Effects of high dose vitamin C administration in Covid-19 patients
et al., Annals of Medical Research, doi:10.5455/annalsmedres.2020.10.1043, Sep 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
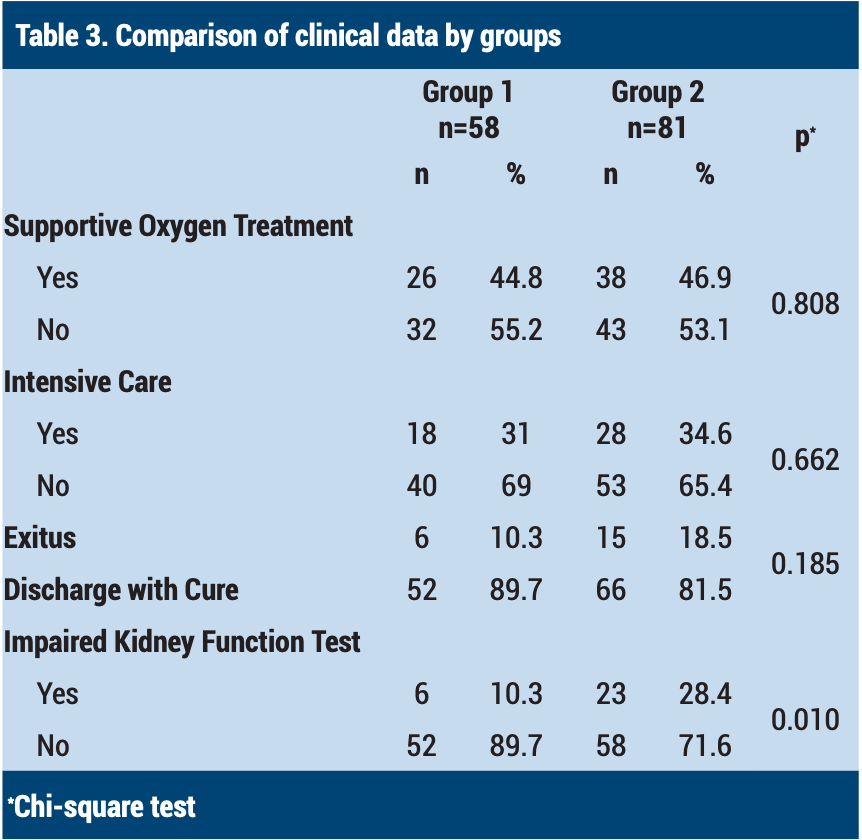
Retrospective 139 hospitalized patients in Turkey, 58 treated with high-dose vitamin C, showing improved kidney functioning with treatment. Mortality was lower with treatment, but not reaching statistical significance with the small sample size.
This is the 33rd of 73 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000076.
20 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0016.
|
risk of death, 44.1% lower, RR 0.56, p = 0.18, treatment 6 of 58 (10.3%), control 15 of 81 (18.5%), NNT 12.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 10.2% lower, RR 0.90, p = 0.66, treatment 18 of 58 (31.0%), control 28 of 81 (34.6%), NNT 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Simsek et al., 27 Sep 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, dosage 25000mg days 1-7.
Effects of high dose vitamin C administration in Covid-19 patients
Annals of Medical Research, doi:10.5455/annalsmedres.2020.10.1043
The outbreak caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which emerged in Wuhan, China, was named as Coronavirus disease 2019 and declared as a pandemic (1). COVID-19 has a wide clinical spectrum, including asymptomatic infection, upper respiratory tract infection (URTI), pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and death (2). About 26% of patients with pneumonia findings due to COVID-19 require intensive care due to the development of ARDS and septic shock (3). There is currently no specific treatment or vaccine with proven safety and efficacy for COVID-19. Studies are ongoing to find an effective treatment and to develop a vaccine that provides complete protection against the disease. Although the treatment protocols of COVID-19 disease differ from country to country, combinations of drugs such as azithromycin, favipiravir, remdesivir, tocilizumab are generally used (2,4). Moreover, some supportive drugs and agents are added to the treatment of patients. One of them is vitamin C (VC), which has been shown to be effective in the treatment of patients developing ARDS (5). Proinflammatory cytokines that increase due to SARS-CoV-2 virus infection cause cytokine storm in the body. This cytokine storm causes the formation of free oxygen radicals and impairs alveolo-capillary membrane permeability, resulting in cellular damage in lungs ( 6 ). Antioxidants such as VC, N-acetyl-cysteine, and selenium are effective in preventing this damage. One of the most important parts of the non-enzymatic antioxidant system is VC (7). Vitamin C decreases organ injury caused by cytokines by activating the immune system, and increases survival (8). It is also involved in the synthesis of steroids and catecholamines, wound healing, carnitine synthesis and endothelial cell function (9). The efficacy of high-dose intravenous VC therapy in COVID-19 has not been clearly demonstrated yet. However, VC, which is used by millions of people, is one
Competing Interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interest. Financial Disclosure: There are no financial supports. Ethical Approval: Our study has ethics committee permission and Ethics Approval (No. 2020/106) was obtained from the local ethics committee of our hospital.
References
Auer, Auer, Rodgers, Relative hyperoxaluria, crystalluria and haematuria after megadose ingestion of vitamin C, Eur J Clin Invest
Bolignano, Cernaro, Gembillo, Antioxidant agents for delaying diabetic kidney disease progression : A systematic review and meta-analysis
Carr, A new clinical trial to test high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19, Crit Care
Carr, Rosengrave, Bayer, Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes, Crit Care
Fowler, Aa, Kim, Lepler, Intravenous vitamin C as adjunctive therapy for enterovirus/rhinovirus induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, World J Crit Care Med
Fowler, Truwit, Hite, Effect of Vitamin C Infusion on Organ Failure and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Vascular Injury in Patients with Sepsis and Severe Acute Respiratory Failure: The CITRIS-ALI Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA -J Am Med Assoc
Hoang, Shaw, Fang, Possible application of high-dose vitamin C in the prevention and therapy of coronavirus infection, J Glob Antimicrob Resist
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Lamarche, Nair, Peguero, Vitamin C-Induced Oxalate Nephropathy, Int J Nephrol
Manuel, Colunga, Berrill, Quercetin and Vitamin C : An Experimental , Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease, COVID
Marik, Khangoora, Rivera, Hydrocortisone, Vitamin C, and Thiamine for the Treatment of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Retrospective Before-After Study, Chest
Nabzdyk, Bittner, Vitamin C in the critically illindications and controversies, World J Crit Care Med
Review, New Coronavirus ( 2019-nCoV / COVID-19 ) and Vitamin C Yeni Koronavirüs ( 2019-nCoV / COVID-19 ), Vitamin C
Teng, Pourmand, Mazer-Amirshahi, Vitamin C: The next step in sepsis management?, J Crit Care
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA -J Am Med Assoc
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5455/annalsmedres.2020.10.1043",
"ISSN": [
"2636-7688"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5455/annalsmedres.2020.10.1043",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simsek",
"given": "Fatih",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yonca",
"given": "Hasan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tahmaz",
"given": "Irmak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kara",
"given": "Umut",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sir",
"given": "Ender",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eksert",
"given": "Sami",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ince",
"given": "Mehmet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Senkal",
"given": "Serkan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ozdemirkan",
"given": "Ilker",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turan",
"given": "Ufuk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Savascı",
"given": "Umit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dogan",
"given": "Deniz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tasci",
"given": "Canturk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yazici",
"given": "Ertugrul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yilmaz",
"given": "Gulden",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cosar",
"given": "Ahmet",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annals of Medical Research",
"container-title-short": "Ann Med Res",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-25T18:51:07Z",
"timestamp": 1632595867000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-25T18:51:54Z",
"timestamp": 1632595914000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T13:28:24Z",
"timestamp": 1670246904318
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/deed.en",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.ejmanager.com/fulltextpdf.php?mno=8468",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "3407",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1699",
"prefix": "10.5455",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "ScopeMed",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ejmanager.com/fulltextpdf.php?mno=8468"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of high dose vitamin C administration in Covid-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "28"
}
