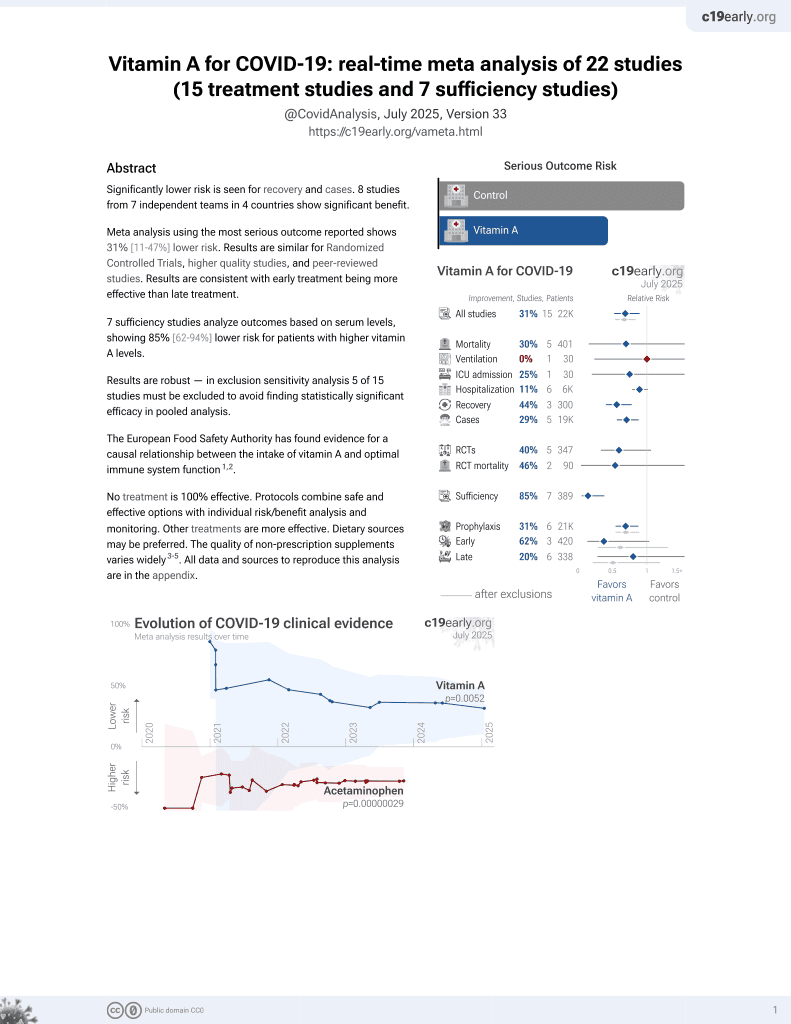
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
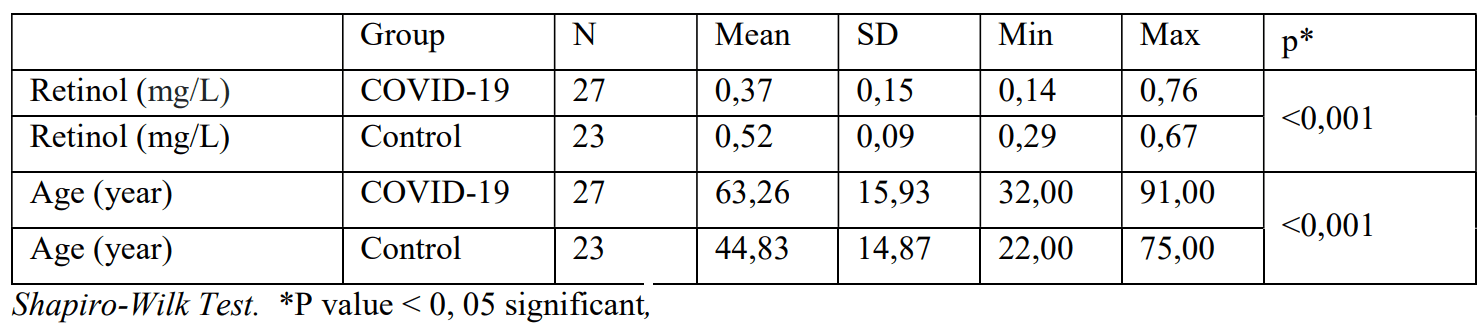
Retrospective 27 severe COVID-19 patients and 23 non-COVID-19 patients, showing significantly lower vitamin A levels in COVID-19 patients (0.37mg/L vs. 0.52 mg/L, p<0.001). 10 of 27 COVID-19 patients received vitamin A, with higher mortality. Group details are not provided but authors note that 8 of 10 had comorbidities.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details, comments suggest significant group differences and confounding.
|
risk of death, 282.5% higher, RR 3.83, p = 0.001, treatment 9 of 10 (90.0%), control 4 of 17 (23.5%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sarohan et al., 1 Feb 2021, retrospective, Turkey, preprint, 4 authors.
Retinol Depletion in Severe COVID-19
doi:10.1101/2021.01.30.21250844
Background and Purpose: Vitamin A is depleted during infections. Vitamin A has been used successfully in measles, RSV and AIDS patients and is an effective vaccine adjuvant. In this study, low retinol levels were found in patients with severe COVID-19. Retinoid signaling impairment in COVID-19 disrupts Type-I interferon synthesis. Material and Method: Two groups were formed in the study. The patient group consisted of 27 (Group 1) severe COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit with respiratory failure, and the control group consisted of 23 (Group 2) patients without COVID-19 symptoms. Serum retinol levels were analyzed by ELIZA and HPLC in both groups. Findings: Retinol levels were found to be significantly lower in the patient group (P <0.001). There was no difference in retinol between two different age groups in the patient group (P> 0.05). There was no significant difference in retinol between men and women (P> 0.05). Comorbidity did not affect serum retinol levels (P >0.05).
Conclusion: Serum retinol levels were low in patients with severe COVID-19. Drugs preventing retinol excretion were not stopped in the patient group. Some patients took vitamin A externally. Despite this, retinol was low in COVID-19 patients. Retinol depletion impairs Type-I interferon synthesis by impairing retinoid signaling. Retinoid signaling may be the main pathogenetic disorder in COVID-19. This pathogenesis can serve as a guide for adjuvants, drug targets, and candidate drugs. Retinol, retinoic acid derivatives, and some CYP450 inhibitors may work on COVID-19.
Disclosure Statement: The authors are not a party of any affiliations, memberships, funding, or financial holdings that might be perceived as affecting the objectivity of this review.
The Basis of the Study and the Decision of the Ethics Committee This study was conducted with the approval of the ethics committee and the approval of Diyarbakır Gazi Yaşargil Training and Research Hospital, University of Health Sciences, and the approval of the Ministry of Health dated 03.06.2020 and numbered T22_10_40.xml. All protocols were implemented within the recommendations of the local ethics committee. All subjects were included in the study following the protocols approved by the local ethics committee. When the patients were hospitalized, they were informed about the study and were included in the study after obtaining their consent for signature.
The Contents of the Formulas and TPN Administered to the Patients The contents of the formulas and TPN administered to the patients were given below: More than one type of TPN and formulas were administered to some patients.
References
Abbott, e220 ml 1.5 kcal/ml. 1.5 g CaHMB 330 kcal. Administered to 2 individuals, 10 pcs and 29 pcs
Acharya, Liu, Gack, Dysregulation of Type-I interferon responses in COVID-19, Nature Reviews Immunology volume
Al Tanoury, Piskunov, Rochette-Egly, Vitamin A and retinoid signaling: genomic and nongenomic effects, J Lipid Res
Allenby, Bocquel, Saunders, Kazmer, Speck et al., Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Aziz, COVID-19: Endogenous Retinoic Acid Theory and Retinoic Acid Depletion Syndrome, Med Hypotheses
Baig, Khaleeq, Ali, Evidence of the COVİD-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms, ACS Chem Neurosci
Balmer, Blomhoff, Gene expression regulation by retinoic acid, J. Lipid Res
Bastard, Rosen, Zhang, Abel, Su et al., Auto-antibodies against Type-I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19, Science
Blomhoff, Blomhoff, Overview of retinoid metabolism and function, J Neurobiol
Bozena, Wrobel, Leopold, Smell and taste disorders, Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am
Britton, SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgA And Limited Inflammatory Cytokines Are Present In The Stool Of Select Patients With Acute COVID-19
Campos, Flores, Underwood, Effect of an infection on vitamin A status of children as measured by the relative dose response (RDR), American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Canrongwu, Yueyingyang, Pengzhang, Wuzhong, Yaliwang et al., Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods, Acta Pharm Sin B
Casanova, Su, Human Genetic Effort. A Global Effort to Define the Human Genetics of Protective Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Cell
Cassani, Vitamin A and Immune Regulation: Role of Retinoic Acid in Gut-Associated Dendritic Cell Education, Immune Protection and Tolerance, Mol Aspects Med
Chen, Hu, Yang, Yun, Wang et al., Study on vitamin A nutritional status of Chinese urban elderly residents in 2010-2012, Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi
Comstock, Serum concentrations of alpha tocopherol, beta carotene, and retinol preceding the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, Ann Rheum Dis
Fang, Zhou, Lin, Ying, Luo et al., Inhibition of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid-Induced Proteasome Activation Potentiates the Differentiating Effect of Retinoid in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells, Mol Carcinog
Gibson, Principles of nutritional assessment
Greaney, Starr, Gilchuk, Carnahan, Crowe et al., Complete Mapping of Mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain that Escape Antibody Recognition, Cell Host & Microbe
Grubaugh, Hanage, Rasmussen, Making Sense of Mutation: What D614G Means for the COVID-19 Pandemic Remains Unclear, Cell
Guan, Ni, Liang, Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med. N Engl J Med
Huang, Liu, Qi, Brand, Guo, Role of Vitamin A in the Immune System, J Clin Med
Huiming, Chaomin, Meng, Vitamin A for treating measles in children, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Hussin, Rothan, Siddappa, The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. Author links, Journal of Autoimmunity
Ivashkiv, Donlin, Regulation of Type-I interferon responses, Nature Reviews. Immunology
Johnson, Vitamin A Deficiency (Retinol Deficiency)
Kell, Gale, RIG-I in RNA virus recognition, Virology
Khawja A Usmani, Tang, Human Cytochrome P450: Metabolism of Testosterone by CYP3A4 and Inhibition by Ketoconazole, Curr Protoc Toxicol
Korber, Fischer, Gnanakaran, Hengartner, Saphire et al., Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that D614G Increases Infectivity of the COVID-19 Virus, Cell
Lane, Bailey, Role of retinoid signalling in the adult brain, Prog Neurobiol
Liu, Olagnier, Lin, Host and Viral Modulation of RIG-I-Mediated Antiviral Immunity, Front. Immunol. Virology
Luiza Nascimento, Da, Diniz, Kruze Grande De Arruda, Vitamin A deficiency in elderly attending the Health Family Programme in Camaragibe, PE, Brazil, Arch Latinoam Nutr
Mantlo, Bukreyeva, Maruyama, Paessler, Huang, Antiviral activities of Type-I interferons to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Antiviral Res
Mao, Wang, Chen, Neurological Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients with COVİD-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective case series study, JAMA Neurol
Mehta, Fawzi, Effects of vitamins, including vitamin A, on HIV/AIDS patients, Vitam Horm
Mora, Ulrich H Von Andrian, Role of Retinoic Acid in the Imprinting of Gut-Homing IgA-secreting Cells, Semin Immunol
Navigatore-Fonzo, Golini, Ponce, Delgado, Plateo et al., Retinoic acid receptors move in time to the clock in the hippocampus. Effect of a vitamin A-deficient diet, J Nutr Biochem
Neill, Toll-like receptors: From the discovery of NFκB to new insights into transcriptional regulations in innate immunity, Biochemical Pharmacology
Nelson, Buttrick, Isoherranen, Therapeutic potential of the inhibition of the retinoic acid hydroxylases CYP26A1 and CYP26B1 by xenobiotics, Curr Top Med Chem
Ni, Wei, Wu, Vitamin A for non-measles pneumonia in children, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Omalla, Olwenyi, Ravi Dyavar, Acharya, Podany et al., Immunoepidemiology and pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), J Mol Med (Berl)
Pantazi, Marks, Stolarczyk, Lycke, Noelle et al., Cutting Edge: Retinoic Acid Signaling in B Cells Is Essential for Oral Immunization and Microflora Composition, J Immunol
Platanias, Mechanisms of type-I-and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling, Nat Rev Immunol
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Clinical Infectious Diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Raverdeau, Mills, Modulation of T cell and innate immune responses with retinoic Acid, J. Immunol
Raverdeau, Modulation of T Cell and Innate Immune Responses by Retinoic Acid, J Immunol
Riva, Yuan, Sumit, Chanda, Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing, Nature volume
Ross, Zolfaghari, Cytochrome P450s in the Regulation of Cellular Retinoic Acid Metabolism, Annu Rev Nutr
Schmitz, Kracht, Vera, Saul, The intricate interplay between RNA viruses and NF-κB, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) -Molecular Cell Research
Shi, Wang, Shao, Huang, Ippolito et al., COVID-19 infection: the perspectives on immune responses. nature, Cell Death & Differentiation Published
Shruti Ahlawat, Sharma, Immunological co-ordination between gut and lungs in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Virus Res
Smith, The role of cytochrome P450 in developmental pharmacology, Journal of Adolescent Health
Sommer, West, Infectious morbidity. In: Vitamin A deficiency, health, survival, and vision
Trasino, A role for retinoids in the treatment of COVID 19? CEEP Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
Vahlquist, Blockhuys, ; Steijlen, Van Rossem, Didona et al., Oral liarozole in the treatment of patients with moderate/severe lamellar ichthyosis: Results of a randomized, double-blind, multinational, placebo-controlled phase II/III trial, The British Journal of Dermatology
Wang, Nie, Wang, Zhao, Xiong, Characteristics of peripheral lymphocyte subset alteration in COVID-19 pneumonia, The Journal of Infectious Diseases
Who/Unicef, Global action plan for prevention and control of pneumonia
Yoneyama, Kikuchi, Natsukawa, Shinobu, Imaizumi, The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses, Nat. Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.30.21250844",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.30.21250844",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background and Purpose</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin A is depleted during infections. Vitamin A has been used successfully in measles, RSV and AIDS patients and is an effective vaccine adjuvant. In this study, low retinol levels were found in patients with severe COVID-19. Retinoid signaling impairment in COVID-19 disrupts Type-I interferon synthesis.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Material and Method</jats:title><jats:p>Two groups were formed in the study. The patient group consisted of 27 (Group 1) severe COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit with respiratory failure, and the control group consisted of 23 (Group 2) patients without COVID-19 symptoms. Serum retinol levels were analyzed by ELIZA and HPLC in both groups.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Findings</jats:title><jats:p>Retinol levels were found to be significantly lower in the patient group (P <0.001). There was no difference in retinol between two different age groups in the patient group (P> 0.05). There was no significant difference in retinol between men and women (P> 0.05). Comorbidity did not affect serum retinol levels (P >0.05).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Serum retinol levels were low in patients with severe COVID-19. Drugs preventing retinol excretion were not stopped in the patient group. Some patients took vitamin A externally. Despite this, retinol was low in COVID-19 patients. Retinol depletion impairs Type-I interferon synthesis by impairing retinoid signaling. Retinoid signaling may be the main pathogenetic disorder in COVID-19. This pathogenesis can serve as a guide for adjuvants, drug targets, and candidate drugs. Retinol, retinoic acid derivatives, and some CYP450 inhibitors may work on COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5794-688X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sarohan",
"given": "Aziz Rodan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akelma",
"given": "Hakan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Araç",
"given": "Eşref",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslan",
"given": "Özgür",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-01T22:49:16Z",
"timestamp": 1612219756000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-14T07:52:51Z",
"timestamp": 1671004371000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-19T06:57:27Z",
"timestamp": 1710831447895
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.01.30.21250844",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.1",
"unstructured": "Weekly Epidemiological Update Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). 21 September 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00109-020-01961-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.3",
"unstructured": "Omalla A. Olwenyi , Shetty Ravi Dyavar , Arpan Acharya , Anthony T. Podany , Courtney V. Fletcher , Caroline L. Ng , St Patrick Reid , and Siddappa N. Byrareddy. Immuno- epidemiology and pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Aug 18 : 1–15."
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.4",
"unstructured": "Canrong Wu , Yang Liu , Yueying Yang , Peng Zhang , Wu Zhong , Yali Wang , Qiqi Wang , Yang Xu , Lixia Chen , Hua Li . Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Feb 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD001479.pub2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.5",
"unstructured": "Huiming Y , Chaomin W , Meng M. Vitamin A for treating measles in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Oct 19; 2005(4): CD001479."
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.6",
"unstructured": "Ni J , Wei J , Wu T. Vitamin A for non-measles pneumonia in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2005, Issue 3, No.: CD003700."
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.7",
"unstructured": "WHO/UNICEF. Global action plan for prevention and control of pneumonia (GAPP). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0083-6729(06)75013-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.8"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.9",
"unstructured": "Larry E. Johnson . Vitamin A Deficiency (Retinol Deficiency). MSD MANUAL Professional Version. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. Last full review/revision Aug 2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/46.1.91",
"article-title": "Effect of an infection on vitamin A status of children as measured by the relative dose response (RDR)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "American Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.10",
"volume": "46",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.11",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization, Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. Vitamin and mineral requirements in human nutrition. World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 01 Jan.2004. 2 edition"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.12",
"unstructured": "Sommer A , West KP Jr . Infectious morbidity. In: Vitamin A deficiency, health, survival, and vision. New York, NY, Oxford University Press, 1996:19–98."
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.13",
"unstructured": "Gibson R , ed. Principles of nutritional assessment. Oxford, UK, Oxford University Press, 2005."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2011.11.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1303245",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.smim.2008.08.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.16"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 infection: the perspectives on immune responses",
"first-page": "1451",
"journal-title": "nature. Cell Death & Differentiation",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.17",
"volume": "27, pages",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "RIG-I in RNA virus recognition",
"first-page": "110",
"issue": "480",
"journal-title": "Virology. 2015",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.18",
"volume": "479-",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3581",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri1604",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1568026611313120004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.21"
},
{
"first-page": "635",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "The role of cytochrome P450 in developmental pharmacology Journal of Adolescent Health. /Volume",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.22",
"volume": "15, Issue",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin A deficiency in elderly attending the Health Family Programme in Camaragibe, PE, Brazil",
"first-page": "213",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Arch Latinoam Nutr",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.23",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Study on vitamin A nutritional status of Chinese urban elderly residents in 2010-2012",
"first-page": "121",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.24",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/0471140856.tx0413s20",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.25",
"unstructured": "Khawja A Usmani , Jun Tang . Human Cytochrome P450: Metabolism of Testosterone by CYP3A4 and Inhibition by Ketoconazole. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2004 Jun; Chapter 4:Unit4.13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ard.56.5.323",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm7090258",
"article-title": "Role of Vitamin A in the Immune System",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "258",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.27",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110250",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Endogenous Retinoic Acid Theory and Retinoic Acid Depletion Syndrome",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110250",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.28",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Doyle and O’Neill",
"first-page": "1102",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Toll-like receptors: From the discovery of NFκB to new insights into transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. iochemical Pharmacology",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.29",
"volume": "72, Issue",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "“Oral liarozole in the treatment of patients with moderate/severe lamellar ichthyosis: Results of a randomized, double-blind, multinational, placebo-controlled phase II/III trial”",
"first-page": "173",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The British Journal of Dermatology",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.30",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1303245",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-nutr-072610-145127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1500989",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.33"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.34",
"unstructured": "Steven E. Trasino . A role for retinoids in the treatment of COVIDLJ19? CEEP Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology. Letter to editor. Willey Online library"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0346-x",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of Type-I interferon responses in COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "397",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Immunology",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.35",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104811",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.36"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.37",
"unstructured": "Paul Bastard , Lindsey B. Rosen , Qian Zhang , Laurent Abel , Helen C. Su , Jean-Laurent Casanova . Auto-antibodies against Type-I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 24 Sep 2020:"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1",
"article-title": "Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.39",
"volume": "586",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1194/jlr.R100015-JLR200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni1087",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.90.1.30",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.42"
},
{
"article-title": "Host and Viral Modulation of RIG-I- Mediated Antiviral Immunity",
"first-page": "110",
"issue": "480",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol. Virology. 03",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.43",
"volume": "479-",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "The intricate interplay between RNA viruses and NF-κB",
"first-page": "2754",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.44",
"volume": "1843, Issue",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198103",
"article-title": "Immunological co-ordination between gut and lungs in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198103",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.45",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.03.20183947",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.46",
"unstructured": "Britton, G. J. et al. (2020). SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgA And Limited Inflammatory Cytokines Are Present In The Stool Of Select Patients With Acute COVID-19. medRxiv preprint."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mc.20687",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00122",
"article-title": "Evidence of the COVİD-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem Neurosci",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.48",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.05.006",
"article-title": "Retinoic acid receptors move in time to the clock in the hippocampus. Effect of a vitamin A-deficient diet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "859",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Biochem",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.49",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.03.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1194/jlr.R030833",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/neu.20242",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa150",
"article-title": "Characteristics of peripheral lymphocyte subset alteration in COVID-19 pneumonia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1762",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.54",
"volume": "221",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3544840",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.55",
"unstructured": "Mao L , Wang M , Chen S et al. Neurological Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients with COVİD-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective case series study. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Apr 10; e201127."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med. N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.56",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fsc.2004.04.006",
"article-title": "Smell and taste disorders",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.57",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.10.292078",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.58",
"unstructured": "Allison J. Greaney , Tyler N. Starr , Pavlo Gilchuk , Robert H. Carnahan , James E. Crowe, Jr. , Jesse D. Complete Mapping of Mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor- Binding Domain that Escape Antibody Recognition, Cell Host & Microbe (2020)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m4857",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.60"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.040",
"article-title": "Making Sense of Mutation: What D614G Means for the COVID-19 Pandemic Remains Unclear",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "794",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.61",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.62",
"unstructured": "SARS-CoV-2 mink-associated variant strain – Denmark. Disease Outbreak News. 6 November 2020. https://www.who.int/csr/don/06-november-2020-mink-associated-sars-cov2-denmark/en/"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.63",
"unstructured": "Rapid Risk Assessment: Detection of new SARS-CoV-2 variants related to mink. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/detection-new-sars-cov-2-variants-mink."
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.64",
"unstructured": "https://www.who.int/hiv/topics/vaccines/Vaccines/en/"
},
{
"key": "2021020402400956000_2021.01.30.21250844v1.65",
"unstructured": "https://www.healthline.com/health/hiv-aids/vaccine-how-close-are-we"
}
],
"reference-count": 65,
"references-count": 65,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.01.30.21250844"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Retinol Depletion in Severe COVID-19",
"type": "posted-content"
}