severe COVID-19. Trial registration number NCT04402957. .
Competing interests DRL, DS, KG and AL are employed by Arch Biopartners Inc. DRL, AL, SMR and DLS hold equity positions in Arch Biopartners. SMR, DLS, AL and DM have patents issued and pending in the areas of dipeptidase-1 and the LSALT peptide. DM is the acting chief science officer for Arch Biopartners and is compensated with an equity position. DM has received research funding from Arch Biopartners. All other authors have no competing interests. Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research. Patient consent for publication Not applicable.
Ethics approval The study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles that have their origins in the Declaration of Helsinki, in compliance with the approved protocol, good clinical practice and applicable regulatory requirements. The study protocol, associated amendments and informed consents in the USA and Canada were approved by each hospital's institutional Research Ethics Committee (ethics approval number: Advarra CIRB MOD00749358 20 August 2020) and respective national regulatory agencies before enrolment began. Ethics approval in Turkey was issued by the Ministry of Health and the two participating institutions. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part. Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed. Data availability statement Data are available..
References
Ali, Azher, Baqi, Remdesivir for the treatment of patients in hospital with COVID-19 in Canada: a randomized controlled trial, CMAJ, doi:10.1503/cmaj.211698
Booth, Reed, Ponzo, Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247461
Cates, Lucero-Obusan, Dahl, Risk for in-hospital complications associated with COVID-19 and influenza -veterans health administration, United States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6942e3
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Choudhury, Babes, Rahn, Dipeptidase-1 is an adhesion receptor for neutrophil recruitment in lungs and liver, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.017
Consortium, Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: final results of the WHO solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses, Lancet
Epidemiology, Surveillance, COVID-19 Australia: epidemiology report 71: reporting period ending 12 February 2023, Commun Dis Intell
Forchette, Sebastian, Liu, A comprehensive review of COVID-19 virology, vaccines, variants, and therapeutics, Curr Med Sci, doi:10.1007/s11596-021-2395-1
Lau, Rahn, Chappellaz, Dipeptidase-1 governs renal inflammation during ischemia reperfusion injury, Sci Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abm0142
Link-Gelles, Levy, Natarajan, Estimation of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine effectiveness and COVID-19 illness and severity by vaccination status during omicron BA.4 and BA.5 sublineage periods, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2598
Malahe, Hoek, Dalm, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of immunocompromised patients with coronavirus disease 2019 caused by the omicron variant: a prospective, observational study, Clin Infect Dis
Murakami, Hayden, Hills, Therapeutic advances in COVID-19, Nat Rev Nephrol, doi:10.1038/s41581-022-00642-4
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021
Zhou, Chi, Lv, Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3377
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076142",
"ISSN": [
"2044-6055",
"2044-6055"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076142",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>Dipeptidase-1 (DPEP-1) is a recently discovered leucocyte adhesion receptor for neutrophils and monocytes in the lungs and kidneys and serves as a potential therapeutic target to attenuate inflammation in moderate-to-severe COVID-19. We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the DPEP-1 inhibitor, LSALT peptide, to prevent specific organ dysfunction in patients hospitalised with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design</jats:title><jats:p>Phase 2a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, trial.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Setting</jats:title><jats:p>Hospitals in Canada, Turkey and the USA.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Participants</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 61 subjects with moderate-to-severe COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Randomisation to LSALT peptide 5 mg intravenously daily or placebo for up to 14 days.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Primary and secondary outcome measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects alive and free of respiratory failure and/or the need for renal replacement therapy (RRT). Numerous secondary and exploratory endpoints were assessed including ventilation-free days, and changes in kidney function or serum biomarkers.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>At 28 days, 27 (90.3%) and 28 (93.3%) of subjects in the placebo and LSALT groups were free of respiratory failure and the need for RRT (p=0.86). On days 14 and 28, the number of patients still requiring more intensive respiratory support (O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub>≥6 L/minute, non-invasive or invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) was 6 (19.4%) and 3 (9.7%) in the placebo group versus 2 (6.7%) and 2 (6.7%) in the LSALT group, respectively (p=0.14; p=0.67). Unadjusted analysis of ventilation-free days demonstrated 22.8 days for the LSALT group compared with 20.9 in the placebo group (p=0.4). LSALT-treated subjects had a significant reduction in the fold expression from baseline to end of treatment of serum CXCL10 compared with placebo (p=0.02). Treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between groups.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>In a Phase 2 study, LSALT peptide was demonstrated to be safe and tolerated in patients hospitalised with moderate-to-severe COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial registration number</jats:title><jats:p><jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" specific-use=\"clinicaltrial \" xlink:href=\"NCT04402957\">NCT04402957</jats:ext-link>.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
26
]
]
},
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076142"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3731-9675",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Somayaji",
"given": "Ranjani",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luke",
"given": "David R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Arthur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guner",
"given": "Rahmet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tabak",
"given": "Ŏ Fehmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hepokoski",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardetto",
"given": "Nancy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4014-969X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Conrad",
"given": "Steven A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Sunil D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "Kalyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robbins",
"given": "Stephen M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Senger",
"given": "Donna L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Daisy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Rachel K S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0282-6346",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Eser",
"given": "Fatma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karaali",
"given": "Ridvan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tremblay",
"given": "Alain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1757-218X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Muruve",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04402957",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov",
"type": "preResults"
},
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct03772678",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
},
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04402957",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
},
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04402957",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "BMJ Open",
"container-title-short": "BMJ Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-23T01:24:28Z",
"timestamp": 1716427468000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-23T01:24:48Z",
"timestamp": 1716427488000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"NCT04402957"
],
"name": "Arch Biopartners Inc."
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-24T00:28:07Z",
"timestamp": 1716510487368
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 14,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1710460800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076142",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e076142",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11596-021-2395-1",
"article-title": "A comprehensive review of COVID-19 virology, vaccines, variants, and therapeutics",
"author": "Forchette",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1037",
"journal-title": "Curr Med Sci",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.3",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41581-022-00642-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.211698",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00519-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2598",
"article-title": "Estimation of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine effectiveness and COVID-19 illness and severity by vaccination status during omicron BA.4 and BA.5 sublineage periods",
"author": "Link-Gelles",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.7",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33321/cdi.2023.47.18",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.8",
"unstructured": "Epidemiology C , Surveillance T . COVID-19 Australia: epidemiology report 71: reporting period ending 12 February 2023. Commun Dis Intell 2018:47."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac571",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of immunocompromised patients with coronavirus disease 2019 caused by the omicron variant: a prospective, observational study",
"author": "Malahe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e172",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.9",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.017",
"article-title": "Dipeptidase-1 is an adhesion receptor for neutrophil recruitment in lungs and liver",
"author": "Choudhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1205",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.10",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abm0142",
"article-title": "Dipeptidase-1 governs renal inflammation during ischemia reperfusion injury",
"author": "Lau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.11",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6942e3",
"article-title": "Risk for in-hospital complications associated with COVID-19 and influenza - veterans health administration, United States",
"author": "Cates",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1528",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.12",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.13",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0247461",
"article-title": "Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Booth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.14",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"article-title": "Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.15",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024052109113520000_14.3.e076142.16"
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076142"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof of concept study of LSALT peptide as prevention of acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute kidney injury in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy",
"volume": "14"
}