Long Neuro-COVID-19: Current Mechanistic Views and Therapeutic Perspectives
et al., Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom14091081, Aug 2024
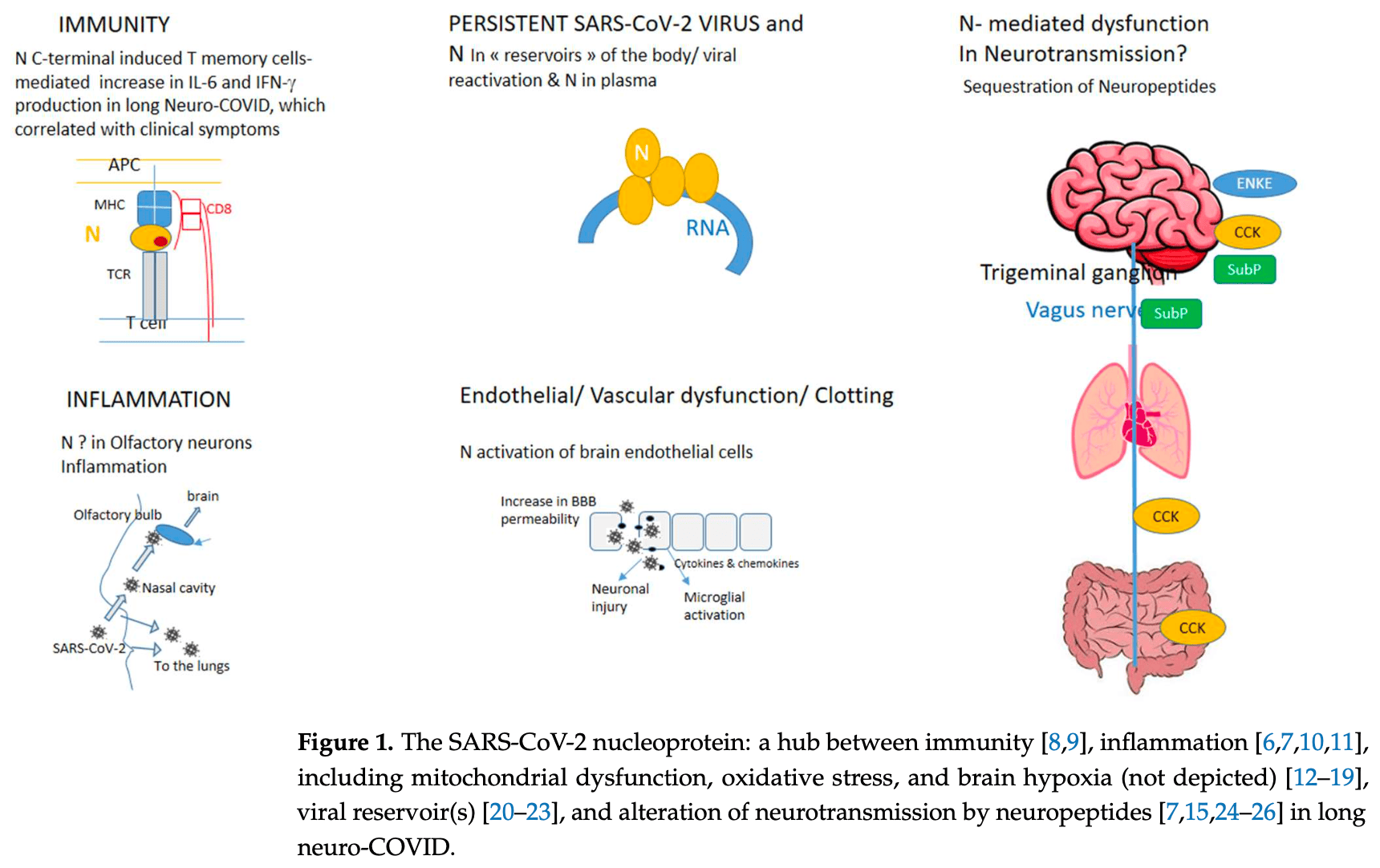
Review of the mechanistic views and therapeutic perspectives for long COVID-19 and long neuro-COVID-19. Authors present hypotheses for the multiple symptoms, including immune dysregulation and prolonged inflammation, persistent viral reservoirs, vascular and endothelial dysfunction, and disruption of neurotransmitter signaling. They suggest the SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein N constitutes a "hub" between the virus and host inflammation, immunity, and neurotransmission. Authors propose that defective neurotransmission by neuropeptides like enkephalin, cholecystokinin, and substance P, through their binding to the N protein, may significantly contribute to neurological and other long COVID symptoms. Authors note that antagonists of the neuropeptide receptors showed clinical benefit in COVID-19 survivors and long COVID patients.
Slama Schwok et al., 28 Aug 2024, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Contact: anny.slama-schwok@inserm.fr (corresponding author), anny.schwok@gmail.com, julien.henri@sorbonne-universite.fr.
Long Neuro-COVID-19: Current Mechanistic Views and Therapeutic Perspectives
Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom14091081
diseases constitute a real life-changing burden for many patients around the globe and, overall, can be considered societal and economic issues. They include a variety of symptoms, such as fatigue, loss of smell (anosmia), and neurological-cognitive sequelae, such as memory loss, anxiety, brain fog, acute encephalitis, and stroke, collectively called long neuro-COVID-19 (long neuro-COVID). They also include cardiopulmonary sequelae, such as myocardial infarction, pulmonary damage, fibrosis, gastrointestinal dysregulation, renal failure, and vascular endothelial dysregulation, and the onset of new diabetes, with each symptom usually being treated individually. The main unmet challenge is to understand the mechanisms of the pathophysiologic sequelae, in particular the neurological symptoms. This mini-review presents the main mechanistic hypotheses considered to explain the multiple long neuro-COVID symptoms, namely immune dysregulation and prolonged inflammation, persistent viral reservoirs, vascular and endothelial dysfunction, and the disruption of the neurotransmitter signaling along various paths. We suggest that the nucleoprotein N of SARS-CoV-2 constitutes a "hub" between the virus and the host inflammation, immunity, and neurotransmission.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Importance of the article for readership: Long COVID diseases are a societal burden and an everyday pain for patients as they often suffer from multiple symptoms. This review paper aims to present the current
References
Amici, Di Caro, Ciucci, Chiappa, Castilletti et al., Indomethacin Has a Potent Antiviral Activity against Sars Coronavirus, Antivir. Ther, doi:10.1177/135965350601100803
Anderson, Carbone, Mazzoccoli, Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Role in Co-Ordinating SARS-CoV-2 Entry and Symptomatology: Linking Cytotoxicity Changes in COVID-19 and Cancers; Modulation by Racial Discrimination Stress, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology9090249
Antar, Yu, Demko, Hu, Tornheim et al., Long COVID brain fog and muscle pain are associated with longer time to clearance of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from the upper respiratory tract during acute infection, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1147549
Barbosa-Silva, Lima, Battaglini, Robba, Pelosi et al., Infectious diseaseassociated encephalopathies, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03659-6
Barde, Aguila, Zhong, Solarz, Mei et al., CCK and their receptors in five brain regions in major depressive disorder with transcriptomic analysis of locus coeruleus neurons, Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2023.09.004
Bert, Tan, Kunasegaran, Tham, Hafezi et al., SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2550-z
Burtscher, Bean, Zangrandi, Kmiec, Agostinho et al., Proenkephalin Derived Peptides Are Involved in the Modulation of Mitochondrial Respiratory Control During Epileptogenesis, Front. Mol. Neurosci, doi:10.3389/fnmol.2018.00351
Casello, Flores, Yarur, Wang, Awanyai et al., Neuropeptide System Regulation of Prefrontal Cortex Circuitry: Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Front. Neural Circuits, doi:10.3389/fncir.2022.796443
Chen, Julg, Mohandas, Bradfute, RECOVER Mechanistic Pathways Task Force. Viral persistence, reactivation, and mechanisms of long COVID, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.86015
Chen, Xiao, Hu, Ge, Tian et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Interacts with RIG-I and Represses RIG-Mediated IFN-β Production, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13010047
Chowdhury, Sahoo, Jena, Hiramani, Behera et al., NOX-2 Inhibitors may be Potential Drug Candidates for the Management of COVID-19 Complications, Curr. Drug Res. Rev, doi:10.2174/2589977515666230706114812
Cohen, Linderman, Moodie, Czartoski, Lai et al., Longitudinal analysis shows durable and broad immune memory after SARS-CoV-2 infection with persisting antibody responses and memory B and T cells, Cell Rep. Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100354
Corder, Castro, Bruchas, Scherrer, Endogenous and Exogenous Opioids in Pain, Annu. Rev. Neurosci, doi:10.1146/annurev-neuro-080317-061522
De Melo, Lazarini, Levallois, Hautefort, Michel et al., COVID-19-related anosmia is associated with viral persistence and inflammation in human olfactory epithelium and brain infection in hamsters, Sci. Transl. Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abf8396
De Melo, Perraud, Alvarez, Vieites-Prado, Kim et al., Neuroinvasion and anosmia are independent phenomena upon infection with SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40228-7
Demarino, Lee, Cowen, Steiner, Inati et al., Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Microvascular Disease in the Brain, Neurology, doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000201682
Deng, Chen, Zhang, Kong, Fang et al., Delta opioid peptide [D-ala2, D-leu5]-Enkephalin's ability to enhance mitophagy via TRPV4 to relieve ischemia/reperfusion injury in brain microvascular endothelial cells, Stroke Vasc. Neurol, doi:10.1136/svn-2023-003080
Di Stadio, Brenner, De Luca, Albanese, Ralli et al., Olfactory Dysfunction, Headache, and Mental Clouding in Adults with Long-COVID-19: What Is the Link between Cognition and Olfaction? A Cross-Sectional Study, Brain Sci, doi:10.3390/brainsci12020154
Dilly, Romero, Solier, Feron, Dessy et al., Targeting M2 Macrophages with a Novel NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox12020440
Ehrlich, Ioannidis, Nasar, Abu Alkian, Daskal et al., Efficacy and safety of metabolic interventions for the treatment of severe COVID-19: In vitro, observational, and non-randomized open-label interventional study, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.79946
Fontes-Dantas, Fernandes, Gutman, De Lima, Antonio et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein induces TLR4-mediated long-term cognitive dysfunction recapitulating post-COVID-19 syndrome in mice, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112189
Foo, Bellot, Pervaiz, Alonso, Mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress during viral infection, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2021.12.011
Fu, Liu, Zhu, Xu, Yao, D-Ala2, D-Leu5] Enkephalin Inhibits TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Protects Rat Brains against Focal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury, Mediat. Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2021/6661620
Gall, Lauterborn, Burks, Seroogy, Co-localization of enkephalin and cholecystokinin in discrete areas of rat brain, Brain Res, doi:10.1016/0006-8993(87)90085-0
Glynne, Tahmasebi, Gant, Gupta, Long COVID following Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Characteristic T Cell Alterations and Response to Antihistamines, J. Investig. Med, doi:10.1136/jim-2021-002051
Hanson, Visvabharathy, Ali, Kang, Patel et al., Plasma Biomarkers of Neuropathogenesis in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 and Those With Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm, doi:10.1212/NXI.0000000000001151
Hao, Shi, Ma, Shao, Yuan et al., A Cholecystokinin Analogue Ameliorates Cognitive Deficits and Regulates Mitochondrial Dynamics via the AMPK/Drp1 Pathway in APP/PS1 Mice, J. Prev. Alzheimer's Dis, doi:10.14283/jpad.2024.6
Heles, Mrozkova, Sulcova, Adamek, Spicarova et al., Chemokine CCL2 prevents opioid-induced inhibition of nociceptive synaptic transmission in spinal cord dorsal horn, J. Neuroinflamm, doi:10.1186/s12974-021-02335-4
Henri, Minder, Mohanasundaram, Dilly, Goupil-Lamy et al., New Ligands of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein, a Potential Link between Replication, Inflammation and Neurotransmission, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27228094
Henrich, Deeks, Peluso, Meyer, Wherry et al., Serotonin reduction in post-acute sequelae of viral infection, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.013
Herskovitz, Gendelman, HIV and the Macrophage: From Cell Reservoirs to Drug Delivery to Viral Eradication, J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s11481-018-9785-6
Ishikura, Nakano, Kitano, Tokuda, Sumi-Akamaru et al., Serum ferritin level during hospitalization is associated with Brain Fog after COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-40011-0
Jalodia, Antoine, Braniff, Dutta, Ramakrishnan et al., Opioid-Use, COVID-19 Infection, and Their Neurological Implications, Front. Neurol, doi:10.3389/fneur.2022.884216
Janket, Fraser, Baird, Tamimi, Sohaei et al., Tachykinins and the potential causal factors for post-COVID-19 condition, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00111-8
Karson, Tang, Milner, Alger, Synaptic Cross Talk between Perisomatic-Targeting Interneuron Classes Expressing Cholecystokinin and Parvalbumin in Hippocampus, J. Neurosci, doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5264-08.2009
Keeney, Hoffman, Farmer, Bodle, Fazzari et al., NADPH oxidase 2 activity in Parkinson's disease, Neurobiol. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105754
Khullar, Zhang, Zang, Xu, Wang et al., Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Post-acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in New York: An EHR-Based Cohort Study from the RECOVER Program, J. Gen. Intern. Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07997-1
Kronstein-Wiedemann, Stadtmüller, Traikov, Georgi, Teichert et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infects Red Blood Cell Progenitors and Dysregulates Hemoglobin and Iron Metabolism, Stem Cell Rev. Rep, doi:10.1007/s12015-021-10322-8
Laracy, Kamboj, Vardhana, Long and persistent COVID-19 in patients with hematologic malignancies: From bench to bedside, Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000000841
Lauritano, Mastrangelo, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga et al., Activation of Mast Cells by Neuropeptides: The Role of Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24054811
Lejal, Tarus, Bouguyon, Chenavas, Bertho et al., Structure-Based Discovery of the Novel Antiviral Properties of Naproxen against the Nucleoprotein of Influenza A Virus, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.02335-12
Lejal, Truchet, Bechor, Bouguyon, Khedkar et al., Turning off NADPH oxidase-2 by impeding p67phox activation in infected mouse macrophages reduced viral entry and inflammation, Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.03.004
Li, Song, Chan, -W.; Chen, Liu et al., Intranasal infection by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants can induce inflammatory brain damage in newly weaned hamsters, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2023.2207678
Li, Tan, Lu, Tsang, Chung et al., Gut-brain circuits for fat preference, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05266-z
Lichtenberger, Szabo, A closer look at endothelial injury-induced platelet hyperactivity and the use of aspirin in the treatment of COVID infection, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-022-01015-w
Loonam, Noailles, Yu, Zhu, Angulo, Substance P and cholecystokinin regulate neurochemical responses to cocaine and methamphetamine in the striatum, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00393-X
Mancini, Natoli, Gardoni, Di Luca, Pisani, Dopamine Transmission Imbalance in Neuroinflammation: Perspectives on Long-Term COVID-19, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24065618
Mehboob, Kurdi, Bamaga, Aldardeir, Nasief et al., Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor, Trigeminal Ganglion, Latency, and Coronavirus Infection-Is There Any Link?, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.727593
Mehboob, Lavezzi, Neuropathological explanation of minimal COVID-19 infection rate in newborns, infants and children-A mystery so far. New insight into the role of Substance P, J. Neurol. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jns.2020.117276
Mehboob, Oehme, Pfaff, The role of Substance P in the defense line of the respiratory tract and neurological manifestations post COVID-19 infection, Front. Neurol, doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1052811
Mikuteit, Baskal, Klawitter, Dopfer-Jablonka, Behrens et al., Amino acids, post-translational modifications, nitric oxide, and oxidative stress in serum and urine of long COVID and ex COVID human subjects, Amino Acids, doi:10.1007/s00726-023-03305-1
Molnar, Varnai, Schranz, Zavori, Peterfi et al., Severe Fatigue and Memory Impairment Are Associated with Lower Serum Level of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Patients with Post-COVID Symptoms, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10194337
Mu, Xu, Zhang, Shu, Wu et al., SARS-CoV-2-encoded nucleocapsid protein acts as a viral suppressor of RNA interference in cells, Sci. China Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s11427-020-1692-1
Niemela, Landtblom, Nyholm, Kneider, Constantinescu et al., Proenkephalin Decreases in Cerebrospinal Fluid with Symptom Progression of Huntington's Disease, Mov. Disord, doi:10.1002/mds.28391
O'kelly, Vidal, Mchugh, Woo, Avramovic et al., Safety and efficacy of low dose naltrexone in a long covid cohort; an interventional pre-post study, Brain Behav. Immun. Health, doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100485
Ogata, Maley, Wu, Gilboa, Norman et al., Ultra-Sensitive Serial Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Antigens and Antibodies in Plasma to Understand Disease Progression in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Disease, Clin. Chem, doi:10.1093/clinchem/hvaa213
Oh, Shin, SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Targets RIG-I-Like Receptor Pathways to Inhibit the Induction of Interferon Response, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10030530
Papasidero, Valli, Marin, Del Sasso, De Magistris et al., Utility of Measuring Circulating Bio-Adrenomedullin and Proenkephalin for 30-Day Mortality Risk Prediction in Patients with COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Interstitial Pneumonia in the Emergency Department, Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina58121852
Park, Han, Kim, Seo, Kang et al., Reduction of Food Intake by Fenofibrate is Associated with Cholecystokinin Release in Long-Evans Tokushima Rats, Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol, doi:10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.3.181
Peluso, Deitchman, Torres, Iyer, Munter et al., Long-term SARS-CoV-2-specific immune and inflammatory responses in individuals recovering from COVID-19 with and without post-acute symptoms, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109518
Pileggi, Parmar, Elkhatib, Stewart, Alecu et al., The SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein interacts with MAO-B and impairs mitochondrial energetics, Curr. Res. Neurobiol, doi:10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100112
Podvin, Jiang, Boyarko, Rossitto, O'donoghue et al., Dysregulation of Neuropeptide and Tau Peptide Signatures in Human Alzheimer's Disease Brain, ACS Chem. Neurosci, doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00222
Proal, Vanelzakker, Aleman, Bach, Boribong et al., SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-023-01601-2
Qian, Lei, Patel, Lee, Monaghan-Nichols et al., Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01396-21
Ravichandran, Mohan, Sukumaran, Kamaraj, Daivasuga et al., An open label randomized clinical trial of Indomethacin for mild and moderate hospitalised COVID-19 patients, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-10370-1
Reinoso-Arija, López-Ramírez, Jimenez-Ruiz, López-Campos, Effectiveness of aprepitant in post-acute COVID19 syndrome, Clin. Case Rep, doi:10.1002/ccr3.4646
Schirinzi, Lattanzi, Maftei, Grillo, Zenuni et al., Substance P and Prokineticin-2 are overexpressed in olfactory neurons and play differential roles in persons with persistent post-COVID-19 olfactory dysfunction, Brain Behav. Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2022.12.017
Sherif, Gomez, Connors, Henrich, Reeves, RECOVER Mechanistic Pathway Task Force. Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.86002
Shi, Du, Wang, Tang, Lei et al., Aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a proviral host factor and a candidate pan-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic target, Sci. Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.adf0211
Sotoyama, Namba, Tohmi, Nawa, Schizophrenia Animal Modeling with Epidermal Growth Factor and Its Homologs: Their Connections to the Inflammatory Pathway and the Dopamine System, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom13020372
Spudich, Nath, Nervous system consequences of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abm2052
Stefano, Büttiker, Weissenberger, Martin, Ptacek et al., The Pathogenesis of Long-Term Neuropsychiatric COVID-19 and the Role of Microglia, Mitochondria, and Persistent Neuroinflammation: A Hypothesis, Med Sci. Monit, doi:10.12659/MSM.933015
Tan, Sisti, Jin, Vignovich, Villavicencio et al., The gut-brain axis mediates sugar preference, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2199-7
Taquet, Sillett, Zhu, Mendel, Camplisson et al., Neurological and psychiatric risk trajectories after SARS-CoV-2 infection: An analysis of 2-year retrospective cohort studies including 1,284,437 patients, Lancet Psychiatry, doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(22)00260-7
Terrier, Dilly, Pizzorno, Chalupska, Humpolickova et al., Antiviral Properties of the NSAID Drug Naproxen Targeting the Nucleoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26092593
Terrier, Pizzorno, Henri, Berenbaum, Lina et al., Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of naproxen: From Influenza A to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.30.069922
Theoharides, Kempuraj, Role of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Protein-Induced Activation of Microglia and Mast Cells in the Pathogenesis of Neuro-COVID, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells12050688
Thompson, Williams, Walker, Mitchell, Niedzwiedz et al., Long COVID burden and risk factors in 10 UK longitudinal studies and electronic health records, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-30836-0
Turski, Wnorowski, Turski, Turski, Turski, AhR and IDO1 in pathogenesis of COVID-19 and the "Systemic AhR Activation Syndrome:" a translational review and therapeutic perspectives, Restor. Neurol. Neurosci, doi:10.3233/RNN-201042
Varnai, Molnar, Zavori, Tőkés-Füzesi, Illes et al., Serum Level of Anti-Nucleocapsid, but Not Anti-Spike Antibody, Is Associated with Improvement of Long COVID Symptoms, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10020165
Visvabharathy, Hanson, Orban, Lim, Palacio et al., Neuro-PASC is characterized by enhanced CD4 + and diminished CD8 + T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155770
Wang, Tsai, Wang, Yen, Chang et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, rather than spike protein, triggers a cytokine storm originating from lung epithelial cells in patients with COVID-19, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-023-02142-4
Wu, Wang, Liang, Chen, Sun et al., SARS-CoV-2 N protein induced acute kidney injury in diabetic db/db mice is associated with a Mincle-dependent M1 macrophage activation, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1264447
Xia, Tang, Wang, Lai, Xu et al., SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Induces Acute Lung Injury in Mice via NF-κB Activation, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.791753
Xu, Gao, Wen, Zhai, Zhang et al., Methionine enkephalin regulates microglia polarization and function, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.037
Yang, Huang, Zhang, Li, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human brain microvascular endothelial cells, J. Neuroinflamm, doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02514-x
Yang, Kern, Losada, Agam, Maat et al., Dysregulation of brain and choroid plexus cell types in severe COVID-19, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03710-0
Yu, Yang, Han, Zhou, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein enhances the level of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, J. Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.29270
Zang, Hou, Schenck, Xu, Zhang et al., Identification of risk factors of Long COVID and predictive modeling in the RECOVER EHR cohorts, Commun. Med, doi:10.1038/s43856-024-00549-0
Zang, Hou, Schenck, Xu, Zhang et al., Risk Factors and Predictive Modeling for Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Findings from EHR Cohorts of the RECOVER Initiative, Commun. Med, doi:10.1038/s43856-024-00549-0
Zheng, Cai, Wang, Zhang, Qian et al., Macrophages are an abundant component of myeloma microenvironment and protect myeloma cells from chemotherapy drug-induced apoptosis, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-220285
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom14091081",
"ISSN": [
"2218-273X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/biom14091081",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Long-lasting COVID-19 (long COVID) diseases constitute a real life-changing burden for many patients around the globe and, overall, can be considered societal and economic issues. They include a variety of symptoms, such as fatigue, loss of smell (anosmia), and neurological–cognitive sequelae, such as memory loss, anxiety, brain fog, acute encephalitis, and stroke, collectively called long neuro-COVID-19 (long neuro-COVID). They also include cardiopulmonary sequelae, such as myocardial infarction, pulmonary damage, fibrosis, gastrointestinal dysregulation, renal failure, and vascular endothelial dysregulation, and the onset of new diabetes, with each symptom usually being treated individually. The main unmet challenge is to understand the mechanisms of the pathophysiologic sequelae, in particular the neurological symptoms. This mini-review presents the main mechanistic hypotheses considered to explain the multiple long neuro-COVID symptoms, namely immune dysregulation and prolonged inflammation, persistent viral reservoirs, vascular and endothelial dysfunction, and the disruption of the neurotransmitter signaling along various paths. We suggest that the nucleoprotein N of SARS-CoV-2 constitutes a “hub” between the virus and the host inflammation, immunity, and neurotransmission.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"biom14091081"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2703-9728",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, INSERM U938, Biology and Cancer Therapeutics, Centre de Recherche Saint Antoine, Saint Antoine Hospital, 75231 Paris, France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Slama Schwok",
"given": "Anny",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0772-8881",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne Université, CNRS UMR 7238, Laboratoire de Biologie Computationnelle et Quantitative, Institut de Biologie Paris-Seine, 75005 Paris, France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Henri",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biomolecules",
"container-title-short": "Biomolecules",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-28T09:34:49Z",
"timestamp": 1724837689000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-28T10:56:48Z",
"timestamp": 1724842608000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Sorbonne University and The Foundation of Sorbonne University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-29T00:28:32Z",
"timestamp": 1724891312662
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1724803200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/14/9/1081/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1081",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-022-07997-1",
"article-title": "Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Post-acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in New York: An EHR-Based Cohort Study from the RECOVER Program",
"author": "Khullar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1127",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2592194/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Zang, C., Hou, Y., Schenck, E., Xu, Z., Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Bian, J., Morozyuk, D., Khullar, D., and Nordvig, A. (2024). Risk Factors and Predictive Modeling for Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Findings from EHR Cohorts of the RECOVER Initiative. Commun. Med., 4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43856-024-00549-0",
"article-title": "Identification of risk factors of Long COVID and predictive modeling in the RECOVER EHR cohorts",
"author": "Zang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Commun. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-30836-0",
"article-title": "Long COVID burden and risk factors in 10 UK longitudinal studies and electronic health records",
"author": "Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3528",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QCO.0000000000000841",
"article-title": "Long and persistent COVID-19 in patients with hematologic malignancies: From bench to bedside",
"author": "Laracy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109518",
"article-title": "Long-term SARS-CoV-2-specific immune and inflammatory responses in individuals recovering from COVID-19 with and without post-acute symptoms",
"author": "Peluso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109518",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27228094",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Henri, J., Minder, L., Mohanasundaram, K., Dilly, S., Goupil-Lamy, A., Di Primo, C., and Schwok, A.S. (2022). Neuropeptides, New Ligands of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein, a Potential Link between Replication, Inflammation and Neurotransmission. Molecules, 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/NXI.0000000000001151",
"article-title": "Plasma Biomarkers of Neuropathogenesis in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 and Those With Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Hanson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1151",
"journal-title": "Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155770",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_9",
"unstructured": "Visvabharathy, L., Hanson, B.A., Orban, Z.S., Lim, P.H., Palacio, N.M., Jimenez, M., Clark, J.R., Graham, E.L., Liotta, E.M., and Tachas, G. (2023). Neuro-PASC is characterized by enhanced CD4+ and diminished CD8+ T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein. Front. Immunol., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10194337",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Molnar, T., Varnai, R., Schranz, D., Zavori, L., Peterfi, Z., Sipos, D., Tőkés-Füzesi, M., Illes, Z., Buki, A., and Csecsei, P. (2021). Severe Fatigue and Memory Impairment Are Associated with Lower Serum Level of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Patients with Post-COVID Symptoms. J. Clin. Med., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10020165",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Varnai, R., Molnar, T., Zavori, L., Tőkés-Füzesi, M., Illes, Z., Kanizsai, A., and Csecsei, P. (2022). Serum Level of Anti-Nucleocapsid, but Not Anti-Spike Antibody, Is Associated with Improvement of Long COVID Symptoms. Vaccines, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnmol.2018.00351",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Burtscher, J., Bean, C., Zangrandi, L., Kmiec, I., Agostinho, A., Scorrano, L., Gnaiger, E., and Schwarzer, C. (2018). Proenkephalin Derived Peptides Are Involved in the Modulation of Mitochondrial Respiratory Control During Epileptogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/2589977515666230706114812",
"article-title": "NOX-2 Inhibitors may be Potential Drug Candidates for the Management of COVID-19 Complications",
"author": "Chowdhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "Curr. Drug Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2021.12.011",
"article-title": "Mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress during viral infection",
"author": "Foo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "679",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "A Cholecystokinin Analogue Ameliorates Cognitive Deficits and Regulates Mitochondrial Dynamics via the AMPK/Drp1 Pathway in APP/PS1 Mice",
"author": "Hao",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105754",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Keeney, M.T., Hoffman, E.K., Farmer, K., Bodle, C.R., Fazzari, M., Zharikov, A., Castro, S.L., Hu, X., Mortimer, A., and Kofler, J.K. (2022). NADPH oxidase 2 activity in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis., 170."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100112",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Pileggi, C.A., Parmar, G., Elkhatib, H., Stewart, C.M., Alecu, I., Côté, M., Bennett, S.A., Sandhu, J.K., Cuperlovic-Culf, M., and Harper, M.-E. (2023). The SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein interacts with MAO-B and impairs mitochondrial energetics. Curr. Res. Neurobiol., 5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/MSM.933015",
"article-title": "Editorial: The Pathogenesis of Long-Term Neuropsychiatric COVID-19 and the Role of Microglia, Mitochondria, and Persistent Neuroinflammation: A Hypothesis",
"author": "Stefano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e933015",
"journal-title": "Med Sci. Monit.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29270",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein enhances the level of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e29270",
"journal-title": "J. Med Virol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.86015",
"article-title": "Viral persistence, reactivation, and mechanisms of long COVID",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e86015",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abf8396",
"article-title": "COVID-19–related anosmia is associated with viral persistence and inflammation in human olfactory epithelium and brain infection in hamsters",
"author": "Lazarini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabf8396",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-40228-7",
"article-title": "Neuroinvasion and anosmia are independent phenomena upon infection with SARS-CoV-2 and its variants",
"author": "Perraud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4485",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.86002",
"article-title": "Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC)",
"author": "Sherif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e86002",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00111-8",
"article-title": "Tachykinins and the potential causal factors for post-COVID-19 condition",
"author": "Janket",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e642",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202302.0148.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Lauritano, D., Mastrangelo, F., D’ovidio, C., Ronconi, G., Caraffa, A., Gallenga, C.E., Frydas, I., Kritas, S.K., Trimarchi, M., and Carinci, F. (2023). Activation of Mast Cells by Neuropeptides: The Role of Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.727593",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Mehboob, R., Kurdi, M., Bamaga, A., Aldardeir, N., Nasief, H., Moshref, L.H., Alsinani, T., Rayes, A.O., and Jabbad, R.H. (2021). Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor, Trigeminal Ganglion, Latency, and Coronavirus Infection-Is There Any Link?. Front. Med., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biology9090249",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Anderson, G., Carbone, A., and Mazzoccoli, G. (2020). Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Role in Co-Ordinating SARS-CoV-2 Entry and Symptomatology: Linking Cytotoxicity Changes in COVID-19 and Cancers; Modulation by Racial Discrimination Stress. Biology, 9."
},
{
"article-title": "AhR and IDO1 in pathogenesis of COVID-19 and the “Systemic AhR Activation Syndrome:” a translational review and therapeutic perspectives",
"author": "Turski",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Restor. Neurol. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.adf0211",
"article-title": "Aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a proviral host factor and a candidate pan-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic target",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eadf0211",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/135965350601100803",
"article-title": "Indomethacin Has a Potent Antiviral Activity against Sars Coronavirus",
"author": "Amici",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1021",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Ther.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02335-12",
"article-title": "Structure-Based Discovery of the Novel Antiviral Properties of Naproxen against the Nucleoprotein of Influenza A Virus",
"author": "Lejal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2231",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-10370-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Ravichandran, R., Mohan, S.K., Sukumaran, S.K., Kamaraj, D., Daivasuga, S.S., Ravi, S.O.A.S., Vijayaraghavalu, S., and Kumar, R.K. (2022). An open label randomized clinical trial of Indomethacin for mild and moderate hospitalised COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26092593",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Terrier, O., Dilly, S., Pizzorno, A., Chalupska, D., Humpolickova, J., Bouřa, E., Berenbaum, F., Quideau, S., Lina, B., and Fève, B. (2021). Antiviral Properties of the NSAID Drug Naproxen Targeting the Nucleoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. Molecules, 26."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.79946",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of metabolic interventions for the treatment of severe COVID-19: In vitro, observational, and non-randomized open-label interventional study",
"author": "Ehrlich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e79946",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05266-z",
"article-title": "Gut–brain circuits for fat preference",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "722",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "610",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01396-21",
"article-title": "Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin",
"author": "Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0139621",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2199-7",
"article-title": "The gut–brain axis mediates sugar preference",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "511",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "580",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-40011-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_38",
"unstructured": "Ishikura, T., Nakano, T., Kitano, T., Tokuda, T., Sumi-Akamaru, H., and Naka, T. (2023). Serum ferritin level during hospitalization is associated with Brain Fog after COVID-19. Sci. Rep., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12015-021-10322-8",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Infects Red Blood Cell Progenitors and Dysregulates Hemoglobin and Iron Metabolism",
"author": "Traikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1809",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Rev. Rep.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.03.004",
"article-title": "Turning off NADPH oxidase-2 by impeding p67phox activation in infected mouse macrophages reduced viral entry and inflammation",
"author": "Lejal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1263",
"journal-title": "Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "1862",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox12020440",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "Dilly, S., Romero, M., Solier, S., Feron, O., Dessy, C., and Schwok, A.S. (2023). Targeting M2 Macrophages with a Novel NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor. Antioxidants, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.30.069922",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Terrier, O.D.S., Pizzorno, A., Henri, J., Berenbaum, F., Lina, B., Fève, B., Adnet, F., Sabbah, M., Rosa-Calatrava, M., and Maréchal, V. (2020). Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of naproxen: From Influenza A to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. BioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-023-02142-4",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, rather than spike protein, triggers a cytokine storm originating from lung epithelial cells in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "955",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.037",
"article-title": "Methionine enkephalin regulates microglia polarization and function",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1264447",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_45",
"unstructured": "Wu, W., Wang, W., Liang, L., Chen, J., Sun, S., Wei, B., Zhong, Y., Huang, X.-R., Liu, J., and Wang, X. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 N protein induced acute kidney injury in diabetic db/db mice is associated with a Mincle-dependent M1 macrophage activation. Front. Immunol., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100354",
"article-title": "Longitudinal analysis shows durable and broad immune memory after SARS-CoV-2 infection with persisting antibody responses and memory B and T cells",
"author": "Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100354",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2550-z",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "457",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jim-2021-002051",
"article-title": "Long COVID following Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Characteristic T Cell Alterations and Response to Antihistamines",
"author": "Glynne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "61",
"journal-title": "J. Investig. Med.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells12050688",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "Theoharides, T.C., and Kempuraj, D. (2023). Role of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Protein-Induced Activation of Microglia and Mast Cells in the Pathogenesis of Neuro-COVID. Cells, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2023.1052811",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "Mehboob, R., Oehme, P., and Pfaff, G. (2023). The role of Substance P in the defense line of the respiratory tract and neurological manifestations post COVID-19 infection. Front. Neurol., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.euroneuro.2023.09.004",
"article-title": "Substance P, NPY, CCK and their receptors in five brain regions in major depressive disorder with transcriptomic analysis of locus coeruleus neurons",
"author": "Barde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fncir.2022.796443",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "Casello, S.M., Flores, R.J., Yarur, H.E., Wang, H., Awanyai, M., Arenivar, M.A., Jaime-Lara, R.B., Bravo-Rivera, H., and Tejeda, H.A. (2022). Neuropeptide System Regulation of Prefrontal Cortex Circuitry: Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Neural Circuits, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/6661620",
"article-title": "[D-Ala2, D-Leu5] Enkephalin Inhibits TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Protects Rat Brains against Focal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6661620",
"journal-title": "Mediat. Inflamm.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina58121852",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_54",
"unstructured": "Papasidero, I.D., Valli, G., Marin, D., Del Sasso, A., De Magistris, A., Cennamo, E., Casalboni, S., De Marco, F., Rocchi, R., and Beumo, B.N. (2022). Utility of Measuring Circulating Bio-Adrenomedullin and Proenkephalin for 30-Day Mortality Risk Prediction in Patients with COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Interstitial Pneumonia in the Emergency Department. Medicina, 58."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00222",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of Neuropeptide and Tau Peptide Signatures in Human Alzheimer’s Disease Brain",
"author": "Podvin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1992",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03710-0",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of brain and choroid plexus cell types in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "595",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5264-08.2009",
"article-title": "Synaptic Cross Talk between Perisomatic-Targeting Interneuron Classes Expressing Cholecystokinin and Parvalbumin in Hippocampus",
"author": "Karson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4140",
"journal-title": "J. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1147549",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "Antar, A.A.R., Yu, T., O Demko, Z., Hu, C., Tornheim, J.A., Blair, P.W., Thomas, D.L., and Manabe, Y.C. (2023). Long COVID brain fog and muscle pain are associated with longer time to clearance of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from the upper respiratory tract during acute infection. Front. Immunol., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2215-0366(22)00260-7",
"article-title": "Neurological and psychiatric risk trajectories after SARS-CoV-2 infection: An analysis of 2-year retrospective cohort studies including 1,284,437 patients",
"author": "Taquet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "815",
"journal-title": "Lancet Psychiatry",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/WNL.0000000000201682",
"article-title": "Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Microvascular Disease in the Brain",
"author": "DeMarino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "624",
"journal-title": "Neurology",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2023.2207678",
"article-title": "Intranasal infection by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants can induce inflammatory brain damage in newly weaned hamsters",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2207678",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2020.117276",
"article-title": "Neuropathological explanation of minimal COVID-19 infection rate in newborns, infants and children—A mystery so far. New insight into the role of Substance P",
"author": "Mehboob",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117276",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "420",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-022-01015-w",
"article-title": "A closer look at endothelial injury-induced platelet hyperactivity and the use of aspirin in the treatment of COVID infection",
"author": "Lichtenberger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-023-03305-1",
"article-title": "Amino acids, post-translational modifications, nitric oxide, and oxidative stress in serum and urine of long COVID and ex COVID human subjects",
"author": "Mikuteit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1173",
"journal-title": "Amino Acids",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.013",
"article-title": "Serotonin reduction in post-acute sequelae of viral infection",
"author": "Henrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4851",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abm2052",
"article-title": "Nervous system consequences of COVID-19",
"author": "Spudich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/clinchem/hvaa213",
"article-title": "Ultra-Sensitive Serial Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Antigens and Antibodies in Plasma to Understand Disease Progression in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Disease",
"author": "Ogata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chem.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13010047",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_68",
"unstructured": "Chen, K., Xiao, F., Hu, D., Ge, W., Tian, M., Wang, W., Pan, P., Wu, K., and Wu, J. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Interacts with RIG-I and Represses RIG-Mediated IFN-β Production. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-020-1692-1",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-encoded nucleocapsid protein acts as a viral suppressor of RNA interference in cells",
"author": "Mu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1413",
"journal-title": "Sci. China Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10030530",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_70",
"unstructured": "Oh, S.J., and Shin, O.S. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Targets RIG-I-Like Receptor Pathways to Inhibit the Induction of Interferon Response. Cells, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.791753",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_71",
"unstructured": "Xia, J., Tang, W., Wang, J., Lai, D., Xu, Q., Huang, R., Hu, Y., Gong, X., Fan, J., and Shu, Q. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Induces Acute Lung Injury in Mice via NF-ĸB Activation. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12974-022-02514-x",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human brain microvascular endothelial cells",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroinflamm.",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.3.181",
"article-title": "Reduction of Food Intake by Fenofibrate is Associated with Cholecystokinin Release in Long-Evans Tokushima Rats",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24065618",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_74",
"unstructured": "Mancini, M., Natoli, S., Gardoni, F., Di Luca, M., and Pisani, A. (2023). Dopamine Transmission Imbalance in Neuroinflammation: Perspectives on Long-Term COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom13020372",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_75",
"unstructured": "Sotoyama, H., Namba, H., Tohmi, M., and Nawa, H. (2023). Schizophrenia Animal Modeling with Epidermal Growth Factor and Its Homologs: Their Connections to the Inflammatory Pathway and the Dopamine System. Biomolecules, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2022.12.017",
"article-title": "Substance P and Prokineticin-2 are overexpressed in olfactory neurons and play differential roles in persons with persistent post-COVID-19 olfactory dysfunction",
"author": "Schirinzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "302",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav. Immun.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100485",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of low dose naltrexone in a long covid cohort; an interventional pre-post study",
"author": "Vidal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100485",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav. Immun. Health",
"key": "ref_77",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0006-8993(87)90085-0",
"article-title": "Co-localization of enkephalin and cholecystokinin in discrete areas of rat brain",
"author": "Gall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "Brain Res.",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "403",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00393-X",
"article-title": "Substance P and cholecystokinin regulate neurochemical responses to cocaine and methamphetamine in the striatum",
"author": "Loonam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2022.884216",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_80",
"unstructured": "Jalodia, R., Antoine, D., Braniff, R.G., Dutta, R.K., Ramakrishnan, S., and Roy, S. (2022). Opioid-Use, COVID-19 Infection, and Their Neurological Implications. Front. Neurol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-neuro-080317-061522",
"article-title": "Endogenous and Exogenous Opioids in Pain",
"author": "Corder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/svn-2023-003080",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_82",
"unstructured": "Deng, Z., Chen, X., Zhang, R., Kong, L., Fang, Y., Guo, J., Shen, B., and Zhang, L. (2024). Delta opioid peptide [D-ala2, D-leu5]-Enkephalin’s ability to enhance mitophagy via TRPV4 to relieve ischemia/reperfusion injury in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Stroke Vasc. Neurol., svn-2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12974-021-02335-4",
"article-title": "Chemokine CCL2 prevents opioid-induced inhibition of nociceptive synaptic transmission in spinal cord dorsal horn",
"author": "Heles",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroinflamm.",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mds.28391",
"article-title": "Proenkephalin Decreases in Cerebrospinal Fluid with Symptom Progression of Huntington’s Disease",
"author": "Niemela",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "481",
"journal-title": "Mov. Disord.",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ccr3.4646",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of aprepitant in post-acute COVID19 syndrome",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e04646",
"journal-title": "Clin. Case Rep.",
"key": "ref_85",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/brainsci12020154",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_86",
"unstructured": "Di Stadio, A., Brenner, M.J., De Luca, P., Albanese, M., D’ascanio, L., Ralli, M., Roccamatisi, D., Cingolani, C., Vitelli, F., and Camaioni, A. (2022). Olfactory Dysfunction, Headache, and Mental Clouding in Adults with Long-COVID-19: What Is the Link between Cognition and Olfaction? A Cross-Sectional Study. Brain Sci., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2009-05-220285",
"article-title": "Macrophages are an abundant component of myeloma microenvironment and protect myeloma cells from chemotherapy drug–induced apoptosis",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3625",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref_87",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112189",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein induces TLR4-mediated long-term cognitive dysfunction recapitulating post-COVID-19 syndrome in mice",
"author": "Fernandes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112189",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-023-01601-2",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC)",
"author": "Proal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1616",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11481-018-9785-6",
"article-title": "HIV and the Macrophage: From Cell Reservoirs to Drug Delivery to Viral Eradication",
"author": "Herskovitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_90",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03659-6",
"article-title": "Infectious disease-associated encephalopathies",
"author": "Lima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 91,
"references-count": 91,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/14/9/1081"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Long Neuro-COVID-19: Current Mechanistic Views and Therapeutic Perspectives",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}