Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of quercetin in the treatment of Covid-19: a systematic review
et al., Observatório de la Economía Latinoamericana, doi:10.55905/oelv22n1-192, Jan 2024
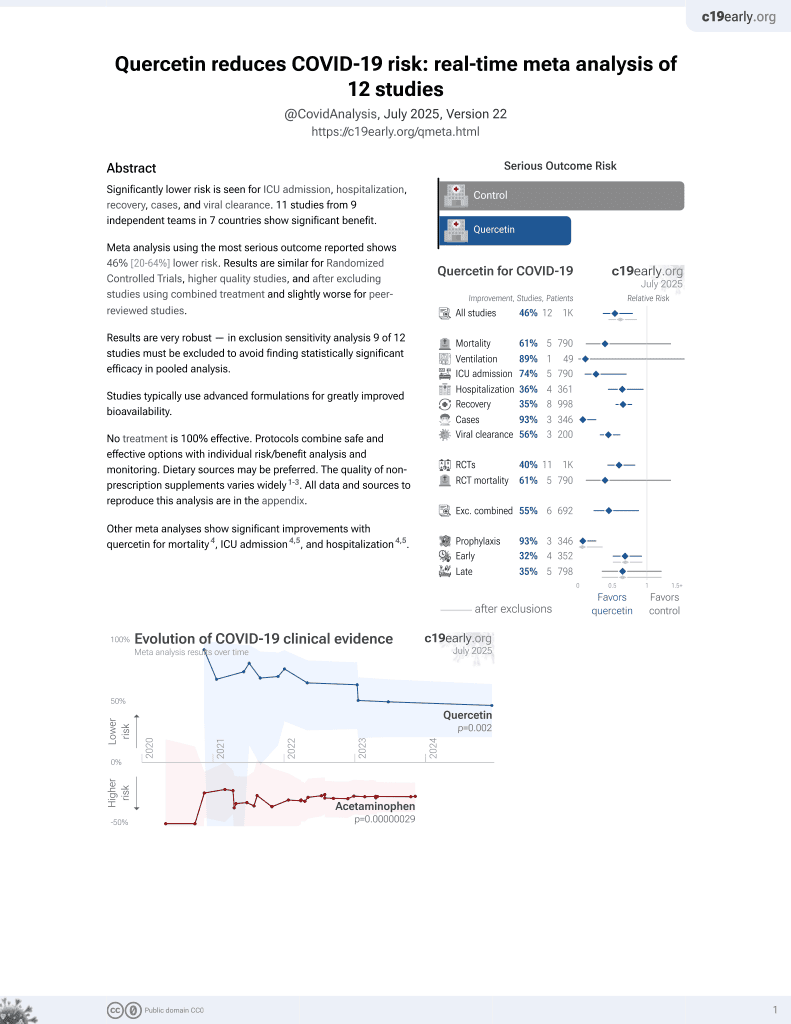
Quercetin for COVID-19
27th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2021, now with p = 0.002 from 12 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review of 8 RCTs showing faster recovery, faster viral clearance, and fewer COVID-19 cases with quercetin. Quercetin was well tolerated with no significant adverse events.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
2 meta-analyses show significant improvements with quercetin for mortality1,
ICU admission1,2, and
hospitalization1,2.
Currently there are 12 quercetin for COVID-19 studies, showing 61% lower mortality [-35‑89%], 89% lower ventilation [-92‑99%], 74% lower ICU admission [29‑90%], 36% lower hospitalization [5‑56%], and 93% fewer cases [73‑98%].
Silva et al., 26 Jan 2024, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: giselly.oliveiras@ufpe.br, elizabethfernanda_7@hotmail.com, damasceno.leao@gmail.com, mgcc@ufpe.br, mammaciel@hotmail.com, jose.ssobrinho@ufpe.br, maria.tscorreia@ufpe.br, teresinha.goncalves@ufpe.br.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of quercetin in the treatment of Covid-19: a systematic review
OBSERVATÓRIO DE LA ECONOMÍA LATINOAMERICANA, doi:10.55905/oelv22n1-192
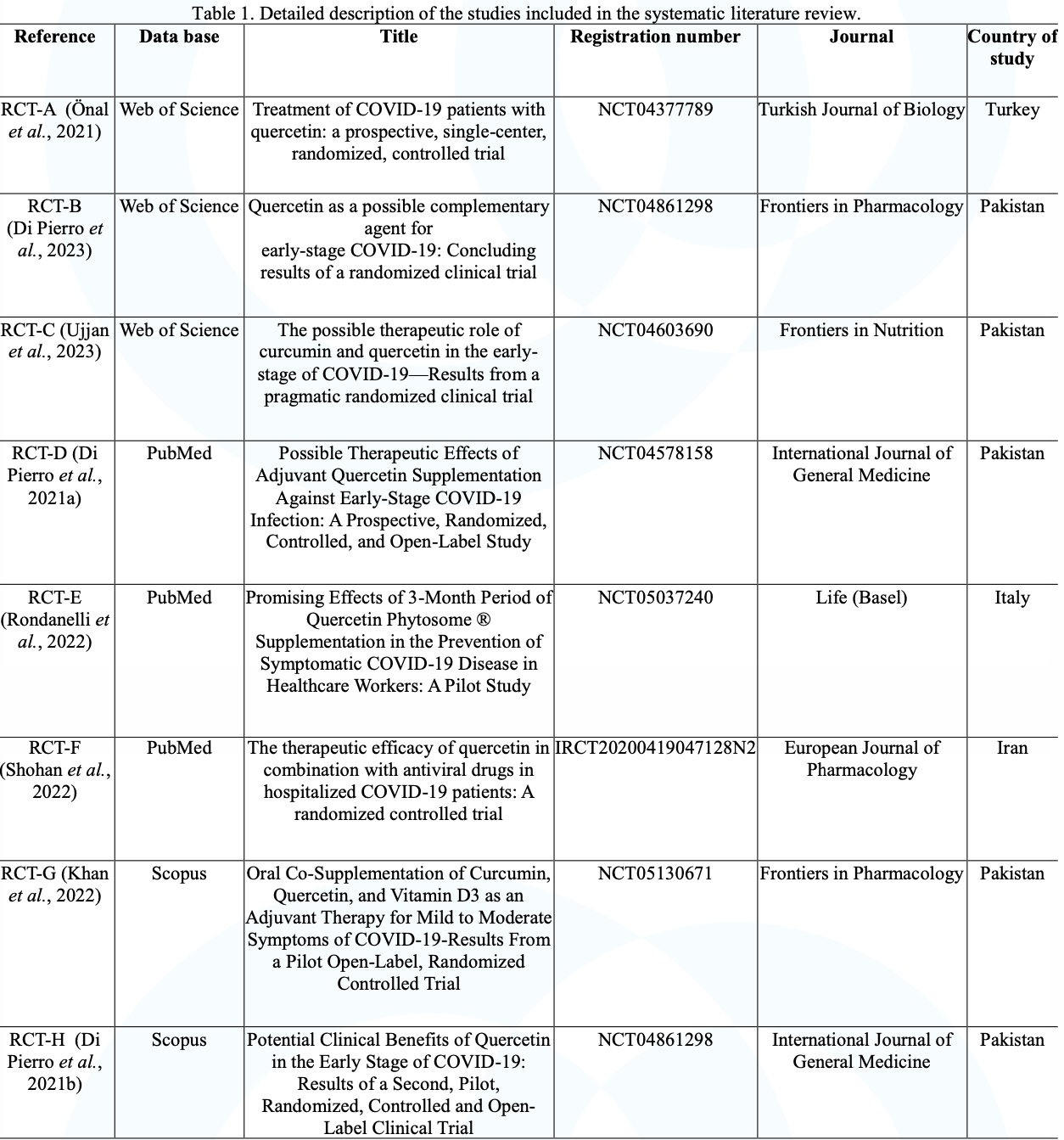
Background: With the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for pharmacological and clinical studies in the search for substances with anti-inflammatory action became evident. To perform a systematic review of randomized controlled trials that evaluated the efficacy and safety of quercetin as a treatment and prevention option for COVID-19 in humans relative to an active comparator, placebo, or standard care alone. Methods: The search for studies was carried out in the following databases: Medline via PubMed, LILACS, Science Direct, Web of Science, and Scopus via Capes periodicals with the descriptors: "Quercetin" AND ''COVID-19" AND "randomized controlled trial". This review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations. Protocol registration number in the PROSPERO database: CRD42022359842, available: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42022359842.Result s: 455 articles were found, and after reading the titles, abstracts, and full text, only 8 randomized clinical trials were included. According to the Cochrane RoB 2 tool, most included studies have some concerns about the risk of bias. The use of quercetin in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 contributed to the rapid evolution of patients compared to standard treatment and protected them against the development of COVID-19 compared to placebo. No adverse events were reported. Conclusion: It is inferred that drug supplementation with quercetin can help in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19, reducing recovery time, laboratory parameters and symptom manifestation, when compared to standard treatment. Thus, further research is needed to confirm the relationship between quercetin in the immune system and the development of COVID-19 in its most severe form. A systematic review carried out with randomized clinical trials for quercetin in is not yet available in the indexes, and this work is unprecedented.
References
Ansari, Ahmad, Protective effect of quercetin in primary neurons against Abeta(1-42): relevance to Alzheimer's disease, The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry
Bastaminejad, Bakhtiyari, Quercetin and its Relative Therapeutic Potential Against COVID-19: A Retrospective Review and Prospective Overview, Current Molecular Medicine
Biancatelli, Manuel, Colunga, Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19), Frontiers in Immunology
Bogoch, Pneumonia of unknown aetiology in Wuhan, China: potential for international spread via commercial air travel, Journal of Travel Medicine
Chilamakuri, Agarwal, COVID-19: Characteristics and Therapeutics, Cells
Derosa, A role for quercetin in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Phytotherapy research: PTR
Diniz, Ricardo Leite, Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin against COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury, Molecules (Basel, Switzerland)
Feng, Yindan Jiedu granules exhibit anti-inflammatory effect in patients with novel Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway, Phytomedicine: International Journal of Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology
Fernandes, Emerging COVID-19 variants and their impact on SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, therapeutics and vaccines, Annals of Medicine
Gasmi, Quercetin in the Prevention and Treatment of Coronavirus Infections: A Focus on SARS-CoV-2, Pharmaceuticals
Hu, Huang, Shaoying, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, Journal of Medical Virology
Imran, The Therapeutic and Prophylactic Potential of Quercetin against COVID-19: An Outlook on the Clinical Studies, Inventive Compositions, and Patent Literature, Antioxidants
Jarrott, LONG COVID"-A hypothesis for understanding the biological basis and pharmacological treatment strategy, Pharmacology Research & Perspectives
Khan, Oral Co-Supplementation of Curcumin, Quercetin, and Vitamin D3 as an Adjuvant Therapy for Mild to Moderate Symptoms of COVID-19-Results From a Pilot Open-Label, Randomized Controlled Trial, Frontiers in Pharmacology
Kim, COVID-19 Drug Development, Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology
Margolin, 20-Week Study of Clinical Outcomes of Over-the-Counter COVID-19 Prophylaxis and Treatment, Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine
Moher, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement, PLoS medicine
Owona, Ayissi, Abia, Angie, Moundipa et al., Natural compounds flavonoids as modulators of inflammasomes in chronic diseases, International Immunopharmacology
Parvathaneni, Vineela, Gupta, Vivek, Utilizing drug repurposing against COVID-19 -Efficacy, limitations, and challenges, Life Sciences
Pierro, Possible Therapeutic Effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation Against Early-Stage COVID-19 Infection: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, and Open-Label Study, International Journal of General Medicine
Pierro, Potential Clinical Benefits of Quercetin in the Early Stage of COVID-19: Results of a Second, Pilot, Randomized, Controlled and Open-Label Clinical Trial, International Journal of General Medicine
Pierro, Quercetin as a possible complementary agent for early-stage COVID-19: Concluding results of a randomized clinical trial, Frontiers in Pharmacology
Pollard, Morran, Nestor-Kalinoski, The COVID-19 pandemic: a global health crisis, Physiological Genomics
Pourkarim, Rezaee, Molnupiravir: A new candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Pharmacology Research & Perspectives
Rashedi, COVID-19 vaccines mix-and-match: The concept, the efficacy and the doubts, Journal of Medical Virology
Rondanelli, Promising Effects of 3-Month Period of Quercetin Phytosome® Supplementation in the Prevention of Symptomatic COVID-19 Disease in Healthcare Workers: A Pilot Study, Life
Saeed, Abdel Monem, Mohamed, Hussein, Owaynat et al., Cholecalciferol level and its impact on COVID-19 patients, The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine
Saeedi-Boroujeni, Ali, Anti-inflammatory potential of Quercetin in COVID-19 treatment, Journal of Inflammation (London
Shohan, The therapeutic efficacy of quercetin in combination with antiviral drugs in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial, European Journal of Pharmacology
Sterne, RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ (Clinical research
Susianti, Low levels of vitamin D were associated with coagulopathy among hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) patients: A single-centered study in Indonesia, Journal of Medical Biochemistry
Ujjan, Din, The possible therapeutic role of curcumin and quercetin in the early-stage of COVID-19-Results from a pragmatic randomized clinical trial, Frontiers in Nutrition
Wen, Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19:a meta-analysis, Annals of Medicine
Önal, Treatment of COVID-19 patients with quercetin: a prospective, single center, randomized, controlled trial, Turkish Journal of Biology = Turk Biyoloji Dergisi
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.55905/oelv22n1-192",
"ISSN": [
"1696-8352",
"1696-8352"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.55905/oelv22n1-192",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: With the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for pharmacological and clinical studies in the search for substances with anti-inflammatory action became evident. To perform a systematic review of randomized controlled trials that evaluated the efficacy and safety of quercetin as a treatment and prevention option for COVID-19 in humans relative to an active comparator, placebo, or standard care alone. Methods: The search for studies was carried out in the following databases: Medline via PubMed, LILACS, Science Direct, Web of Science, and Scopus via Capes periodicals with the descriptors: “Quercetin” AND ''COVID-19” AND “randomized controlled trial”. This review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations. Protocol registration number in the PROSPERO database: CRD42022359842, available: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42022359842.Results: 455 articles were found, and after reading the titles, abstracts, and full text, only 8 randomized clinical trials were included. According to the Cochrane RoB 2 tool, most included studies have some concerns about the risk of bias. The use of quercetin in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 contributed to the rapid evolution of patients compared to standard treatment and protected them against the development of COVID-19 compared to placebo. No adverse events were reported. Conclusion: It is inferred that drug supplementation with quercetin can help in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19, reducing recovery time, laboratory parameters and symptom manifestation, when compared to standard treatment. Thus, further research is needed to confirm the relationship between quercetin in the immune system and the development of COVID-19 in its most severe form. A systematic review carried out with randomized clinical trials for quercetin in COVID-19 is not yet available in the indexes, and this work is unprecedented.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silva",
"given": "Giselly de Oliveira",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borba",
"given": "Elizabeth Fernanda de Oliveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leão",
"given": "Amanda Damasceno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carneiro-da-Cunha",
"given": "Maria das Graças",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maciel",
"given": "Maria Aparecida Medeiros",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobrinho",
"given": "José Lamartine Soares",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Correia",
"given": "Maria Tereza dos Santos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Da Silva",
"given": "Teresinha Gonçalves",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "OBSERVATÓRIO DE LA ECONOMÍA LATINOAMERICANA",
"container-title-short": "OLEL",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-26T14:09:38Z",
"timestamp": 1706278178000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-30T14:13:41Z",
"timestamp": 1706624021000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-31T00:37:52Z",
"timestamp": 1706661472693
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
2
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1706227200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://ojs.observatoriolatinoamericano.com/ojs/index.php/olel/article/download/2969/2100",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://ojs.observatoriolatinoamericano.com/ojs/index.php/olel/article/download/2969/2100",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "30764",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3668-3693",
"prefix": "10.55905",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "South Florida Publishing LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://ojs.observatoriolatinoamericano.com/ojs/index.php/olel/article/view/2969"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of quercetin in the treatment of Covid-19: a systematic review",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "22"
}