Reversal of SARS-CoV2-Induced Hypoxia by Nebulized Sodium Ibuprofenate in a Compassionate Use Program
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2, NCT04382768, Aug 2021
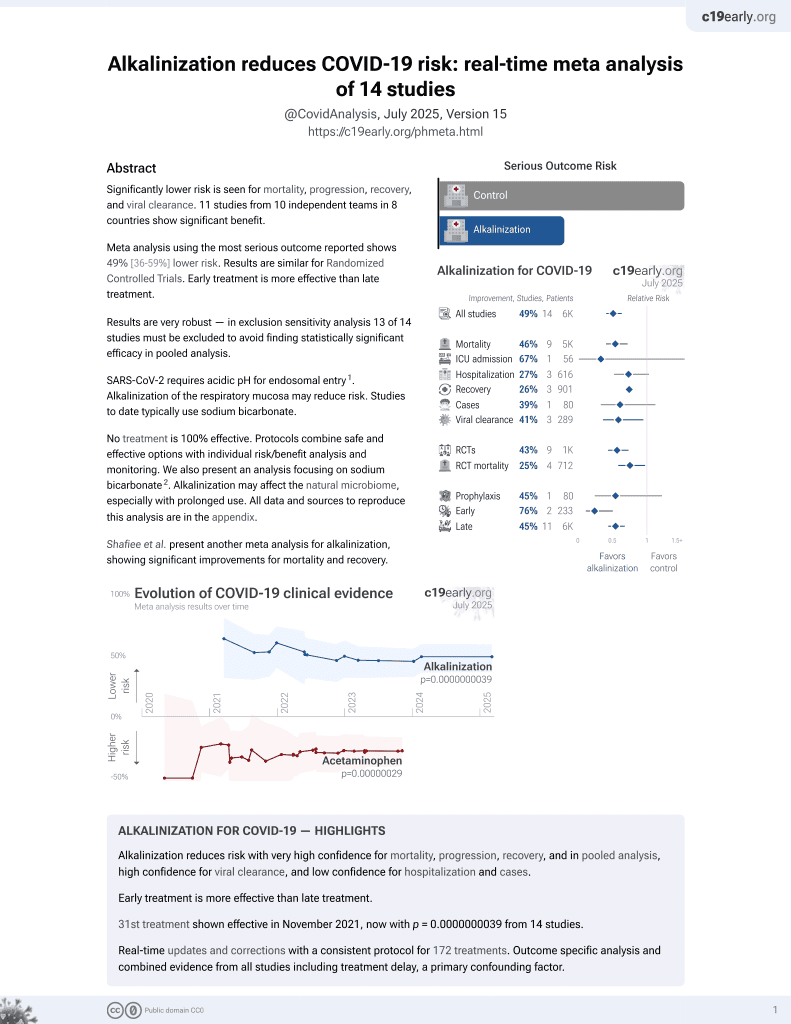
32nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0000000039 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
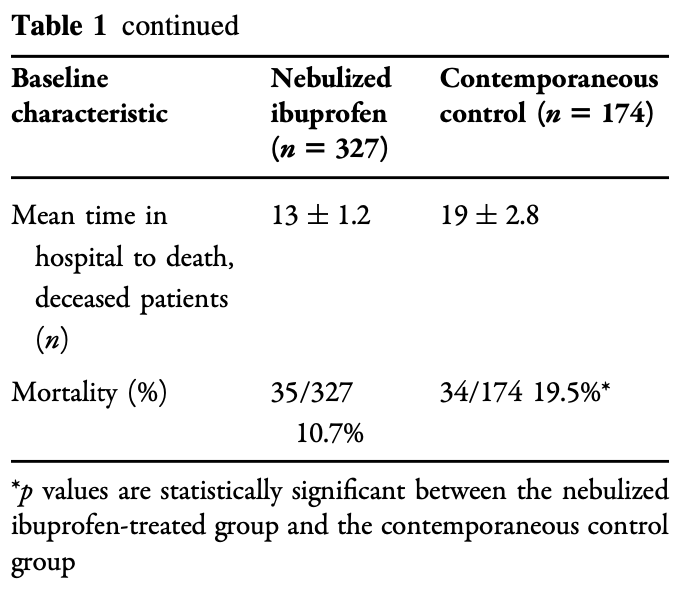
Retrospective 383 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Argentina showing signifcantly lower mortality and shorter hospital stay with nebulized sodium ibuprofenate compared to 195 contemporaneous controls.
The treatment appears to be the same as detailed in1, which reports a pH of 8.5. Kreutzberger et al. showed that SARS-CoV-2 requires an acidic pH (between 6.2-6.8) for membrane fusion and cell entry, even when the viral spike protein is primed by proteases like TMPRSS2. Efficacy seen here may be more due to alkalinization, which shows more consistent higher efficacy than ibuprofen in studies to date.
Baseline SpO2 was significantly different for the patients on mechanical ventilation at baseline.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
Study covers ibuprofen and alkalinization.
|
risk of death, 45.2% lower, RR 0.55, p = 0.009, treatment 35 of 327 (10.7%), control 34 of 174 (19.5%), NNT 11, patients not on mechanical ventilation at baseline.
|
|
risk of death, 75.7% lower, RR 0.24, p < 0.001, treatment 11 of 56 (19.6%), control 17 of 21 (81.0%), NNT 1.6, patients on mechanical ventilation at baseline.
|
|
hospitalization time, 13.5% lower, relative time 0.86, p < 0.001, treatment mean 11.5 (±0.3) n=327, control mean 13.3 (±0.9) n=174, patients not on mechanical ventilation at baseline.
|
|
hospitalization time, 17.8% lower, relative time 0.82, p < 0.001, treatment mean 14.8 (±1.4) n=56, control mean 18.0 (±5.6) n=21, patients on mechanical ventilation at baseline.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Salva et al., 30 Aug 2021, retrospective, Argentina, peer-reviewed, 26 authors, study period 4 April, 2020 - 31 October, 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with sodium ibuprofenate) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial NCT04382768 (history).
Contact: garcia.nestor@conicet.gov.ar.
Reversal of SARS-CoV2-Induced Hypoxia by Nebulized Sodium Ibuprofenate in a Compassionate Use Program
Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2
Introduction: Sodium ibuprofenate in hypertonic saline (NaIHS) administered directly to the lungs by nebulization and inhalation has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, with the potential to deliver these benefits to hypoxic patients. We describe a compassionate use program that offered this therapy to hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Methods: NaIHS (50 mg ibuprofen, tid) was provided in addition to standard of care (SOC) to hospitalized COVID-19 patients until oxygen saturation levels of[94% were achieved on ambient air. Patients wore a containment hood to diminish aerosolization. Outcome data from participating patients treated at multiple hospitals in Argentina between April 4 and October 31, 2020, are summarized.
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Baraniuk, Lundgren, Mizoguchi, Peden, Gawin et al., Bradykinin and respiratory mucous membranes: analysis of bradykinin binding site distribution and secretory responses in vitro and in vivo, Am Rev Respir Dis
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Brito-Azevedo, Pinto, Preta, Bouskela, SARS-CoV-2 infection causes pulmonary shunt by vasodilatation, J Med Virol
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Azevedo, Veiga et al., Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Das, Can bioactive lipids inactivate coronavirus (COVID-19)?, Arch Med Res
Dill, Patel, Yang, Bachoo, Powell et al., A molecular mechanism for ibuprofen-mediated RhoA inhibition in neurons, J Neurosci
Freeman, Peek, Becker, Smith, Denison, Coronaviruses induce entry-independent, continuous macropinocytosis, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.01340-14
Garcı ´a, Porta, Alasino, Mun ˜oz, Se et al., Ibuprofen, a traditional drug that may impact the course of COVID-19 new effective formulation in nebulizable solution, Med Hypotheses
Garvin, Alvarez, Miller, Prates, Walker et al., A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm, Elife
Gholamreza-Fahimi, Bisha, Hahn, Straßen, Krybus et al., Cyclooxygenase activity in bradykinin-induced dermal extravasation. A study in mice and humans, Biomed Pharmacother
Hammock, Gilligan, Panigrahy, Eicosanoids, Am J Pathol
Konstan, Byard, Hoppel, Davis, Effect of high-dose ibuprofen in patients with cystic fibrosis, N Engl J Med
Magro, Mulvey, Berlin, Nuovo, Salvatore et al., Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases, Transl Res
Mccullagh, Nelder, Generalized linear models (monographs on statistics and applied probability)
Mcfadyen, Stevens, Peter, The emerging threat of (Micro)thrombosis in COVID-19 and its therapeutic implications, Circ Res
Mcintyre, Philp, Inwood, Effect of ibuprofen on platelet function in normal subjects and hemophiliac patients, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Mun ˜oz, Alasino, Garro, Heredia, Garcı ´a et al., High concentrations of sodium chloride improve microbicidal activity of ibuprofen against common cystic fibrosis pathogens, Pharmaceuticals
Serhan, Systems approach to inflammation resolution: identification of novel anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediators, J Thromb Haemost
Shi, Han, Jiang, Cao, Alwalid et al., Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-study, Lancet Infect Dis
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, Beruto, Vallone et al., A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in COVID-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Smith, Redfern, Pimentel, Collins, Malycha, The National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2), Clin Med
Stone, Frigault, Serling-Boyd, Fernandes, Harvey et al., Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Swaine, Dittmar, CDC42 use in viral cell entry processes by RNA viruses, Viruses
Tsubouchi, Mukai, Kawahito, Yamada, Kohno et al., Meloxicam inhibits the growth of non-small cell lung cancer, Anticancer Res
Walsh, Low-dose aspirin: treatment for the imbalance of increased thromboxane and decreased prostacyclin in preeclampsia, Am J Perinatol
Zamudio-Meza, Castillo-Alvarez, Gonza ´lez-Bonilla, Meza, Cross-talk between Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases regulates formation of filopodia required for dengue virus type-2 entry into HMEC-1 cells, J Gen Virol
Zhou, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can lower amyloidogenic A 42 by inhibiting rho, Science
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2",
"ISSN": [
"2193-8229",
"2193-6382"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2",
"alternative-id": [
"527"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "14 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "12 August 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "30 August 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Funding",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "This work was supported by funds from the Química Luar SRL, who provided NaIHS under compassionate use. This funding body had no role in: the design of the study; the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; and the writing of the manuscript. The journal’s Rapid Service Fee was funded by the Química Luar SRL."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Authorship",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Authorship Contributions",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Conceptualization: Pablo Alexis Doreski, Germán Ambasch, Luis Alberto Argañarás, Nicolás Martínez Ríos, Dante Miguel Beltramo and Néstor Horacio García. Data curation: Sonia Edith Muñoz, Mariana Natalia Carrillo, Daniela Josefina Porta, Hernán Alejandro Pérez, Néstor Horacio García. Formal analysis: Pablo Alexis Doreski, Sonia Edith Muñoz, Mariana Natalia Carrillo, Daniela Josefina Porta, Hernán Alejandro Pérez, Dante Miguel Beltramo, Néstor Horacio García. Funding acquisition: Luis Alberto Argañarás, Nicolás Martínez Ríos and Galia Ines Kalayan. Investigation: Oscar Salva, Celia Sara Giler, Dario Conrado Quinodoz, Lucia Guadalupe Guzmán, Germán Ambasch, Esteban Coscia, Jorge Luis Tambini Díaz, Germán David Bueno, Jorge Oscar Fandi, Miriam Angélica Maldonado, Leandro Eugenio Peña Chiappero, Fernando Fournier, Hernán Alejandro Pérez, Mauro Andrés Quiroga, Javier Agustín Sala Mercado, Marcelo Alejandro Beltrán, Carlos Martínez Picco, Methodology: Luis Alberto Argañarás, Nicolás Martínez Ríos, Dante Miguel Beltramo, Néstor Horacio García. Project administration: Luis Alberto Argañarás, Nicolás Martínez Ríos, Galia Inés Kalayan. Resources: Luis Alberto Argañarás and Nicolás Martínez Ríos. Supervision: Luis Alberto Argañarás, Nicolás Martínez Ríos, Néstor Horacio García. Software: Hernán Alejandro Pérez. Validation: Oscar Salva, Pablo Alexis Doreski, Néstor Horacio García. Visualization: Néstor Horacio García. Writing—original draft: Néstor Horacio García. Writing—review and editing: Pablo Alexis Doreski, Dario Conrado Quinodoz, Luis Alberto Argañarás, Nicolás Martínez Ríos, Dante Miguel Beltramo, Néstor Horacio García."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Disclosures",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "All named authors confirm that they have no conflicts of interest to declare."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Compliance with Ethics Guidelines",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 5,
"value": "Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Independent Ethics Committees and district regulatory agencies of Córdoba and Mendoza Provinces for the compassionate use of Luarprofeno<sup>®</sup> (sodium ibuprofenate in hypertonic saline, or NaIHS, for nebulization). The program was carried out in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki for Buenos Aires. All participating individuals were ≥ age 18 and provided written informed consent, obtained by the treating physician."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Data Availability",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 6,
"value": "The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author in response to reasonable requests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salva",
"given": "Oscar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doreski",
"given": "Pablo A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giler",
"given": "Celia S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quinodoz",
"given": "Dario C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guzmán",
"given": "Lucia G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muñoz",
"given": "Sonia E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carrillo",
"given": "Mariana N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Porta",
"given": "Daniela J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ambasch",
"given": "Germán",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coscia",
"given": "Esteban",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diaz",
"given": "Jorge L. Tambini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bueno",
"given": "Germán D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fandi",
"given": "Jorge O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maldonado",
"given": "Miriam A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peña Chiappero",
"given": "Leandro E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fournier",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pérez",
"given": "Hernán A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quiroga",
"given": "Mauro A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sala Mercado",
"given": "Javier A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martínez Picco",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beltrán",
"given": "Marcelo Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Argañarás",
"given": "Luis A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ríos",
"given": "Nicolás Martínez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalayan",
"given": "Galia I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beltramo",
"given": "Dante M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9057-9030",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "García",
"given": "Néstor H.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04382768",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases and Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Infect Dis Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-30T10:03:15Z",
"timestamp": 1630317795000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-07T14:15:01Z",
"timestamp": 1636294501000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Quimica Luar SRL"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-31T20:13:07Z",
"timestamp": 1698783187602
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630281600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630281600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2511-2524",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "527_CR1",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard [Internet]. https://covid19.who.int. Accessed 2021 June 29."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"author": "The RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR2",
"unstructured": "The RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):693–704.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "527_CR3",
"unstructured": "Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19—Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(6):497–511."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"author": "VA Simonovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "619",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR4",
"unstructured": "Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, Beruto MV, Vallone MG, Vázquez C, et al. A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in COVID-19 severe pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(7):619–29.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"author": "B Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1787",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR5",
"unstructured": "Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, et al. A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(19):1787–99.",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"author": "AB Cavalcanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2041",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR6",
"unstructured": "Cavalcanti AB, Zampieri FG, Rosa RG, Azevedo LCP, Veiga VC, Avezum A, et al. Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(21):2041–52.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028836",
"author": "JH Stone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2333",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR7",
"unstructured": "Stone JH, Frigault MJ, Serling-Boyd NJ, Fernandes AD, Harvey L, Foulkes AS, et al. Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(24):2333–44.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30086-4",
"author": "H Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "425",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "527_CR8",
"unstructured": "Shi H, Han X, Jiang N, Cao Y, Alwalid O, Gu J, et al. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(4):425–34.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015432",
"author": "M Ackermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "120",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR9",
"unstructured": "Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(2):120–8.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.59177",
"author": "MR Garvin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e59177",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "527_CR10",
"unstructured": "Garvin MR, Alvarez C, Miller JI, Prates ET, Walker AM, Amos BK, et al. A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm. Elife. 2020;9:e59177.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26342",
"author": "A Brito-Azevedo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "573",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "527_CR11",
"unstructured": "Brito-Azevedo A, Pinto EC, Cata Preta CGA, Bouskela E. SARS-CoV-2 infection causes pulmonary shunt by vasodilatation. J Med Virol. 2021;93(1):573–5.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.706",
"author": "JN Baraniuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "706",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am Rev Respir Dis",
"key": "527_CR12",
"unstructured": "Baraniuk JN, Lundgren JD, Mizoguchi H, Peden D, Gawin A, Merida M, et al. Bradykinin and respiratory mucous membranes: analysis of bradykinin binding site distribution and secretory responses in vitro and in vivo. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;141(3):706–14.",
"volume": "141",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109797",
"author": "E Gholamreza-Fahimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109797",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "527_CR13",
"unstructured": "Gholamreza-Fahimi E, Bisha M, Hahn J, Straßen U, Krybus M, Khosravani F, et al. Cyclooxygenase activity in bradykinin-induced dermal extravasation. A study in mice and humans. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;123:109797.",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317447",
"author": "JD McFadyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "571",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "527_CR14",
"unstructured": "McFadyen JD, Stevens H, Peter K. The emerging threat of (Micro)thrombosis in COVID-19 and its therapeutic implications. Circ Res. 2020;127(4):571–87.",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007",
"author": "C Magro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Res",
"key": "527_CR15",
"unstructured": "Magro C, Mulvey JJ, Berlin D, Nuovo G, Salvatore S, Harp J, et al. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases. Transl Res. 2020;220:1–13.",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt1978245616",
"author": "BA Mcintyre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "616",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "527_CR16",
"unstructured": "Mcintyre BA, Philp RB, Inwood MJ. Effect of ibuprofen on platelet function in normal subjects and hemophiliac patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978;24(5):616–21.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2007-999562",
"author": "S Walsh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "124",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "Am J Perinatol",
"key": "527_CR17",
"unstructured": "Walsh S. Low-dose aspirin: treatment for the imbalance of increased thromboxane and decreased prostacyclin in preeclampsia. Am J Perinatol. 1989;6(02):124–32.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.06.010",
"author": "BD Hammock",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1782",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Am J Pathol",
"key": "527_CR18",
"unstructured": "Hammock BD, Wang W, Gilligan MM, Panigrahy D. Eicosanoids. Am J Pathol. 2020;190(9):1782–8.",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03396.x",
"author": "CN Serhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "527_CR19",
"unstructured": "Serhan CN. Systems approach to inflammation resolution: identification of novel anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediators. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7:44–8.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.03.004",
"author": "UN Das",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "282",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "527_CR20",
"unstructured": "Das UN. Can bioactive lipids inactivate coronavirus (COVID-19)? Arch Med Res. 2020;51(3):282–6.",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph11020047",
"author": "A Muñoz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "47",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals",
"key": "527_CR21",
"unstructured": "Muñoz A, Alasino R, Garro A, Heredia V, García N, Cremonezzi D, et al. High concentrations of sodium chloride improve microbicidal activity of ibuprofen against common cystic fibrosis pathogens. Pharmaceuticals. 2018;11(2):47.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v7122955",
"author": "T Swaine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6526",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "527_CR22",
"unstructured": "Swaine T, Dittmar M. CDC42 use in viral cell entry processes by RNA viruses. Viruses. 2015;7(12):6526–36.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01340-14",
"author": "MC Freeman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "mBio [Internet]",
"key": "527_CR23",
"unstructured": "Freeman MC, Peek CT, Becker MM, Smith EC, Denison MR. Coronaviruses induce entry-independent, continuous macropinocytosis. mBio [Internet]. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01340-14.",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.014159-0",
"author": "H Zamudio-Meza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2902",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Gen Virol",
"key": "527_CR24",
"unstructured": "Zamudio-Meza H, Castillo-Alvarez A, González-Bonilla C, Meza I. Cross-talk between Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases regulates formation of filopodia required for dengue virus type-2 entry into HMEC-1 cells. J Gen Virol. 2009;90(12):2902–11.",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1090154",
"author": "Y Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1215",
"issue": "5648",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "527_CR25",
"unstructured": "Zhou Y. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can lower amyloidogenic A 42 by inhibiting rho. Science. 2003;302(5648):1215–7.",
"volume": "302",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5045-09.2010",
"author": "J Dill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "963",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Neurosci",
"key": "527_CR26",
"unstructured": "Dill J, Patel AR, Yang X-L, Bachoo R, Powell CM, Li S. A molecular mechanism for ibuprofen-mediated RhoA inhibition in neurons. J Neurosci. 2010;30(3):963–72.",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110079",
"author": "NH García",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110079",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "527_CR27",
"unstructured": "García NH, Porta DJ, Alasino RV, Muñoz SE, Beltramo DM. Ibuprofen, a traditional drug that may impact the course of COVID-19 new effective formulation in nebulizable solution. Med Hypotheses. 2020;144:110079.",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmedicine.19-3-260",
"author": "GB Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "260",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Med",
"key": "527_CR28",
"unstructured": "Smith GB, Redfern OC, Pimentel MA, Gerry S, Collins GS, Malycha J, et al. The National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2). Clin Med. 2019;19(3):260–260.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"author": "P McCullagh",
"edition": "2",
"key": "527_CR29",
"unstructured": "McCullagh P, Nelder JA. Generalized linear models (monographs on statistics and applied probability). 2nd ed. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC; 1998.",
"volume-title": "Generalized linear models (monographs on statistics and applied probability)",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"author": "JH Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR30",
"unstructured": "Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(19):1813–26.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199503303321303",
"author": "MW Konstan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "848",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "527_CR31",
"unstructured": "Konstan MW, Byard PJ, Hoppel CL, Davis PB. Effect of high-dose ibuprofen in patients with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(13):848–54.",
"volume": "332",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"author": "Y Tsubouchi",
"first-page": "2867",
"issue": "5A",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res",
"key": "527_CR32",
"unstructured": "Tsubouchi Y, Mukai S, Kawahito Y, Yamada R, Kohno M, Inoue K, et al. Meloxicam inhibits the growth of non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2000;20(5A):2867–72.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2000"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Reversal of SARS-CoV2-Induced Hypoxia by Nebulized Sodium Ibuprofenate in a Compassionate Use Program",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "10"
}
salva