Use of indomethacin in COVID-19 patients: experience from two medical centres
et al., Journal of the Indian Medical Association, 119:7, ISRCTN11970082, Jul 2021
2nd treatment shown to increase risk in
November 2020, now with p = 0.00000029 from 27 studies, but still recommended in 103 countries.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
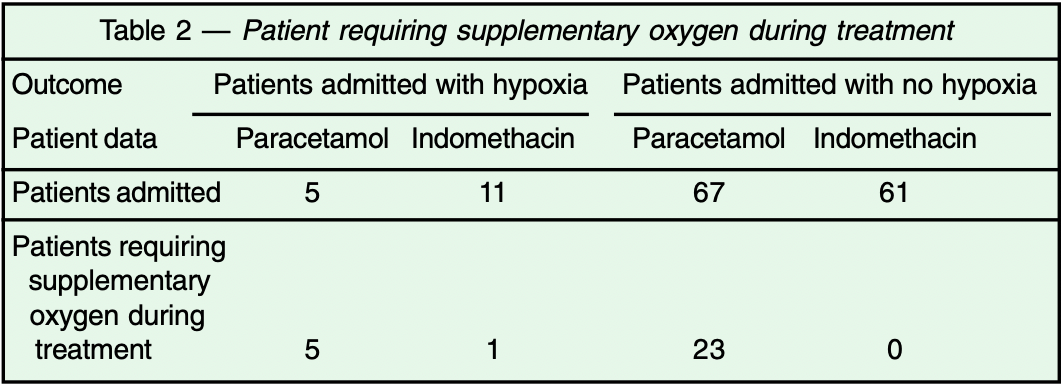
PSM retrospective 72 indomethacin and 72 paracetamol patients in India, showing higher progression and worse recovery with acetaminophen.
Acetaminophen is also known as paracetamol, Tylenol, Panadol, Calpol, Tempra, Calprofen, Doliprane, Efferalgan, Grippostad C, Dolo, Acamol, Fevadol, Crocin, and Perfalgan.
Study covers acetaminophen and indomethacin.
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 2700.0% higher, RR 28.00, p < 0.001, treatment 28 of 72 (38.9%), control 1 of 72 (1.4%), propensity score matching.
|
|
recovery time, 75.0% higher, relative time 1.75, p < 0.001, treatment median 7.0 IQR 1.0 n=72, control median 4.0 IQR 1.0 n=72, fever.
|
|
recovery time, 116.7% higher, relative time 2.17, p < 0.001, treatment median 6.5 IQR 3.25 n=72, control median 3.0 IQR 2.0 n=72, myalgia.
|
|
recovery time, 166.7% higher, relative time 2.67, p < 0.001, treatment median 8.0 IQR 2.0 n=72, control median 3.0 IQR 2.0 n=72, cough.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ravichandran et al., 31 Jul 2021, retrospective, India, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo, trial ISRCTN11970082.
Use of Indomethacin in COVID-19 Patients -Experience from Two Medical Centres
Background : Indomethacin is a widely used drug belonging to the class of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), which has also a proven anti-viral effect. This academic study describes our experience in treating hospitalised symptomatic COVID-19 positive patients with it. Materials and Methods : Patients with COVID-19 (detected by the real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction) admitted to our department were provided the option of receiving Indomethacin 25mg (bid) or 75mg SR (sustained release), (OD) along with proton pump inhibitor, along with the standard care of treatment of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). Patients who did not agree to the Indomethacin option were offered standard care of treatment which included paracetamol. Development of hypoxia was considered as the endpoint. Time period to become afebrile and resolution of cough and myalgia; was considered as the secondary endpoint. Propensity Score Matching was used for the purpose of comparison between these two arms. A separate group of patients with COVID-19 having severe disease, who were admitted with hypoxemia were given Indomethacin 75mg SR; admission to the intensive care unit or need for mechanical ventilation were considered as the endpoints. Results : Twenty-eight of 72 patients in paracetamol arm developed hypoxia and required oxygen; whereas, only one patient out of 72 in the Indomethacin arm, developed hypoxia in the mild-moderate Covid patients. None of the patients in severe disease group treated with indomethacin needed mechanical ventilation. More rapid symptomatic relief was observed in indomethacin group than paracetamol group. Also, no systemic adversity including renal/liver functions observed.
Conclusion : In our experience Indomethacin is very effective and safe for treating COVID-19 patients.
References
Amici, Caro, Ciucci, Chiappa, Castilletti et al., Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS coronavirus, Antivir Ther
Beth, Gincy, Andrew, Sophie, Associations between immune-suppressive and stimulating drugs and novel COVID-19-a systematic review of current evidence
Beth, Mieke, COVID-19 and treatment with NSAIDs and corticosteroids: should we be limiting their use in the clinical setting?, ecancer
Bour, Westendorp, Laterveer, Bollen, Remarque, Interaction of Indomethacin with cytokine production in whole blood. Potential mechanism for a brain-protective effect, Exp Gerentol
Donnelly, Lloyd, Campbell, Indomethacin in rheumatoid arthritis: an evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and side effects, Br Med J
First, Schroeder, Hariharan, Alexander, The effect of Indomethacin on the febrile response following OKT3 therapy, Transplantation
Gaughan, Francos, Dunn, Francos, Burke, A retrospective analysis of the effect of Indomethacin on adverse reactions to orthoclone OKT3 in the therapy of acute renal allograft rejection, Am J Kidney Dis
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature
Guang, COVID 19 drug repurposing: A review of computational screening methods, clinical trials, and protein interaction assays, Med Res Rev
Kanakaraj, Ravichandran, Low dose Indomethacin in the outpatient treatment of covid-19 in kidney transplant recipients-a case series, Open Access Library Journal
Napolitano, Gambardella, Carella, Gao, Bernardo, Computational drug repositioning and elucidation of mechanism of action of compounds against SARS-CoV-2
Raghav, Kamboj, Singh, Effect of some steroidal & non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on purified goat brain cathepsin L, Indian J Med Res
Ravichandran, Subramanian, Clark, Low dose Indomethacin for symptomatic treatment of Covid-19, Int J Med Rev Case Rep
Sotoudehmanesh, Khatibian, Kolahdoozan, Ainechi, Malboosbaf, Indomethacin may reduce the incidence and severity of acute pancreatitis after ERCP, Am J Gastroenterol
Tay, The trinity of Covid-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Xu, Gao, Wu, Selinger, Zhou, Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS CoV-2 in vitro and canine coronavirus in vivo, doi:BioRxiV202010.1101/2020.04.01.017624
Zhao, Yang, Yang, Zhang, Huang et al., Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development, Sig Transduct Target Ther
ravichandran2