Immune-boosting effect of natural remedies and supplements on progress of, and recovery from COVID-19 infection
et al., Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.4314/tjpr.v21i2.13, Feb 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective survey-based analysis of 349 COVID-19 patients, showing a lower risk of severe cases with vitamin D, zinc, turmeric, and honey prophylaxis in unadjusted analysis, without statistical significance. REC/UG/2020/03.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of severe case, 47.4% lower, RR 0.53, p = 0.24, treatment 4 of 65 (6.2%), control 22 of 188 (11.7%), NNT 18, unadjusted, severe vs. mild cases.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Shehab et al., 28 Feb 2022, retrospective, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, survey, 7 authors, study period September 2020 - March 2021.
Immune-boosting effect of natural remedies and supplements on progress of, and recovery from COVID-19 infection
doi:10.4314/tjpr.v21i2.13
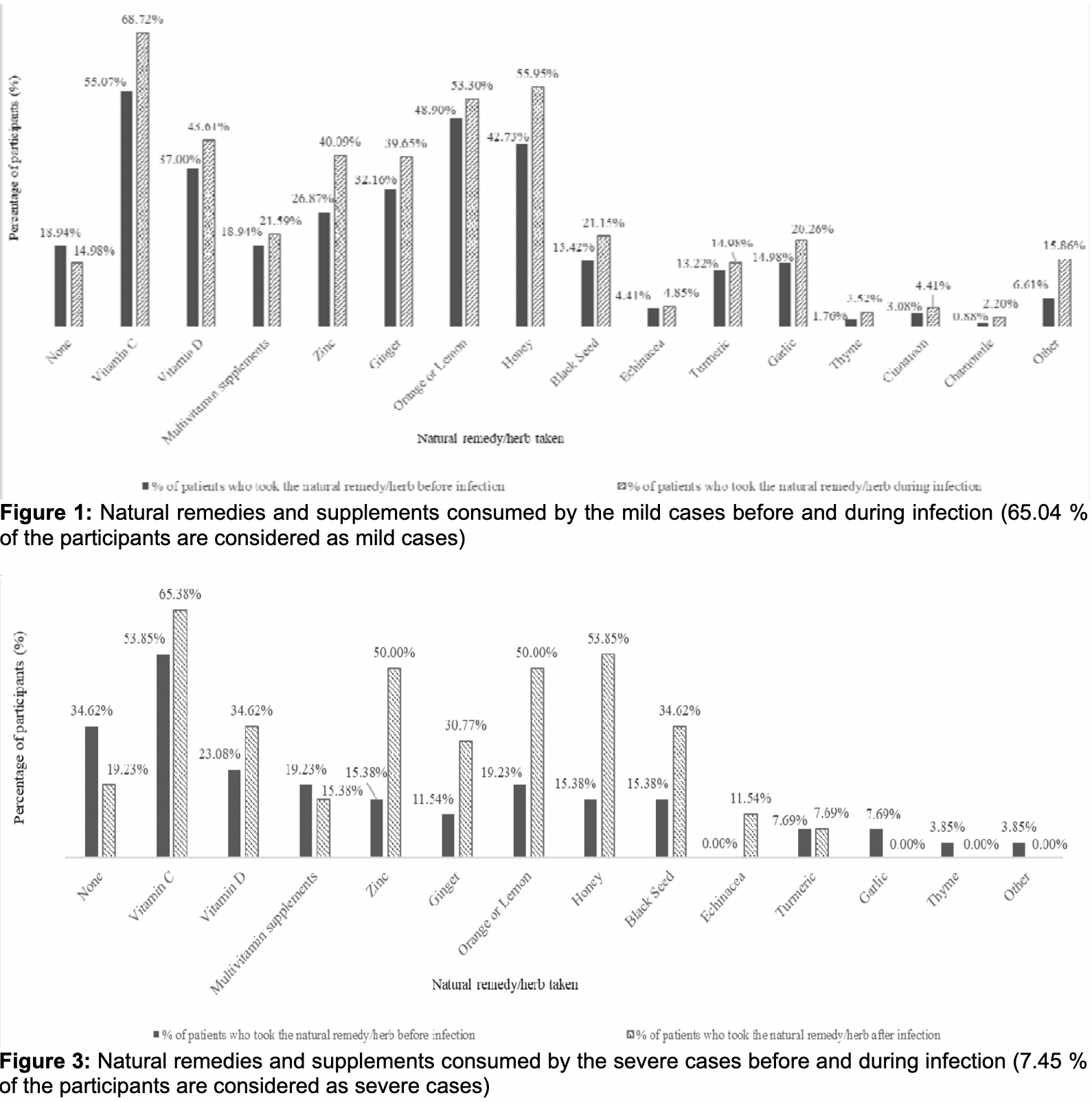
To investigate the effect of natural remedies and supplements on the progress of and recovery from COVID-19 infection, and the role of safety precautions in controlling the spread of its causative pathogen. Methods: A questionnaire was designed and electronically distributed among previously infected individuals across countries. The survey included questions about the participants' demographic information, medical history, how they were infected, symptoms they have experienced, where they were isolated, the degree of precautions taken against the virus, and their consumption of natural remedies or supplements before and during the infection period.
Results: The results showed that natural remedies and supplements are widely consumed among COVID-19 patients both before and during infection, either as a single remedy or in combination with other remedies. As the age of the participants increased, the incidence of their hospitalization increased. Significant results were observed when comparing the severity of infection with the number of natural remedies and supplements taken before (P 0.000) and during the infection (P 0.003).
Conclusion: Increasing the intake of natural remedies and/or supplements before and during COVID-19 infection lowers the severity of the infection. Vitamin C, honey, and citrus fruits such as orange and lemon were the major remedies consumed before and during infection. A large number of the participants that experienced severe COVID-19 conditions, did not consume any natural remedies or supplements.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that no conflict of interest is associated with this work.
Contribution of authors We declare that this work was done by the authors named in this article and all liabilities pertaining to claims relating to the content of this article will be borne by the authors. Dr. Naglaa Gamil Shehab, Prof. in the Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacotherapeutics Department, Dubai Pharmacy College, Dubai, UAE conceived and designed this study. All authors contributed in data collection, analysis, manuscript writing and proofreading for publication.
Open Access This is an Open Access article that uses a funding model which does not charge readers or their institutions for access and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/ 4.0) and the Budapest Open Access Initiative (http://www.budapestopenaccessinitiative.org/rea d), which permit unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited.
References
Aranow, Vitamin D and the immune system, J Investig Med
Carr, Maggini, Vitamin C and Immune Function, Nutrients
Chaplin, Overview of the immune response, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Chowdhury, Hossain, Kashem, Shahid, Alam, Immune response in COVID-19: A review, J Infect Public Health
Fonseca, Lukacs, Ptaschinski, Factors Affecting the Immunity to Respiratory Syncytial Virus: From Epigenetics to Microbiome, Front Immunol
Guo, Cao, Hong, Tan, Chen et al., The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -an update on the status, Mil Med Res
Jolad, Lantz, Solyom, Chen, Bates et al., Fresh organically grown ginger (Zingiber officinale): composition and effects on LPSinduced PGE2 production, Phytochemistry
Lesourd, Nutrition: a major factor influencing immunity in the elderly, J Nutr Health Aging
Lotfi, Hamblin, Rezaei, COVID-19: Transmission, prevention, and potential therapeutic opportunities, Clin Chim Acta
Macgillivray, Kollmann, The Role of Environmental Factors in Modulating Immune Responses in Early Life, Front Immunol
Marshall, Warrington, Watson, Kim, An introduction to immunology and immunopathology, Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol
Miguel, Antunes, Faleiro, Honey as a Complementary Medicine, Integr Med Insights
Sultan, Buttxs, Qayyum, Suleria, Immunity: Plants as Effective Mediators, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr
Thompson, The Immune System, JAMA
Wu, Chen, Chan, The outbreak of COVID-19: An overview, J Chin Med Assoc
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4314/tjpr.v21i2.13",
"ISSN": [
"1596-9827",
"1596-5996"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v21i2.13",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Purpose: To synthesize anticonvulsant drug derivatives that target protease-activated receptor generated epileptic seizures.Method: Varieties of carbamazepine-based Schiff bases were designed with different aldehydes and ketones, and evaluated for in silico computer-aided drug design prediction of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME), and potential drug targets. The resultant compounds were synthesized and characterized by various spectroscopic techniques, including FTIR, 1H-NMR and 13CNMR, analysis. Thereafter, they were screened for antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticonvulsant potential.Results: Prominent anti-protease potential was shown by C7 and C3 compounds and the order of activity was C7 > C3 > C5 > C2 > C6 > C4 > C2 > C1 (p < 0.05). The anticonvulsant activity of C7 and C5 was comparable with the standard drug; C3, C4, C6 and C8 had mild activity while C1 and C4 showed the least activity. The synthesized compounds exhibited significant (p < 0.05) antioxidant potential (rank order: C3 > C4 > C5 > C7 > C8 > C6 > C1 > C2) and antimicrobial activity against S.aureus and B. bronchiseptica (rank order: C5 > C2 > C8 > C1 > C4 > C3 > C7).Conclusion: Synthesized derivatives retained their potential for anticonvulsant and antitrypsin activity, unlike their mother moiety, i.e., carbamazepine. The additional antibacterial activity effectively treats neurological disorders associated with bacterial infections.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "Taha",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Mohsin Abbas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "Irshad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Fahad Mehmood",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research",
"container-title-short": "Trop. J. Pharm Res",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T12:25:01Z",
"timestamp": 1683721501000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T12:25:29Z",
"timestamp": 1683721529000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-11T04:39:34Z",
"timestamp": 1683779974862
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
28
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.ajol.info/index.php/tjpr/article/download/224485/211774",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.ajol.info/index.php/tjpr/article/download/224485/211774",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2895",
"original-title": [],
"page": "303-312",
"prefix": "10.4314",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "African Journals Online (AJOL)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ajol.info/index.php/tjpr/article/view/224485"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmaceutical Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Design, synthesis and biological activities of 5Hdibenzo[ b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide derivatives; Targeted hippocampal trypsin inhibition as a novel approach to treat epileptogenesis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "21"
}
shehab
