Effectiveness of budesonide formoterol fixed-dose combination MDI in reducing cough symptoms in COVID-19 patients: A real-world evidence study
et al., Lung India, doi:10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_268_22, Mar 2023
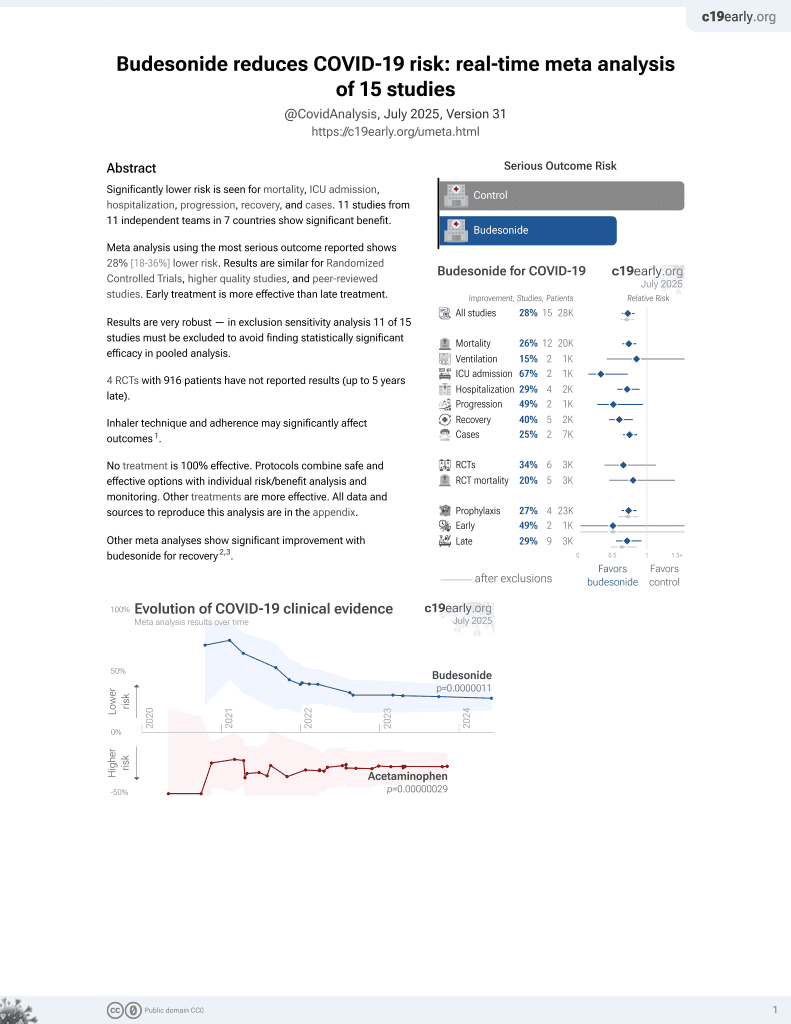
Budesonide for COVID-19
27th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2021, now with p = 0.0000042 from 14 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 102 patients in India, showing improved recovery of cough with budesonide+formoterol. Authors note better results with earlier treatment. Budesonide 800mcg + formoterol 12mcg bid for 7 days.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
|
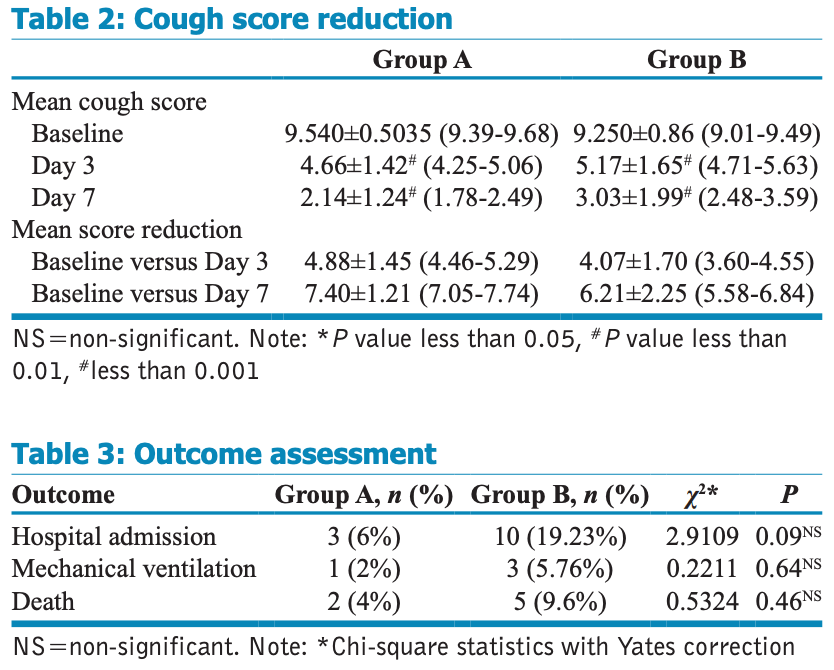
risk of death, 58.4% lower, RR 0.42, p = 0.44, treatment 2 of 50 (4.0%), control 5 of 52 (9.6%), NNT 18.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 65.3% lower, RR 0.35, p = 0.62, treatment 1 of 50 (2.0%), control 3 of 52 (5.8%), NNT 27.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 68.8% lower, RR 0.31, p = 0.07, treatment 3 of 50 (6.0%), control 10 of 52 (19.2%), NNT 7.6.
|
|
cough score, 29.4% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.008, treatment mean 2.14 (±1.24) n=50, control mean 3.03 (±1.99) n=52, day 7.
|
|
cough score, 9.9% lower, RR 0.90, p = 0.10, treatment mean 4.66 (±1.42) n=50, control mean 5.17 (±1.65) n=52, day 3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Samajdar et al., 3 Mar 2023, prospective, India, peer-reviewed, mean age 47.2, 6 authors, study period January 2021 - June 2021, average treatment delay 5.98 days, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with formoterol) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Contact: shambo_sa2001@yahoo.co.in.
Effectiveness of budesonide formoterol fixed-dose combination MDI in reducing cough symptoms in COVID-19 patients: A real-world evidence study
Lung India, doi:10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_268_22
Background: Cough is a wearisome and exasperating symptom affecting the daily life of the infected patient. Cough due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) causes excessive morbidity in human populations globally. Apart from the morbidity associated with cough, it also enhances the transmission of this viral infection through droplets. Therefore, curbing cough is crucial to limit its spread. Patients often administer over-the-counter products and antitussive agents, which have no proven benefit. The present study was undertaken to find out if cough associated with COVID-19 and other indicative clinical outcomes is alleviated with a budesonide/formoterol fixed-dose combination (FDC) metered-dose inhaler (MDI). Materials and Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted in mild COVID-19 patients who presented with a cough score ≥8 at presentation. Patients who were initiated on ICS-LABA MDI were observed as group A and those who were not initiated on MDI were observed as Group B. Cough symptom score (at baseline and on day 3 and day 7), the incidence of hospital admission and/or death, and need for mechanical ventilation were documented. Prescribing patterns of anti-cough medications were also noted and analysed. Results: Compared to group B, a higher mean cough score reduction was noted for group A patients at day 3 and day 7 when compared to the baseline, and this was significant at P < 0.001. A significant negative correlation was also observed between mean latency of MDI initiation from the symptom onset and mean cough score reduction. Analysis of the proportion of patients prescribed medications to treat cough showed that overall, 10.78% did not require these, with a greater proportion in group A compared to group B. Conclusion: Patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) COVID-19 who were treated with ICS-LABA MDI along with usual care benefitted significantly in terms of symptom reduction compared to usual care.
Ethical approval The study has been approved by the Ethics Committee vide letter no HREC-AARC/13.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest There are no conflicts of interest.
References
Anderson, Formoterol: Pharmacology, molecular basis of agonism, and mechanism of long duration of a highly potent and selective beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist bronchodilator, Life Sci
Becker, Hom, Villasis-Keever, Der Wouden, Beta2-agonists for acute cough or a clinical diagnosis of acute bronchitis, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Finney, Glanville, Farne, Aniscenko, Fenwick et al., Inhaled corticosteroids downregulate the SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 in COPD through suppression of type I interferon, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Footitt, Johnston, Cough and viruses in airways disease: Mechanisms, Pulm Pharmacol Ther
Freund-Michel, Birrell, Giembycz, Hele, Haj-Yahia et al., Beta(2)-agonists block tussive responses in pigs via an atypical cAMP-dependent pathway, Eur Respir J
Gibson, Saltos, Fakes, Acute anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide in asthma: A randomized controlled trial, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Grant, Geoghegan, Arbyn, Mohammed, Mcguinness et al., The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries, PLoS One
Griesel, Wagner, Mikolajewska, Stegemann, Fichtner et al., Inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Hsu, Stone, Worsdell, Busst, Chung, Coughing frequency in patients with persistent cough: Assessment using a 24 hour ambulatory recorder, Eur Respir J
Jacoby, Virus-induced asthma attacks, JAMA
Jeon, Ko, Lee, Choi, Byun et al., Identification of antiviral drug candidates against SARS-CoV-2 from FDA-approved drugs, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Jintana, Prasertsopon, Puthavathana, Lerdsamran, Antiviral effect in association with anti-apoptosis and anti-autophagy of repurposing formoterol fumarate dihydrate on enterovirus A71-infected neuronal cells, Virus Res
Korn, Jerre, Brattsand, Effects of formoterol and budesonide on GM-CSF and IL-8 secretion by triggered human bronchial epithelial cells, Eur Respir J
Lipworth, Kuo, Lipworth, Chan, Inhaled Corticosteroids and COVID-19, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Mahmoudvand, Shokri, Interactions between SARS coronavirus 2 papain-like protease and immune system: A potential drug target for the treatment of COVID-19, Scand J Immunol
Peters, Sajuthi, Deford, Christenson, Rios et al., NHLBI severe asthma research program-3 investigators. COVID-19-related genes in sputum cells in asthma: Relationship to demographic features and corticosteroids, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Ramakrishnan, Nicolau, Jr, Langford, Mahdi et al., Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): A phase 2, open-label, andomized controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Sulaiman, Aljuhani, Aamer, Shaya, Shaya et al., The role of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) in critically Ill patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, cohort study, J Intensive Care Med
Wallin, Sandstrom, Soderberg, Howarth, Lundbäck et al., The effects of regular inhaled formoterol, budesonide and placebo on mucosal inflammation and clinical indices in mild asthma, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Yamaya, Nishimura, Deng, Sugawara, Watanabe et al., Inhibitory effects of glycopyrronium, formoterol, and budesonide on coronavirus HcoV-229E replication and cytokine production by primary cultures of human nasal and tracheal epithelial cells, Respir Investig
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors formortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_268_22",
"ISSN": [
"0970-2113"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_268_22",
"alternative-id": [
"370941"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samajdar",
"given": "ShamboSamrat",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mukherjee",
"given": "Shatavisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moitra",
"given": "Saibal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pal",
"given": "Jyotirmoy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "Shashank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tripathi",
"given": "SantanuKumar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Lung India",
"container-title-short": "Lung India",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T15:18:22Z",
"timestamp": 1677683902000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T16:32:48Z",
"timestamp": 1677688368000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-02T05:25:46Z",
"timestamp": 1677734746377
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"member": "2581",
"original-title": [],
"page": "107",
"prefix": "10.4103",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"publisher": "Medknow",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0234765",
"article-title": "The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0234765",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors formortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pupt.2008.12.022",
"article-title": "Cough and viruses in airways disease: Mechanisms",
"author": "Footitt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Pulm Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-3",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "Beta2-agonists for acute cough or a clinical diagnosis of acute bronchitis",
"author": "Becker",
"first-page": "CD001726",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.00034009",
"article-title": "Beta(2)-agonists block tussive responses in guinea pigs via an atypical cAMP-dependent pathway",
"author": "Freund-Michel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198692",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect in association with anti-apoptosis and anti-autophagy of repurposing formoterol fumarate dihydrate on enterovirus A71-infected neuronal cells",
"author": "Jintana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198692",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0024-3205(93)90729-M",
"article-title": "Formoterol: Pharmacology, molecular basis of agonism, and mechanism of long duration of a highly potent and selective beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist bronchodilator",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2145",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-7",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.94.07071246",
"article-title": "Coughing frequency in patients with persistent cough: Assessment using a 24 hour ambulatory recorder",
"author": "Hsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1246",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-8",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) in critically Ill patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, cohort study",
"author": "Al",
"first-page": "248",
"journal-title": "J Intensive Care Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0",
"article-title": "Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): A phase 2, open-label, andomized controlled trial",
"author": "Ramakrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "763",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Griesel",
"first-page": "CD015125",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-2000LE",
"article-title": "Inhaled Corticosteroids and COVID-19",
"author": "Lipworth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "899",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202003-0821OC",
"article-title": "NHLBI severe asthma research program-3 investigators.COVID-19–related genes in sputum cells in asthma: Relationship to demographic features and corticosteroids",
"author": "Peters",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.09.034",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-14",
"unstructured": "Finney LJ, Glanville N, Farne H, Aniscenko J, Fenwick P, Kemp SV, et al. Inhaled corticosteroids downregulate the SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 in COPD through suppression of type I interferon. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2021;147:510-9.e5."
},
{
"article-title": "Identification of antiviral drug candidates against SARS-CoV-2 from FDA-approved drugs",
"author": "Jeon",
"first-page": "e00819",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Interactions between SARS coronavirus 2 papain-like protease and immune system: A potential drug target for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Mahmoudvand",
"first-page": "e13044",
"journal-title": "Scand J Immunol",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.287.6.755",
"article-title": "B.Virus-induced asthma attacks",
"author": "Jacoby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-17",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"article-title": "The effects of regular inhaled formoterol, budesonide and placebo on mucosal inflammation and clinical indices in mild asthma",
"author": "Wallin",
"first-page": "79",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-18",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.163.1.9807061",
"article-title": "Acute anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide in asthma: A randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Gibson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-19",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of formoterol and budesonide on GM-CSF and IL-8 secretion by triggered human bronchial epithelial cells.Eur Respir J",
"author": "Korn",
"first-page": "1070",
"journal-title": "",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-20",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.resinv.2019.12.005",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effects of glycopyrronium, formoterol, and budesonide on coronavirus HcoV-229E replication and cytokine production by primary cultures of human nasal and tracheal epithelial cells",
"author": "Yamaya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Respir Investig",
"key": "key-10.4103/0970-2113.370941-21",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_268_22"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness of budesonide formoterol fixed-dose combination MDI in reducing cough symptoms in COVID-19 patients: A real-world evidence study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "40"
}