Promising clinical outcomes of nano‐curcumin treatment as an adjunct therapy in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: A randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled trial
et al., Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7844, IRCT20170128032241N3, Apr 2023
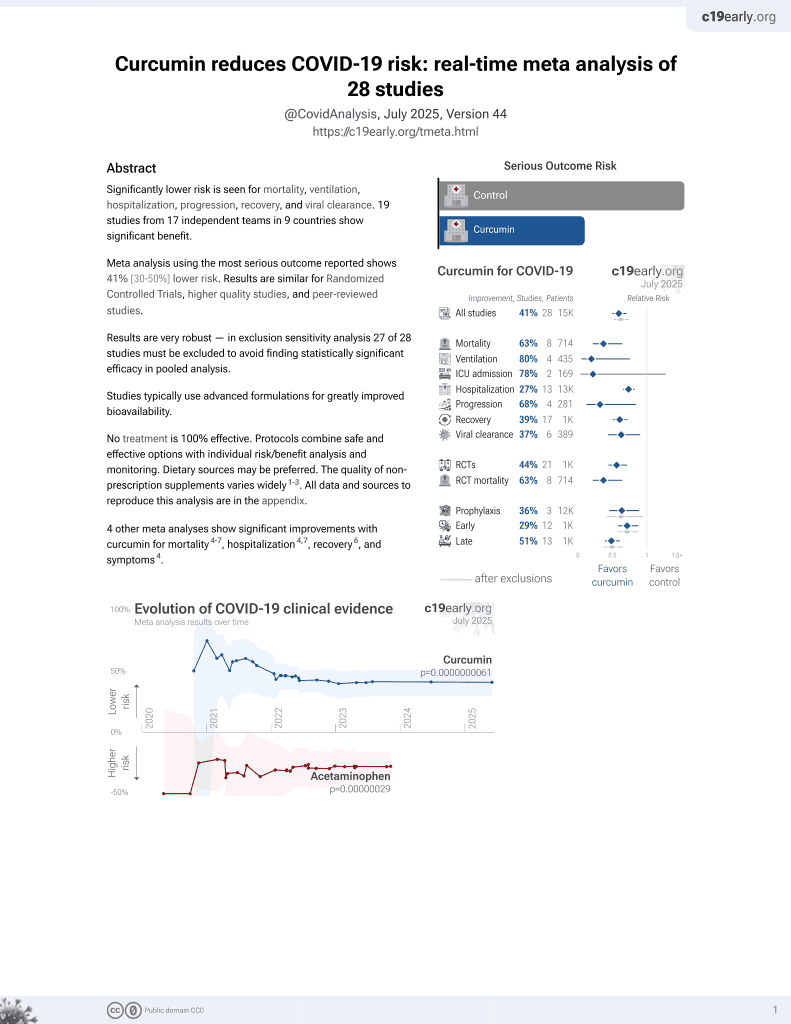
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
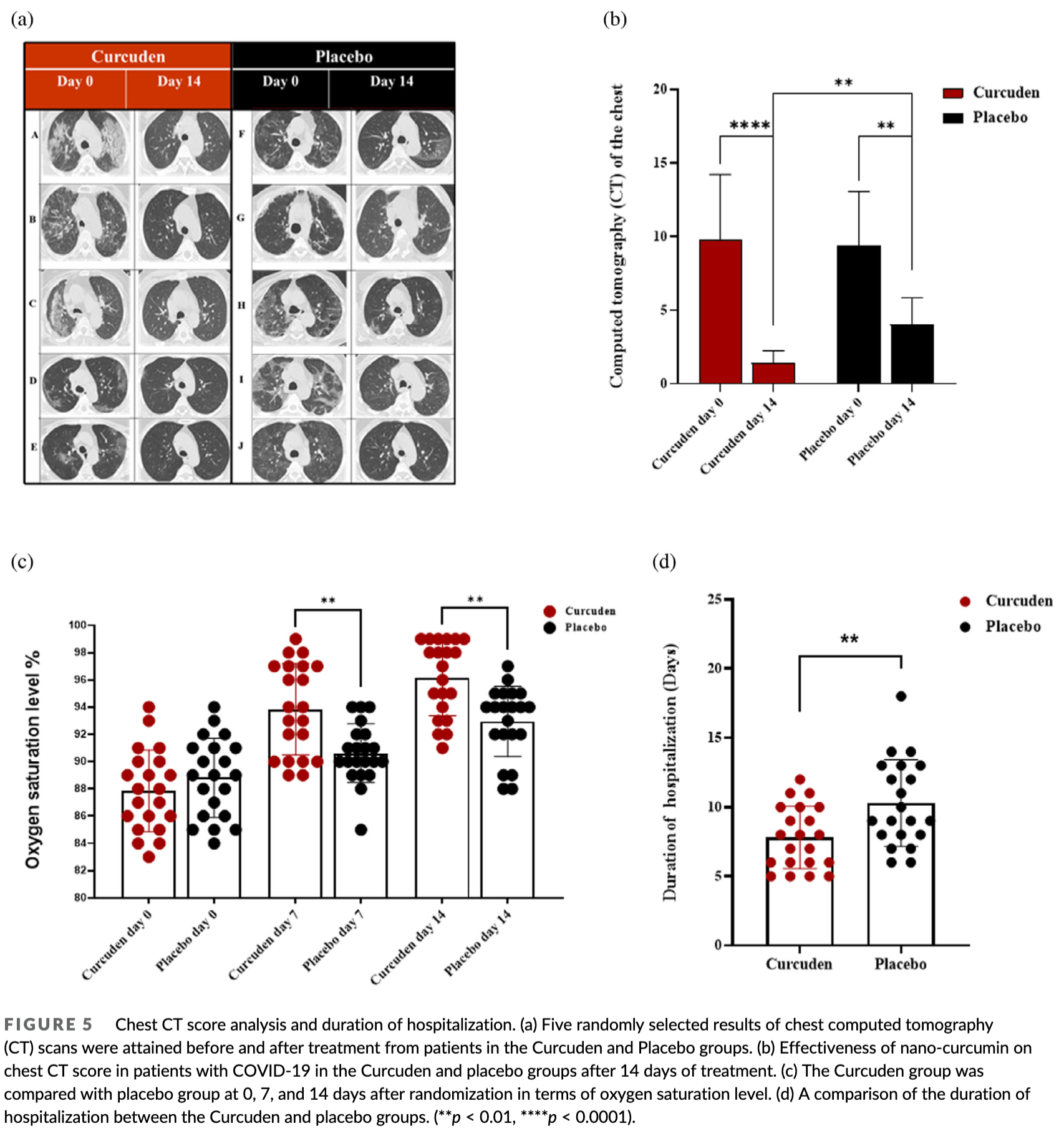
RCT 42 hospitalized moderate/severe COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing lower progression and improved recovery with nano-curcumin. Nano-curcumin 70mg bid for 14 days.
This is the 18th of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000022.
This is the 24th of 28 COVID-19 controlled studies for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000000061.
|
risk of progression, 92.3% lower, RR 0.08, p = 0.02, treatment 0 of 21 (0.0%), control 6 of 21 (28.6%), NNT 3.5, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
hospitalization time, 24.5% lower, relative time 0.75, p = 0.007, treatment mean 7.7 (±2.3) n=21, control mean 10.2 (±3.3) n=21.
|
|
relative chest CT score, 67.5% better, RR 0.33, p < 0.001, treatment mean 1.3 (±0.82) n=21, control mean 4.0 (±1.8) n=21, day 14.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.61, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 3 of 21 (14.3%), NNT 10, day 14, dyspnea/oxygen need.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 80.0% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.18, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 5 of 21 (23.8%), NNT 5.2, day 14, fever.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.04, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 7 of 21 (33.3%), NNT 3.5, day 14, cough.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 80.0% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.49, treatment 0 of 21 (0.0%), control 2 of 21 (9.5%), NNT 10, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 14, headache.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 75.0% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.34, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 4 of 21 (19.0%), NNT 7.0, day 14, fatigue.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 75.0% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.34, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 4 of 21 (19.0%), NNT 7.0, day 14, myalgia.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 21 (0.0%), control 1 of 21 (4.8%), NNT 21, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 14, diarrhea.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 21 (4.8%), control 2 of 21 (9.5%), NNT 21, day 14, inappetence.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 21 (0.0%), control 1 of 21 (4.8%), NNT 21, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 14, nausea.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sadeghizadeh et al., 29 Apr 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, trial IRCT20170128032241N3.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7844",
"ISSN": [
"0951-418X",
"1099-1573"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7844",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/ptr.7844"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2497-3152",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Genetics, Faculty of Biological Sciences Tarbiat Modares University Tehran Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sadeghizadeh",
"given": "Majid",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Genetics, Faculty of Biological Sciences Tarbiat Modares University Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Asadollahi",
"given": "Elahe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Genetics, Faculty of Biological Sciences Tarbiat Modares University Tehran Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Medicine, Institute of Medical Biotechnology National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (NIGEB) Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Jahangiri",
"given": "Babak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Firoozgar Medical & Educational Hospital Department of Internal Medicine School of Medicine Iran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Yadollahzadeh",
"given": "Mahdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Alborz Nanomed Tech Company Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Mohajeri",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cancer Control Research Center, Cancer Control Foundation Iran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Afsharpad",
"given": "Mandana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Resin and Additives Institute for Color Science and Technology Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Najafi",
"given": "Farhood",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonology Firouzgar Hospital, Iran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Rezaie",
"given": "Nader",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Firoozgar Medical & Educational Hospital Department of Internal Medicine School of Medicine Iran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Eskandari",
"given": "Mohana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Tavakoli‐Ardakani",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Feizabadi",
"given": "Faezeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cancer Control Research Center, Cancer Control Foundation Iran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary Medicine Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
},
{
"name": "Tobacco Control Research Center (TCRC) Iranian Anti‐tobacco Association, Iran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Masjedi",
"given": "Mohammad Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"container-title-short": "Phytotherapy Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-29T07:00:15Z",
"timestamp": 1682751615000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-29T07:01:12Z",
"timestamp": 1682751672000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100006485",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-30T04:25:49Z",
"timestamp": 1682828749749
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
29
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682726400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ptr.7844",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1",
"unstructured": "(FDA) U.S.f.a.d.a. (2022).Coronavirus (COVID‐19) | Drugs. [cited 12/22/2022]; Available from:https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/coronavirus-covid-19-drugs"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w",
"article-title": "The efficacy of curcumin‐piperine co‐supplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in COVID‐19 outpatients: A randomized double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial",
"author": "Askari G.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0057285",
"article-title": "Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral‐induced acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Avasarala S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152236",
"article-title": "Deciphering the balance of IL‐6/IL‐10 cytokines in severe to critical COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Azaiz M. B.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Immunobiology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1",
"volume": "227",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020200463",
"article-title": "Chest CT findings in coronavirus disease‐19 (COVID‐19): Relationship to duration of infection",
"author": "Bernheim A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "200463",
"journal-title": "Radiology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092706",
"article-title": "Chlorogenic acid potentiates the anti‐inflammatory activity of curcumin in LPS‐stimulated THP‐1 cells",
"author": "Bisht A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2706",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid‐19",
"author": "Cao B.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109946",
"article-title": "Curcumin regulates the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells and activates IL‐10 immune modulation against acute lung injury in mice",
"author": "Chai Y.‐s.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imm.13443",
"article-title": "New‐onset autoimmune phenomena post‐COVID‐19 vaccination",
"author": "Chen Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "386",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.025",
"article-title": "Mechanism of inflammatory response in associated comorbidities in COVID‐19",
"author": "Lucena T. M. C.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "597",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06155",
"article-title": "IL‐6 and IL‐10 as predictors of disease severity in COVID‐19 patients: Results from meta‐analysis and regression",
"author": "Dhar S. K.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/11772719211013363",
"article-title": "IL‐6 and other biomarkers associated with poor prognosis in a cohort of hospitalized patients with COVID‐19 in Madrid",
"author": "Donoso‐Navarro E.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomarker Insights",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111578",
"article-title": "Will curcumin nanosystems be the next promising antiviral alternatives in COVID‐19 treatment trials?",
"author": "Dourado D.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1",
"volume": "139",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S63762",
"article-title": "A novel diblock of copolymer of (monomethoxy poly [ethylene glycol]‐oleate) with a small hydrophobic fraction to make stable micelles/polymersomes for curcumin delivery to cancer cells",
"author": "Erfani‐Moghadam V.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5541",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Nanomedicine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-020-07033-y",
"article-title": "Chest CT score in COVID‐19 patients: Correlation with disease severity and short‐term prognosis",
"author": "Francone M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6808",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "European Radiology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Co‐delivery of doxorubicin and curcumin with polypeptide nanocarrier for synergistic lymphoma therapy",
"author": "Guo W.",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Scientific Reports",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12248-012-9432-8",
"article-title": "Therapeutic roles of curcumin: Lessons learned from clinical trials",
"author": "Gupta S. C.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The AAPS Journal",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129",
"article-title": "Profiling serum cytokines in COVID‐19 patients reveals IL‐6 and IL‐10 are disease severity predictors",
"author": "Han H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1123",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerging Microbes & Infections",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7294",
"article-title": "A triple‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of curcumin‐containing nanomicelles on cellular immune responses subtypes and clinical outcome in COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Hassaniazad M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6417",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0369",
"article-title": "Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): A meta‐analysis",
"author": "Henry B. M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1021",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM)",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods6100092",
"article-title": "Curcumin: A review of its effects on human health",
"author": "Hewlings S. J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "92",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Food",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2020.08.011",
"article-title": "The novel coronavirus Disease‐2019 (COVID‐19): Mechanism of action, detection and recent therapeutic strategies",
"author": "Hosseini E. S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1",
"volume": "551",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113072",
"article-title": "Synergistic effects of curcumin and its analogs with other bioactive compounds: A comprehensive review",
"author": "Hosseini‐Zare M. S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1",
"volume": "210",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13318-019-00545-z",
"article-title": "Enhancing curcumin oral bioavailability through nanoformulations",
"author": "Ipar V. S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.677008",
"article-title": "Elevated interleukin‐10 levels in COVID‐19: Potentiation of pro‐inflammatory responses or impaired anti‐inflammatory action?",
"author": "Islam H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "677008",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12249-020-01756-3",
"article-title": "Diagnostic and treatment strategies for COVID‐19",
"author": "Jamshaid H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "AAPS PharmSciTech",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.898062",
"article-title": "Oral Co‐supplementation of curcumin, quercetin, and vitamin D3 as an adjuvant therapy for mild to moderate symptoms of COVID‐19—Results from a pilot open‐label, randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Khan A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12325-020-01351-9",
"article-title": "Anti COVID‐19 drugs: Need for more clinical evidence and global action",
"author": "Khan Z.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2575",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Advances in Therapy",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.13621",
"article-title": "Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: Multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases",
"author": "Kunnumakkara A. B.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1325",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Pharmacology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119201",
"article-title": "COVID‐19, cytokines, inflammation, and spices: How are they related?",
"author": "Kunnumakkara A. B.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Life Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1",
"volume": "284",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.017",
"article-title": "Curcumin use in pulmonary diseases: State of the art and future perspectives",
"author": "Lelli D.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Pharmacological Research",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.00479",
"article-title": "The inhibitory effect of curcumin on virus‐induced cytokine storm and its potential use in the associated severe pneumonia",
"author": "Liu Z.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294",
"article-title": "Repositioning ivermectin for Covid‐19 treatment: Molecular mechanisms of action against SARS‐CoV‐2 replication",
"author": "Low Z. Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)‐Molecular Basis of Disease",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1",
"volume": "1868",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ane.13417",
"article-title": "The potential neurological effect of the COVID‐19 vaccines: A review",
"author": "Lu L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Neurologica Scandinavica",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2020.10.012",
"article-title": "A potential role of interleukin 10 in COVID‐19 pathogenesis",
"author": "Lu L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trends in Immunology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_36_1",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding",
"author": "Lu R.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"issue": "10224",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "e_1_2_10_37_1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155507",
"article-title": "IL‐6 and IL‐10 are associated with disease severity and higher comorbidity in adults with COVID‐19",
"author": "Luporini R. L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_38_1",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.017",
"article-title": "Antiviral potential of curcumin",
"author": "Mathew D.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "Journal of Functional Foods",
"key": "e_1_2_10_39_1",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: Pathophysiology and treatment",
"author": "Matuschak G. M.",
"first-page": "252",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Missouri Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_40_1",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103026",
"article-title": "A linear prognostic score based on the ratio of interleukin‐6 to interleukin‐10 predicts outcomes in COVID‐19",
"author": "McElvaney O. J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "eBioMedicine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_41_1",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.018",
"article-title": "Exploring the use of nanocarrier systems to deliver the magical molecule; curcumin and its derivatives",
"author": "Mehanny M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Controlled Release",
"key": "e_1_2_10_42_1",
"volume": "225",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.07.013",
"article-title": "Polymerized nano‐curcumin attenuates neurological symptoms in EAE model of multiple sclerosis through down regulation of inflammatory and oxidative processes and enhancing neuroprotection and myelin repair",
"author": "Mohajeri M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "156",
"journal-title": "Neuropharmacology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_43_1",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.03.014",
"article-title": "Curcumin inhibits zika and chikungunya virus infection by inhibiting cell binding",
"author": "Mounce B. C.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "148",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Research",
"key": "e_1_2_10_44_1",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.20556",
"article-title": "Cytokine regulation in SARS coronavirus infection compared to other respiratory virus infections",
"author": "Okabayashi T.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "417",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_45_1",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115094",
"article-title": "Clinical, molecular, and epidemiological characterization of the SARS‐CoV‐2 virus and the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19), a comprehensive literature review",
"author": "Ortiz‐Prado E.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease",
"key": "e_1_2_10_46_1",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138577",
"article-title": "COVID‐19: Current understanding of its pathophysiology, clinical presentation and treatment",
"author": "Parasher A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "312",
"issue": "1147",
"journal-title": "Postgraduate Medical Journal",
"key": "e_1_2_10_47_1",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Curcumin as adjuvant therapy in COVID‐19: Friend or foe?",
"author": "Pawitan J. A.",
"first-page": "824",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of International Dental and Medical Research",
"key": "e_1_2_10_48_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.00912",
"article-title": "Anti‐infective properties of the golden spice curcumin",
"author": "Praditya D.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "912",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Microbiology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_49_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101619",
"article-title": "Positive result of Sars‐Cov‐2 in sputum from a cured patient with COVID‐19",
"author": "Qu Y.‐M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease",
"key": "e_1_2_10_50_1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Rajnik M.",
"key": "e_1_2_10_51_1",
"volume-title": "Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID‐19)",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID‐19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan Q.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "846",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_52_1",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7004",
"article-title": "Oral nano‐curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease‐19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial",
"author": "Saber‐Moghaddam N.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2616",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "e_1_2_10_53_1",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_728_20",
"article-title": "Preventive and treatment strategies of COVID‐19: From community to clinical trials",
"author": "Sahu K. K.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2149",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care",
"key": "e_1_2_10_54_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdmv.2020.05.003",
"article-title": "Association between D‐dimer levels and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): A systematic review and pooled analysis",
"author": "Sakka M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JMV‐Journal de Médecine Vasculaire",
"key": "e_1_2_10_55_1",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c3ra46396f",
"article-title": "Curcumin, a promising anti‐cancer therapeutic: A review of its chemical properties, bioactivity and approaches to cancer cell delivery",
"author": "Salem M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10815",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "RSC Advances",
"key": "e_1_2_10_56_1",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-food-032818-121738",
"article-title": "Curcumin: Recent advances in the development of strategies to improve oral bioavailability",
"author": "Sanidad K. Z.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "597",
"journal-title": "Annual Review of Food Science and Technology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_57_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01021",
"article-title": "Turmeric and its major compound curcumin on health: Bioactive effects and safety profiles for food, pharmaceutical, biotechnological and medicinal applications",
"author": "Sharifi‐Rad J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1021",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_58_1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-137785",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and COVID‐19",
"author": "Sinha N.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Postgraduate Medical Journal",
"key": "e_1_2_10_59_1",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10565-016-9354-9",
"article-title": "Curcumin confers protection to irradiated THP‐1 cells while its nanoformulation sensitizes these cells via apoptosis induction",
"author": "Soltani B.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "543",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Biology and Toxicology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_60_1",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173551",
"article-title": "Curcumin, a traditional spice component, can hold the promise against COVID‐19?",
"author": "Soni V. K.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Pharmacology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_61_1",
"volume": "886",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Curcumin suppression of cytokine release and cytokine storm. A potential therapy for patients with Ebola and other severe viral infections",
"author": "Sordillo P. P.",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Vivo",
"key": "e_1_2_10_62_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm in COVID‐19: Pathogenesis and overview of anti‐inflammatory agents used in treatment",
"author": "Soy M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2085",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clinical Rheumatology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_63_1",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abj9256",
"article-title": "COVID‐19 vaccine side effects: The positives about feeling bad",
"author": "Sprent J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "60",
"journal-title": "Science Immunology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_64_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2010.08.014",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory and therapeutic activity of curcumin",
"author": "Srivastava R. M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "331",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "International Immunopharmacology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_65_1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID‐19",
"author": "Struyf T.",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "e_1_2_10_66_1",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0968-0896(00)82152-5",
"article-title": "Inhibition of the HIV‐1 and HIV‐2 proteases by curcumin and curcumin boron complexes",
"author": "Sui Z.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "415",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry",
"key": "e_1_2_10_67_1",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/nnm.12.80",
"article-title": "Advances in nanotechnology‐based delivery systems for curcumin",
"author": "Sun M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1085",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nanomedicine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_68_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06350",
"article-title": "Antiviral and immunomodulatory activity of curcumin: A case for prophylactic therapy for COVID‐19",
"author": "Thimmulappa R. K.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "e_1_2_10_69_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14020256",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of curcumin on outcomes of hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review of clinical trials",
"author": "Vahedian‐Azimi A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "256",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_10_70_1",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088",
"article-title": "Nano‐curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Valizadeh H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "International Immunopharmacology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_71_1",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metop.2021.100096",
"article-title": "Anti‐viral treatment for SARS‐CoV‐2 infection: A race against time amidst the ongoing pandemic",
"author": "Vallianou N. G.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Metabolism Open",
"key": "e_1_2_10_72_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa272",
"article-title": "Clinical features of 69 cases with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan",
"author": "Wang Z.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "769",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "China. Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "e_1_2_10_73_1",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280215588241",
"article-title": "Estimating the sample size for a pilot randomised trial to minimise the overall trial sample size for the external pilot and main trial for a continuous outcome variable",
"author": "Whitehead A. L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1057",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Statistical Methods in Medical Research",
"key": "e_1_2_10_74_1",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22115457",
"article-title": "Can the COVID‐19 pandemic disrupt the current drug development practices?",
"author": "Won J.‐H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5457",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Molecular Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_10_75_1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110500",
"article-title": "Clinical retrospective study on the efficacy of Qingfei Paidu decoction combined with Western medicine for COVID‐19 treatment",
"author": "Xin S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy",
"key": "e_1_2_10_76_1",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41571-018-0036-9",
"article-title": "Extracellular vesicles in cancer—Implications for future improvements in cancer care",
"author": "Xu R.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "617",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_77_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12459",
"article-title": "Curcumin alleviates macrophage activation and lung inflammation induced by influenza virus infection through inhibiting the NF‐κB signaling pathway",
"author": "Xu Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "457",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses",
"key": "e_1_2_10_78_1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117900",
"article-title": "The immune system and COVID‐19: Friend or foe?",
"author": "Yazdanpanah F.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Life Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_10_79_1",
"volume": "256",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6738",
"article-title": "Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID‐19 infection",
"author": "Zahedipour F.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2911",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "e_1_2_10_80_1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/186864",
"article-title": "A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin",
"author": "Zorofchian Moghadamtousi S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BioMed Research International",
"key": "e_1_2_10_81_1",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 80,
"references-count": 80,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ptr.7844"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Promising clinical outcomes of nano‐curcumin treatment as an adjunct therapy in hospitalized\n <scp>COVID</scp>\n ‐19 patients: A randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}