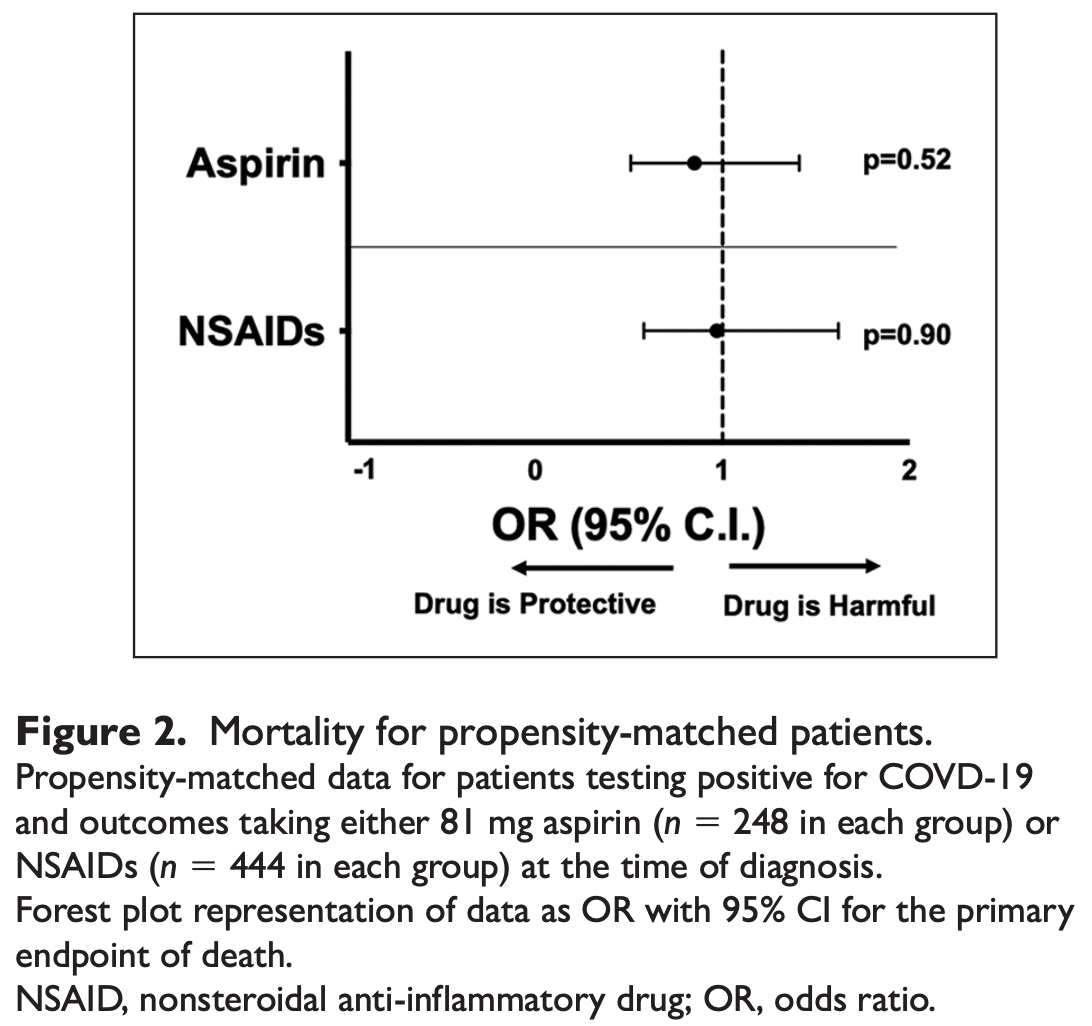
Effect of aspirin on short-term outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
et al., Vascular Medicine, doi:10.1177/1358863X211012754, May 2021
PSM retrospective 1,994 PCR+ patients in the USA, not showing a significant difference in mortality with aspirin treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 13.2% lower, RR 0.87, p = 0.53, treatment 33 of 248 (13.3%), control 38 of 248 (15.3%), NNT 50.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sahai et al., 19 May 2021, retrospective, propensity score matching, USA, peer-reviewed, 18 authors.
Effect of aspirin on short-term outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
Vascular Medicine, doi:10.1177/1358863x211012754
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 is an ongoing viral pandemic marked by increased risk of thrombotic events. However, the role of platelets in the elevated observed thrombotic risk in COVID-19 and utility of antiplatelet agents in attenuating thrombosis is unknown. We aimed to determine if the antiplatelet effect of aspirin may mitigate risk of myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, and venous thromboembolism in COVID-19. We evaluated 22,072 symptomatic patients tested for COVID-19. Propensity-matched analyses were performed to determine if treatment with aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) affected thrombotic outcomes in COVID-19. Neither aspirin nor NSAIDs affected mortality in COVID-19. Thus, aspirin does not appear to prevent thrombosis and death in COVID-19. The mechanisms of thrombosis in COVID-19, therefore, appear distinct and the role of platelets as direct mediators of SARS-CoV-2-mediated thrombosis warrants further investigation.
Declaration of conflicting interests The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Supplementary material The supplementary material is available online with the article.
References
Barnes, Adrover, Baxter-Stoltzfus, Targeting potential drivers of COVID-19: Neutrophil extracellular traps, J Exp Med
Barrett, Lee, Xia, Platelet and vascular biomarkers associate with thrombosis and death in coronavirus disease, Circ Res
Bekelis, Missios, Ahmad, Ischemic stroke occurs less frequently in patients with COVID-19: A multicenter cross-sectional study, Stroke
Bertram, Heurich, Lavender, Influenza and SARS-coronavirus activating proteases TMPRSS2 and HAT are expressed at multiple sites in human respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, PLoS One
Cameron, Ture, Mickelsen, Platelet extracellular regulated protein kinase 5 is a redox switch and triggers maladaptive platelet responses and myocardial infarct expansion, Circulation
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Anesth Analg
Der Thüsen, Van Bommel, Kros, Case report: A fatal combination of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with extensive pulmonary microvascular damage in COVID-19 pneumonia, J Hematopathol
Ding, Vanderweele, Sensitivity analysis without assumptions, Epidemiology
Elbadawi, Elgendy, Sahai, Incidence and outcomes of thrombotic events in symptomatic patients with COVID-19, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol
Ellul, Benjamin, Singh, Neurological associations of COVID-19, Lancet Neurol
Erlich, Talmor, Cartin-Ceba, Prehospitalization antiplatelet therapy is associated with a reduced incidence of acute lung injury: A population-based cohort study, Chest
Giollo, Adami, Gatti, Coronavirus disease 19 (Covid-19) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), Ann Rheum Dis
Goshua, Pine, Meizlish, Endotheliopathy in COVID-19-associated coagulopathy: Evidence from a single-centre, cross-sectional study, Lancet Haematol
Group, Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J Pathol
Harmer, Gilbert, Borman, Quantitative mRNA expression profiling of ACE 2, a novel homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme, FEBS Lett
Haynes, Wright, Gadd, Is aspirin a prodrug for antioxidant and cytokine-modulating oxymetabolites?, Agents Actions
He, Mäe, Sun, Pericyte-specific vascular expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 -Implications for microvascular inflammation and hypercoagulopathy in COVID-19 patients, bioRxiv
Helms, Tacquard, Severac, High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study, Intensive Care Med
Hikmet, Méar, Edvinsson, The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues, Mol Syst Biol
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Hottz, Azevedo-Quintanilha, Palhinha, Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19, Blood
Hu, Chang, Zhang, Platelets express activated P2Y12 receptor in patients with diabetes mellitus, Circulation
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19, Thromb Res
Kor, Carter, Park, Effect of aspirin on development of ARDS in at-risk patients presenting to the emergency department: The LIPS-A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Koupenova, Corkrey, Vitseva, The role of platelets in mediating a response to human influenza infection, Nat Commun
Li, Thomas, Li, Addressing extreme propensity scores via the overlap weights, Am J Epidemiol
Liang, Feng, Rao, Diarrhoea may be underestimated: A missing link in 2019 novel coronavirus, Gut
Manne, Denorme, Middleton, Platelet gene expression and function in COVID-19 patients, Blood
Merkler, Parikh, Mir, Risk of ischemic stroke in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vs patients with influenza, JAMA Neurol
Mitra, Reiter, A comparison of two methods of estimating propensity scores after multiple imputation, Stat Methods Med Res
Nassa, Giurato, Cimmino, Splicing of platelet resident pre-mRNAs upon activation by physiological stimuli results in functionally relevant proteome modifications, Sci Rep
Nicolai, Leunig, Brambs, Immunothrombotic dysregulation in COVID-19 pneumonia is associated with respiratory failure and coagulopathy, Circulation
Qi, Qian, Zhang, Single cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and receptors of human coronaviruses, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Rovas, Osiaevi, Buscher, Microvascular dysfunction in COVID-19: The MYSTIC study, Angiogenesis
Schmidt, Morrell, Ling, The platelet phenotype in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction is different from non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, Transl Res
Shahjouei, Naderi, Li, Risk of stroke in hospitalized SARS-CoV-2 infected patients: A multinational study, EBioMedicine
Shang, Wan, Luo, Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Sharif-Askari, Sharif-Askari, Alabed, Airways expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 is lower in children than adults and increases with smoking and COPD, Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev
Skendros, Mitsios, Chrysanthopoulou, Complement and tissue factor-enriched neutrophil extracellular traps are key drivers in COVID-19 immunothrombosis, J Clin Invest
Smith, Emsley, Gavin, Peak plasma interleukin-6 and other peripheral markers of inflammation in the first week of ischaemic stroke correlate with brain infarct volume, stroke severity and long-term outcome, BMC Neurol
Sungnak, Huang, Bécavin, SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes, Nat Med
Talasaz, Sadeghipour, Kakavand, Recent randomized trials of antithrombotic therapy for patients with COVID-19: JACC State-of-the-Art Review, J Am Coll Cardiol
Veras, Pontelli, Silva, SARS-CoV-2-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps mediate COVID-19 pathology, J Exp Med
Wang, Li, Yin, Excessive neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, Front Immunol
Zaid, Puhm, Allaeys, Platelets can associate with SARS-CoV-2 RNA and are hyperactivated in COVID-19, Circ Res
Zhang, Liu, Wang, SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19, J Hematol Oncol
Zhao, Zhao, Wang, Single-cell RNA expression profiling of ACE2, the receptor of SARS-CoV-2, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Zuo, Yalavarthi, Shi, Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, JCI Insight
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1358863x211012754",
"ISSN": [
"1358-863X",
"1477-0377"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1358863X211012754",
"abstract": "<jats:p> Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 is an ongoing viral pandemic marked by increased risk of thrombotic events. However, the role of platelets in the elevated observed thrombotic risk in COVID-19 and utility of antiplatelet agents in attenuating thrombosis is unknown. We aimed to determine if the antiplatelet effect of aspirin may mitigate risk of myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, and venous thromboembolism in COVID-19. We evaluated 22,072 symptomatic patients tested for COVID-19. Propensity-matched analyses were performed to determine if treatment with aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) affected thrombotic outcomes in COVID-19. Neither aspirin nor NSAIDs affected mortality in COVID-19. Thus, aspirin does not appear to prevent thrombosis and death in COVID-19. The mechanisms of thrombosis in COVID-19, therefore, appear distinct and the role of platelets as direct mediators of SARS-CoV-2-mediated thrombosis warrants further investigation. </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/1358863X211012754"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Sahai",
"given": "Aditya",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1063-6291",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
},
{
"name": "Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bhandari",
"given": "Rohan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Godwin",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "McIntyre",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Chung",
"given": "Mina K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Iskandar",
"given": "Jean-Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kamran",
"given": "Hayaan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hariri",
"given": "Essa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Aggarwal",
"given": "Anu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Burton",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kalra",
"given": "Ankur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Bartholomew",
"given": "John R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
},
{
"name": "Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "McCrae",
"given": "Keith R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4248-781X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Elbadawi",
"given": "Ayman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Quantitative Health Science, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Bena",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Svensson",
"given": "Lars G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kapadia",
"given": "Samir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9616-1540",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Vascular Medicine, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine; Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
},
{
"name": "Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
},
{
"name": "Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cameron",
"given": "Scott J",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Vascular Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Vasc Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-19T18:25:19Z",
"timestamp": 1621448719000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-19T00:48:45Z",
"timestamp": 1652921325000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000050",
"award": [
"K08HL128856"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000050",
"award": [
"LRPHL120200"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000050",
"award": [
"R01 HL143402"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-01T02:28:53Z",
"timestamp": 1711938533846
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 25,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1621382400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1358863X211012754",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/1358863X211012754",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1358863X211012754",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "626-632",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr1-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.2730",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06062-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2003138117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.omtm.2020.05.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202001-0179LE",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0035876",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"author": "He L",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "bibr12-1358863X211012754",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03640-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.20209610",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-09607-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"author": "Zuo Y",
"first-page": "e138999",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "bibr17-1358863X211012754",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30216-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007214",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317703",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280212445945",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"author": "Li F",
"first-page": "250",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "bibr22-1358863X211012754",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/EDE.0000000000000457",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217598",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.015656",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026995",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317803",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2021.02.035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"author": "Elbadawi A",
"first-page": "545",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol",
"key": "bibr30-1358863X211012754",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20200652",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"author": "Wang J",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "bibr33-1358863X211012754",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20201129",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI141374",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr35-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048488",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr36-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12308-020-00423-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr37-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10456-020-09753-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr38-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr39-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.10-0891",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr40-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2016.6330",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr41-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30221-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr42-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102939",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr43-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031217",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr44-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2377-4-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr45-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01975714",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr46-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-020-00954-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr47-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2017.11.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr48-1358863X211012754"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-18985-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr49-1358863X211012754"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1358863X211012754"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of aspirin on short-term outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "26"
}